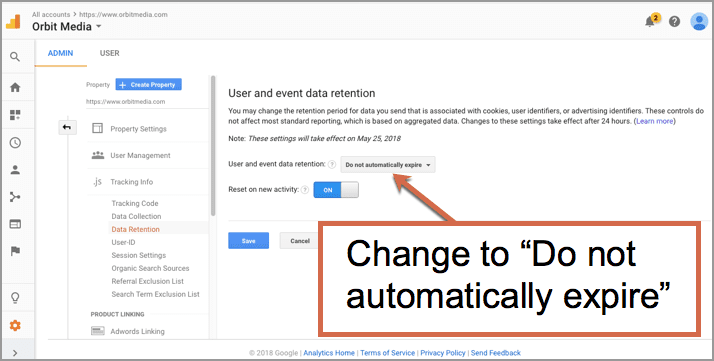
Google Makes Changes to Data Retention Laws Implications Explained
Google makes changes to its data retention laws, raising important questions about user privacy and the future of online services. These changes will likely impact how Google handles user data, from search queries to location history, potentially altering the scope and timeframe of data retention. Understanding the specifics of these modifications is crucial for users, businesses, and legal professionals alike.
This article delves into the specifics, analyzing the potential impact on individuals and the wider tech landscape.
Google’s existing data retention policies, encompassing a vast array of user information, have been a subject of debate. The new policies introduce adjustments to the timeframe for storing various data types. A comparison with competitor policies reveals interesting nuances in data management strategies across the industry. This shift in policy necessitates a careful examination of its potential consequences, which will be explored in detail in the subsequent sections.
Overview of Google’s Data Retention Policies
Google’s data retention policies are complex and multifaceted, encompassing a vast amount of user-generated and collected information. Understanding these policies is crucial for users to comprehend how their data is handled and for businesses to ensure compliance. This overview provides a summary of Google’s current data retention practices, highlighting the scope and timeframe of data storage.Google’s data retention policies are designed to balance the need to provide services with the user’s right to privacy and data security.
These policies are constantly evolving to address changing technological advancements and legal requirements. The policies also address the global nature of Google’s operations, acknowledging the varying data protection regulations across different countries.
Summary of Google’s Data Retention Policies
Google retains various types of data, including user accounts, search queries, location data, and communications data. The specifics of retention vary depending on the type of data and the user’s interactions with Google services.
Scope of Data Covered
Google’s data retention policies encompass a wide range of user data. This includes but is not limited to: user accounts, including personal information, such as name, email address, and contact details; search queries, which record user searches and related information; location data, collected through GPS or Wi-Fi signals; and communication data, encompassing emails, messages, and other forms of interactions within Google services.
Furthermore, Google collects data on device usage patterns and user interactions with its products and services.
Google’s recent data retention policy changes are definitely causing a stir, and it’s interesting to see how other legal developments are impacting digital data management. For instance, the Department of Justice’s recent “Safe Harbor” policy for Massachusetts transactions, detailed in Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions , seems to suggest a broader shift in how data privacy is being addressed.
Ultimately, Google’s changes are just one piece of a larger puzzle in the ever-evolving landscape of digital data security.
Typical Timeframe for Data Retention
The typical timeframe for data retention varies significantly based on the type of data and the specific Google service. For example, search queries might be retained for a shorter period than user account information. This flexibility is crucial to accommodate diverse needs and legal requirements. The retention period may also differ based on the user’s location and applicable local laws.
Specific data types and their corresponding retention periods may vary based on the services utilized and user activity.
Comparison of Data Retention Policies
| Data Category | Microsoft | Amazon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Account Data | Retained for the duration of the account’s active status, and potentially beyond, in compliance with legal requirements. | Retained for the duration of the account’s active status, and potentially beyond, in compliance with legal requirements. | Retained for the duration of the account’s active status, and potentially beyond, in compliance with legal requirements. |
| Search Queries | Retained for a shorter period than user account information. | Retained for a shorter period than user account information. | Retained for a shorter period than user account information. |
| Location Data | Retained for a period depending on the specific service and user settings. | Retained for a period depending on the specific service and user settings. | Retained for a period depending on the specific service and user settings. |
| Communication Data | Retained based on the service and user interaction. | Retained based on the service and user interaction. | Retained based on the service and user interaction. |
This table provides a general comparison, and the specific details may vary. The exact retention periods for each data category can differ based on the service used, user preferences, and legal requirements. Moreover, these policies are subject to change over time.
