Harnessing AI to Thwart Ransomware Threats A Strategic Approach
Harnessing ai to thwart ransomware threats a strategic approach – Harnessing AI to thwart ransomware threats: a strategic approach. That’s the challenge, and it’s a big one. Ransomware isn’t just a tech problem anymore; it’s a business crisis, a societal headache. We’re seeing attacks grow bolder, more sophisticated, and more financially devastating. But the tide might be turning.
Artificial intelligence offers a powerful countermeasure, promising to not only detect these attacks but also predict and even prevent them. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of modern cybersecurity, and we’re diving deep into how AI is changing the game.
This post explores the evolving landscape of ransomware, detailing how AI is being deployed to detect malicious activity, automate data backups, and accelerate incident response. We’ll also touch on the ethical considerations and legal implications surrounding AI’s role in cybersecurity, and peek into the future of AI-powered ransomware defense. Get ready for a fascinating journey into the heart of the fight against this digital plague.
Understanding the Ransomware Threat Landscape
The ransomware threat landscape is constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and financially devastating for organizations worldwide. Understanding this evolution is crucial for developing effective preventative and responsive strategies. The sheer scale and impact of successful attacks necessitate a proactive approach that leverages the power of AI to stay ahead of the curve.The evolution of ransomware attacks showcases a clear trend towards increased sophistication.
Early ransomware attacks were relatively simple, often relying on mass-mailing campaigns and easily detectable malware. Today’s attacks are far more targeted, utilizing advanced techniques like phishing, exploiting software vulnerabilities, and employing double extortion tactics. This means attackers not only encrypt data but also steal it, threatening to leak sensitive information publicly unless a ransom is paid. The use of ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) platforms further exacerbates the problem, making it easier for less technically skilled individuals to launch devastating attacks.
Prevalent Ransomware Families and Attack Vectors
Several ransomware families dominate the threat landscape, each with its preferred attack vectors. Ryuk, Conti, and REvil (Sodinokibi) are notable examples, known for their aggressive encryption techniques and high ransom demands. These families often leverage various attack vectors, including phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links, exploiting vulnerabilities in software and systems (often unpatched), and utilizing compromised credentials obtained through credential stuffing or other means.
The attackers often gain initial access through spear-phishing campaigns targeting specific individuals within an organization, then moving laterally to gain access to critical systems and data.
Financial and Operational Impact of Ransomware Attacks
Successful ransomware attacks inflict significant financial and operational damage on organizations. Direct costs include ransom payments (often in cryptocurrency), incident response expenses (hiring cybersecurity experts, forensic analysis, legal counsel), and data recovery costs. Indirect costs can be even more substantial, encompassing business disruption, loss of productivity, reputational damage, and potential legal liabilities. For example, a hospital hit by a ransomware attack might face delays in patient care, leading to potential harm and significant financial penalties.
A large corporation might experience a complete shutdown of operations, leading to lost revenue and potential contract breaches. The impact extends beyond immediate financial losses; it includes long-term damage to customer trust and brand image.
Ransomware Protection Strategies
Understanding the various protection strategies is vital for mitigating the risk of ransomware attacks. A multi-layered approach is necessary, combining preventative measures with robust detection and response capabilities.
| Strategy | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Backups | Maintaining frequent and secure backups of critical data. | Data recovery is possible even after encryption. | Requires robust backup infrastructure and testing. |
| Security Awareness Training | Educating employees about phishing and social engineering tactics. | Reduces human error, a primary attack vector. | Requires ongoing effort and reinforcement. |
| Vulnerability Management | Regularly patching software and systems to address known vulnerabilities. | Reduces the attack surface. | Can be time-consuming and require careful planning. |
| Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) | Utilizing advanced security tools to detect and respond to malicious activity on endpoints. | Provides real-time threat detection and response capabilities. | Can be complex to manage and require specialized expertise. |
AI-Powered Threat Detection and Prevention

The rise of ransomware necessitates a similarly advanced defense. AI offers a powerful toolset to proactively identify and neutralize these threats, moving beyond reactive measures to a more strategic, predictive approach. By leveraging machine learning and sophisticated algorithms, we can significantly improve our ability to detect and prevent ransomware attacks before they cripple our systems.Machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in identifying malicious code and suspicious network activity.
These algorithms are trained on vast datasets of known ransomware samples and benign software, learning to distinguish between them based on various characteristics like code execution patterns, file system modifications, and network communication behaviors. This allows for the identification of even novel ransomware variants that haven’t been seen before, based on learned patterns and anomalies.
