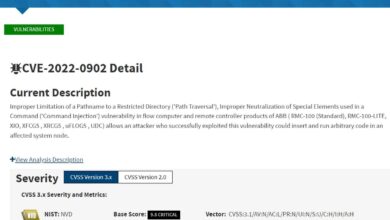
Follow these 3 mobile security measures to protect your enterprise networks
Follow these 3 mobile security measures to protect your enterprise networks – Follow these 3 mobile security measures to protect your enterprise networks – it sounds serious, right? But securing your company’s data from the ever-growing threat of mobile device breaches doesn’t have to be a headache. This post breaks down three crucial steps you can take
-right now* to significantly boost your network’s security, focusing on practical solutions and actionable advice.
We’ll explore how simple changes can make a huge difference in safeguarding sensitive information accessed through employee mobile devices. Get ready to tighten up your security posture!
In today’s mobile-first world, employees access company data from a variety of devices – smartphones, tablets, laptops – all presenting potential vulnerabilities. Ignoring mobile security is like leaving your front door unlocked. This post will cover essential strategies including implementing robust Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions, fortifying authentication processes with multi-factor authentication (MFA), and implementing strong data encryption and loss prevention (DLP) measures.
By understanding and implementing these key areas, you’ll be well on your way to creating a more secure mobile environment for your business.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Solutions
Securing enterprise networks in today’s mobile-first world requires robust mobile device management (MDM) solutions. These solutions provide a centralized platform for managing and securing company-owned and employee-owned devices accessing sensitive data. Understanding the capabilities and nuances of different MDM solutions is crucial for choosing the right fit for your organization’s specific needs and security posture.
Core Functionalities of MDM Solutions
MDM solutions offer a range of core functionalities designed to enhance security and streamline device management. These typically include device enrollment and onboarding, remote device wiping, application management (installation, updates, and removal), policy enforcement (password complexity, data encryption, VPN usage), location tracking, and inventory management. Advanced solutions may also incorporate features like containerization (isolating corporate data from personal data), threat detection, and compliance reporting.
The specific features available vary considerably between different MDM vendors and pricing tiers.
Comparison of Three MDM Solutions
Let’s compare three popular MDM solutions: Microsoft Intune, VMware Workspace ONE, and MobileIron. Each offers a comprehensive suite of features, but their strengths and weaknesses differ.Microsoft Intune excels in its tight integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, making it a natural choice for organizations heavily invested in Microsoft products. Its strength lies in its ease of use and strong security features, particularly for Windows devices.
However, its management of non-Microsoft devices might be less intuitive.VMware Workspace ONE boasts a unified endpoint management (UEM) approach, handling not just mobile devices but also laptops and desktops. This simplifies management for organizations with diverse device fleets. A potential weakness could be the complexity of its configuration, requiring more technical expertise for optimal deployment.MobileIron focuses heavily on security and compliance, making it ideal for organizations with strict regulatory requirements.
Its advanced security features and robust data protection capabilities are significant advantages. However, its pricing can be higher compared to other solutions, and the user interface might be considered less user-friendly than some competitors.
MDM Solution Implementation Process
Implementing an MDM solution involves several key steps. First, you need to choose a vendor and license the software. Next, you’ll configure the MDM server and establish policies based on your organization’s security requirements. Device enrollment is the next crucial step, typically involving a user downloading an agent app or enrolling via a company portal. Once enrolled, devices automatically receive and apply the configured policies.
Regular monitoring and updates are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of the solution. Finally, comprehensive documentation and training for both IT staff and end-users are vital for successful implementation and ongoing management.
