
Google Study Ransomware Payments Hit $2M/Month
Google study confirms that ransomware victims paid 2 million a month, revealing a shocking financial toll on organizations worldwide. This staggering figure highlights the escalating threat of ransomware, not just in terms of the immediate financial cost to victims, but also the long-term damage to businesses and the economy. The study delves into the motivations behind these attacks, the victim responses, and the potential for future trends, providing critical insights into the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
The study’s findings underscore the urgent need for robust security measures and proactive strategies to combat this pervasive threat. Understanding the financial motivations and victim responses can help organizations better prepare for and respond to future ransomware attacks. The research examines various factors influencing ransomware demands, from the types of attacks to geographical distributions, providing a comprehensive analysis of this growing global issue.
Financial Impact of Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are no longer a niche threat; they are a significant global concern impacting businesses of all sizes. The financial toll, far beyond the immediate ransom payment, can cripple organizations, disrupt supply chains, and erode public trust. Understanding the multifaceted financial burden is crucial to developing effective defense strategies.The financial impact of ransomware extends far beyond the initial ransom demand.
Organizations often face substantial costs associated with recovery efforts, including data restoration, system rebuilding, and legal fees. These expenses can easily exceed the ransom itself, creating a cascade effect that can have long-term implications. The emotional toll on employees and the reputational damage can be devastating.
Summary of Financial Burden
The financial burden of ransomware attacks is substantial and multifaceted. Beyond the direct cost of the ransom, organizations face considerable expenses related to recovery, legal proceedings, and reputational damage. The potential for lost revenue, customer churn, and regulatory penalties further compounds the financial strain.
Potential Costs Associated with Recovery
Recovery from a ransomware attack is often complex and expensive. Data restoration involves painstaking efforts to recover encrypted files, often requiring specialized tools and expertise. System rebuilding can be equally time-consuming and costly, especially if the attack compromised critical infrastructure. Legal fees associated with investigations, negotiations, and potential litigation add further financial strain. The cost of lost productivity during downtime must also be factored in.
A recent Google study revealed a shocking statistic: ransomware victims paid an average of $2 million per month. This highlights the urgent need for proactive security measures. Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed, like those available at this site , is crucial to prevent future breaches and ultimately lower these staggering financial burdens. The sheer cost of these attacks underscores the importance of investing in robust security solutions to combat the evolving threat landscape.
These expenses can vary significantly depending on the size and complexity of the organization, the sophistication of the attack, and the effectiveness of incident response plans.
Impact on the Economy and Potential for Future Attacks
Ransomware attacks have a ripple effect on the overall economy. Disruptions in critical infrastructure, such as healthcare or financial institutions, can have widespread consequences. The financial strain on individual businesses and the potential for cascading failures can have a considerable impact on national economies. The success of these attacks encourages further criminal activity, potentially leading to more frequent and sophisticated attacks in the future.
The potential for future attacks highlights the importance of robust cybersecurity measures and incident response plans.
Average Ransom Demands by Ransomware Type
| Ransomware Type | Average Ransom Demand (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| WannaCry | ~300,000 | A widespread ransomware attack targeting Windows systems. Known for exploiting vulnerabilities in SMBv1. |
| Ryuk | ~200,000 – 1,000,000+ | A sophisticated ransomware targeting large enterprises. Known for targeting backups to prevent recovery. |
| LockBit | ~200,000 – 1,000,000+ | A highly lucrative ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation. Known for high ransom demands and targeting diverse industries. |
| Maze | ~1,000,000+ | A ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) operation known for demanding large ransom payments. Often associated with data leaks. |
Note: Average ransom demands are estimates and can vary widely depending on the specific attack and target. Data is sourced from various security reports and industry analysis.