Impact of Changes on Users
Google’s recent data retention policy adjustments are sure to stir up a mix of anxieties and hopes among its users. Understanding the potential ramifications is crucial for navigating the evolving digital landscape. These changes, while seemingly technical, directly affect how Google handles user data, impacting privacy, potential legal recourse, and overall user experience.These adjustments to Google’s data retention policies introduce a complex interplay of benefits and drawbacks for users.
On one hand, users might find reassurance in streamlined data management and enhanced security measures. Conversely, some users might feel their privacy is compromised due to expanded data collection and storage practices. The key is to analyze these changes through the lens of both individual and societal implications.
Potential Privacy Impacts
The changes in Google’s data retention policies have the potential to significantly affect user privacy. Increased retention periods for certain data types might lead to a wider scope of data being analyzed and potentially used for purposes beyond the original consent. This could raise concerns about the extent of Google’s access to personal information and the potential for misuse.
The policies might also have implications for users in different regions, as data protection laws vary.
Google’s recent data retention policy changes are a big deal, especially when considering the security implications of cloud storage. This shift raises questions about data handling, but it’s also worth noting the recent vulnerability discovered in Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB. Learning about the specifics of this vulnerability can help us better understand the potential risks associated with different cloud platforms, which are critical to consider when assessing Google’s new data retention laws.
Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details offer valuable insights into this crucial area. Ultimately, these changes to Google’s data retention policies necessitate careful consideration of the entire ecosystem, including vulnerabilities like those seen in Azure Cosmos DB.
Potential Benefits for Users
Improved data security and enhanced service reliability are potential benefits for users. By retaining data for a longer period, Google might be better equipped to identify and prevent fraudulent activities or malicious attacks. This could enhance the overall safety of user accounts and transactions. The changes might also facilitate faster troubleshooting and support for users experiencing issues with Google services.
Potential Drawbacks for Users
While longer retention periods could enhance security, they might also increase the risk of data breaches. The potential for malicious actors to access vast amounts of retained data is a significant concern. Furthermore, the increased storage of user data could potentially raise concerns about the potential for misuse or unauthorized access. These are critical considerations for users.
Implications for Legal Rights and Recourse
Changes in data retention policies can affect users’ legal rights and potential avenues for recourse. Users may have the right to access, rectify, or delete their data, depending on applicable data protection laws. Understanding these rights and how the changes might affect them is crucial. Users should be aware of their rights and the potential avenues for legal recourse in case of data misuse or breach.
Potential Scenarios and User Impact
The table below illustrates potential scenarios and how changes to Google’s data retention policies may affect users.
| Scenario | Potential User Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased data retention for user activity data | Potential for more comprehensive analysis, but also greater risk of data breaches. Users may face increased surveillance. |
| Data retention aligned with legal requirements in different regions | Users in specific regions may experience variations in data protection, impacting their rights and recourse options. |
| Improved security measures due to longer data retention | Users may feel more secure with improved fraud prevention and troubleshooting, but also need to be aware of the implications for their privacy. |
| Data retention period shorter than before | Users may find that their data is not being retained as long as before, potentially reducing access to support and troubleshooting services. |
Analysis of the Changes

Google’s recent adjustments to its data retention policies warrant a closer look. These modifications likely stem from a confluence of factors, including evolving legal landscapes, internal strategic shifts, and broader industry trends. Understanding the reasoning behind these changes is crucial for users and stakeholders to adapt to the evolving digital environment.The decisions likely involve a complex balancing act between user expectations, regulatory compliance, and business considerations.
Google, as a dominant player in the digital sphere, likely prioritizes maintaining user trust while simultaneously optimizing its operational efficiency and financial performance.
Motivations and Considerations Behind the Changes, Google makes changes to its data retention laws
Google’s motivations for modifying data retention policies likely include a desire to improve operational efficiency and streamline data management. Reducing the amount of data stored could lead to lower storage costs and increased processing speeds. Furthermore, a more streamlined data management system might reduce the potential for errors and security breaches.
