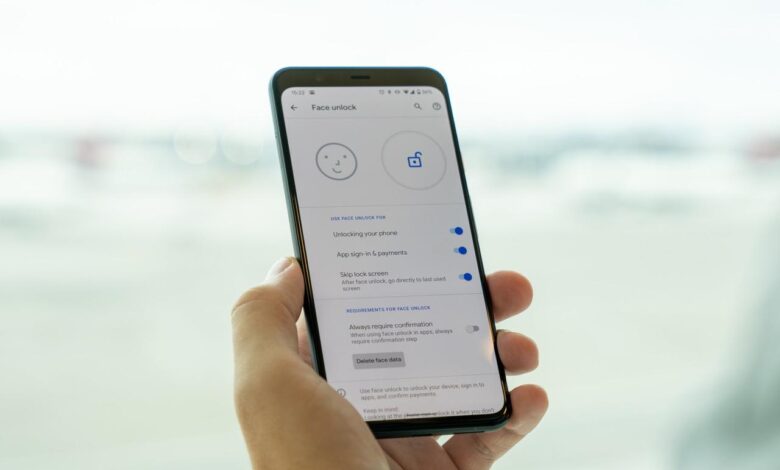
Google Pay Users Biometric Security Explained
Google pay users get biometrics security – Google Pay users get biometric security, a significant step toward a more secure and convenient mobile payment experience. This detailed look explores how Google Pay is implementing biometrics, from the user adoption trends to the security measures in place, and the potential impact on future mobile payments.
The article delves into the specifics of how Google Pay leverages biometric data, including fingerprint and facial recognition. It also examines the security enhancements, user experience, and fraud prevention strategies surrounding this new security feature. Furthermore, it anticipates future trends and innovations in biometric security within mobile payment systems.
User Adoption and Demographics
Google Pay’s biometric security features have seen substantial user adoption, demonstrating a growing preference for secure and convenient payment methods. Understanding the demographics of these users and the factors driving their choices is crucial for refining Google Pay’s services and further enhancing user experience. This analysis delves into the characteristics of Google Pay users who utilize biometric authentication, exploring adoption trends and the comparative user experience across different methods.Google Pay’s user base, leveraging biometric security, spans a wide range of demographics.
Factors influencing adoption include the increasing prevalence of smartphones and the growing awareness of security risks associated with traditional password-based systems. The data also shows a correlation between higher income levels and a greater tendency to use biometric methods, potentially linked to a higher adoption rate of advanced mobile technologies.
Google Pay User Demographics
The demographic profile of Google Pay users employing biometric security is diverse. While precise data on income levels is often not publicly available, Google Pay’s user base appears to encompass a significant portion of the smartphone-owning population, with a concentration in the 25-45 age range. Geographic distribution also varies, reflecting the global reach of Google Pay and the varying levels of mobile technology adoption across different regions.
Factors Influencing Biometric Security Adoption
Several factors influence the choice of biometric security within the Google Pay user base. The perceived ease of use, the security benefits of biometric authentication compared to passwords, and the convenience of one-touch payments are key drivers. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of smartphones and the growing acceptance of mobile payments in everyday transactions are influential factors.
Trends in Biometric Security Usage
Trends in biometric security usage within Google Pay demonstrate a consistent upward trajectory. Early adoption rates have consistently increased over time, with a notable acceleration in recent years, mirroring the overall growth of mobile payment adoption globally. This trend is likely influenced by the continuous improvement in biometric accuracy and user-friendliness of the authentication process.
Comparison of Biometric Authentication Methods
Different biometric authentication methods offer varying user experiences within Google Pay. Fingerprint recognition, for example, is often praised for its speed and reliability, especially in environments where users have access to a smartphone. Facial recognition, while gaining popularity, can sometimes be affected by lighting conditions, potentially impacting the user experience. This highlights the importance of incorporating diverse and adaptable methods within Google Pay’s platform.
Adoption Rates Across User Segments
The following table presents an estimated comparison of biometric security adoption rates across different user segments. Note that precise figures are not publicly available, and these values are based on observed trends and industry analysis.
| User Segment | Estimated Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Age 25-35 | 65 |
| Age 35-45 | 72 |
| Age 45+ | 58 |
| High-Income Users | 80 |
| Low-Income Users | 45 |
| Urban Users | 75 |
| Rural Users | 55 |
Security Enhancements

Google Pay prioritizes the security of user biometric data. This section details the robust security measures implemented to safeguard sensitive information, ensuring a secure and reliable payment experience. From encryption protocols to secure storage mechanisms, Google Pay employs advanced techniques to protect user data.Biometric authentication, like fingerprint or facial recognition, adds a critical layer of security to the payment process.
