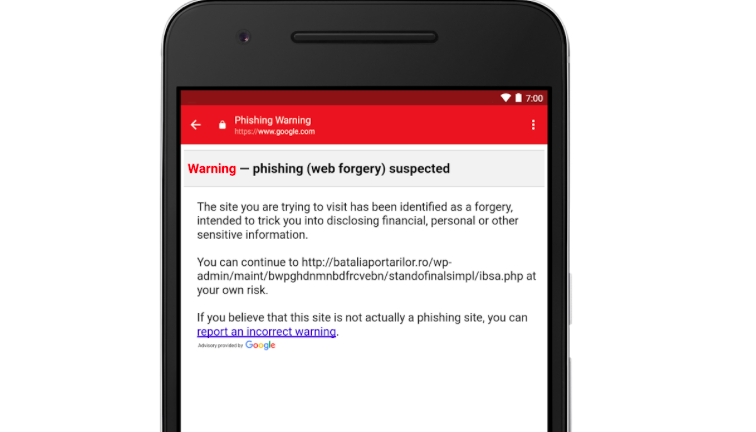
Gmail Users Vulnerable to Phishing Cyber Attacks
Gmail users vulnerable to the following phishing cyber attacks: It’s a scary thought, isn’t it? We all rely on Gmail for so much – from personal communication to sensitive financial transactions. But lurking in our inboxes are sophisticated phishing scams designed to steal our information and compromise our accounts. This post dives deep into the various types of attacks, how to spot them, and most importantly, how to protect yourself.
We’ll explore the sneaky tactics used by phishers, from cleverly crafted emails to exploiting vulnerabilities in Gmail itself. We’ll also cover the devastating consequences of a successful attack, ranging from identity theft to financial ruin. But don’t worry, this isn’t just a doom and gloom post. We’ll arm you with practical tips and strategies to safeguard your Gmail account and stay ahead of these cybercriminals.
Types of Phishing Attacks Targeting Gmail Users
Gmail, being one of the world’s most popular email services, is a prime target for phishing attacks. These attacks exploit the trust users place in the platform and the familiarity they have with its interface to trick them into revealing sensitive information. Understanding the different types of these attacks is crucial for effective protection.
Phishing attacks constantly evolve, employing increasingly sophisticated techniques to bypass security measures. Attackers leverage various methods to gain access to Gmail accounts, often exploiting human psychology and vulnerabilities in the system.
Credential-Stuffing Attacks
Credential-stuffing attacks are a brute-force approach where attackers use lists of stolen usernames and passwords obtained from data breaches on other websites to attempt to log into Gmail accounts. These attacks rely on the fact that many users reuse passwords across multiple online services. If a user’s password has been compromised on another platform, attackers can use that same credential to try and access their Gmail account.
This method is highly automated and can be carried out on a massive scale. Success rates depend on password strength and the uniqueness of passwords used across different accounts. A strong, unique password for each account significantly reduces the risk of successful credential stuffing.
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a more targeted approach than general phishing attacks. Attackers research their victims, gathering personal information to craft highly personalized emails designed to appear legitimate. These emails might seem to come from a trusted source, such as a colleague, a bank, or a company the victim does business with. The emails often contain urgent requests or threats to pressure the victim into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments.
The personalization significantly increases the chance of success, as the email appears authentic and trustworthy to the recipient. For example, a spear phishing email might impersonate a supervisor requesting immediate action on a supposedly urgent project, leading the victim to click a malicious link that redirects them to a fake login page.
Whaling
Whaling is a particularly dangerous type of spear phishing that targets high-profile individuals, such as CEOs, executives, or celebrities. Attackers invest significant time and resources into researching their target, crafting highly sophisticated and believable emails. The goal is to gain access to sensitive information or financial accounts. The success of a whaling attack can have significant financial and reputational consequences for both the victim and their organization.
The emails often exploit the victim’s position and knowledge of internal processes to increase credibility.
Table of Phishing Attack Types
| Attack Type | Description | Method of Delivery | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credential Stuffing | Automated attempts to log in using stolen credentials. | Automated scripts targeting multiple accounts. | Using a list of leaked usernames and passwords to try accessing Gmail accounts. |
| Spear Phishing | Highly targeted emails designed to appear legitimate and trick the victim. | Email with malicious links or attachments. | An email appearing to be from a colleague requesting urgent action on a project, leading to a fake login page. |
| Whaling | Spear phishing targeting high-profile individuals. | Highly personalized emails exploiting the victim’s position and knowledge. | An email impersonating a board member requesting confidential financial information. |
Analyzing Phishing Email Characteristics
Phishing emails are designed to look legitimate, tricking you into revealing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. Understanding the common characteristics of these deceptive emails is crucial for protecting yourself. By learning to spot these red flags, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to a phishing attack.These emails employ a variety of deceptive techniques to bypass your defenses.