Industry Trends Influencing Modifications
Several industry trends influence Google’s data retention policy changes. The increasing prevalence of data privacy regulations globally, such as GDPR and CCPA, compels companies to adopt more stringent data handling practices. The growing emphasis on data minimization and user control further underscores the importance of these changes.
- Increased Data Privacy Regulations: Globally, governments are enacting stricter regulations around data privacy and handling. These regulations often require companies to limit the amount of data they collect and retain. Examples like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) demonstrate this trend, pushing businesses to prioritize user data rights.
- Data Minimization and User Control: There’s a growing shift towards data minimization principles. Companies are recognizing the importance of collecting only the necessary data and storing it for the shortest possible duration. User control over their data is also increasingly valued, leading to policies that empower users to request data deletion or access it more easily.
- Cloud Computing and Data Storage Costs: The rising costs of cloud storage and data processing are impacting companies’ decisions regarding data retention. Optimizing storage space and reducing the volume of retained data becomes a crucial aspect of cost-effectiveness.
Comparison with Existing Data Privacy Regulations
Comparing the proposed changes to existing data privacy regulations is essential. Regulations like GDPR mandate specific data retention periods for different types of data. Google’s modifications should align with these standards to avoid potential legal challenges.
| Regulation | Key Requirement | Potential Impact on Google |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data retention limited to the necessary time for the purpose it was collected | Google must ensure its retention policies adhere to the defined timeframes for specific data categories. |
| CCPA | Right to deletion of personal information | Google needs to incorporate mechanisms for user requests to delete their data within the specified timeframes. |
| Other Regional Regulations | Similar requirements on data minimization and retention periods | Google needs to adjust its policies to ensure compliance with the various regional and national data protection regulations. |
Potential Legal Implications

Google’s recent data retention policy changes inevitably raise concerns about potential legal challenges. These adjustments could spark legal battles over user privacy rights, data security, and the scope of Google’s responsibility in handling user information. The implications extend beyond Google, impacting the legal landscape surrounding data handling and potentially setting precedents for other tech companies.
Potential Legal Challenges
The modifications to Google’s data retention policies could trigger legal actions from various stakeholders. Users who feel their privacy rights have been compromised might initiate lawsuits. These lawsuits could allege violations of data protection laws, demanding compensation for damages or seeking injunctions to restrict Google’s practices. Furthermore, regulatory bodies or governments might initiate investigations or legal proceedings if the changes are deemed to violate existing data protection regulations.
Relevant Laws and Regulations
Numerous laws and regulations govern data retention and privacy worldwide. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and other regional data protection laws could be directly implicated by Google’s changes. These regulations often stipulate specific requirements for data retention periods, access rights, and user consent. The impact of these laws and regulations on Google’s operations will likely be substantial.
Potential Ramifications for Google’s Business Operations
Google’s data retention policies are integral to its core business functions. Any legal challenges could result in substantial financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Legal battles can significantly impact Google’s resources, diverting time and financial investments away from product development and other core business activities. Furthermore, unfavorable court rulings could lead to substantial legal fees and compliance costs.
