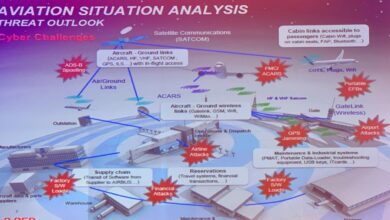
Healthcare Alert Medical Devices Under Attack
Healthcare alert medical devices are more prone to cyber attacks – Healthcare alert: medical devices are more prone to cyber attacks than ever before. From pacemakers to insulin pumps, the increasing reliance on these devices in modern healthcare makes them tempting targets for malicious actors. These devices, while crucial for patient care, often have vulnerabilities that can be exploited, leading to devastating consequences for patients and the entire healthcare system.
This article delves into the risks, explores the types of attacks, and discusses the measures that can be taken to mitigate these threats.
Medical devices are becoming increasingly sophisticated, yet their security often lags behind. This complexity creates opportunities for hackers to exploit vulnerabilities, leading to potential harm. Understanding the different types of medical devices, their unique vulnerabilities, and the potential consequences of cyberattacks is crucial to developing effective security measures. We will examine specific examples, from the potential for remote manipulation of pacemakers to data breaches affecting patient records.
Introduction to Medical Device Cybersecurity
Medical device cybersecurity is the protection of medical devices from cyberattacks. It encompasses the security of the hardware, software, and data associated with these devices. This protection is critical as medical devices are increasingly integrated into healthcare systems, impacting patient care and potentially leading to serious harm if compromised. As these devices become more sophisticated, they also become more vulnerable to malicious actors.The healthcare industry is rapidly transitioning towards a more interconnected and technology-driven environment.
Medical devices are increasingly connected to networks, enabling remote monitoring, diagnostics, and automated processes. This increasing reliance on medical devices necessitates a heightened awareness and robust security measures to protect them from cyberattacks.
Vulnerabilities of Medical Devices
Medical devices, ranging from pacemakers to sophisticated imaging equipment, are vulnerable to a variety of cyberattacks. These attacks can disrupt essential functions, leading to adverse health outcomes and patient harm. Cyberattacks on medical devices can result in a wide range of consequences, from minor malfunctions to catastrophic failures, impacting patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Examples of Susceptible Medical Devices
Various types of medical devices are susceptible to cyberattacks, posing significant risks to patient safety. Examples include:
- Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs): These devices are crucial for managing cardiac conditions, but their vulnerability to malicious code execution or remote control could have devastating consequences. Unauthorized commands could disrupt their function, leading to potentially fatal outcomes.
- Insulin Pumps: Insulin pumps are essential for diabetes management. Cyberattacks could lead to incorrect insulin dosages, potentially causing hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, and significantly impacting patient well-being.
- Imaging Equipment (e.g., X-ray machines, CT scanners): These devices are integral to diagnostics, and unauthorized access could compromise diagnostic accuracy or even manipulate images, leading to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment.
- Hospital Information Systems (HIS) and Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems: These systems are often connected to medical devices, making them susceptible to attacks that could compromise patient data or disrupt the functioning of devices. Data breaches, unauthorized access to patient information, and disruption of critical hospital functions are potential risks.
Categorization of Medical Devices and Vulnerabilities
The table below Artikels different categories of medical devices and their potential vulnerabilities. Mitigation strategies are also included to help address these issues.
| Device Category | Potential Vulnerabilities | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Pacemakers | Malicious code execution, remote control, data breaches | Robust authentication, encryption, regular updates, secure communication protocols |
| Insulin Pumps | Unauthorized access, data breaches, medication errors | Secure communication protocols, remote monitoring, tamper-resistant design, regular updates |
| Imaging Equipment | Unauthorized access, data breaches, image manipulation | Robust authentication, encryption, regular updates, secure communication protocols, monitoring of network access |
Types of Cyberattacks Targeting Medical Devices

Medical devices, critical for patient care, are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. These attacks can disrupt essential functionalities, compromise patient data, and ultimately jeopardize patient safety. Understanding the various attack vectors and their potential consequences is crucial for developing robust security measures.
Healthcare alert medical devices are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, a serious concern for patient safety. While the Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions, this initiative doesn’t directly address the specific security gaps in these devices. Ultimately, robust security measures are needed across the board to protect these crucial systems from malicious actors.