Anomaly Detection and Predictive Capabilities of AI
AI excels at identifying anomalies within network traffic and system behavior. By establishing a baseline of normal activity, AI-powered security systems can flag deviations that might indicate a ransomware attack. This includes unusual file access patterns, encrypted data transfers, or spikes in outbound network connections. Furthermore, AI can analyze historical data to predict potential ransomware attacks, identifying vulnerable systems or emerging attack vectors.
For example, by analyzing the frequency and success of phishing campaigns targeting a specific organization, AI could predict a future ransomware attack and recommend preemptive measures.
Examples of AI-Driven Security Tools
Several AI-driven security tools are available that proactively thwart ransomware attacks. These tools often incorporate a combination of techniques, including: Sandboxing (running suspicious files in an isolated environment to observe their behavior), Static and Dynamic Analysis (examining code for malicious patterns and observing runtime behavior), and Behavioral Analysis (monitoring system activity for unusual patterns). Examples include solutions from companies like CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, and Darktrace, each employing unique AI algorithms and approaches.
These tools can automatically detect and quarantine malicious files, block suspicious network connections, and even roll back systems to a pre-infection state.
AI-Powered Ransomware Detection and Response System Flowchart
The following describes a typical workflow for an AI-powered ransomware detection and response system:
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps:
- Data Ingestion: The system collects data from various sources, including network traffic logs, endpoint security agents, and cloud security platforms.
- Preprocessing: The raw data is cleaned and transformed into a format suitable for machine learning algorithms.
- Feature Extraction: Relevant features are extracted from the preprocessed data. These features could include file hashes, network connections, process IDs, and system calls.
- Model Training: Machine learning models are trained on labeled datasets of benign and malicious activities.
- Anomaly Detection: The trained models analyze real-time data and identify anomalies that deviate from established baselines.
- Threat Classification: Anomalies are classified as potential ransomware attacks based on their characteristics and contextual information.
- Alert Generation: The system generates alerts when potential ransomware attacks are detected.
- Automated Response: Based on predefined rules, the system automatically takes action, such as quarantining infected files, isolating infected systems, or blocking malicious network connections.
- Incident Response: Security analysts investigate the alerts and take further actions as needed.
AI for Data Backup and Recovery
The relentless evolution of ransomware necessitates a similarly advanced approach to data protection. Traditional backup and recovery methods often struggle to keep pace with sophisticated encryption techniques and the sheer volume of data modern organizations manage. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in, offering powerful tools to automate, enhance, and fundamentally improve the resilience of our data against ransomware attacks.
By leveraging AI’s capabilities, we can move beyond reactive measures to a proactive, intelligent defense.AI significantly enhances data backup and recovery processes through automation and intelligent analysis. It streamlines tasks that were previously time-consuming and error-prone, allowing for faster recovery times and reduced operational overhead. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and potential financial losses associated with ransomware incidents.
The integration of AI doesn’t simply automate existing processes; it fundamentally re-engineers them for greater efficiency and resilience.
AI-Driven Data Deduplication and Compression
AI algorithms can analyze data to identify and eliminate redundant copies, significantly reducing storage requirements and backup times. This process, known as deduplication, is further enhanced by AI-driven compression techniques that minimize the size of backup files without compromising data integrity. For example, an AI system might identify that multiple versions of a document contain largely the same information, retaining only the unique changes across different versions.
This intelligent compression saves significant storage space and network bandwidth, leading to cost savings and faster backups. The result is a more efficient and cost-effective backup strategy, freeing up valuable resources.
AI-Assisted Ransomware Data Restoration
AI plays a crucial role in identifying and restoring data affected by ransomware encryption. Advanced machine learning models can analyze encrypted files, identify patterns associated with specific ransomware families, and even predict the encryption method used. This information allows for faster and more targeted decryption efforts, potentially reducing the time and resources needed for recovery. Furthermore, AI can assist in prioritizing the recovery of critical data, ensuring business continuity is maintained during and after an attack.
For instance, an AI system could identify a company’s financial records as high-priority and focus restoration efforts there first.
Best Practices for Data Recoverability, Harnessing ai to thwart ransomware threats a strategic approach
Effective data recovery hinges on a robust and well-tested strategy. Here are key best practices that leverage AI to bolster data recoverability against ransomware attacks:
Implementing these best practices ensures that your data recovery process is not only efficient but also resilient against increasingly sophisticated ransomware attacks. A multi-layered approach that combines regular backups, AI-powered monitoring, and a well-defined recovery plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a ransomware incident.
- Regular, Automated Backups: Implement AI-powered systems that automate backups, ensuring consistent and timely data protection. This includes offsite backups to geographically dispersed locations for added security.