Cost and Feature Comparison of Three MDM Solutions
| Feature | Microsoft Intune | VMware Workspace ONE | MobileIron |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (per device/month) | Varies based on features and user count; generally affordable for smaller organizations. | Varies based on features and user count; typically mid-range pricing. | Higher cost per device; generally more expensive, especially for larger deployments. |
| Device Support | Strong support for Windows, iOS, Android; good support for macOS. | Broad support across all major platforms (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android). | Excellent support for all major platforms with a focus on enterprise-grade security. |
| Security Features | Conditional access, data loss prevention (DLP), app protection policies. | Advanced threat detection, app control, and strong data encryption capabilities. | Industry-leading security features; strong focus on compliance and data protection. |
| Ease of Use | Generally user-friendly, especially for organizations already using Microsoft products. | Can be complex to configure, requiring higher technical expertise. | Steeper learning curve compared to Intune, requiring more specialized training. |
Strong Authentication and Access Control
Securing mobile access to enterprise networks requires a robust strategy beyond just passwords. A multi-layered approach encompassing strong authentication and granular access control is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with mobile devices and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive company data. This involves implementing strong authentication methods and carefully managing who can access what information.Implementing strong authentication and access control measures significantly reduces the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access.
By combining multiple verification methods and restricting access based on user roles, organizations can significantly bolster their mobile security posture and protect valuable information. This layered approach minimizes the impact of compromised credentials and ensures that only authorized individuals can access the resources they need to perform their jobs.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Mobile Access
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security beyond traditional password-based logins. By requiring users to verify their identity through multiple factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if one factor (like a password) is compromised. This layered approach ensures that even if a hacker obtains a password, they still need additional verification to gain access.
For example, if a password is compromised, a second factor, like a one-time code from an authenticator app, is needed to access the system. This makes it exponentially more difficult for attackers to gain access.
Examples of Robust MFA Methods for Mobile Devices
Several robust MFA methods are well-suited for mobile devices. These include:
- Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP): These codes are generated by authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy, changing every 30 seconds. This provides a dynamic, constantly changing verification code, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to intercept and use.
- Push Notifications: A notification is sent to the user’s mobile device, requiring them to approve the login attempt. This method is convenient and user-friendly, relying on the user having possession of their device.
- Biometrics: Using fingerprint or facial recognition adds another layer of security. This leverages the user’s unique biological characteristics for verification, adding a highly secure and convenient authentication method.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for Mobile Users
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a crucial component of mobile security. It assigns permissions based on a user’s role within the organization, ensuring that individuals only have access to the data and resources necessary for their job functions. This principle of least privilege significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, as even if a user’s account is compromised, the attacker’s access is limited to the resources associated with that specific role.
Implementing RBAC simplifies administration and reduces the risk of accidental or malicious data exposure.
Sample RBAC Policy for Mobile Access to Sensitive Company Data
A sample RBAC policy might include the following roles and permissions:
| Role | Permissions |
|---|---|
| Executive | Access to all company data, including financial reports, strategic plans, and confidential client information. |
| Sales Representative | Access to customer relationship management (CRM) system, sales reports, and client contact information. No access to financial data or strategic plans. |
| Marketing Analyst | Access to marketing campaign data, analytics dashboards, and market research reports. No access to financial data or client contact information. |
| IT Support | Access to company IT systems and infrastructure for troubleshooting and maintenance. Limited access to user data, only as needed for support purposes. |
This policy demonstrates how different roles have varying levels of access, limiting the potential damage from a security breach. Each role is granted only the necessary permissions, minimizing the risk associated with compromised accounts.
Data Security and Encryption

Protecting sensitive data on mobile devices is paramount for any enterprise. With employees increasingly working remotely and using personal devices for work, the risk of data breaches has significantly increased. Robust data security and encryption are crucial components of a comprehensive mobile security strategy, minimizing the impact of potential threats and ensuring business continuity.
Following those 3 mobile security measures is crucial for enterprise network protection, especially with the increasing reliance on cloud services. Understanding the broader context is key, which is why I recommend checking out this insightful article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to see how cloud security impacts overall mobile device security. Ultimately, robust mobile security practices are your first line of defense against breaches, complementing broader cloud security strategies.
Common Mobile Security Threats
Mobile devices are vulnerable to a range of threats that can compromise enterprise networks. These include malware infections, phishing attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data breaches resulting from lost or stolen devices. Malware can steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, and install backdoors for further attacks. Phishing attempts trick users into revealing credentials, while man-in-the-middle attacks intercept communication between the device and the network.
