Germany Accuses Russia of Cyberattacks
Germany accuses Russia of launching cyber attacks on its defense and interior ministries – a bombshell accusation that has sent shockwaves through the international community. This isn’t just another cyber incident; it’s a direct challenge to a NATO member’s security, potentially escalating tensions already high due to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. The alleged attacks, reportedly sophisticated and targeted, raise serious questions about Russia’s intentions and the vulnerabilities of even the most advanced nations’ digital infrastructure.
We’ll delve into the evidence, the fallout, and what this means for the future of cybersecurity.
The German government has provided details of the attacks, outlining the methods used and the sensitive data potentially compromised. Russia, predictably, has denied any involvement, offering its own counter-narrative. This leaves us with a crucial question: how can we definitively attribute such attacks and what steps can be taken to prevent future incidents? The international response has been swift, with allies expressing concern and pledging support.
But the underlying tension remains: are we on the precipice of a new era of cyber warfare?
Germany’s Accusation
Germany’s recent accusation against Russia of launching sophisticated cyberattacks targeting its defense and interior ministries has sent shockwaves through the international community. This escalation in cyber warfare underscores the growing tensions between the two nations and highlights the vulnerability of even the most advanced digital infrastructures. The accusations, while serious, require careful examination of the evidence and context to fully understand their implications.
Timeline of Events
Pinpointing the precise start of these alleged cyberattacks is difficult, as such operations often unfold subtly over extended periods. However, German authorities have indicated that the attacks likely began sometime in the latter half of 2022, intensifying in the lead-up to and following Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Reports suggest a gradual increase in suspicious network activity, initially dismissed as routine intrusions, before escalating to more targeted and disruptive actions against critical government systems.
The official public accusation came only after a thorough internal investigation and assessment of the damage, suggesting a deliberate and calculated response by the German government. The timing also coincides with heightened geopolitical tensions and increased cyber activity globally, further complicating the attribution of responsibility.
Nature of the Alleged Cyberattacks
The alleged attacks reportedly involved a range of sophisticated techniques, aiming to disrupt and compromise sensitive data within both the German defense and interior ministries. Reports suggest the use of advanced malware, possibly custom-designed to exploit specific vulnerabilities within the ministries’ systems. The attackers likely aimed to steal classified information, including intelligence reports, strategic plans, and personal data of ministry employees.
Germany’s accusations against Russia for cyberattacks on its defense and interior ministries highlight the urgent need for robust digital security. Building secure systems requires efficient development, which is why I’ve been researching the advancements in domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , to see how it can help improve resilience against such attacks. These sophisticated attacks underscore the importance of constantly upgrading our digital defenses.
The methods employed are consistent with the capabilities and tactics observed in previous Russian-linked cyber operations, although definitive proof remains challenging to obtain. Targets within the ministries likely included databases containing sensitive information, communication systems, and potentially even operational control systems, potentially impacting critical national security functions.
Evidence Presented by Germany
While Germany has been understandably reticent about publicly disclosing all the evidence supporting its accusations, some details have emerged. The precise nature of this evidence remains classified for national security reasons, but the available information suggests a strong case. It is important to note that the credibility of any evidence relies on rigorous analysis and verification, and the complete picture may only emerge over time.
| Evidence Type | Source | Description | Credibility Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Logs and Traffic Analysis | German Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) | Analysis of network traffic patterns revealing unusual activity, data exfiltration, and attempts to compromise critical systems. | High (assuming rigorous internal review and validation by the BSI) |
| Malware Samples | German Federal Criminal Police Office (BKA) | Recovered malware samples exhibiting characteristics consistent with known Russian-linked APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) groups. | Medium to High (dependent on forensic analysis and comparison to known threat actor signatures) |
| Witness Testimony | Internal Ministry Personnel | Reports from ministry employees detailing observed anomalies and disruptions in systems. | Medium (subject to potential biases and the need for corroboration with technical evidence) |
| Geolocation Data | Various Intelligence Agencies | Data pinpointing the origin of the cyberattacks to servers or infrastructure located within Russia or under its control. | High (assuming the geolocation data is accurate and verifiable) |
Russia’s Response and Denials
Russia’s official response to Germany’s accusations of cyberattacks targeting its defense and interior ministries has been swift and categorical: denial. The Kremlin has consistently rejected any involvement, characterizing the accusations as unfounded and politically motivated. This response is typical of Russia’s approach to similar allegations in the past, often dismissing them without providing substantial counter-evidence. The lack of a detailed rebuttal, however, leaves room for speculation regarding the true nature of Russia’s involvement (or lack thereof).The discrepancy between Germany’s evidence and Russia’s denials is stark.
