Google New Password Manager Raises Security Concerns
Google new password manager raises security concerns – Google’s new password manager launch has, unfortunately, been overshadowed by serious security concerns. The buzz around its innovative features quickly faded as users and experts alike raised red flags about potential vulnerabilities. This isn’t just about a minor glitch; we’re talking about the potential compromise of sensitive personal data, and the implications are far-reaching. Let’s dive into the details and explore what this means for your online security.
The initial excitement surrounding the new manager’s sleek interface and cross-platform compatibility was quickly replaced by anxieties about its encryption methods and lack of robust two-factor authentication options. News outlets and tech blogs have been abuzz with analyses of its security architecture, highlighting potential weaknesses that could leave users vulnerable to phishing attacks and data breaches. The situation underscores the critical importance of thoroughly vetting even the most well-known tech giants’ security practices.
Overview of Google’s New Password Manager: Google New Password Manager Raises Security Concerns
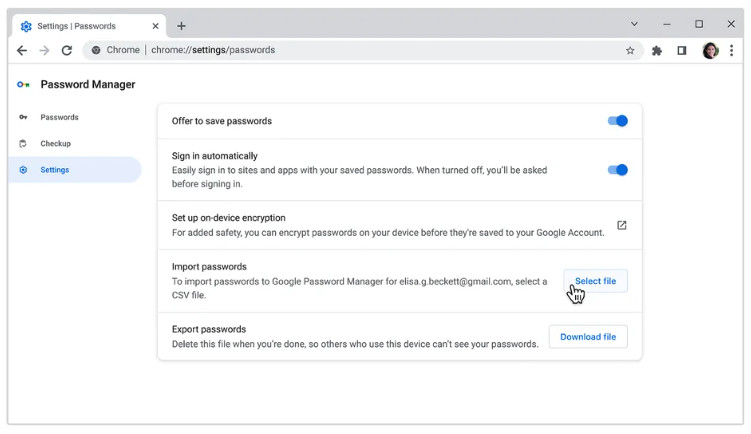
Google’s revamped password manager aims to simplify password management and enhance security for its vast user base. It builds upon existing features while incorporating improvements based on user feedback and evolving security threats. This new iteration offers a more streamlined interface and enhanced security protocols, making password management more accessible and secure for a wider range of users.Google’s new password manager boasts several key features designed to improve the overall user experience and security.
These features are intended to address common password management pain points, such as remembering complex passwords and protecting against phishing attacks. The focus is on ease of use, coupled with robust security measures.
Key Features of Google’s New Password Manager
The updated password manager offers features like automatic password generation, secure storage, cross-device synchronization, and improved phishing detection. Automatic password generation creates strong, unique passwords for each account, eliminating the need for users to remember complex strings. Secure storage utilizes end-to-end encryption to protect passwords from unauthorized access, even from Google itself. Cross-device synchronization ensures that passwords are accessible across all devices linked to the user’s Google account.
The enhanced phishing detection system analyzes websites and alerts users to potential threats before they enter their credentials. These features work together to provide a comprehensive and user-friendly password management solution.
Target Audience for Google’s New Password Manager
The target audience is broad, encompassing anyone who uses a Google account. This includes casual internet users who struggle with password management, as well as more tech-savvy individuals seeking a convenient and secure solution. The simplified interface makes it accessible to less technically inclined users, while the robust security features appeal to those concerned about online security. Essentially, Google aims to provide a password manager that caters to all levels of technical expertise within its user base.
Comparison with Existing Password Managers
Compared to other password managers on the market, Google’s offering stands out due to its seamless integration with the Google ecosystem. Users already accustomed to Google services will find the transition intuitive and straightforward. While established password managers like LastPass and 1Password offer similar functionalities, Google’s integration advantage simplifies the onboarding process and reduces the learning curve for many users.
However, features such as advanced security audits or family sharing options might be more comprehensive in some competing products. The choice ultimately depends on individual needs and preferences, but Google’s offering provides a strong, readily accessible option for millions of existing Google users.