Malware Attacks
Malicious software, or malware, poses a significant threat to medical devices. Malware can infiltrate these devices through various means, including infected software updates or compromised networks. Once inside, malware can disrupt the device’s operations, corrupt data, or even gain control of its functionalities. Examples include ransomware, which can encrypt critical data, and spyware, which can monitor and collect sensitive information.
The consequences of malware attacks on medical devices can range from minor inconveniences to severe patient harm. For instance, a compromised pacemaker could malfunction, leading to potentially fatal arrhythmias. A malfunctioning insulin pump could result in uncontrolled blood sugar levels, potentially leading to diabetic complications.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks, often targeting individuals involved in device maintenance or management, aim to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or access codes. These attacks frequently involve fraudulent emails or messages mimicking legitimate communications from healthcare providers or manufacturers. By obtaining these credentials, attackers can gain unauthorized access to medical devices and networks, leading to data breaches and system compromises.
For example, an attacker might send a phishing email that appears to be from a device manufacturer, prompting a technician to download malicious software. This compromised account can then allow the attacker to gain control of the device, potentially altering vital parameters.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial-of-service attacks aim to overwhelm medical devices or networks with excessive traffic, rendering them unusable. This type of attack can disrupt essential services, such as remote monitoring or critical alerts. The consequences of a DoS attack on a critical care device can be dire, potentially leading to delays in treatment or even patient death. A disruption to a remote monitoring system for a patient in a remote location could hinder prompt interventions.
An attack targeting a vital sign monitoring system might prevent medical staff from receiving critical data, potentially leading to a delay in diagnosis or treatment.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
Attackers often exploit vulnerabilities in the software or firmware of medical devices. These vulnerabilities, if not patched, can provide attackers with entry points to the device’s systems. For example, outdated or poorly secured operating systems can be exploited to install malware. The methods used to exploit vulnerabilities can vary significantly, depending on the specific device and its design.
Sophisticated attackers may leverage zero-day exploits, vulnerabilities that were unknown to the software vendor, to gain unauthorized access.
Cyberattack Impact Comparison
| Attack Type | Target Functionality | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Malware | Data transmission, device control | Data breaches, system malfunction, patient harm |
| Phishing | User credentials | Unauthorized access, system compromise |
| DoS | Network availability | Disruption of services, delays in treatment |
Implications of Cyberattacks on Healthcare Systems
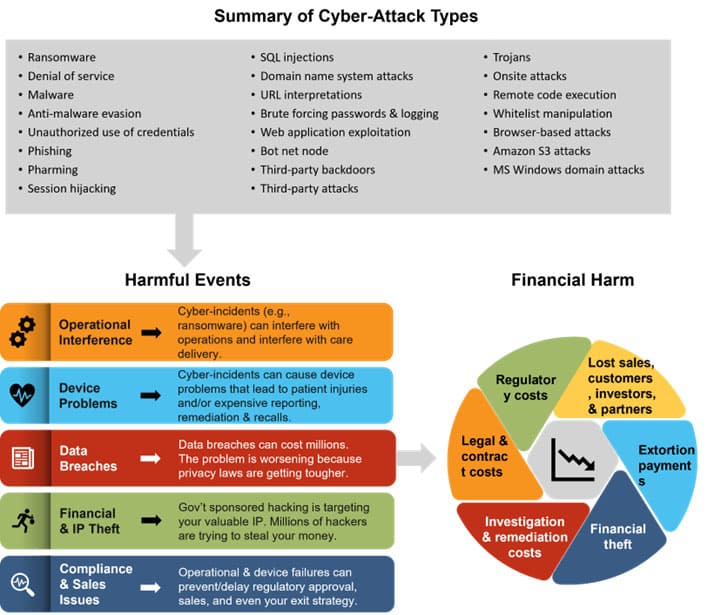
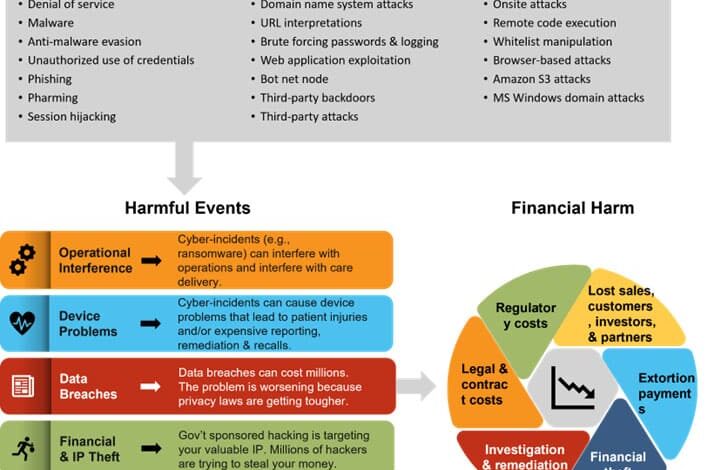
Medical device cybersecurity is no longer a theoretical concern; it’s a pressing reality with significant implications for healthcare providers, patients, and the entire system. The interconnected nature of modern healthcare, relying heavily on digital systems, makes it vulnerable to sophisticated cyberattacks. These attacks can disrupt operations, compromise patient data, and inflict substantial financial and reputational damage. Understanding the ramifications of these attacks is crucial for developing robust defenses and mitigating potential harm.