Table: Legal Aspects Potentially Impacted
| Legal Aspect | Potential Impact on Google |
|---|---|
| Data Subject Rights | Google could face lawsuits for not adequately fulfilling user requests for data access, rectification, or erasure, potentially violating GDPR and CCPA. |
| Data Security | If the changes compromise data security, leading to breaches or unauthorized access, Google could be liable for damages under various data breach notification laws. |
| International Data Transfer | Google’s global operations may be affected if changes to data retention policies violate international data transfer agreements, such as the Safe Harbor agreement. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Google might face fines and penalties for non-compliance with evolving data protection regulations, including those concerning data minimization and purpose limitation. |
| Contractual Obligations | If Google’s data retention policies violate contractual agreements with third-party partners or customers, it could face potential litigation. |
Industry Response and Public Perception: Google Makes Changes To Its Data Retention Laws
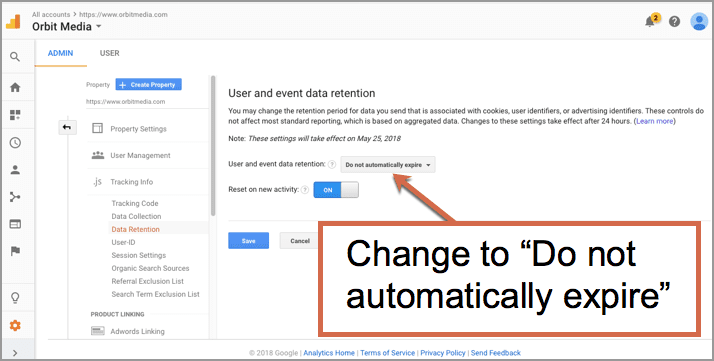
Google’s recent data retention policy adjustments have sparked a flurry of reactions, ranging from cautious acceptance to outright criticism. The changes, while aiming to balance user privacy with operational needs, have undeniably raised eyebrows within the tech industry and among privacy advocates. Public perception is complex, reflecting diverse viewpoints on the extent to which these modifications affect individual rights and the overall trustworthiness of tech giants.
Reactions from Tech Competitors
Several tech companies have publicly commented on Google’s data retention policy shifts. Some competitors have expressed concern regarding potential competitive advantages gained by Google due to its access to broader datasets. Others have acknowledged the need for data retention policies in the modern digital landscape, but have also voiced concerns about the potential for misuse or overreach. A notable example is the statement by a major social media platform, which highlighted the importance of user data security, while simultaneously expressing concern about potential biases introduced by such practices.
Privacy Advocate Perspectives
Privacy advocates have consistently emphasized the need for transparency and user control in data handling. They argue that Google’s changes, though potentially justified from a business standpoint, may not adequately address the potential for data misuse or harm. These advocates are often concerned with the implications for individuals’ fundamental rights and the ability of users to exercise control over their personal information.
Their calls for greater scrutiny of data retention practices underscore the importance of safeguarding user privacy in the digital age. Key demands often revolve around stronger user consent mechanisms, more robust data deletion policies, and increased transparency about how data is used and stored.
Public Perception Summary
Public perception of Google’s data retention changes is largely mixed. While some users may view the changes as necessary for maintaining services, others express concern about the potential for their data to be misused or exploited. This uncertainty, coupled with the inherent complexity of data retention policies, creates a climate of apprehension among many. The lack of clear and accessible information about how these changes impact individual users has undoubtedly contributed to the mixed sentiment.
The evolving nature of data protection regulations and the growing awareness of data privacy issues further fuel the complexity of public perception.
Potential for Increased Scrutiny
The adjustments to Google’s data retention policies have significantly increased the scrutiny of data retention practices across the entire tech sector. Regulatory bodies and legal experts are now more likely to scrutinize similar policies in the future. The need for greater transparency and accountability in data handling is likely to become a major focus for future discussions and policy developments.
The potential for legal challenges and stricter regulations in response to these changes is undeniable, given the heightened awareness of data privacy issues. Instances of past controversies surrounding data handling practices, including instances of data breaches and questionable data usage practices, have further heightened the expectation for greater oversight and stricter policies.
Regional Variations in Public Perception
The impact of Google’s data retention policy changes is not uniform across different regions. In regions with strong data privacy laws, public perception may be more negative due to the potential conflicts between these changes and existing legal frameworks. Conversely, regions with less stringent data privacy regulations may view the changes with less concern. For example, European Union citizens, with their stringent data protection regulations, are likely to be more critical of the changes than users in regions with weaker legal frameworks.
This difference in regional response highlights the varying levels of protection afforded to users in different jurisdictions and the need for globally consistent standards in data privacy.
Future Implications for Google
Google’s recent data retention policy adjustments are a significant turning point, potentially reshaping the company’s future trajectory. These changes, while aimed at specific legal and regulatory requirements, will undoubtedly impact Google’s market position, user trust, and internal data handling strategies. Understanding these potential implications is crucial for assessing the long-term consequences for both Google and its users.