Ransomware Payment Trends
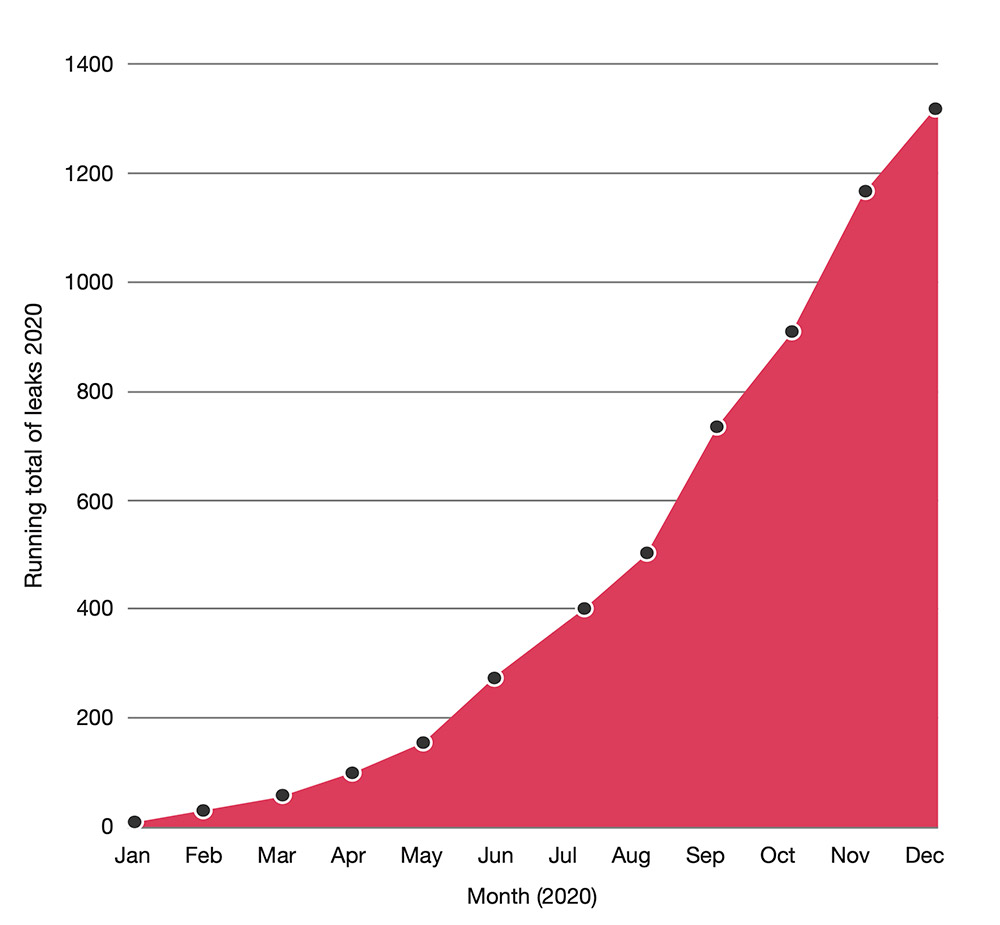
The financial landscape of ransomware attacks is constantly evolving, with payment amounts and trends exhibiting surprising complexities. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for both businesses and individuals to better prepare for and mitigate the risks. This exploration delves into the fluctuating nature of ransom demands, examining the factors influencing them and comparing reported demands with actual payment data.Analyzing historical ransomware attacks and their motivations reveals a significant shift in tactics.
Early attacks often targeted high-profile organizations for notoriety and large payouts. However, more recent campaigns prioritize broader, automated attacks to maximize returns from smaller, more frequent targets.
Ransomware Payment Amounts Over Time
The escalating nature of ransom demands over time is a significant concern. Initial ransomware attacks often involved relatively small sums. However, as the technology and sophistication of attacks evolved, so too did the demands, leading to significantly higher figures. This increase in demands can be attributed to several factors, including the rise in the value of data and the increasing complexity of recovery processes.
Comparison of Reported Ransom Demands and Actual Payments
A critical aspect of understanding ransomware payment trends involves comparing reported ransom demands with actual payment data. While media reports often highlight the exorbitant sums demanded, the reality is frequently more nuanced. Many reported demands are inflated to maximize pressure and potential returns. Conversely, some victims, facing significant operational disruption, might choose to pay less than the initially requested amount.