- Immutable Backups: Employ backup solutions that prevent modification or deletion of backup files, protecting them from ransomware encryption. This ensures a clean and reliable source for data restoration.
- AI-Driven Anomaly Detection: Continuously monitor your systems for unusual activity using AI-powered security information and event management (SIEM) tools. Early detection can prevent widespread encryption.
- Versioning and Recovery Testing: Regularly test your backup and recovery procedures to ensure they function correctly and that your data can be restored effectively. This includes restoring from different versions of your backups.
- Robust Security Posture: Implement strong cybersecurity practices, including regular software updates, employee training, and multi-factor authentication, to reduce the likelihood of a ransomware infection in the first place.
AI in Incident Response and Remediation
Ransomware attacks can cripple organizations, leaving them scrambling to contain the damage and restore operations. The speed and scale of modern attacks often overwhelm traditional incident response methods. This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in, offering a powerful arsenal of tools to accelerate the response, minimize damage, and potentially recover data without succumbing to the attacker’s demands.AI significantly accelerates the process of identifying and isolating infected systems.
Traditional methods rely on manual analysis of network traffic and system logs, a process that can take hours or even days. AI, however, can analyze vast datasets in real-time, identifying anomalies indicative of a ransomware infection far more quickly. Machine learning models trained on known ransomware behaviors can flag suspicious activity, such as unusual file access patterns or encrypted files, allowing for immediate isolation of affected systems to prevent further spread.
This rapid identification and isolation is crucial in limiting the impact of the attack.
AI-Accelerated Identification and Isolation of Infected Systems
AI algorithms, specifically those employing unsupervised machine learning techniques like anomaly detection, can continuously monitor network traffic and system logs for deviations from established baselines. These deviations, often subtle indicators of malicious activity, might go unnoticed by human analysts. For example, an AI system might detect an unusually high volume of outbound network connections from a specific server or a sudden spike in file encryption activity.
Upon detecting such anomalies, the AI can automatically trigger alerts, initiate network segmentation to isolate affected systems, and even initiate automated remediation steps such as disabling affected accounts or shutting down compromised services. The speed and automation offered by AI are crucial in mitigating the damage caused by ransomware.
AI-Driven Data Recovery from Encrypted Files
While complete data recovery from sophisticated ransomware encryption is not always possible, AI can significantly improve the chances of partial or even full recovery. AI techniques, such as deep learning, can analyze encrypted data to identify patterns and potential weaknesses in the encryption algorithm. This analysis can potentially allow for the decryption of certain file types or even entire datasets.
Furthermore, AI can assist in identifying and recovering unencrypted backups or shadow copies of files that might have been overlooked during manual recovery efforts. While paying a ransom remains a last resort, AI offers a powerful alternative by increasing the probability of successful data recovery through technical means.
AI-Enhanced Forensic Analysis of Ransomware Attacks
Determining the origin and methods of a ransomware attack is critical for preventing future incidents. AI can significantly enhance forensic analysis by automating the process of analyzing massive datasets of system logs, network traffic, and malware samples. AI algorithms can identify the initial infection vector, the ransomware variant used, the command-and-control servers involved, and the attacker’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
This detailed analysis allows security teams to understand the attack lifecycle, identify vulnerabilities exploited by the attackers, and implement appropriate security controls to prevent similar attacks in the future. For example, AI can correlate seemingly unrelated events from different systems to reconstruct the attacker’s actions, revealing intricate attack chains that might otherwise remain hidden.
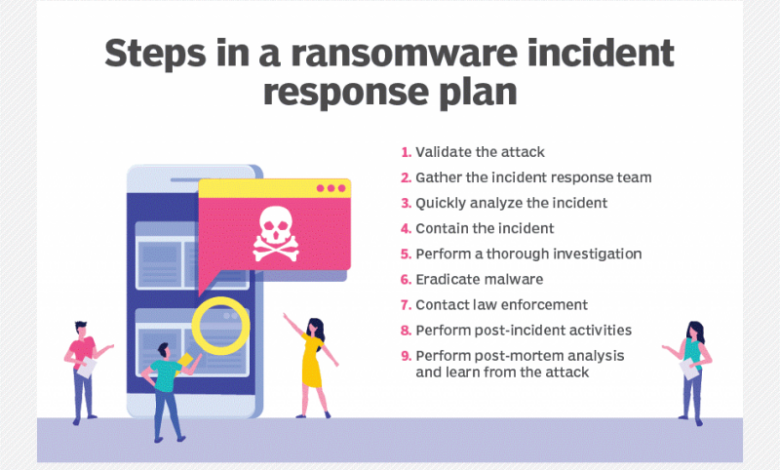
A Step-by-Step Procedure for AI in Ransomware Incident Response
A robust ransomware incident response plan incorporating AI should follow these steps:
1. Real-time threat detection
Employ AI-powered security information and event management (SIEM) systems and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to continuously monitor systems for suspicious activity.