They often mimic the appearance of legitimate emails from trusted sources, such as banks, online retailers, or social media platforms. A careful examination of the email’s components, however, often reveals its true nature.
Subject Line Analysis
Subject lines are often the first point of contact, and phishers craft them to pique your interest and encourage immediate action. Generic greetings or overly urgent language are common tactics. For example, a subject line like “Urgent Security Alert!” or “Your Account Has Been Compromised!” is designed to create a sense of panic and pressure you into clicking without thinking.
Legitimate emails usually have more specific and descriptive subject lines. For instance, an email from your bank might be titled “Your Recent Transaction Summary” rather than a generic security alert.
Sender Address Examination
While the “From” field might appear to belong to a trusted organization, a closer look reveals inconsistencies. Phishers often use slightly altered email addresses, employing similar-looking domains or adding extra characters to mimic legitimate senders. For example, an email seemingly from “google.com” might actually come from “googlee.com” or “googl3.com”. Always double-check the sender’s email address for any discrepancies.
Link Scrutiny
Hyperlinks within phishing emails rarely lead to the intended destination. Hovering your mouse over a link (without clicking) will display the actual URL in a tooltip. This allows you to compare the displayed URL with the expected URL of the legitimate website. Phishing links often contain misspellings, unusual characters, or redirect to suspicious domains. For instance, a link claiming to go to “www.paypal.com” might actually lead to “www.paypa1.com” or a completely different, unrelated website.
Attachment Inspection
Attachments in phishing emails can contain malicious software designed to infect your computer. Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or those that seem unexpected or irrelevant. If you receive an attachment from a known sender but are unsure of its legitimacy, contact the sender directly through a known and trusted communication method to verify the authenticity of the email and attachment before opening it.
Red Flag Checklist for Identifying Phishing Emails
It’s crucial to develop a keen eye for suspicious elements. Here’s a checklist of red flags to watch out for:
- Urgent or threatening language: Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency to pressure you into acting quickly without thinking.
- Generic greetings: Legitimate emails usually address you by name.
- Suspicious sender address: Check for misspellings or unusual characters in the email address.
- Suspicious links: Hover over links to check the actual URL before clicking.
- Unexpected attachments: Avoid opening attachments from unknown senders or those that seem irrelevant.
- Grammar and spelling errors: Phishing emails often contain grammatical errors or poor spelling.
- Requests for personal information: Legitimate organizations rarely request sensitive information via email.
- Unusual formatting or design: Phishing emails may have a different look and feel compared to legitimate emails from the same organization.
Vulnerabilities Exploited in Gmail Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks targeting Gmail users succeed by exploiting weaknesses in both the Gmail platform itself and, more frequently, the human element – the users themselves. These attacks leverage a combination of technical vulnerabilities and psychological manipulation to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial to bolstering your online security.Gmail’s security measures are robust, but they can’t account for every user action.
Phishing attacks often rely on exploiting user behavior and circumventing security features through clever social engineering techniques. The success of these attacks hinges on the attacker’s ability to create a sense of urgency, trust, or fear to manipulate users into making hasty decisions.
Weaknesses in User Practices
Successful phishing attacks often hinge less on technical flaws within Gmail and more on exploiting predictable user behaviors. For instance, many users are conditioned to quickly scan emails and click links without fully verifying the sender’s identity or the email’s content. This haste is often exploited by creating convincing fake emails that mimic legitimate communications from banks, online retailers, or even Gmail itself.
Another common vulnerability is a lack of awareness regarding email authentication methods like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, which help verify the sender’s authenticity. Users who are unfamiliar with these methods are more susceptible to phishing emails that appear legitimate despite being fraudulent. Finally, a common vulnerability is the tendency to trust emails that appear personalized, even if the personalization is superficial.
Phishing attackers often gather personal information to create seemingly tailored messages that increase the likelihood of a user falling victim.
Social Engineering Techniques
Social engineering plays a pivotal role in the success of Gmail phishing attacks. It’s the art of manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise their security. A common technique is to create a sense of urgency, such as claiming an account has been compromised and immediate action is required. Another tactic is to prey on users’ fear of missing out (FOMO) by offering limited-time deals or exclusive access to something desirable.