Germany, while not publicly releasing all the specifics of its investigation to protect intelligence sources and methods, has pointed to sophisticated hacking techniques and the scale of the intrusion as indicators of a state-sponsored actor. They have emphasized the level of expertise required to breach their systems, suggesting a highly skilled and well-resourced adversary. Russia, on the other hand, offers only blanket denials, failing to address the technical details presented by the German authorities.
This absence of specific counterarguments weakens Russia’s position and fuels further suspicion.
Potential Motivations Behind Russia’s Actions
If the accusations are true, Russia’s motivations could stem from a range of geopolitical objectives. Gathering intelligence on German defense and internal security capabilities could be a primary goal, aiding in the development of future military strategies or influencing political decisions. Alternatively, the attacks might aim to sow discord within the German government and its alliances, undermining trust and potentially hindering cooperation on matters of mutual concern, such as sanctions against Russia or support for Ukraine.
Such actions align with a broader pattern of alleged Russian cyber operations aimed at destabilizing Western democracies.Conversely, if the accusations are false, Russia’s vehement denials could serve several purposes. Firstly, a strong denial helps to maintain a public image of strength and defiance, avoiding any perception of weakness or vulnerability. Secondly, the denial could be a strategic maneuver to deflect attention from other, potentially more damaging, activities.
Finally, it could be a preemptive measure to discredit future accusations, establishing a pattern of consistent denial that might make future allegations harder to prove. This approach reflects a broader strategy of disinformation and information warfare employed by Russia in various international contexts.
International Implications and Reactions
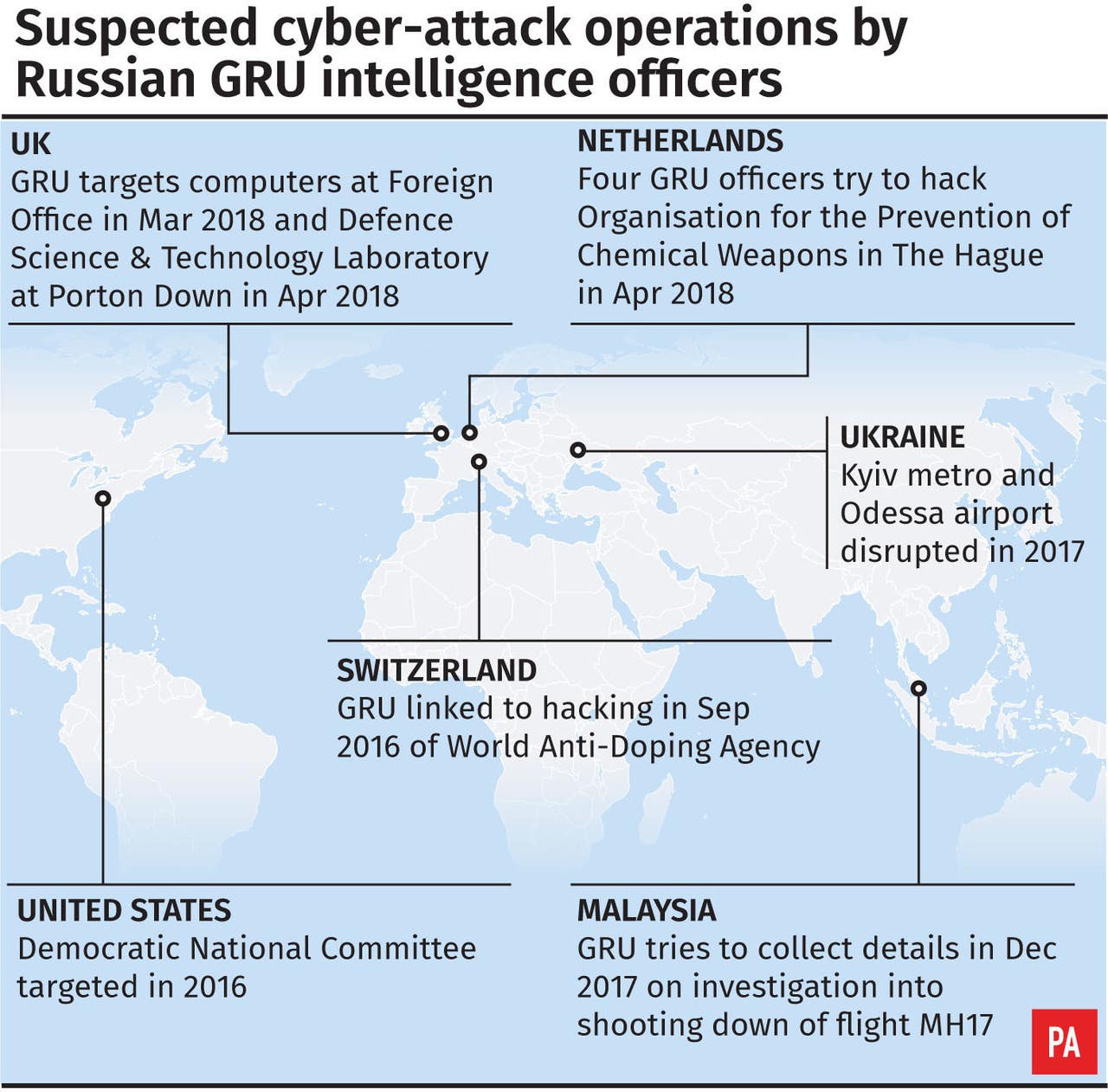