2. Automated isolation
Harnessing AI to fight ransomware is a game-changer, offering proactive defenses we couldn’t dream of before. Building robust, adaptable security systems requires powerful development tools, which is where exploring options like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future becomes crucial. Ultimately, leveraging both AI and efficient development methodologies is key to staying ahead of the ever-evolving ransomware threat landscape.
Upon detection of a ransomware attack, automatically isolate infected systems from the network to prevent lateral movement.
3. Data recovery attempts
Utilize AI-driven data recovery tools to attempt decryption of encrypted files and recovery of unencrypted backups.
4. Forensic analysis
Employ AI-powered forensic analysis tools to investigate the attack, identify the attacker’s TTPs, and determine the root cause.
5. Vulnerability remediation
Based on the forensic analysis, identify and remediate the vulnerabilities exploited by the attackers.
6. Security enhancements
Implement enhanced security controls, such as multi-factor authentication, strong password policies, and regular security awareness training, to prevent future attacks.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Implications: Harnessing Ai To Thwart Ransomware Threats A Strategic Approach

The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into cybersecurity, while promising significant advancements in combating ransomware, introduces a complex web of ethical considerations and legal implications that demand careful attention. The power of AI to analyze vast datasets and identify threats with speed and accuracy is undeniable, but this power must be wielded responsibly, acknowledging the potential for misuse and unintended consequences.
Balancing the benefits of AI-driven security with the potential risks is crucial for building a secure and trustworthy digital future.AI systems, particularly those trained on large datasets, can inherit and amplify existing societal biases. For instance, if a ransomware detection system is trained primarily on data from one geographic region or type of organization, it may be less effective at identifying attacks targeting other demographics or sectors.
This could lead to disproportionate impacts, leaving certain groups more vulnerable. Furthermore, the autonomous nature of some AI systems raises concerns about accountability. When an AI system makes a decision that leads to a security breach or data loss, determining responsibility can be challenging.
AI Bias and Discrimination in Cybersecurity
Algorithmic bias in AI-powered ransomware detection systems can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. If the training data reflects existing societal biases, the AI may be more likely to flag threats from certain sources or individuals while overlooking others. For example, an AI system trained primarily on data from Western countries might be less effective at detecting ransomware originating from other regions, potentially leading to increased vulnerabilities in those areas.
Mitigating this requires careful curation of training data to ensure it represents a diverse range of threat actors and attack vectors, and ongoing monitoring for signs of bias in the system’s outputs. Regular audits and independent evaluations are vital to identify and address potential biases.
Legal Liability and Accountability for AI-Driven Security Failures
The legal implications of using AI in cybersecurity are still evolving. Determining liability in the event of a security breach involving an AI system can be complex. Is the developer of the AI, the organization deploying it, or the user ultimately responsible? Current legal frameworks may not adequately address these scenarios, potentially leading to protracted legal battles and uncertainty.
The lack of clear legal guidelines could also discourage innovation in the field, as organizations may hesitate to adopt AI-based security solutions due to the potential legal risks. Establishing clear lines of responsibility and accountability is crucial to fostering trust and encouraging wider adoption of AI in cybersecurity.
Transparency and Accountability in AI-Based Ransomware Countermeasures
Transparency and accountability are paramount in the development and deployment of AI-based ransomware countermeasures. Users need to understand how these systems work, what data they collect, and how their decisions are made. This includes clear documentation of the AI’s algorithms, training data, and performance metrics. Regular audits and independent evaluations can help ensure that the systems are functioning as intended and are not exhibiting unintended biases or vulnerabilities.
Organizations deploying AI-based security solutions should also be transparent about their security practices and be prepared to account for their actions in the event of a security breach. Openness and accountability build trust with users and stakeholders, promoting the responsible use of AI in cybersecurity.
Regulatory Approaches to AI in Cybersecurity
Different approaches to regulating the use of AI in cybersecurity are being explored globally. Some jurisdictions favor a more hands-off approach, allowing the market to self-regulate, while others advocate for more stringent government oversight. The challenge lies in finding a balance between promoting innovation and ensuring responsible development and deployment of AI-based security solutions. Regulatory frameworks should focus on promoting transparency, accountability, and fairness, while avoiding overly burdensome regulations that could stifle innovation.