Building trust is also critical; phishing emails often mimic the style and tone of legitimate communications to appear authentic. This might involve using familiar logos, branding, or even mimicking the language used by the legitimate organization. The ultimate goal is to exploit human psychology to bypass security measures and gain access to sensitive information.
Comparison of Vulnerabilities Across Phishing Attack Types, Gmail users vulnerable to the following phishing cyber attacks
Different phishing attack types exploit various vulnerabilities. For example, spear phishing, which targets specific individuals with highly personalized emails, relies heavily on social engineering and detailed research about the target. In contrast, whaling attacks, which target high-profile individuals (like CEOs or executives), often combine social engineering with more sophisticated technical methods to gain access to sensitive information. On the other hand, mass phishing campaigns, which send out thousands of generic emails, rely on the sheer volume of emails to achieve a certain success rate, exploiting the common vulnerabilities of users rushing through emails without proper verification.
Each type of attack adjusts its approach to maximize its effectiveness given the target and resources available. Understanding these variations is crucial for developing effective countermeasures.
Consequences of Successful Phishing Attacks on Gmail Accounts: Gmail Users Vulnerable To The Following Phishing Cyber Attacks
A successful phishing attack on your Gmail account can have far-reaching and devastating consequences, impacting not only your email but also your broader digital life. The severity of these consequences varies greatly depending on the information stolen and the actions taken by the attacker. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for proactive protection.The repercussions of a compromised Gmail account extend beyond simple email access.
The attacker gains a foothold into your digital identity, potentially leading to a cascade of further problems. This section Artikels the potential consequences, ordered from most to least severe.
Severity of Impacts from Compromised Gmail Accounts
The impact of a compromised Gmail account can be devastating, potentially leading to significant financial and personal losses. The following list details the potential consequences, ordered by severity:
- Identity Theft: This is arguably the most severe consequence. Phishing attacks often aim to obtain personal identifying information (PII) such as your full name, address, date of birth, Social Security number (or equivalent national identification number), and passport details. With this information, attackers can open fraudulent accounts, apply for loans in your name, file taxes fraudulently, and commit other identity-related crimes.
The recovery process from identity theft is lengthy, complex, and stressful.
- Financial Loss: Attackers might gain access to your online banking details, credit card information, or other financial accounts linked to your Gmail account. This can result in direct financial theft, unauthorized transactions, and significant financial hardship. They may also use your account to send fraudulent payment requests to your contacts.
- Data Breaches: Your Gmail account likely contains a wealth of sensitive personal information, including photos, documents, contact lists, and private communications. A data breach exposes this information to malicious actors, potentially leading to blackmail, reputation damage, and further exploitation.
- Account Takeover of Other Online Services: Many online services use Gmail for password recovery or account verification. Compromising your Gmail account gives attackers access to these services, allowing them to take control of your social media accounts, online shopping accounts, and other platforms.
- Malware Infection: Phishing emails often contain malicious attachments or links that download malware onto your devices. This malware can steal further information, damage your system, or use your computer for illicit activities like sending spam or participating in botnets.
- Reputational Damage: Attackers might use your compromised Gmail account to send spam or phishing emails to your contacts, damaging your reputation and relationships. This can be particularly damaging if you use your Gmail account for professional communication.
Secondary Risks Associated with Compromised Gmail Accounts
The initial compromise of your Gmail account is rarely an isolated incident. The attacker gains a significant advantage, potentially leading to a chain of further compromises and risks.The attacker’s access to your email can provide them with valuable information for further attacks. For instance, they might use your contact list to target your friends and family with similar phishing attempts, perpetuating the cycle of malicious activity.
Gmail users are constantly targeted, making strong security crucial. I’ve been thinking a lot about secure application development lately, especially after reading about the exciting advancements in domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , which could help create more robust systems. Ultimately, though, even the best tech can’t fully protect against sophisticated phishing attacks aimed at Gmail users, highlighting the need for user vigilance.
They might also use information gleaned from your emails to tailor future attacks, making them more convincing and harder to detect. Access to your email could reveal passwords to other accounts (either directly or through password reset links), providing the attacker with access to a wider range of your online services and personal data. This secondary spread of compromise amplifies the overall risk significantly.
A single compromised Gmail account can be the key that unlocks a vast amount of personal information and digital assets.