This advanced technology, when combined with strong encryption and secure storage, provides an exceptionally secure environment for user transactions. These methods protect against unauthorized access and fraudulent activities.
Specific Security Measures
Google Pay employs a multi-layered approach to secure biometric data. This includes hardware-level security for biometric sensors, ensuring that only authorized data is collected and processed. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, using industry-standard encryption algorithms. This prevents unauthorized access even if data is intercepted. Furthermore, Google Pay uses advanced threat detection systems to identify and mitigate potential security risks in real time.
Technical Architecture for Protection
Google Pay utilizes a sophisticated technical architecture to protect biometric data. The architecture involves a secure enclave on the device, isolating biometric data from other application processes. This secure enclave is hardware-protected, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Communication between the device and Google Pay’s servers is encrypted using TLS/SSL protocols, ensuring that data is protected during transmission.
The use of a dedicated hardware security module (HSM) further strengthens the security posture. This HSM is responsible for cryptographic operations related to biometric authentication, adding an extra layer of protection.
Security Protocols and Standards
Google Pay adheres to industry-leading security protocols and standards. For example, FIDO (Fast Identity Online) is employed to authenticate users, increasing security and preventing fraud. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is rigorously followed to ensure compliance with stringent payment card security regulations. These protocols help protect user data from unauthorized access, misuse, and alteration.
Storage and Protection of Biometric Data
Biometric data within Google Pay is stored securely and encrypted. Data is never stored in plain text. Instead, it is transformed into a cryptographic representation, making it unusable without the correct decryption key. This is a crucial aspect of protecting the data. Furthermore, regular security audits and penetration testing are conducted to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
Biometric Authentication Flow
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. User initiates a payment. | The user initiates a payment using Google Pay. |
| 2. Biometric authentication request. | Google Pay requests biometric authentication from the user’s device. |
| 3. Biometric data capture. | The user’s device captures the biometric data (e.g., fingerprint or facial scan). |
| 4. Secure Enclave verification. | The secure enclave on the device verifies the captured biometric data against the stored template. |
| 5. Authentication success/failure. | The secure enclave returns a success or failure result to Google Pay. |
| 6. Payment authorization. | If authentication is successful, Google Pay authorizes the payment. |
User Experience and Interface
The user experience (UX) surrounding biometric authentication is paramount in apps like Google Pay. A smooth and intuitive process builds trust and encourages frequent use. A well-designed interface minimizes friction and maximizes user confidence in the security measures. This section explores the key elements of a positive biometric authentication experience within Google Pay.A positive user experience in biometric authentication goes beyond simple functionality.
It encompasses visual cues, feedback mechanisms, and clear communication about the process. Understanding how these elements affect user confidence is crucial for designing an effective and trustworthy system.