Security Concerns Raised by Users and Experts
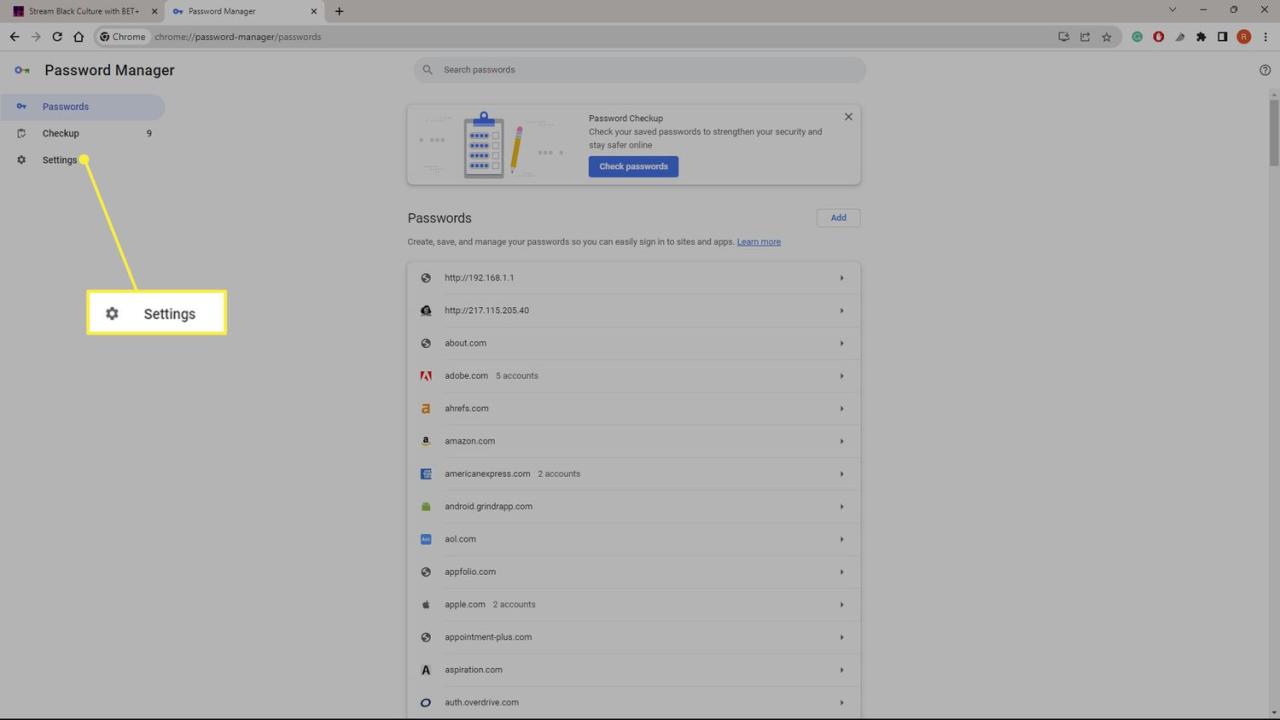
Google’s new password manager, while promising improved functionality, has faced scrutiny regarding its security implications. Concerns raised by users and security experts highlight potential vulnerabilities that could compromise user data and privacy. These concerns are not to be dismissed lightly, as they involve the sensitive information users entrust to such a service.The primary focus of these concerns centers around the centralization of user data within Google’s infrastructure.
While Google employs robust security measures, the potential for a large-scale breach impacting millions of users remains a significant risk. The sheer volume of data held by Google makes it a highly attractive target for malicious actors.
Data Breach and Unauthorized Access Risks
A successful breach of Google’s password manager could expose a vast amount of sensitive information, including usernames, passwords, website addresses, and potentially even credit card details if integrated with other Google services. The potential consequences are severe, ranging from identity theft and financial loss to account hijacking and data manipulation. The scale of such a breach could have far-reaching implications, impacting not only individual users but also potentially compromising the security of numerous online services.