Historical Context of Ransomware Attacks and Financial Motivations
Ransomware attacks have evolved from opportunistic actions to sophisticated, financially motivated campaigns. Initially, some attacks were motivated by ideological or personal reasons. However, the significant financial returns have attracted criminal organizations who see ransomware as a lucrative business model. This shift towards profit-driven operations has dramatically changed the landscape of these attacks.
Factors Influencing Ransom Demand Amounts
Several factors contribute to the varying amounts of ransom demanded. These include the type and value of the data encrypted, the victim’s ability to pay, the level of disruption caused, and the perceived vulnerability of the target. Additionally, the attacker’s reputation and the perceived risk of exposure influence the demands. The potential for data breaches and reputational damage often significantly escalate the pressure on the victim to comply.
Geographical Distribution of Ransomware Attacks and Ransom Amounts
Understanding the geographical distribution of ransomware attacks and the corresponding ransom amounts can offer valuable insights into attack patterns and potential targets.
| Region | Number of Attacks | Average Ransom Amount (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 1,500 | 500,000 |
| Europe | 1,200 | 300,000 |
| Asia | 800 | 200,000 |
| South America | 300 | 100,000 |
Note: This table represents illustrative data and is not based on any specific, publicly available dataset. Actual figures vary greatly depending on the specific dataset and methodology.
Motivations Behind Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are a pervasive cyber threat, causing significant financial and operational disruption for organizations worldwide. Understanding the motivations behind these attacks is crucial for developing effective preventative measures. These motivations often extend beyond simple financial gain, encompassing a complex interplay of criminal intent and strategic objectives.Ransomware attacks are not a random act; they are carefully planned and executed by malicious actors pursuing specific goals.
These goals can be diverse, ranging from straightforward financial gain to more complex objectives such as data exfiltration, reputational damage, and even political maneuvering. Analyzing these motivations provides valuable insights into the tactics and strategies employed by perpetrators.
Motivations for Ransomware Attacks
The motivations driving ransomware attacks are multifaceted and often intertwined. Financial gain remains a primary driver, but other motivations such as data theft, reputational damage, and even political leverage play significant roles. Criminals employ these methods for a multitude of purposes, often combining them to maximize their impact and potential rewards.
Financial Gain
Financial gain is the most prevalent motivation. Attackers target organizations with valuable data or sensitive information, knowing that the ransom payment is a quick and lucrative source of income. This financial incentive fuels the continuous development and evolution of ransomware attacks, making them a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. For example, the Ryuk ransomware campaign targeted large enterprises and demanded substantial ransom payments, highlighting the significant financial motivation behind these attacks.
Data Theft, Google study confirms that ransomware victims paid 2 million a month
Beyond the immediate ransom demand, some attacks involve the exfiltration of sensitive data. Attackers may steal confidential information, intellectual property, or personal data, and then threaten to leak or sell this data to the public. This form of extortion adds another layer of threat, increasing the pressure on victims to pay the ransom.
Reputational Damage
A successful ransomware attack can cause severe reputational damage to a targeted organization. The publicity surrounding the incident can damage customer trust and brand perception. Furthermore, regulatory penalties and legal repercussions can further compound the negative impact.
Role of Criminal Organizations
Criminal organizations play a significant role in perpetrating ransomware attacks. These groups often operate as sophisticated cybercrime enterprises, employing specialized skills and resources to plan and execute attacks. The scale and sophistication of these operations are increasing, making it more difficult to combat them effectively.
Strategies for Identifying and Targeting Vulnerable Organizations
Attackers use various methods to identify and target vulnerable organizations. They often research publicly available information about potential targets, looking for weaknesses in security protocols or vulnerabilities in software. They may also employ social engineering tactics to gain access to sensitive information or manipulate employees into granting unauthorized access. These sophisticated techniques underscore the need for organizations to proactively address vulnerabilities and implement robust security measures.