Germany’s accusation against Russia ignited a firestorm of international reaction, highlighting the escalating tensions in the cyber domain and its implications for the broader geopolitical landscape. The incident underscores the increasingly blurred lines between conventional warfare and cyberattacks, forcing a reassessment of national security strategies and international cooperation. The response from various actors reveals a complex web of alliances, concerns, and varying levels of commitment to collective security.The reactions from NATO members and international organizations were swift and varied, reflecting the diverse geopolitical interests at play.
Germany’s accusation that Russia launched cyberattacks on its ministries is seriously worrying. It highlights the vulnerability of government systems, but it’s not just governments that are targeted; I was shocked to read about this concerning issue on facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users , which shows how widespread these threats are. This makes you wonder how many other institutions are similarly exposed to these kinds of attacks, emphasizing the need for stronger cybersecurity measures across the board.
The gravity of the situation demanded a concerted response, although the specifics of that response varied depending on the individual nation’s relationship with both Russia and Germany.
Reactions of NATO Members and International Organizations
The accusations prompted a wave of statements and actions from various international actors. The immediate responses ranged from expressions of concern and solidarity with Germany to calls for increased cybersecurity cooperation and further investigation into the alleged attacks. A unified, forceful condemnation of Russia, however, remained elusive, reflecting the complex geopolitical dynamics within the alliance.
- NATO issued a statement expressing its “serious concern” about the alleged attacks, reaffirming its commitment to collective defense and emphasizing the importance of strengthening cyber defenses across the alliance.
- The United States, a key NATO ally, condemned the alleged Russian actions and offered its support to Germany in investigating the attacks. The US also reiterated its commitment to deterring further Russian aggression in cyberspace.