This risk is amplified by the increasing reliance on password managers for securing access to sensitive accounts across multiple platforms.
Implications for User Privacy and Data Protection
The centralized nature of Google’s password manager raises questions about user privacy and data protection. Even with strong encryption, the potential for unauthorized access, either through a direct breach or through legal or governmental requests for data, remains a valid concern. The lack of complete transparency regarding Google’s data handling practices and the potential for data sharing with third parties also contributes to user apprehension.
The potential misuse of collected data, whether for targeted advertising or other purposes, represents a significant threat to user autonomy and privacy.
Comparison of Security Features
The following table compares the security features of Google’s new password manager to other popular options. Note that security features and policies are subject to change, and independent verification is always recommended.
| Password Manager Name | Encryption Method | Two-Factor Authentication Support | Audit History |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Password Manager | AES-256 (claimed) | Yes (integrated with Google accounts) | Limited; details not publicly available |
| 1Password | AES-256 | Yes | Detailed audit logs available |
| LastPass | AES-256 | Yes | Limited audit history; details vary by plan |
| Bitwarden | AES-256 | Yes | Detailed audit logs available (some features require paid subscription) |
Google’s Response to Security Concerns
Google’s new password manager rollout wasn’t without its bumps. Following significant user and expert concerns regarding security vulnerabilities and data handling practices, Google was quick to address the criticisms, though the response itself became a subject of further discussion. Their actions demonstrate a complex interplay between addressing user anxieties and maintaining a strong position in the competitive password management market.Google’s official statements acknowledged the validity of some of the raised concerns.
They released several blog posts and updates on their security pages, outlining their commitment to user data privacy and security. These communications emphasized Google’s ongoing efforts to improve the password manager’s security architecture and to address specific vulnerabilities that were identified. The tone was generally conciliatory, acknowledging the importance of user trust and transparency. However, the level of detail in their explanations varied, leading to some continued skepticism among security experts.
Google’s Implemented Updates and Patches
Following the initial wave of criticism, Google rolled out several updates to their password manager. These included improvements to encryption algorithms, enhanced security protocols for data transmission, and bug fixes addressing specific vulnerabilities that had been reported. While Google hasn’t released detailed patch notes for every individual update, their communication emphasized improvements in areas such as key management, data storage security, and user authentication processes.
For example, they highlighted enhancements to their zero-knowledge architecture to better protect user passwords from unauthorized access, even from within Google’s own systems. The impact of these updates on the overall security posture of the password manager remains a subject of ongoing evaluation by independent security researchers.
Google’s Communication Strategies
Google employed a multi-pronged approach to address user anxieties. This included proactive blog posts outlining security enhancements, responses to user inquiries on social media platforms like Twitter and Reddit, and participation in security conferences and forums to directly engage with the security community. The strategy aimed to showcase their commitment to improving the product’s security, foster open communication, and regain user trust.
However, some critics argued that Google’s responses lacked sufficient technical detail, making it difficult for users to fully assess the effectiveness of the implemented changes. The use of general statements about improved security, rather than specific technical specifications, was a point of contention. This approach, while intended to reassure users, may have inadvertently amplified existing concerns for a segment of the user base.
Alternative Password Management Strategies
So, you’re concerned about the security of your passwords, and rightly so. Even with a password manager, a robust security strategy requires multiple layers of protection. Let’s explore some alternative approaches and best practices to strengthen your overall password security. This isn’t about replacing a password manager entirely (unless you choose to), but rather supplementing it with other strong security measures.
Ultimately, a layered approach is the most effective. Relying on a single method, even a sophisticated password manager, leaves you vulnerable. Diversifying your security strategies significantly reduces your overall risk.
Best Practices for Enhanced Password Security
Regardless of the password manager (or lack thereof) you use, these practices are crucial for robust password security. They form the bedrock of a strong security posture.