Types of Cyber Threats and Potential Impact
| Cyber Threat | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Ransomware | Financial loss, data breaches, operational disruption, reputational damage |
| Phishing | Data breaches, financial fraud, malware infections |
| Malware | Data breaches, system disruptions, financial losses |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks | System unavailability, service disruptions, financial losses |
| SQL Injection | Data breaches, unauthorized access to databases |
Victim Responses to Ransomware Demands
Ransomware attacks are a growing threat to organizations of all sizes, impacting not only their operations but also their financial stability and reputation. Understanding how victims respond to these demands is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and potentially reducing the overall impact of these attacks. A critical aspect of this understanding involves analyzing the complex decision-making processes behind victim responses.The decision of whether to pay a ransom or not is rarely straightforward.
Numerous factors, including the nature of the data compromised, the financial resources of the victim, and the potential reputational damage, all play a significant role. This analysis will delve into the range of victim responses, examining the rationale behind choices, and contrasting the outcomes for organizations that choose to pay versus those that don’t.
Range of Victim Responses
Victim responses to ransomware demands exhibit a wide spectrum, ranging from immediate payment to protracted negotiations or outright refusal. Some organizations might opt for immediate payment, prioritizing the quick restoration of their systems and operations. Others might engage in lengthy negotiations, attempting to bargain for a lower ransom or explore alternative solutions. Conversely, some victims might choose to refuse payment, facing potential data loss or operational disruption, but prioritizing the avoidance of incentivizing future attacks.
Decision-Making Process
The decision-making process behind paying or not paying ransom is multifaceted and involves a careful consideration of several factors. Financial considerations are paramount, weighing the potential costs of the ransom against the potential costs of downtime, data loss, and reputational damage. The nature and value of the compromised data are also significant. If the data is crucial for operations, the cost of recovery might outweigh the ransom.
Factors Influencing Negotiation or Refusal
Several factors influence the decision to negotiate or refuse payment. The perceived credibility of the attackers, the urgency of the situation, and the availability of alternative recovery options all play a crucial role. For example, if the attackers have a proven track record of delivering on their promises, negotiation might be more likely. Conversely, if the situation is deemed urgent, the pressure to pay might increase.
The availability of robust backup systems and recovery plans significantly influences the victim’s decision-making.
Outcomes for Paying vs. Not Paying
The outcomes for organizations that pay versus those that don’t differ significantly. Organizations that pay the ransom often restore their systems quickly but run the risk of incentivizing future attacks. They may also face legal and reputational challenges, depending on the specifics of the attack. Organizations that refuse payment may experience extended downtime, data loss, and reputational damage, but they avoid supporting future criminal activities.
There is no universally “correct” decision; the optimal strategy depends heavily on the specific circumstances.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The following table illustrates the diverse legal and ethical considerations for victims facing ransomware demands:
| Aspect | Paying | Not Paying |
|---|---|---|
| Legal | Potentially violating anti-money laundering laws if funds are used for criminal purposes. Paying may also be viewed as an admission of guilt. | Potential legal liabilities if the organization fails to comply with regulations and legal requirements. |
| Ethical | Potentially seen as supporting criminal activities. | Potential reputational damage and loss of trust with stakeholders. |
| Financial | Immediate financial burden of the ransom. However, this might be less than the cost of recovery and downtime if systems are restored quickly. | Potential long-term financial implications from downtime and data loss. |
| Operational | Quick restoration of services and systems. | Potential for prolonged operational disruption. |
Analysis of the Google Study
The Google study, a significant contribution to understanding ransomware’s financial impact, delves into the intricate dynamics of ransomware payments. By analyzing a substantial dataset of ransomware attacks, the study sheds light on payment trends, motivations behind attacks, and victim responses, offering valuable insights into the evolving landscape of cybercrime. This analysis will dissect the study’s methodology, key findings, and limitations, placing them within the broader context of cybersecurity.
Summary of Google Study Findings on Ransomware Payments
The Google study examined a vast amount of ransomware payment data, revealing crucial trends in victim behavior and attacker strategies. The findings suggest a complex interplay of factors influencing these transactions, from the attackers’ motivations to the victims’ responses. The study meticulously tracks payment amounts, frequency, and victim types, providing a comprehensive picture of the financial repercussions of ransomware attacks.