Financial Repercussions
Healthcare providers face substantial financial burdens from medical device cyberattacks. These attacks can lead to downtime of critical systems, resulting in lost revenue from patient care and administrative functions. Remediation efforts, including system restoration, data recovery, and legal fees, can also be extremely costly. The cost of a cyberattack extends beyond immediate expenses, encompassing long-term reputational damage and reduced patient trust.
The potential for significant financial penalties for non-compliance with data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the US, further compounds the financial strain.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Cyberattacks on medical devices raise complex legal and ethical considerations. Healthcare providers are legally obligated to protect patient data and maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient information. Breaches of these obligations can result in substantial fines and legal liabilities. Furthermore, ethical considerations arise regarding the responsibility for the safety and well-being of patients when medical devices are compromised.
These attacks can lead to serious patient harm, highlighting the ethical duty to prioritize patient safety above all else. The legal and ethical frameworks surrounding medical device cybersecurity are still evolving, creating uncertainty and requiring ongoing vigilance.
Impact on Patient Trust and Confidence
Patient trust and confidence in the healthcare system are crucial for maintaining a healthy and functional environment. Cyberattacks on medical devices can erode this trust. Patients may be concerned about the security of their personal information and the safety of medical procedures performed using compromised devices. The perceived lack of security can lead to a decline in patient enrollment and utilization of healthcare services, impacting both the immediate and long-term health of the population.
Maintaining patient trust requires transparency, accountability, and proactive measures to safeguard medical devices from cyber threats.
Examples of Past Incidents
Several past incidents highlight the vulnerabilities of medical devices to cyberattacks. One notable example involved a hospital network that experienced a disruption in its medical device operations after a successful cyberattack, resulting in significant delays in patient care. Another incident involved a hospital where a compromised medical device directly impacted patient treatment, highlighting the potential for severe harm.
These real-world examples emphasize the need for comprehensive security measures to mitigate the risks of cyberattacks.
Disruption of Healthcare Operations
Cyberattacks on medical devices can severely disrupt healthcare operations. Downtime of critical systems can lead to delays in patient care, treatment interruptions, and operational inefficiencies. The cascading effects of these attacks can have widespread consequences, affecting the entire healthcare facility and potentially impacting the wider community. These disruptions can exacerbate existing healthcare challenges and create new, complex problems.
Cascading Effects of a Medical Device Cyberattack
| Stage | Effect | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Attack | System disruption, potential for unauthorized access to sensitive data. | Robust security protocols, threat intelligence, incident response plans. |
| Data Breach | Compromised patient data, potential for misuse of sensitive information. | Secure data storage, encryption, access control, data loss prevention. |
The table above illustrates how a medical device cyberattack can have cascading effects throughout a healthcare facility, highlighting the importance of proactive security measures. Implementing these strategies can help to minimize the impact of these attacks.
Security Measures to Protect Medical Devices
Protecting medical devices from cyberattacks is paramount to ensuring patient safety and the reliability of healthcare systems. Vulnerabilities in these devices can lead to severe consequences, ranging from inaccurate diagnoses to life-threatening malfunctions. Robust security measures are crucial for mitigating these risks and maintaining the integrity of medical data.
Healthcare alert medical devices are increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, posing a serious threat to patient safety. This vulnerability extends beyond the immediate device itself; consider the broader implications of a security breach, like the recent details about a vulnerability in Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB, which highlights the critical need for robust security measures. Understanding these issues, like those explored in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details , is crucial to mitigating risks in the healthcare sector and preventing potential harm to patients.