- Other European NATO members, including France and the UK, expressed similar concerns and offered support to Germany, though the level of public condemnation varied. Some countries emphasized the need for a coordinated European response to cyber threats.
- The European Union, while not directly involved in the military alliance, also condemned the alleged attacks, highlighting the need for stronger cybersecurity measures and cooperation among member states.
- Several international organizations, including the UN, issued statements emphasizing the importance of international law in cyberspace and called for a thorough investigation into the alleged attacks.
Impact on Transatlantic Relations and the Ukraine Conflict
The cyberattacks, and the subsequent accusations, have the potential to further strain already fragile transatlantic relations and exacerbate the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. The incident underscores the interconnectedness of traditional warfare and cyber warfare, blurring the lines between different forms of aggression. The response from Western powers could be seen as a further escalation of the conflict, potentially prompting a retaliatory response from Russia.
Conversely, a lack of unified action could embolden Russia and other state-sponsored actors to engage in more aggressive cyber operations in the future. The incident could also lead to a reevaluation of Western support for Ukraine, potentially influencing future aid packages and military assistance. For example, a significant cyberattack disrupting critical infrastructure could influence the timing or nature of military aid deployments.
Implications for Cybersecurity and International Law
The alleged attacks highlight the urgent need for improved cybersecurity measures and the development of stronger international norms and legal frameworks to govern state behavior in cyberspace. The incident underscores the limitations of existing international law in addressing cyberattacks, especially those that fall short of traditional acts of war. The lack of a clear international consensus on what constitutes a cyberattack and how to respond to it complicates efforts to deter and punish such actions.
This situation necessitates a renewed focus on international cooperation in developing clear guidelines and mechanisms for attribution, accountability, and response in the digital sphere. The development of effective international treaties and agreements that address cyber warfare is crucial to prevent future escalations and ensure global security in the digital age. The potential for miscalculation and unintended escalation remains high, emphasizing the critical need for enhanced international cooperation and the establishment of clear rules of engagement in cyberspace.
Cybersecurity Measures and Vulnerabilities: Germany Accuses Russia Of Launching Cyber Attacks On Its Defense And Interior Ministries
The alleged cyberattacks on Germany’s defense and interior ministries highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity infrastructure within government agencies. Understanding the existing security measures and potential vulnerabilities is crucial to improving national security and preventing future incidents. While precise details of German government cybersecurity protocols are naturally classified, we can analyze publicly available information and draw inferences about potential weaknesses.The German government, like many others, likely employs a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity, incorporating firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
Data encryption, access control mechanisms, and employee training programs on cybersecurity best practices are also likely components. However, even the most sophisticated systems are vulnerable to sophisticated attacks.
Existing Cybersecurity Measures at German Ministries
German ministries likely utilize a combination of technical and procedural safeguards. Technical measures could include advanced firewall systems, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and data loss prevention (DLP) tools. Procedural measures might involve strict access control policies, regular security awareness training for employees, and incident response plans. Furthermore, the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) and regular security audits are also probable components of their security posture.
However, the specifics remain undisclosed for security reasons.
Potential Vulnerabilities Exploited
The precise vulnerabilities exploited in the alleged attacks remain unknown, pending official investigations. However, several common attack vectors could have been utilized. These include phishing attacks targeting employees, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities in software, or leveraging supply chain compromises to gain unauthorized access. Sophisticated attacks might have involved a combination of these methods, potentially exploiting vulnerabilities in less secure systems to gain a foothold and then moving laterally within the network to access more sensitive data.
For example, a successful phishing campaign could have delivered malware that allowed attackers to bypass firewalls and access sensitive information. Similarly, a vulnerability in a seemingly insignificant piece of software could have served as an entry point for a larger attack.
Hypothetical Plan to Improve German Cybersecurity Infrastructure
A comprehensive improvement plan should focus on both technical upgrades and procedural enhancements. Technically, this would involve investing in advanced threat detection systems utilizing AI and machine learning to identify and respond to evolving threats in real-time. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments by independent cybersecurity firms should be mandated. Furthermore, a robust system for patching and updating software across all government systems needs to be implemented and rigorously enforced.