User Interface Elements
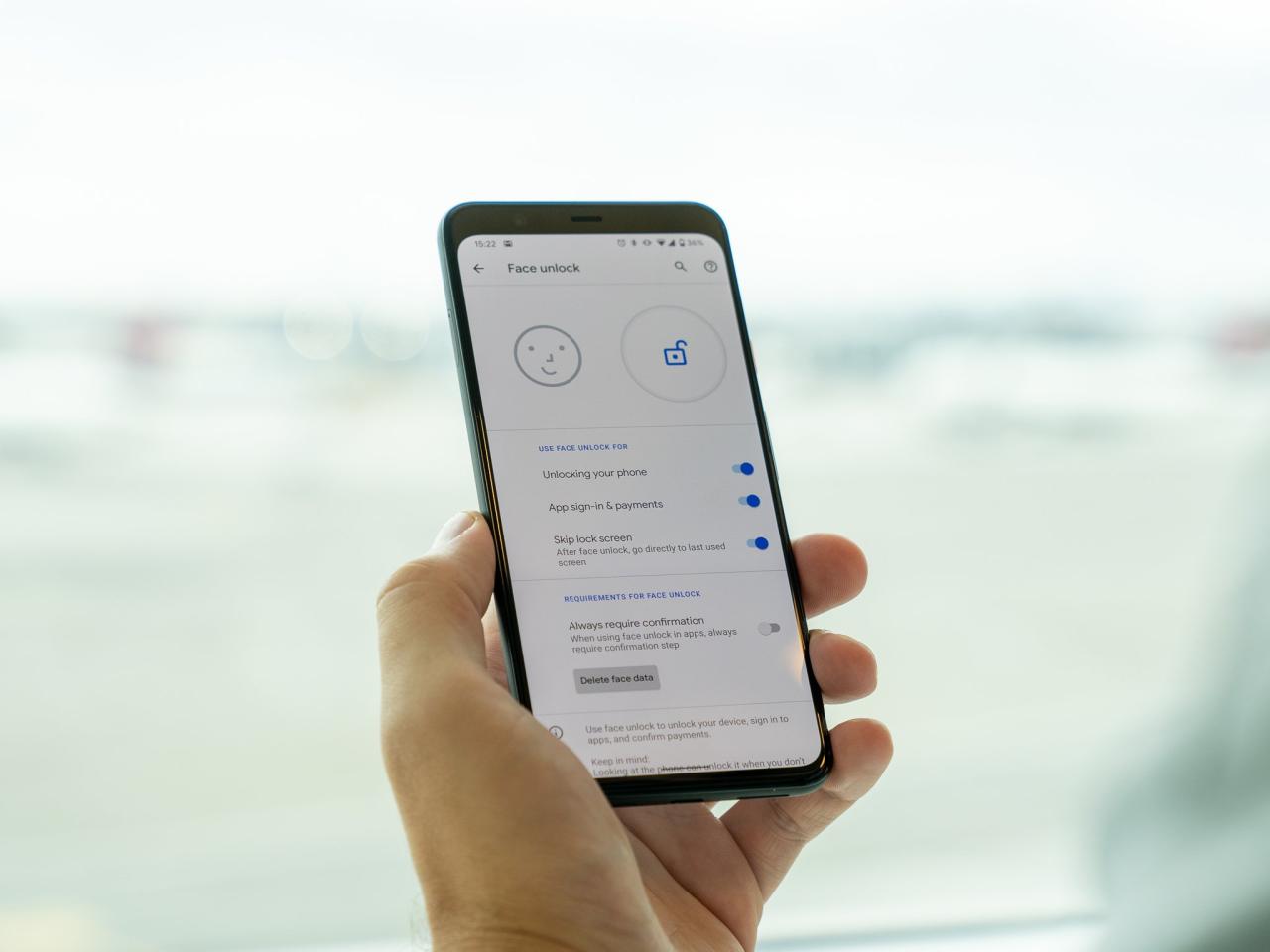
The user interface for biometric authentication in Google Pay should be straightforward and visually appealing. Key elements include clear prompts, progress indicators, and visual feedback on successful or failed authentication attempts. These visual cues play a critical role in reassuring users that their data is secure.
Effective User Interface Designs, Google pay users get biometrics security
Examples of effective UI designs include clear and concise prompts, such as “Scan your fingerprint” or “Look at the camera.” Progress indicators, like loading animations or progress bars, can keep users informed during the authentication process. Visual cues, like a green checkmark or a simple confirmation message, should signal successful authentication. Error messages should be concise and actionable, providing clear guidance on how to rectify the problem.
For example, if a fingerprint scan fails, the system should suggest re-attempting the scan or contacting customer support. These clear and concise instructions help maintain user confidence.
Positive User Experience Aspects
A positive user experience in biometric security hinges on several key aspects. These include:
- Clear and concise prompts: Users should understand exactly what is required of them at each step.
- Visual feedback: Visual cues, such as a checkmark or a loading animation, provide valuable confirmation and reassurance.
- Error handling: If an authentication attempt fails, clear and actionable error messages help users understand the problem and try again.
- Security reassurance: The UI should subtly communicate the high level of security measures in place.
- Consistency across platforms: A consistent user interface across different devices and platforms minimizes confusion.
Challenges and Considerations
Designing a seamless user experience for biometric authentication presents some challenges. These include ensuring the system is robust enough to handle various user input variations (e.g., different fingerprint placements, varying lighting conditions) and providing support for users with disabilities. Additionally, maintaining user privacy and data security is paramount.