The loss or theft of a device containing sensitive data can lead to direct exposure and significant reputational damage.
Mitigation of Mobile Security Threats
Effective mitigation strategies involve a multi-layered approach. Regular security updates for the operating system and applications are essential to patch known vulnerabilities. Implementing strong password policies and multi-factor authentication significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Utilizing mobile device management (MDM) solutions allows for remote wiping of data in case of loss or theft. Employee training on security awareness, including phishing recognition and safe browsing practices, is also crucial.
Finally, employing robust data encryption safeguards data even if the device is compromised. For example, a company might implement a policy where all sensitive data on employee devices is encrypted using a strong, company-managed encryption key.
Mobile Data Encryption Methods
Several encryption methods are available for securing mobile data. Full-disk encryption encrypts all data on the device, protecting it even if the device is physically accessed. File-level encryption protects individual files, offering granular control over data access. End-to-end encryption secures data in transit and at rest, ensuring confidentiality even if the communication channels or storage locations are compromised.
A comparison of these methods might highlight that full-disk encryption provides the broadest protection, but file-level encryption offers more flexibility in managing access rights. End-to-end encryption, while highly secure, might require more complex implementation. The choice of method depends on the specific security requirements and the sensitivity of the data.
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
Data loss prevention (DLP) measures are critical for preventing sensitive data from leaving the enterprise network. These measures can include restricting access to sensitive data based on user roles and device security posture. Implementing data encryption, as discussed above, is a key component of DLP. Mobile device management (MDM) solutions often include DLP features such as data loss prevention policies and application control, allowing administrators to monitor and restrict data movement.
For example, an MDM solution could be configured to prevent employees from copying sensitive data to unapproved cloud storage services or sharing it via unencrypted email.
Best Practices for Securing Sensitive Data on Mobile Devices
Implementing robust data security requires a proactive approach. Here are some best practices:
- Enable full-disk encryption on all mobile devices.
- Use strong, unique passwords and implement multi-factor authentication.
- Regularly update the operating system and applications.
- Install and maintain robust anti-malware software.
- Implement mobile device management (MDM) solutions to control access and enforce security policies.
- Educate employees on security awareness and best practices.
- Develop and enforce a clear mobile device security policy.
- Utilize data loss prevention (DLP) tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data leakage.
- Regularly back up important data to a secure location.
- Implement a secure remote wipe capability in case of device loss or theft.
Security Awareness Training for Mobile Users

Protecting your enterprise network isn’t just about robust technology; it’s about empowering your employees to be the first line of defense. Security awareness training is crucial for mitigating mobile security risks, as human error remains a significant vulnerability. By educating your workforce on best practices, you significantly reduce the likelihood of phishing attacks, malware infections, and data breaches originating from mobile devices.
A comprehensive mobile security awareness training program should cover various aspects, from recognizing phishing attempts to understanding the importance of strong passwords and secure Wi-Fi usage. This training should be engaging, easy to understand, and reinforced regularly to ensure lasting impact. Regular refresher courses are essential to keep employees updated on evolving threats and best practices.
Sample Training Module: Mobile Security Best Practices
This module Artikels key mobile security practices for employees. The training uses a blended approach, combining interactive elements with clear explanations to maximize understanding and retention.
The training begins with a short introductory video explaining the importance of mobile security within the context of the company’s overall security posture. The video uses simple language and relatable scenarios, emphasizing the potential consequences of insecure mobile practices, such as data breaches and financial losses. Following the video, the module proceeds to a series of interactive lessons covering specific topics.
Phishing and Social Engineering
This section explains how phishing attacks work, focusing on identifying suspicious emails, texts, and websites. It provides examples of common phishing techniques, such as fake login pages and urgent requests for personal information. Employees are taught to verify the sender’s identity, look for suspicious links and attachments, and report any suspicious communications immediately. A short interactive exercise challenges employees to identify phishing attempts in various scenarios.