This should include a proactive approach to identifying and addressing zero-day vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.Procedurally, increased employee training on cybersecurity awareness and best practices is paramount. This training should cover phishing recognition, password management, and secure handling of sensitive data. Regular simulations of cyberattacks would allow ministries to test their incident response plans and identify areas for improvement.
Moreover, establishing a clear chain of command and communication protocols for handling cybersecurity incidents is crucial for effective response and mitigation. Finally, increased collaboration and information sharing between government agencies and the private sector can contribute to a more resilient national cybersecurity posture. This collaborative approach would allow for the faster identification and mitigation of emerging threats.
Attribution Challenges and Evidence Analysis

Pinpointing the perpetrators of sophisticated cyberattacks is notoriously difficult, even with compelling evidence. The decentralized and anonymous nature of the internet, coupled with the ability of attackers to mask their origins, creates a significant hurdle for investigators. This inherent complexity makes definitively attributing attacks to specific state actors, like Russia in this case, a challenging, often drawn-out process.The process of attribution relies heavily on digital forensic evidence, meticulously collected and analyzed to build a case.
Successfully linking an attack to a particular actor requires a chain of evidence that links specific tools, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to a known actor’s past activity. This requires expertise in malware analysis, network forensics, and intelligence gathering.
Digital Forensic Evidence in Cyberattack Attribution
Digital forensic analysis plays a crucial role in building a case. Investigators meticulously examine various forms of digital evidence to establish links between the attack and a potential perpetrator. This evidence can include:
Malware samples: Analysis of the malicious code itself can reveal clues about its origin, including code similarities to previously identified malware attributed to specific actors. Researchers look for unique code signatures, compilation timestamps, and embedded comments that might reveal the developer’s identity or location.
Network traffic logs: Examining network logs from the victim’s systems and network infrastructure can reveal the source IP addresses, communication patterns, and data exfiltrated during the attack. However, these logs can be easily spoofed or obscured, requiring sophisticated analysis techniques.
System logs and registry entries: Analysis of system logs on compromised machines can provide valuable insights into the attacker’s actions, including the commands executed, files accessed, and data modified. Registry entries on Windows systems can also reveal persistent mechanisms used by attackers to maintain access.
Germany’s accusations against Russia for cyberattacks on its defense and interior ministries highlight the critical need for robust cybersecurity. Strengthening defenses means proactively managing cloud security risks, which is why understanding solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management is crucial. These sophisticated attacks underscore the importance of investing in advanced security measures to protect against increasingly sophisticated threats like those allegedly launched by Russia.
Compromised infrastructure: Investigators may find that the attackers used compromised servers or infrastructure located in a specific country or region. This can provide geographical clues, though these could also be deliberately misleading.
Hypothetical False Flag Operation Scenario, Germany accuses russia of launching cyber attacks on its defense and interior ministries
Imagine a scenario where a rival nation wants to frame Russia for the attack on Germany’s ministries. They could use malware with known Russian TTPs, but subtly alter it to leave a unique, undetectable fingerprint pointing away from themselves and towards Russia. They might even use compromised servers within Russia’s borders to launch the attack, further obfuscating the true origin.
The attackers could then leak seemingly credible “intelligence” to the media, supporting the narrative of Russian involvement. This carefully orchestrated false flag operation could make it incredibly difficult to determine the true culprit, even with thorough digital forensic analysis. The complexity of the digital landscape and the ability to manipulate digital evidence makes such scenarios a very real threat to accurate attribution.
Future Implications and Preventative Strategies
The recent cyberattacks targeting Germany’s defense and interior ministries underscore a worrying trend: the increasing sophistication and frequency of state-sponsored cyber warfare. The long-term implications for Germany’s national security are significant, extending beyond immediate data breaches to encompass broader vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure, economic stability, and public trust. Failure to adequately address these vulnerabilities could lead to significant disruptions and damage to Germany’s ability to function effectively as a nation.The incident highlights the need for a proactive and multi-faceted approach to cybersecurity.