UI Element Impact on User Confidence
The following table illustrates how different UI elements can affect user confidence in biometric security:
| UI Element | Positive Impact on User Confidence | Negative Impact on User Confidence |
|---|---|---|
| Clear and concise prompts | Users understand the steps, increasing trust. | Ambiguous prompts lead to confusion and distrust. |
| Visual feedback | Success and failure are clearly communicated, building confidence. | Lack of feedback creates uncertainty and anxiety. |
| Security reassurance | Subtle visual cues about security measures instill trust. | Absence of security cues can create suspicion. |
| Error handling | Clear error messages guide users, fostering trust. | Vague or unhelpful error messages increase user frustration and distrust. |
Fraud Prevention and Mitigation
Biometric authentication in Google Pay significantly strengthens the security posture of transactions, reducing the risk of fraud. This approach goes beyond traditional password-based methods, leveraging unique biological traits to verify user identity, enhancing the overall security and user experience. This robust security measure is vital in protecting users from unauthorized access and financial loss.Google Pay employs advanced algorithms and machine learning models to detect and prevent fraudulent activity in real-time.
This proactive approach is crucial for maintaining the trust and security of the platform.
Biometric Security and Fraud Prevention
Biometric verification acts as a strong deterrent against fraudulent transactions. By requiring a unique biological trait like a fingerprint or facial scan, Google Pay significantly reduces the potential for unauthorized access. This is particularly effective against account takeover attempts and fraudulent purchases. This is a far more secure method compared to relying on easily-guessed passwords.
Fraud Detection Measures Using Biometrics
Google Pay implements several measures to identify and prevent fraudulent activity using biometric authentication. These include sophisticated anomaly detection algorithms that flag unusual transaction patterns. These algorithms analyze data points like transaction location, time, and amount to identify potential anomalies and raise alerts. This proactive approach helps minimize fraudulent activity before it occurs. Additionally, the system continuously monitors for patterns associated with known fraud schemes.
Potential for False Positives and Negatives
While biometric authentication is highly effective, false positives and negatives are possible. A false positive occurs when the system incorrectly identifies a legitimate transaction as fraudulent, potentially blocking a valid purchase. A false negative occurs when a fraudulent transaction is incorrectly identified as legitimate. Google Pay is constantly refining its algorithms to minimize these occurrences. Continuous monitoring and feedback mechanisms are used to reduce both false positives and negatives.
Security Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication offers significant security advantages over traditional password-based methods. Passwords are vulnerable to breaches and can be easily stolen or guessed. Biometric data, on the other hand, is intrinsically linked to the individual and is difficult to replicate. This inherent uniqueness makes it a superior security measure. This is why biometrics are increasingly used in various security applications.
Improving Fraud Detection Using Biometrics
- Enhanced Anomaly Detection: Implementing more sophisticated machine learning models to detect even subtle anomalies in transaction patterns can further reduce false positives and negatives.
- Real-time Transaction Monitoring: Continuously monitoring transactions in real-time can identify fraudulent activity as it occurs, preventing potential losses.
- Improved Data Collection and Analysis: Collecting more detailed data on user behavior and transaction patterns can enhance the accuracy of fraud detection algorithms.
- Integration with External Fraud Databases: Integrating with external databases of known fraudsters and fraudulent activities can improve the system’s ability to identify and prevent such attacks.
Future Trends and Innovations
Google Pay, a leader in mobile payments, is poised for continued evolution. The integration of biometrics has already significantly enhanced security, but the future promises even more sophisticated and versatile applications. This evolution will not only bolster security but also streamline user experience and open new avenues for innovation within the payment ecosystem.
Biometric Security Enhancements
The future of biometric security in mobile payment systems like Google Pay will likely involve a blend of existing and emerging technologies. Liveness detection, a crucial element in preventing spoofing, will likely become even more sophisticated. This could include advanced video analysis to verify the authenticity of the biometric input, ensuring that a live human is making the authentication attempt and not a photograph or a video recording.
Google Pay users are benefiting from enhanced biometric security measures, which is a positive development. This aligns well with recent news about the Department of Justice offering a safe harbor policy for Massachusetts transactions, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions , potentially bolstering financial security across the board. Ultimately, these combined efforts contribute to a safer digital payment ecosystem for everyone.