Potential Impacts on Google’s Market Position and Reputation
Google’s reputation is intricately linked to its data handling practices. A perceived shift towards stricter data retention, while potentially complying with legal mandates, could impact public perception. If the changes are seen as overly restrictive or invasive, it could damage Google’s brand image, particularly among privacy-conscious consumers. Conversely, a perceived focus on transparency and user control could enhance its reputation and attract users who prioritize data security.
This could lead to a shift in market share, as competitors emphasize user privacy. Examples from other technology companies illustrate this dynamic. Facebook’s controversies regarding user data privacy have significantly impacted its market valuation and public image. Similarly, Apple’s emphasis on user privacy has positioned it as a preferred choice for many users.
Potential Implications for User Trust and Engagement
User trust is a critical component of Google’s success. Changes in data retention policies could affect user engagement. Users who feel their data is less secure or more vulnerable to misuse might choose alternative services. A transparent approach to data handling, including clear explanations of how data is used and retained, could help maintain and build user trust.
Conversely, ambiguity or a perceived lack of control over their data might deter users, impacting Google’s market share. The rise of privacy-focused search engines demonstrates user sensitivity to data protection. DuckDuckGo, for instance, has gained popularity among users concerned about privacy, showcasing the potential impact of user concerns on market share.
Possible Adjustments in Google’s Data Handling Strategies
Google’s internal data handling strategies will likely undergo adjustments. The company might invest more in data encryption and security measures to ensure compliance with evolving regulations. Enhanced data governance policies and procedures could become paramount. This could involve more robust data retention policies and stricter access controls. Google may also need to prioritize transparency, providing users with more control over their data.
The introduction of clearer data usage policies and more intuitive user interfaces for data management could be essential. This approach aligns with the trend of user-centric data management seen in the tech industry.
Possible Future Scenarios for Google’s Business
| Scenario | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Positive User Response | Users trust Google’s commitment to data security and transparency. | Increased user engagement and loyalty. Potential for market share growth. |
| Scenario 2: Negative User Response | Users perceive the changes as a threat to their privacy and data security. | Reduced user engagement, potential market share loss, and damage to reputation. |
| Scenario 3: Mixed User Response | A portion of users are satisfied, while others express concerns. | Potential for market share fluctuations and a need for more nuanced data handling strategies. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Google’s recent data retention policy adjustments are likely to have a significant impact on users, and understanding how these changes play out in specific scenarios is crucial. This section provides hypothetical examples to illustrate potential outcomes for various user types, alongside analysis of similar privacy violations in the past. By examining these case studies, we can better grasp the implications of Google’s updated policies.
Hypothetical User Scenarios
Different user groups will experience varying consequences from these changes. A frequent user heavily reliant on Google services will face different challenges compared to a casual user who only uses Google for specific tasks.
- Frequent Google User: A user who relies heavily on Google services for communication, storage, and productivity tools might see their historical data more readily accessible to Google for analysis or potential use in targeted advertising. This could lead to a feeling of reduced privacy and control over personal information. For example, a teacher who uses Google Workspace extensively might find their years of lesson plans and student data more readily available for Google’s review, potentially impacting their classroom practices or leading to new targeted advertising based on the student’s educational needs.
- Casual Google User: A casual user who only uses Google services for specific tasks, such as searching or using Google Maps, will likely experience less immediate impact. Their data, while still subject to the policy, might not be as comprehensively reviewed or used for personalized services. This user might not see a drastic change in advertising, but their data may still be subject to the broader implications of the policy.
- Data Protection Advocates: Individuals who value their privacy and actively seek to protect their personal information might take steps to minimize Google’s access to their data. This could involve using alternative services, opting out of certain features, or regularly reviewing and managing their Google account settings. These users might experience frustration and require additional steps to maintain their data privacy.
Potential Outcomes for Different User Types
The outcomes of these changes will vary significantly based on the individual’s usage patterns and sensitivity to data privacy.
Google’s recent changes to data retention policies are a significant development, especially considering the increasing reliance on AI. This necessitates a proactive approach to securing code, particularly as AI systems become more sophisticated. We need to equip ourselves with robust tools like those discussed in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed to ensure responsible and safe AI development.