Mitigation Strategies and Best Practices
Protecting your Gmail account from phishing attacks requires a multi-layered approach. It’s not about relying on a single solution, but rather implementing a combination of strategies to minimize your vulnerability. This involves being vigilant, employing strong security practices, and understanding how phishing attacks operate. The following strategies will significantly enhance your email security.
Proactive measures are far more effective than reactive ones. Instead of waiting for a phishing attempt to occur, actively work to prevent them. This involves strengthening your account’s defenses and educating yourself on common phishing tactics.
Password Management
Strong, unique passwords are fundamental to online security. A compromised password can grant attackers access to your entire Gmail account, including sensitive emails and personal information. Avoid using easily guessable passwords like birthdays or pet names. Instead, opt for long, complex passwords combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store these complex passwords for all your online accounts.
A password manager can also help you avoid reusing passwords across multiple platforms. Regularly updating your passwords, especially after any suspected security breach, is also crucial.
Email Filtering and Spam Management
Gmail’s built-in spam filters are a valuable first line of defense. However, they are not foolproof. Familiarize yourself with Gmail’s spam settings and adjust them to your needs. Mark suspicious emails as spam to help train the filter. Consider using additional email security add-ons or extensions that offer more robust filtering capabilities, scanning emails for malicious links and attachments before they reach your inbox.
Regularly review your spam folder to ensure that legitimate emails aren’t being incorrectly filtered.
Suspicious Link and Attachment Handling
Never click on links or open attachments from unknown senders or those that seem suspicious. Even if the email appears to be from a trusted source, verify the sender’s identity independently before clicking any links. Hover your mouse over links to see the actual URL – this can reveal if the link is legitimate or a cleverly disguised phishing attempt.
Avoid opening attachments from unknown sources, as these can contain malware. If you’re unsure about an email’s legitimacy, contact the purported sender directly using a known and verified contact method (e.g., phone number or a separate email address) to confirm.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your Gmail account. Even if someone obtains your password, they’ll still need access to your phone or another authentication device to log in. 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, making it much harder for phishers to compromise your account, even if they’ve successfully tricked you into revealing your password.
This method uses a secondary verification step, such as a code sent to your phone or an authenticator app, in addition to your password.
Regular Security Audits
Periodically review your Gmail account’s security settings and connected apps. Check for any unusual activity or unauthorized access attempts. Review the list of apps and devices that have access to your Gmail account and revoke access to any that you don’t recognize or no longer use. This proactive approach helps identify potential vulnerabilities and ensures that only trusted applications have access to your account.
Regularly checking your account activity for any suspicious logins or changes is a crucial preventative measure.
| Mitigation Strategy | Detailed Explanation |
|---|---|
| Strong Passwords & Password Manager | Use long, complex passwords combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Utilize a password manager to generate and securely store these passwords. |
| Email Filtering & Spam Management | Utilize Gmail’s built-in spam filters and consider additional email security add-ons. Regularly review your spam folder. |
| Suspicious Link & Attachment Handling | Never click links or open attachments from unknown senders. Hover over links to verify URLs and contact senders directly if unsure. |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Enable 2FA to add an extra layer of security. This requires a secondary verification method beyond your password. |
| Regular Security Audits | Periodically review your Gmail security settings, connected apps, and account activity for any unusual activity. |
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure that significantly enhances the protection of Gmail accounts against phishing attacks. By requiring multiple forms of verification, MFA creates a much stronger barrier against unauthorized access, even if a phisher successfully obtains a user’s password. It adds layers of security, making it exponentially more difficult for attackers to gain control of an account.MFA works by demanding more than just a password to log in.
This means that even if a phishing email successfully tricks a user into revealing their password, the attacker will still be blocked without the additional verification factor. This significantly reduces the success rate of phishing campaigns.
MFA Methods and Their Characteristics
Several MFA methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences is vital in choosing the most suitable approach for individual security needs.
- Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP): These codes are generated by authenticator apps (like Google Authenticator or Authy) and change every 30 seconds. They offer strong security because the codes are dynamic and short-lived. However, they require a smartphone or other device with the authenticator app installed. A weakness is reliance on a secondary device being available.
- Security Keys: These physical devices (USB, NFC, or Bluetooth) generate unique codes when plugged in or held near a device. They are extremely secure as they are resistant to phishing and malware. However, they require a physical device, which can be inconvenient to carry around. Loss or damage renders the key unusable.