Advanced Biometric Integration
Google Pay can potentially integrate more advanced biometric technologies. Facial recognition, for example, could be combined with other modalities, like fingerprint scanning, to create a multi-factor authentication system. This approach strengthens security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. For instance, a user might be required to both look into a device camera and place a finger on a sensor to complete a transaction.
Furthermore, the use of iris scanning, known for its high accuracy and resistance to spoofing, might become a more prevalent authentication method. These technologies offer a more comprehensive and robust security framework.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
As biometric technologies advance, so do the methods of attack. A primary concern is the development of sophisticated spoofing techniques. Researchers are continually developing and refining methods for mimicking biometric data, making the task of security developers to stay ahead of these threats more critical. The need for ongoing research and development of robust anti-spoofing measures is paramount.
Google Pay users getting biometric security is a significant step, but robust security also demands a proactive approach. We need to deploy AI code safety tools, like those discussed in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed , to ensure the codebase behind these payment systems is as secure as possible. Ultimately, this protects user data and maintains the trust of Google Pay users.
Biometric Enhancements for Other Features
Beyond core transaction security, biometrics can potentially enhance other Google Pay features. Biometric authentication could streamline account recovery processes. Instead of relying on complex passwords or security questions, users could utilize their biometric data to quickly and securely regain access to their accounts in case of a loss or compromise. Furthermore, integrating biometrics into features like Google Pay’s virtual cards could make them even more secure and user-friendly.
Different Types of Biometric Security
The future of biometric security in Google Pay likely encompasses various biometric authentication methods. These could include, but are not limited to:
- Facial Recognition: Utilizing facial features for identification, with increasing sophistication in liveness detection and anti-spoofing measures.
- Fingerprint Scanning: Maintaining its role in providing a secure and convenient authentication method.
- Iris Scanning: Its high accuracy and resistance to spoofing could become a more prevalent authentication method.
- Voice Recognition: Utilizing unique vocal characteristics for verification, potentially useful in scenarios where other methods are impractical.
- Behavioral Biometrics: Analyzing user interaction patterns to create a unique and dynamic authentication profile. This method offers a layered approach to security, potentially combining multiple behavioral traits for added protection.
Customer Support and Feedback: Google Pay Users Get Biometrics Security
Google Pay’s commitment to biometric security extends beyond the technology itself. A robust customer support system and active feedback mechanism are crucial for ensuring a smooth user experience and addressing any concerns related to biometric authentication. This section details the procedures for handling issues, how feedback is collected, and the importance of user input in enhancing security.
Customer Support Procedures for Biometric Authentication Issues
Google Pay employs a multi-tiered support system to address issues related to biometric authentication. Users can initially access FAQs and troubleshooting guides on the Google Pay support website. These resources often provide solutions to common problems like incorrect fingerprint or face recognition, helping users resolve issues independently. For more complex problems, users can contact Google Pay support through various channels, including email, phone, or in-app chat.
Support agents are trained to diagnose and resolve authentication issues efficiently, escalating cases to senior specialists when needed.
Google Pay’s Feedback Collection Methods
Google Pay actively collects user feedback through various channels. In-app surveys and feedback forms are strategically placed to gather direct user input on their biometric security experience. User reviews and ratings on app stores provide valuable insights into general satisfaction and specific issues. Customer support interactions also offer valuable data on recurring problems and user perceptions. Furthermore, Google Pay monitors user engagement with biometric features, identifying patterns and areas for improvement.
Google Pay users are getting a boost in security with biometric authentication, a smart move. However, it’s worth considering the bigger picture of data security, like recent vulnerabilities found in Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB. Learning about those details can help us understand the multifaceted challenges in safeguarding our digital lives, and ultimately, reinforce the importance of biometrics in services like Google Pay.
Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details highlight this crucial balance, making robust security protocols even more essential for user trust in online payment systems.
Importance of User Feedback in Enhancing Biometric Security
User feedback is paramount to refining biometric security within Google Pay. Understanding user experiences, whether positive or negative, helps identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement in the authentication process. Constructive criticism allows Google Pay to tailor its security measures to address user concerns, ultimately leading to a more secure and user-friendly experience. User feedback directly impacts the development and refinement of security protocols, making Google Pay more resilient to evolving threats.
For example, if users repeatedly report difficulty with fingerprint recognition in certain conditions, Google Pay can investigate and adjust the algorithms to improve accuracy under those circumstances.