Ultimately, these changes highlight the growing need for careful consideration of data handling and security in the AI age.
| User Type | Potential Outcome | Illustrative Example |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent Google User | Increased data accessibility, potential for targeted advertising, possible feeling of reduced privacy | A frequent Gmail user might see their emails used for more precise advertising, influencing the product recommendations they receive. |
| Casual Google User | Less noticeable impact, but still subject to broader policy implications | A user who primarily uses Google Search will likely notice minimal impact on their daily search experience, but their data is still subject to Google’s new retention policies. |
| Data Protection Advocates | Active measures to minimize Google’s data access, possible frustration with additional steps to maintain privacy | An individual with heightened privacy concerns might choose to utilize alternative search engines or limit their Google account usage. |
Data Breaches and Privacy Violations
Historical examples of data breaches related to similar data retention policies demonstrate the potential for harm. Past incidents highlight the importance of robust data security measures and transparency in data handling practices. The 2018 Facebook data breach, for instance, demonstrated how seemingly minor data collection practices can lead to significant privacy violations when combined with a lack of security.
“Data breaches are a serious concern, and a clear understanding of data retention policies is critical to mitigating risks.”
Impact on Data Security
Google’s recent data retention policy changes, while aiming to enhance user privacy, introduce new complexities regarding data security. These alterations in how and where Google stores user data necessitate a careful assessment of potential risks and vulnerabilities. The shift in policies may inadvertently create new attack vectors and weaken existing security measures, demanding a proactive approach to safeguard user information.Data retention policies directly influence data security strategies.
Changes in these policies, no matter how well-intentioned, can introduce new points of weakness in the system. Google must ensure its security infrastructure adapts to the modifications to maintain robust protection against malicious actors. A thorough review of security protocols and an assessment of potential vulnerabilities are paramount in the face of these changes.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Changes in data retention policies can create new avenues for unauthorized access. If data is stored for a shorter period than previously, the potential for unauthorized access and exploitation increases. Data breaches may occur due to insufficient protection during shorter retention periods. Additionally, the transfer of data to new locations, or the adjustment of access controls, might present unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Data Breach Likelihood Increase Areas
Data retention policies play a significant role in the likelihood of data breaches. A shortened retention period could potentially make it more difficult to detect and respond to malicious activities. Furthermore, changes to data storage locations and access controls could introduce new attack vectors. A lack of preparedness for these changes could lead to increased risks.
Security Implications Analysis
| Data Security Concern | Possible Mitigation Strategy ||—|—|| Shorter Retention Periods: Increased risk of data breaches during shorter periods of data storage. | Implementing enhanced data encryption and access controls during the shorter retention period. Using secure data deletion methods. || Data Transfer: Increased risk of data breaches during the transfer of data to new locations. | Employing secure transfer protocols and robust encryption methods during the transfer.
Regular security audits of the transfer process. || Access Control Adjustments: Changes in access control policies could introduce new vulnerabilities. | Conducting thorough security assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and implementing new security protocols. Review and adjust access controls for staff with access to the affected data. || Lack of Preparedness: Insufficient preparation for changes in data retention policies could lead to increased vulnerabilities.
| Develop a comprehensive data security plan that Artikels procedures for handling data retention policy changes. Conduct regular security awareness training for employees. |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, Google’s revisions to its data retention laws represent a significant shift in the digital landscape. The changes hold implications for users, businesses, and the future of online services. The potential legal ramifications, industry responses, and future adjustments to Google’s data handling strategies are all worthy of further consideration. Ultimately, these modifications will reshape how we interact with technology and how our data is handled.
FAQ Section
What specific types of data are affected by the changes?
The changes impact various data types, including search queries, location data, browsing history, and user account information. The precise scope will depend on the specific terms of the revised policies.
How long will Google retain my data after these changes?
The duration of data retention will vary depending on the type of data and the specific policy. The updated policies should specify the new retention periods.
What are the potential legal challenges to Google’s changes?
Potential legal challenges could arise if the changes violate existing data privacy regulations or user rights. The specifics will depend on regional laws and interpretations.
How will these changes affect my experience with Google services?
The changes could potentially impact features and functionalities of Google services, especially those directly reliant on the retained data. The specifics will depend on the implementation of the new policies.