- SMS-Based Verification: This method sends a verification code to a registered phone number. It’s convenient but less secure than TOTP or security keys because it’s vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks, where a malicious actor gains control of a user’s phone number.
- Backup Codes: These codes are provided when MFA is enabled. They are a safety net for situations where access to other verification methods is unavailable. However, they should be stored securely and offline; compromised backup codes negate the benefit of MFA.
How MFA Protects Against Phishing
The effectiveness of MFA in thwarting phishing attacks lies in its multi-layered approach. Imagine a scenario where a user receives a convincing phishing email mimicking Gmail’s login page. If the user enters their credentials, the attacker only has half the puzzle. Even if they manage to capture the password, they are still blocked from accessing the account because they lack the second factor, such as the code from the authenticator app or the security key.
This second layer of verification renders the stolen password useless, effectively nullifying the phishing attempt. The added layer of protection provided by MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of a successful phishing attack leading to account compromise. Even sophisticated phishing attacks aiming to steal both the password and the secondary verification factor are incredibly difficult to execute successfully.
Visual Representation of Attack Vectors

Understanding the visual flow of a phishing attack helps illustrate how seemingly innocuous actions can lead to significant security breaches. A typical attack unfolds in several distinct stages, each exploiting a specific vulnerability in the Gmail user’s security posture. This visual representation will detail these stages and the corresponding attack vectors.The following description depicts a visual representation of a phishing attack targeting a Gmail user, progressing from initial contact to account compromise.
Imagine a flowchart, starting with a large box labeled “Phishing Email Sent.” Arrows branch out from this box, representing different attack vectors.
Stages of a Gmail Phishing Attack
This section details the sequential steps involved in a typical phishing attack targeting a Gmail account, focusing on the vulnerabilities exploited at each stage. The visual representation would show these stages as connected boxes in a flowchart, with arrows indicating the progression of the attack.The first box, “Phishing Email Sent,” depicts the initial stage. From here, multiple arrows point to different boxes representing various attack vectors: one labeled “Spoofed Sender Address,” another “Urgent/Threatening Subject Line,” and a third “Malicious Link/Attachment.” Each of these arrows represents a different tactic used to lure the victim into interacting with the malicious email.The next stage, represented by a box labeled “User Interaction,” shows the point where the victim interacts with the phishing email.
This box could have arrows pointing to different outcomes, depending on the type of interaction: clicking a malicious link, opening a malicious attachment, or simply replying to the email.The following box, “Compromised Credentials,” shows the consequence of successful interaction. This stage illustrates how the attacker gains access to the victim’s Gmail credentials. For example, if the victim clicked a malicious link, the arrow from “User Interaction” would lead to this box, representing the redirection to a fake login page.Finally, the last box, “Account Access,” shows the attacker’s successful access to the Gmail account.
This box could contain further branching arrows, depicting different malicious activities the attacker might undertake, such as accessing personal information, sending spam, or stealing financial data. Each of these actions represents a consequence of the successful phishing attack.The overall visual representation would clearly show the linear progression of the attack, from the initial email to the final compromise of the Gmail account.
The use of clear labels and arrows would make it easy to understand the different stages and the vulnerabilities exploited at each point. The visual would highlight how a simple click or interaction can have significant consequences.
Gmail’s Security Features and Their Effectiveness
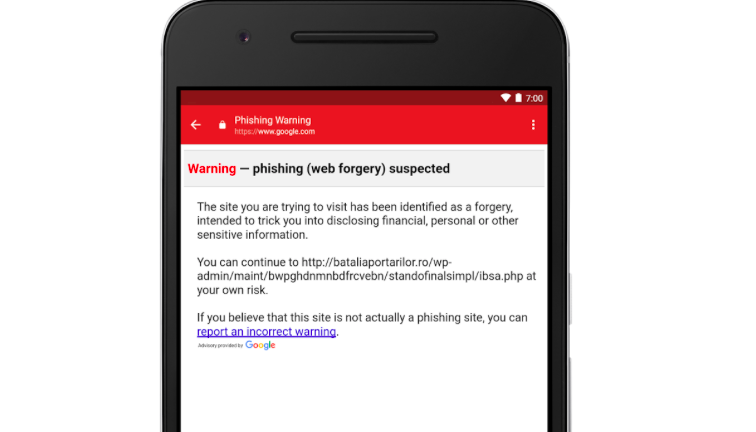
Gmail boasts a robust suite of security features designed to protect users from phishing attacks. These range from basic spam filters to more advanced technologies like machine learning, but their effectiveness varies depending on the sophistication of the phishing attempt. Understanding both their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for maintaining a secure inbox.Gmail’s security features work in multiple layers.