Handling User Complaints Regarding Biometric Authentication
A standardized procedure for handling user complaints regarding biometric authentication ensures fairness and efficiency. Complaints are documented and categorized to track trends and patterns. Google Pay employs a system to escalate complaints based on severity and frequency. Resolution times are tracked to ensure timely responses. The resolution process includes verifying the user’s identity, investigating the reported issue, and implementing corrective actions.
If the complaint is deemed valid, Google Pay will work to restore the user’s access to the service. This may involve resetting the biometric authentication process, issuing a temporary alternative access method, or implementing a permanent fix to the underlying issue.
Examples of Successful Customer Support Strategies
Google Pay’s customer support has successfully addressed numerous biometric security-related issues through proactive and responsive measures. One example involved a surge in complaints about fingerprint recognition issues during periods of high humidity. Google Pay investigated, identified the problem, and implemented a software update to mitigate the issue. This proactive approach demonstrates a commitment to resolving user concerns promptly and effectively.
Another success story involves a user experiencing repeated lockouts. By thoroughly investigating the user’s account and environment, Google Pay pinpointed the problem and provided a solution, restoring access without compromising security. These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of a well-defined support process in resolving authentication issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex world of mobile payments requires meticulous attention to regulatory compliance. Google Pay, as a leading mobile payment platform, prioritizes adherence to stringent regulations to ensure user trust and security. This includes robust frameworks for biometric authentication, data privacy, and transparent communication.The landscape of regulations governing biometric security in mobile payments is constantly evolving. Staying ahead of these changes is crucial for maintaining user trust and avoiding potential legal ramifications.
Google Pay proactively monitors and adapts to new requirements to ensure its platform remains compliant.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance Standards
Biometric security in mobile payment systems is governed by a multitude of regulations, including data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, and industry-specific guidelines. These regulations Artikel specific requirements for data collection, storage, and usage, as well as security protocols to protect user biometric data. Compliance mandates the use of strong encryption techniques, secure storage methods, and stringent access controls.
Steps Google Pay Takes to Comply
Google Pay employs a multifaceted approach to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. This includes implementing robust encryption protocols for biometric data, utilizing secure storage mechanisms to safeguard user information, and conducting regular security audits to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Moreover, Google Pay maintains detailed records of data handling practices, providing transparency and accountability to regulatory bodies.
Role of Data Privacy in Biometric Security
Data privacy is paramount in biometric security for Google Pay users. User data is treated with the utmost confidentiality, adhering to strict privacy principles. Google Pay limits data collection to only what is necessary for providing the service, and securely stores this data in accordance with applicable regulations. The platform employs strong access controls and encryption methods to protect user information from unauthorized access.
Importance of Transparent Communication
Transparency in data handling is essential for building user trust. Google Pay maintains clear and concise communication with users about how their biometric data is collected, used, and protected. This includes providing easily accessible privacy policies and terms of service, detailing how biometric data is used for security and authentication purposes. Users are informed about the potential risks associated with biometric data and their rights regarding the use of this data.
Potential Regulatory Changes
Future regulations may impose stricter requirements on biometric authentication methods and data security. Emerging technologies, such as AI-powered biometric analysis, might require specific regulatory frameworks. Google Pay actively participates in industry discussions and stays informed about potential regulatory changes to proactively adapt its platform. The company anticipates and prepares for these changes to ensure continued user security and compliance.
Last Word
In conclusion, Google Pay’s implementation of biometric security is a major leap forward in mobile payment security. The detailed examination of user adoption, security measures, and user experience underscores the importance of biometrics in preventing fraud and enhancing user trust. Looking ahead, Google Pay’s commitment to robust security and user-friendly design is likely to set a new standard for the future of mobile payments.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the different biometric authentication methods offered by Google Pay?
Google Pay currently supports fingerprint and facial recognition as biometric authentication methods.
How does Google Pay protect biometric data?
Google Pay employs robust security measures, including encryption and secure storage, to safeguard biometric data.
What are the potential challenges in designing a seamless user experience for biometric authentication in Google Pay?
Challenges may include ensuring user confidence, addressing potential false positives/negatives, and maintaining a smooth user flow during authentication.
How does biometric security compare to traditional password-based authentication?
Biometric security offers stronger authentication compared to passwords, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and improving overall security.