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Avoid easily guessable passwords. Aim for a minimum of 12 characters, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Each account should have a unique password.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code from your phone or a security key, in addition to your password. Enable it wherever possible.
- Regularly Update Passwords: Change passwords periodically, especially for sensitive accounts like banking and email. A good rule of thumb is to change passwords every 90 days, or even more frequently if you suspect a breach.
- Beware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of suspicious emails, links, and websites that ask for your login credentials. Never enter your password on an unverified site.
- Use a Password Manager (Strategically): A password manager can simplify password management, but choose a reputable one and follow its security guidelines. Don’t rely solely on it; it’s one piece of a larger puzzle.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, browser, and applications to patch security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Comparison of Password Management Approaches
Different methods offer varying levels of security and convenience. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for selecting the right approach for your needs.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Password Managers (e.g., Bitwarden, 1Password) |
|
|
| Physical Security Keys (e.g., YubiKey, Google Titan) |
|
|
| Password Writing (Notebooks, etc.) |
|
|
Impact on User Trust and Adoption
The revelation of security concerns surrounding Google’s new password manager has the potential to significantly impact user trust and, consequently, its adoption rate. This isn’t simply about a single product; it affects Google’s broader reputation for security, a cornerstone of its brand identity. The long-term consequences could be far-reaching, affecting not only the password manager’s success but also the uptake of other Google services.The immediate impact is likely to be a decrease in adoption.
Users, particularly those highly concerned about online security, will likely hesitate to migrate their sensitive data to a system plagued by reported vulnerabilities. The negative press and expert commentary surrounding the security flaws will undoubtedly deter many potential users, forcing Google to work harder to regain their trust. This hesitancy will be especially pronounced among users who already rely on alternative, established password managers.
The cost of regaining user confidence could be substantial, requiring significant investment in addressing the concerns and rebuilding trust.
User Trust Erosion
The damage to user trust extends beyond the immediate concerns about the password manager itself. Google prides itself on its robust security infrastructure. This incident, however, raises questions about the company’s internal security processes and its commitment to user data protection across its entire product ecosystem. If users lose confidence in Google’s ability to secure one crucial aspect of their online lives – their passwords – they may question the security of other Google services they use, leading to a potential exodus of users towards competing platforms that offer perceived higher security standards.
For example, a significant drop in Google Workspace subscriptions could be a potential consequence, as businesses might switch to providers they deem more trustworthy after this incident.
Adoption Rate Impact
The initial adoption rate of Google’s new password manager was likely to be influenced by factors such as integration with other Google services and its ease of use. However, the security concerns have significantly altered this projection. Instead of a smooth, rapid adoption, Google is now facing a much steeper climb. The company will need to invest heavily in public relations and security updates to regain user confidence and encourage adoption.
We can compare this situation to the launch of other products that faced similar setbacks. For example, the initial launch of a new social media platform with significant privacy issues faced a much slower adoption rate than projected, ultimately hindering its overall success.
Brand Reputation Damage
The negative publicity surrounding the security concerns directly impacts Google’s overall brand reputation. Google has cultivated a reputation for innovation and security, and this incident challenges that image. The longer the issues remain unresolved, the greater the potential damage to its brand. This is particularly relevant considering Google’s position as a leading technology company. Any perceived weakness in security can severely undermine consumer trust and potentially impact their usage of other Google products.
We can see parallels in the impact on other tech giants who have faced similar security breaches. These breaches have led to significant reputational damage and, in some cases, legal repercussions.
So, Google’s new password manager is causing a stir, raising legitimate security concerns about data handling. It makes you think about the importance of robust, secure application development, and how platforms like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future are crucial for building trustworthy systems. Ultimately, the debate around Google’s new manager highlights the ongoing need for developers to prioritize security above all else.