Password Security
This section emphasizes the importance of creating strong, unique passwords for all accounts. It explains password best practices, including using a password manager, avoiding easily guessable passwords, and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. The training includes a demonstration of a password manager and provides a list of reputable password managers to use.
Secure Wi-Fi Usage
This section explains the risks associated with using public Wi-Fi networks and emphasizes the importance of using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) when connecting to unsecured networks. The training clarifies the difference between public and private Wi-Fi and provides guidance on recognizing secure networks. It also covers the risks of connecting to unsecured networks and the benefits of using a VPN.
App Security
This section highlights the importance of downloading apps only from official app stores and regularly updating apps to patch security vulnerabilities. It emphasizes the risks associated with downloading apps from untrusted sources and encourages employees to carefully review app permissions before installation. The training also covers the need to promptly remove unused or suspicious apps from their devices.
Quiz: Assessing Employee Understanding
The following quiz assesses employee understanding of the key mobile security concepts covered in the training module. Each question has one correct answer.
| Question | Answer Choices | Correct Answer |
|---|---|---|
| Which of the following is a sign of a phishing email? | A) Professional-looking email from a known sender. B) Urgent request for personal information. C) Grammatically correct email with a clear subject line. D) Email from your bank with a secure link. |
B |
| What is the best practice for creating a strong password? | A) Using a simple, easy-to-remember password. B) Using the same password for all accounts. C) Using a long, complex password with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. D) Using your birthday as a password. |
C |
| Why is it important to use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi? | A) To increase internet speed. B) To encrypt your internet traffic and protect your data. C) To access blocked websites. D) To save battery life. |
B |
| Where should you download apps from to minimize security risks? | A) Untrusted websites. B) Official app stores (e.g., Google Play Store, Apple App Store). C) File-sharing websites. D) Email attachments. |
B |
Regular Security Updates and Patching

Keeping your mobile devices updated is more than just getting the latest features; it’s a critical component of a robust mobile security strategy. Regular updates often include crucial security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by malicious actors. Neglecting these updates leaves your enterprise network exposed to significant risks.Regular security updates and patching are essential for mitigating the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Mobile operating systems and applications are constantly being targeted by cybercriminals seeking to exploit weaknesses. These updates often include fixes for known vulnerabilities, preventing attackers from gaining unauthorized access to sensitive data. A proactive approach to patching is significantly more cost-effective than dealing with the aftermath of a successful cyberattack.
Implementing a Regular Patching Schedule
Implementing a regular patching schedule requires a structured approach. This involves establishing clear guidelines for which devices need updating, the frequency of updates, and a process for deploying those updates. A centralized Mobile Device Management (MDM) solution can significantly simplify this process by allowing for remote deployment and management of updates across all enterprise devices. Consider scheduling updates during off-peak hours to minimize disruption to employees’ workflows.
So, you’re thinking about beefing up your mobile security – smart move! Following those 3 key measures is crucial, especially when you consider how much data travels on those devices. Building secure apps is equally vital, which is why I’ve been researching the exciting developments in domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , to ensure our apps are as robust as possible.
Ultimately, strong mobile security and well-designed apps work hand-in-hand to protect your enterprise networks.
Thorough testing of updates in a controlled environment before wider deployment is also crucial to avoid unexpected issues. This staged rollout minimizes the risk of widespread problems and allows for quick identification and resolution of any compatibility conflicts. For example, a company could implement a phased rollout, starting with a pilot group of users before deploying the updates to the entire organization.
This allows for feedback and troubleshooting before a complete deployment.
Consequences of Neglecting Timely Security Updates
The consequences of neglecting timely security updates can range from minor inconveniences to catastrophic data breaches. Outdated software leaves devices vulnerable to malware infections, data theft, and denial-of-service attacks. A single successful attack can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Consider the case of a company whose outdated mobile banking app was exploited, leading to a substantial financial loss.
Following those 3 mobile security measures to protect your enterprise networks is crucial, especially considering how easily things can go wrong. For example, I recently read about a serious security breach where, according to this article, facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users was reported, highlighting the importance of strong security practices. So, let’s double-check those mobile security settings and ensure our networks are truly protected!