International collaboration is essential to develop harmonized standards and best practices for the responsible use of AI in cybersecurity. A collaborative approach ensures that regulatory frameworks are effective and consistent across different jurisdictions.
Future Trends in AI-Powered Ransomware Defense
The fight against ransomware is a constantly evolving arms race. As attackers become more sophisticated, so too must our defenses. AI is already proving invaluable, but the future holds even more potent tools and strategies for combating these malicious threats. The integration of emerging technologies promises a significant leap forward in our ability to prevent, detect, and respond to ransomware attacks.
The next generation of AI-powered ransomware defense will leverage advancements in several key areas, creating a more proactive and resilient security posture. This will move beyond simply reacting to attacks to actively predicting and preventing them before they can cause significant damage.
Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms
The development and deployment of more sophisticated machine learning algorithms will be crucial. Current AI models primarily rely on supervised and unsupervised learning. However, reinforcement learning, a type of machine learning where an AI agent learns to make optimal decisions through trial and error in a simulated environment, holds significant promise. This allows for the training of AI systems to identify and respond to novel attack vectors and evolving ransomware techniques without requiring extensive labeled datasets.
Imagine an AI system that can anticipate and preemptively block a new ransomware variant based on its observed behavior in a simulated network environment. This proactive approach will be a game-changer.
Quantum Computing’s Potential
Quantum computing, while still in its nascent stages, offers the potential to revolutionize cryptography and cybersecurity. Quantum computers possess the power to break currently used encryption algorithms significantly faster than classical computers. This presents a challenge, but also an opportunity. The development of quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, alongside AI systems capable of managing and deploying these new algorithms, will be essential to ensure data remains secure in the quantum era.
This means preparing for a future where current encryption methods are no longer sufficient, requiring a shift towards more robust and quantum-resistant alternatives. The integration of AI will be critical in managing the transition and ensuring seamless security.
AI and Blockchain Integration
The integration of AI and blockchain technology offers exciting possibilities for enhanced ransomware defense. Blockchain’s immutable ledger can provide a secure record of data integrity and provenance, allowing for quick verification of data authenticity post-attack. AI can analyze this blockchain data to identify anomalies and potential compromises, speeding up the recovery process. For instance, AI could analyze blockchain records to pinpoint the exact moment a file was altered or encrypted, providing crucial information for targeted data recovery.
This combination allows for a more efficient and transparent approach to data management and security auditing. However, the challenge lies in effectively integrating these two technologies and addressing scalability issues.
The effective implementation of these technologies requires careful consideration of their limitations and potential vulnerabilities. Over-reliance on any single technology can create new points of failure. A multi-layered, holistic approach is essential.
Future Advancements in AI-Driven Ransomware Mitigation
Several exciting advancements are on the horizon, promising a more robust and resilient defense against ransomware.
- Self-healing systems: AI-powered systems that automatically detect and repair damaged files or systems without human intervention.
- Predictive threat intelligence: AI models that can predict future ransomware attacks based on patterns and trends.
- Automated incident response: AI-driven systems that automatically contain and remediate ransomware attacks with minimal human involvement.
- Decentralized ransomware detection networks: Collaborative networks of AI systems that share information and threat intelligence to improve collective defense.
- Advanced behavioral analysis: AI systems capable of identifying subtle behavioral anomalies that indicate a ransomware infection, even before encryption begins.
Concluding Remarks

The fight against ransomware is far from over, but the integration of AI is a game-changer. From proactive threat detection and prevention to streamlined data recovery and faster incident response, AI offers a powerful arsenal of tools to combat this persistent threat. While ethical and legal considerations remain crucial, the potential of AI to significantly reduce the impact of ransomware attacks is undeniable.
The future of cybersecurity is intelligent, and it’s here to stay. Staying informed and adapting our strategies is key to winning this ongoing battle.
Question Bank
What types of AI are most effective against ransomware?
Machine learning algorithms, particularly those focused on anomaly detection and behavior analysis, are proving most effective. Deep learning models are also showing promise in identifying complex patterns indicative of ransomware attacks.
Can AI completely eliminate the risk of ransomware?
No, AI is a powerful tool, but it’s not a silver bullet. A multi-layered security approach combining AI with other preventative measures is crucial for comprehensive protection.
How much does AI-powered ransomware protection cost?
The cost varies significantly depending on the specific tools and services implemented, the size of the organization, and the level of customization required. It’s important to weigh the cost against the potential financial losses from a ransomware attack.
Is AI-powered ransomware protection suitable for small businesses?
Yes, many affordable and user-friendly AI-powered security solutions are available for businesses of all sizes. Small businesses are increasingly vulnerable to ransomware attacks, making AI-based protection a valuable investment.