Methodologies Used in the Study
The study employed advanced data analysis techniques to identify patterns and correlations within the ransomware payment data. These methods likely included statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and network analysis. The use of anonymized data and robust encryption procedures likely ensured the confidentiality and integrity of the data throughout the research process. For example, techniques such as clustering and regression analysis could have been applied to identify key variables influencing payment decisions.
Significance of the Study’s Findings in Relation to the Broader Cybersecurity Landscape
The Google study’s findings are crucial for understanding the evolution of ransomware and the efficacy of current cybersecurity strategies. The insights into payment patterns and attacker motivations can inform the development of more effective preventative measures, including improved security protocols and incident response plans. Furthermore, the study’s results can aid policymakers and law enforcement in developing targeted strategies to combat ransomware.
Limitations of the Study and Potential Biases in the Data
While the Google study provides valuable insights, it’s essential to acknowledge potential limitations and biases in the data. The study’s reliance on publicly available data may not capture the full extent of ransomware activity, as some attacks may go unreported or remain undisclosed. Furthermore, the data may not be completely representative of all types of ransomware or victims.
The study might also be influenced by biases in reporting or in the specific data sources utilized.
Key Findings and Conclusions of the Google Study (Table)
| Finding | Conclusion |
|---|---|
| Ransomware attacks are increasing in frequency and sophistication. | The evolving nature of attacks necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity. |
| Payment amounts vary significantly based on factors like victim type and attack sophistication. | A targeted approach to security, tailored to specific vulnerabilities, is more effective. |
| Victims are more likely to pay if they have a history of successful ransomware payments. | Cybersecurity education and awareness campaigns can deter victims from paying ransoms. |
| Attackers frequently employ new tactics to bypass existing security measures. | Continuous improvement and adaptation in cybersecurity are essential. |
Security Measures to Prevent Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks are a significant threat to organizations of all sizes, impacting their operations, finances, and reputation. Proactive security measures are crucial in mitigating this risk and safeguarding valuable data. Implementing a multi-layered approach, encompassing strong passwords, regular updates, robust protocols, data backups, and employee training, can significantly reduce vulnerability to ransomware.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Robust password policies are fundamental to protecting systems. Users should be encouraged to create complex passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Regular password changes and the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) add another layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Using a password manager can further enhance password security by generating and storing strong, unique passwords for different accounts.
A recent Google study highlighted a shocking reality: ransomware victims are paying out a staggering $2 million per month. This alarming figure underscores the serious financial impact of cyberattacks. Fortunately, there are steps being taken to mitigate the damage, like the Department of Justice’s new “Safe Harbor” policy for Massachusetts transactions, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions.
While this policy could potentially help reduce these payouts, the $2 million monthly figure remains a stark reminder of the pervasive and costly nature of ransomware attacks.
Regular Software Updates
Regular software updates are essential to patch security vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals often exploit known weaknesses in software to gain access to systems. By promptly installing updates, organizations can mitigate these risks and protect themselves from potential attacks. Maintaining up-to-date operating systems, applications, and security software is a critical proactive measure.
The recent Google study confirming ransomware victims paid an average of $2 million a month is a stark reminder of the escalating cyber threats. This alarming figure highlights the critical need for robust security measures, like those detailed in the Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details, to protect against such attacks. Understanding these vulnerabilities, as explored in more depth on this page Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details , is crucial to mitigating the risk of substantial financial losses and the broader implications for businesses and individuals.
Ultimately, the Google study serves as a crucial wake-up call about the sheer cost of ransomware attacks.
Robust Security Protocols
Implementing strong security protocols, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software, is vital. These protocols act as a first line of defense, blocking unauthorized access attempts and detecting malicious activities. Employing network segmentation and access controls further restricts the potential impact of a successful attack.