Moving forward, Germany must prioritize strengthening its defenses, improving international cooperation, and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness across all levels of government and society. This requires a significant investment in both technological solutions and human capital.
Long-Term Implications for German National Security
The attack’s long-term implications are multifaceted. Successful breaches of this nature could lead to compromised national security secrets, potentially impacting Germany’s intelligence gathering capabilities and defense strategies. Disruption of essential government services, such as citizen identification systems or emergency response networks, could severely impact public trust and societal stability. Furthermore, economic damage from data theft or the disruption of critical infrastructure could be substantial, affecting everything from financial markets to energy grids.
The erosion of public trust in the government’s ability to protect sensitive information poses a significant threat to social cohesion and political stability. The incident also serves as a stark reminder of the interconnected nature of modern society, demonstrating how attacks on one nation can have far-reaching global consequences. For example, similar attacks on other nations’ infrastructure could cripple global supply chains, leading to widespread economic instability.
Recommendations for Preventing Future Attacks
The following table Artikels key recommendations for preventing similar attacks, categorized by implementation difficulty, cost, and expected effectiveness. It is important to note that the effectiveness of any single measure is contingent upon the implementation of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
| Recommendation | Implementation Difficulty | Cost | Expected Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengthening network security through advanced firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication. | Medium | High | High |
| Implementing robust data encryption and access control policies. | Medium | Medium | High |
| Investing in employee cybersecurity training and awareness programs. | Low | Low | Medium |
| Developing and regularly testing incident response plans. | Medium | Medium | High |
| Improving information sharing and collaboration with international partners. | High | Medium | High |
| Investing in research and development of advanced cybersecurity technologies. | High | Very High | High |
Improved International Cooperation in Cybersecurity
Effective international cooperation is crucial in combating state-sponsored cyberattacks. Sharing threat intelligence, developing common cybersecurity standards, and coordinating responses to incidents are vital steps towards building a more resilient global cybersecurity ecosystem. The creation of international legal frameworks to address cybercrime and hold perpetrators accountable is also essential. This requires a collaborative effort among nations, with a focus on building trust and fostering open communication channels.
The establishment of joint task forces and information-sharing platforms can facilitate the rapid identification and response to emerging cyber threats. International cooperation should also extend to capacity building, assisting less developed nations in strengthening their cybersecurity infrastructure. The absence of such collaboration leaves nations vulnerable to attacks and hampers efforts to deter future incidents. Examples of successful international cooperation include initiatives such as the Budapest Convention on Cybercrime, although further advancements are needed to address the evolving nature of cyber threats.
Final Wrap-Up
The accusation that Russia launched cyberattacks against Germany’s defense and interior ministries is a serious escalation, highlighting the increasingly blurred lines between traditional warfare and cyber conflict. While definitive proof remains elusive in the shadowy world of cyberattacks, the implications are undeniable. This incident underscores the urgent need for stronger international cooperation on cybersecurity, improved national defenses, and a more robust framework for attributing responsibility in the digital realm.
The fallout from this event will likely shape the future of international relations and cybersecurity strategies for years to come. It’s a stark reminder that the digital battlefield is as real, and potentially as devastating, as any physical one.
Top FAQs
What specific data is believed to have been targeted in the cyberattacks?
While the exact nature of the compromised data hasn’t been fully disclosed for security reasons, it’s likely to include sensitive information related to national security, defense strategies, and potentially personnel records.
What are the potential long-term consequences of this incident for Germany?
The long-term consequences could include a reassessment of Germany’s cybersecurity infrastructure, increased defense spending, and potentially a shift in its foreign policy approach towards Russia.
What role does NATO play in responding to these accusations?
NATO is likely to offer support to Germany through intelligence sharing, technical assistance, and possibly joint cybersecurity exercises to bolster the defenses of its member states.