This highlights the critical need for a proactive approach to security updates. Further, neglecting updates can expose sensitive customer data, leading to legal liabilities and fines under regulations like GDPR. A robust patching schedule is an essential component of a comprehensive security strategy, mitigating these risks and protecting the organization’s valuable assets.
Secure Mobile Application Development: Follow These 3 Mobile Security Measures To Protect Your Enterprise Networks
Building secure mobile applications is paramount for protecting enterprise data and maintaining user trust. Insecure apps can expose sensitive information to attackers, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. This section Artikels key practices for developers to create robust and secure mobile applications.Secure coding practices and rigorous code reviews are fundamental to building secure mobile apps.
Neglecting these steps can leave applications vulnerable to a wide range of attacks. This involves not only writing clean, efficient code but also proactively considering potential security threats during the entire development lifecycle.
Secure Coding Practices
Secure coding goes beyond simply making an app functional. It’s about proactively designing and implementing security measures throughout the development process. This includes input validation to prevent injection attacks, proper handling of sensitive data to avoid data leaks, and using secure libraries and APIs to minimize vulnerabilities. Failing to validate user inputs, for example, can leave your app susceptible to SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Similarly, improper handling of sensitive data like passwords or location information can lead to significant security breaches. Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial to identify and address vulnerabilities before deployment.
Code Reviews and Static Analysis
Formal code reviews, where multiple developers examine each other’s code, are vital for identifying security flaws. This process allows for the detection of vulnerabilities that might be missed during individual development. Static analysis tools automatically scan code for potential security issues, providing another layer of protection. These tools can detect common vulnerabilities like buffer overflows, insecure data handling, and improper use of cryptographic functions.
The combination of manual code reviews and automated static analysis significantly improves the overall security posture of the application.
Common Mobile App Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
Several common vulnerabilities frequently plague mobile applications. Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is crucial.
Data Leakage
Improper data handling is a major source of vulnerabilities. Sensitive data, such as user credentials, financial information, or personal health data, should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Developers should also implement robust access control mechanisms to limit data access to authorized users only. Failure to encrypt data, or to implement appropriate access controls, can result in significant data breaches.
For instance, an app that stores user passwords in plain text is highly vulnerable to attack.
Insecure Authentication
Weak or easily guessable passwords, lack of multi-factor authentication, and insufficient session management are all significant security risks. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), significantly enhances security. Using robust password policies and implementing secure session management practices further mitigate the risk of unauthorized access. A real-world example is the use of MFA by many banking apps, which requires a second verification step beyond a password, often a one-time code sent via SMS or email.
Broken Access Control, Follow these 3 mobile security measures to protect your enterprise networks
Insufficient access control can allow unauthorized users to access sensitive data or functionalities. Properly implementing authorization and authentication mechanisms is essential to prevent this. This involves verifying user identities and ensuring that users only have access to the data and functionalities they are authorized to use. A poorly implemented access control system could allow a user to access another user’s data or perform actions they shouldn’t be able to.
Last Word
Securing your enterprise network against mobile threats isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process. By consistently implementing and updating these three key mobile security measures – robust MDM solutions, strong authentication, and data encryption – you’ll significantly reduce your risk profile. Remember, proactive security is cheaper and less stressful than reacting to a data breach. So, take the time to review your current mobile security practices, and start implementing these changes today.
Your peace of mind (and your company’s data) will thank you for it!
Commonly Asked Questions
What are some examples of common mobile security threats?
Common threats include phishing attacks targeting login credentials, malware infections through malicious apps, and loss or theft of devices containing sensitive data.
How often should I update my mobile security software and operating system?
Ideally, you should update your mobile OS and security apps as soon as updates are available. These updates often contain critical security patches.
What if an employee loses their mobile device? What steps should be taken?
Immediately initiate a remote wipe of the device to erase all company data. Then, report the loss to your IT department and initiate a password reset.
Are there any free MDM solutions available?
While many MDM solutions are subscription-based, some offer limited free plans or trials that can be useful for smaller businesses. However, the features in free plans are usually more basic.