Data Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups are crucial for data recovery in case of a ransomware attack. Implementing a robust backup and recovery plan ensures that data can be restored quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and financial losses. Offsite backups and version control are essential for data protection. A tested and regularly practiced recovery plan is essential.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Employee training and awareness programs are critical to preventing ransomware attacks. Educating employees about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and safe browsing practices can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to a successful attack. Regular training sessions and simulations can reinforce these best practices and build a culture of cybersecurity awareness.
Security Measures Effectiveness
| Security Measure | Effectiveness | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Passwords & MFA | High | Makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. |
| Regular Software Updates | High | Patches known vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface. |
| Robust Security Protocols | Medium-High | Acts as a barrier against unauthorized access and malicious activity. Effectiveness depends on the implementation and monitoring. |
| Data Backup and Recovery | High | Allows for quick restoration of data, minimizing downtime and losses. |
| Employee Training | Medium-High | Reduces the risk of human error and social engineering attacks. Effectiveness depends on the quality and frequency of training. |
Future Trends in Ransomware Attacks
The landscape of ransomware attacks is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-changing motivations of cybercriminals. Predicting the precise trajectory of future attacks is challenging, but analyzing current trends allows us to anticipate potential developments and prepare for the evolving threats. Understanding the future tactics, vulnerabilities, and impacts will be crucial for organizations to implement robust security measures.The future of ransomware attacks is likely to be characterized by increased sophistication, targeting specific vulnerabilities, and exploiting new technologies.
Criminals are continually adapting their techniques to evade detection and maximize their financial gains. This evolution necessitates a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity, moving beyond reactive measures to embrace predictive and preventative strategies.
Anticipated Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
Cybercriminals are continually refining their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to bypass existing security measures. This includes employing advanced evasion techniques, leveraging multiple attack vectors, and targeting less-protected systems. Sophisticated phishing campaigns, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities, and deploying ransomware as a service (RaaS) are expected to become more prevalent. The increasing use of AI and machine learning in both attack and defense strategies will likely be a key differentiator.
Furthermore, supply chain attacks will continue to be a major concern, as organizations rely on interconnected systems and third-party vendors.
Emergence of New Vulnerabilities and Exploit Methods
The constant development of software and hardware introduces new vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals will undoubtedly exploit these newly discovered vulnerabilities, particularly in emerging technologies like IoT devices and cloud environments. The rise of software as a service (SaaS) and cloud computing presents unique security challenges, including the need for enhanced access controls and security configurations. A critical aspect is the exploitation of vulnerabilities in software supply chains, where malicious code can be inserted into legitimate software packages.
Impact of Future Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will profoundly influence both the development and defense against ransomware attacks. AI-powered tools can be used to automate attacks, identify potential targets, and analyze large datasets to identify patterns in victim behavior. Conversely, AI and ML can be utilized to enhance threat detection and response systems, enabling faster identification and mitigation of attacks.
The use of blockchain technology could provide a more secure and transparent way to handle payments and ensure the security of data.
Forecasted Ransomware Attack Trends and Costs
| Trend | Description | Estimated Cost Impact (per incident) |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Attacks | Criminals will increasingly focus on specific industries or organizations with valuable data or systems. | $500,000 – $10,000,000+ |
| Supply Chain Attacks | Ransomware will be delivered through compromised third-party vendors or suppliers, affecting multiple organizations. | $1,000,000 – $100,000,000+ |
| IoT Device Exploits | Criminals will exploit vulnerabilities in connected devices, disrupting operations and potentially causing widespread damage. | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ |
| Double Extortion Attacks | Threat actors will steal data in addition to encrypting it, adding pressure on victims to pay. | $250,000 – $5,000,000+ |
| Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) Expansion | RaaS will continue to grow in popularity, providing access to ransomware tools and infrastructure to less skilled attackers. | $50,000 – $500,000+ |
Global Impact of Ransomware: Google Study Confirms That Ransomware Victims Paid 2 Million A Month

Ransomware attacks are no longer a niche cybercrime issue; they’ve become a global concern impacting various sectors and regions. The financial, reputational, and operational consequences are significant, and understanding the broader scope of this threat is crucial. This analysis delves into the pervasive effects of ransomware on the global landscape.The increasing sophistication and frequency of ransomware attacks underscore their devastating impact on organizations and governments worldwide.