Future Implications and Recommendations
The recent unveiling of Google’s new password manager, while aiming for improved functionality, has sparked legitimate concerns regarding its security architecture. Addressing these concerns and proactively mitigating future risks is crucial not only for Google’s reputation but also for the security of millions of users who rely on their services. Failure to do so could lead to a significant erosion of trust and a potential shift towards alternative password management solutions.The path forward requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on enhanced security features, transparent communication, and a demonstrable commitment to user privacy.
This will involve both immediate actions to address current vulnerabilities and a long-term strategy to build a more robust and trustworthy system.
Recommendations for Improving Security
Strengthening the security of Google’s password manager requires a holistic approach, encompassing both technical and procedural improvements. This includes implementing robust encryption algorithms, enhancing audit trails for all password-related actions, and incorporating advanced threat detection mechanisms. Specifically, a move towards end-to-end encryption, where only the user possesses the decryption key, would significantly bolster security. Regular security audits by independent third-party experts should be conducted and the findings made publicly available to foster transparency and accountability.
Furthermore, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a mandatory feature, rather than an optional one, would provide an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. Finally, a comprehensive bug bounty program, offering substantial rewards for identifying vulnerabilities, could help proactively identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Steps to Regain User Trust, Google new password manager raises security concerns
Regaining user trust after the security concerns raised requires more than just technical fixes. Google needs to demonstrate a clear commitment to transparency and user privacy. This involves openly acknowledging the shortcomings of the current system, detailing the steps taken to address the identified vulnerabilities, and providing regular updates on the progress made. A public roadmap outlining future security improvements and planned features would foster a sense of accountability and reassure users that their concerns are being taken seriously.
Actively engaging with the user community through open forums and feedback mechanisms is crucial to address individual concerns and build a stronger relationship based on trust and collaboration. Transparency regarding data handling practices and clear, concise privacy policies are also paramount. For example, Google could publish detailed white papers explaining the cryptographic algorithms used and the security protocols implemented, making this information easily accessible to security experts and the general public.
Ideal Security Features for a Future Iteration
An ideal future iteration of Google’s password manager should incorporate several key security enhancements. This includes seamless integration with hardware security modules (HSMs) for enhanced key management and protection against sophisticated attacks. Advanced threat detection capabilities, using machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious activity, would provide an extra layer of security. Furthermore, the implementation of differential privacy techniques could protect user data while still enabling aggregate data analysis for security improvement purposes.
The system should also support passwordless authentication options, leveraging technologies like WebAuthn and FIDO2, to eliminate the reliance on passwords altogether. Finally, a robust and user-friendly password generation feature that incorporates entropy-maximizing techniques would ensure that generated passwords are highly resistant to brute-force attacks. These features, coupled with a steadfast commitment to transparency and user privacy, would position Google’s password manager as a leader in the field, regaining user trust and solidifying its position as a reliable and secure solution.
Final Review
The unveiling of Google’s new password manager has turned into a cautionary tale about the complexities of online security. While Google has responded to the criticism with promises of improvements, the initial concerns have significantly impacted user trust and adoption rates. This situation highlights the crucial need for transparency and rigorous security testing in the development of password management tools.
Ultimately, users must remain vigilant, prioritizing robust security practices and exploring diverse password management strategies to safeguard their valuable data.
FAQ Corner
What specific encryption methods does Google’s new password manager use?
The exact details of the encryption are often proprietary and not fully disclosed. However, understanding the general approach (e.g., AES-256) is key. It’s crucial to look for independent security audits to gain more confidence.
How does Google’s response compare to how other companies handle similar security issues?
Comparing Google’s response to others requires a case-by-case analysis. Some companies are quicker to acknowledge and address issues, while others might be slower. The transparency and communication strategies employed differ significantly.
Are there any known workarounds or temporary solutions to mitigate the identified security risks?
Until Google releases updates, using a secondary, more established password manager alongside Google’s new one could offer some added protection. Strong, unique passwords remain crucial, regardless of the password manager used.