Initial defenses involve spam filters that analyze incoming emails for suspicious characteristics like unusual sender addresses, links to malicious websites, and the presence of known phishing s. More advanced features leverage machine learning algorithms to identify subtle patterns indicative of phishing, constantly adapting to new techniques employed by attackers. Google also employs sophisticated techniques to verify the authenticity of emails, checking for digital signatures and comparing sender information against known legitimate sources.
Finally, Gmail actively warns users about potentially dangerous links and attachments before they’re opened, providing an additional layer of protection.
Spam and Phishing Filters
Gmail’s spam filters are a first line of defense against phishing emails. These filters analyze various email characteristics, including sender reputation, email content, and the presence of known phishing s or patterns. While highly effective in catching many obvious phishing attempts, sophisticated attacks that use spoofed sender addresses or cleverly crafted content can sometimes slip through. For example, a phishing email might mimic a legitimate email from a bank or social media platform, using carefully chosen wording and branding to deceive the recipient.
Gmail users are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated phishing attacks, often disguised as legitimate communications. These scams can lead to serious financial losses, similar to what’s happening with Facebook, where I recently read about a disturbing trend of facebook asking bank account info and card transactions of users. This highlights the importance of staying vigilant and recognizing the red flags of phishing attempts to protect your Gmail account and financial data.
It’s a scary world out there!
The effectiveness of these filters depends heavily on Google’s ability to keep pace with the evolving tactics of phishers.
Suspicious Link and Attachment Warnings
Before a user clicks on a link or downloads an attachment, Gmail often displays a warning if the link or attachment is deemed suspicious. This warning usually includes information about the potential risk, such as the link leading to an unknown or untrusted website. This feature helps users to identify potentially malicious content and avoid interacting with it. However, highly sophisticated phishing campaigns might employ techniques to bypass these warnings, such as using shortened URLs or embedding malicious code within seemingly harmless attachments.
The effectiveness of this feature relies on the accuracy of Gmail’s risk assessment algorithms.
Machine Learning and Advanced Threat Detection
Gmail employs machine learning algorithms to analyze email content and behavior patterns to identify phishing attempts. This technology allows Gmail to detect subtle indicators of phishing that may be missed by simpler filters. Machine learning algorithms continuously adapt and improve as they are exposed to new phishing techniques. This makes them a valuable tool in the fight against phishing, but they are not foolproof.
Highly sophisticated phishing attacks, especially those employing social engineering tactics, can still evade these advanced detection methods. For example, a highly personalized phishing email tailored to a specific individual might be difficult to detect even by sophisticated machine learning systems.
Gmail users are increasingly vulnerable to sophisticated phishing attacks, making robust security crucial. Understanding how to mitigate these threats is key, and learning about solutions like cloud security posture management is a great starting point. Check out this insightful article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to see how better security can protect your inbox from these increasingly common attacks.
Ultimately, proactive measures are essential to safeguard your Gmail account from phishing scams.
Areas for Improvement
While Gmail’s security features are strong, there’s always room for improvement. One area is enhancing the detection of highly personalized phishing emails that exploit social engineering tactics. These emails often evade detection by traditional filters because they don’t contain obvious red flags. Another area is improving the clarity and effectiveness of warning messages. Sometimes, the warnings are too generic or difficult to understand, leading users to dismiss them.
Finally, stronger integration with other security measures, such as password managers and anti-virus software, could further enhance the overall security of Gmail accounts.
Final Review
So, are you ready to strengthen your Gmail security? Remember, staying vigilant and informed is your best defense against phishing attacks. By understanding the tactics used by phishers and implementing the preventative measures discussed, you can significantly reduce your risk. Don’t let your inbox become a gateway for cybercriminals – take control of your online security today!
Q&A
What is credential stuffing?
Credential stuffing is when hackers use stolen usernames and passwords from other data breaches to try and access your Gmail account.
How can I tell if a link is suspicious?
Hover over links before clicking to see the actual URL. Look for misspellings in the website address or unusual characters.
What should I do if I think I’ve been phished?
Immediately change your Gmail password, enable two-factor authentication, and report the phishing email to Gmail.
Is two-factor authentication really necessary?
Absolutely! It adds a crucial layer of security, making it much harder for hackers to access your account even if they have your password.