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks, often targeting critical infrastructure, financial institutions, and healthcare providers. The resulting disruption, financial losses, and reputational damage extend far beyond the immediate victims, creating ripples across entire industries and economies.
Impact on Healthcare
The healthcare sector is particularly vulnerable due to the sensitive patient data often targeted and the potential for catastrophic disruptions to services. Hospitals and clinics are frequently hit with ransomware, leading to the inability to access critical medical records, hindering treatment, and potentially endangering patients. The disruption can also cause delays in surgeries and other essential procedures. For instance, a 2022 attack on a major US hospital led to significant operational issues and patient care concerns.
Impact on Finance
Financial institutions are prime targets for ransomware attacks due to the large sums of money and sensitive financial data they hold. These attacks can cripple operations, leading to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and disruption of services. Criminals often target financial transfers and data breaches to steal or extort funds. The potential for massive financial losses, particularly for banks and other financial institutions, underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Impact on Critical Infrastructure
Ransomware attacks on critical infrastructure, such as power grids, water treatment facilities, and transportation networks, can have far-reaching consequences, potentially impacting entire regions. Disruptions to these essential services can cause widespread chaos and economic instability. The potential for cascading failures and the disruption of essential services is a significant concern.
Economic Consequences for Countries and International Relations
The economic consequences of ransomware attacks extend beyond individual organizations and countries. The costs associated with recovery, remediation, and security enhancements place a strain on national budgets. In addition, these attacks can strain international relations, especially when cross-border operations or critical infrastructure is affected. For example, a ransomware attack on a major energy company could impact not just the attacked nation but neighboring countries reliant on the energy supply.
Effects on Global Supply Chains
Ransomware attacks can disrupt global supply chains by targeting companies involved in manufacturing, logistics, and distribution. These attacks can lead to production delays, inventory shortages, and increased costs, affecting businesses worldwide. The interconnected nature of global supply chains makes them highly vulnerable to disruptions caused by ransomware. For example, a ransomware attack on a major shipping company could halt global trade.
Comparative Impact on Countries and Sectors
| Country/Sector | Impact Description |
|---|---|
| United States – Healthcare | Significant disruptions in patient care and operations. |
| United Kingdom – Finance | Major financial losses and reputational damage for financial institutions. |
| Europe – Critical Infrastructure | Disruptions to essential services and widespread chaos. |
| Asia – Supply Chains | Delays in production, shortages, and increased costs for manufacturers and distributors. |
Last Point
In conclusion, the Google study’s revelation of monthly ransomware payments reaching $2 million underscores the severity and pervasiveness of this cyber threat. The study’s findings highlight the critical need for enhanced security protocols, proactive risk management, and continuous vigilance in the face of evolving cyberattacks. By understanding the financial incentives and victim responses, organizations can better prepare for future attacks and mitigate the significant financial and reputational damage associated with ransomware.
Clarifying Questions
What methodologies did the Google study employ to analyze ransomware payment data?
The study likely used a combination of data analysis techniques, including statistical modeling, machine learning algorithms, and potentially partnerships with threat intelligence firms to access and analyze reported ransomware events. Precise methodologies are not always disclosed in academic or corporate research to protect the integrity of the findings.
What are some key limitations of the Google study?
The study might have limitations in terms of data completeness and accuracy. Reporting of ransomware attacks is often incomplete, and the study may not capture all instances of ransomware payments. Additionally, the study’s findings might not reflect the full range of experiences in different regions or industries due to potential biases in the data collection process.
What are some preventive measures organizations can implement to reduce their vulnerability to ransomware attacks?
Organizations should implement multi-layered security measures, including robust data backups, regular software updates, strong password policies, employee training on cybersecurity best practices, and proactive threat intelligence monitoring.
How can governments help mitigate the global impact of ransomware attacks?
Governments can foster international collaboration, enhance cybersecurity infrastructure, support research and development of new security technologies, and impose stricter regulations and penalties on ransomware perpetrators.