Ultimately, stronger defenses are needed for these devices to prevent serious consequences.
Secure Communication Protocols for Medical Devices
Secure communication protocols are essential for safeguarding the data transmitted between medical devices and other systems. Encrypted communication channels, such as TLS/SSL, are vital for preventing unauthorized access and manipulation of sensitive information. These protocols ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data exchanged, thereby reducing the risk of malicious actors intercepting or altering critical medical information. Implementing these protocols is crucial for maintaining patient privacy and data security.
Role of Device Manufacturers in Developing Secure Devices
Device manufacturers play a critical role in building security into medical devices from the design phase. Secure device development requires incorporating robust security measures, such as access controls, authentication mechanisms, and intrusion detection systems, into the hardware and software. This proactive approach to security minimizes the attack surface and reduces the likelihood of vulnerabilities being exploited. Manufacturers should prioritize security throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Regular Software Updates and Security Patches
Regular software updates and security patches are essential for maintaining the security of medical devices. These updates often address critical vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Hospitals and clinics must adhere to manufacturers’ recommendations for software updates, ensuring devices are running the most recent, secure versions. Failure to apply these updates can leave devices susceptible to attacks.
Security Measures in Hospitals and Clinics, Healthcare alert medical devices are more prone to cyber attacks
Implementing robust security measures within hospitals and clinics is vital for protecting the entire network. These measures should encompass physical security of devices, network segmentation to isolate critical systems, and strict access controls to limit access to sensitive data. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and mitigating potential threats. Examples of such measures include restricting access to devices based on user roles and implementing multi-factor authentication.
Security Awareness Training for Healthcare Professionals
Security awareness training for healthcare professionals is crucial to educate them about the potential threats and the importance of secure practices. Training should cover topics such as identifying phishing attempts, recognizing suspicious emails, and understanding the importance of strong passwords. This proactive approach fosters a culture of security within the healthcare environment, reducing the likelihood of human error contributing to a security breach.
Training programs should be ongoing and adaptable to evolving threats.
Security Measures for Different Types of Medical Devices
| Device Type | Security Measure | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Pacemakers | Secure communication protocols | Use of encrypted communication channels, ensuring secure transmission of data between the pacemaker and the monitoring system. |
| Imaging Equipment | Regular software updates | Automated patch management systems to ensure that the software is updated regularly and securely. |
Regulatory and Policy Frameworks: Healthcare Alert Medical Devices Are More Prone To Cyber Attacks
The digital transformation of healthcare has brought about a surge in connected medical devices, significantly enhancing patient care. However, this connectivity also introduces vulnerabilities, making these devices susceptible to cyberattacks. This necessitates robust regulatory frameworks to ensure the security of these devices and safeguard patient safety. These frameworks must address the unique challenges posed by medical device cybersecurity.Effective cybersecurity regulations are crucial for mitigating risks and maintaining patient trust in the healthcare system.
They provide a common standard for manufacturers, ensuring that devices meet baseline security requirements, thereby reducing the likelihood of harmful cyberattacks. This, in turn, fosters a more secure and reliable healthcare ecosystem.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a critical role in overseeing the security of medical devices. They establish and enforce standards, ensuring that manufacturers prioritize security throughout the entire lifecycle of the device. This includes rigorous testing, validation, and verification procedures to assess and mitigate vulnerabilities. Their oversight is paramount to maintaining patient safety and preventing the misuse of connected medical devices.
Need for Updated Cybersecurity Standards and Regulations
Existing cybersecurity standards and regulations for medical devices often lag behind the rapidly evolving threat landscape. This necessitates the development of updated regulations that incorporate advanced threat models and emerging technologies, like artificial intelligence and machine learning. This dynamic approach is essential for maintaining the effectiveness of cybersecurity measures in the face of increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Healthcare alert medical devices are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks, a serious concern for patient safety. This vulnerability highlights the urgent need for robust security measures. Fortunately, deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed here can help to mitigate these risks by identifying potential coding flaws in the software used to create these devices. Ultimately, this proactive approach will be critical in securing these vital medical tools from future cyber threats.
Examples of Existing Cybersecurity Regulations for Medical Devices
Several countries and regions have established regulations concerning medical device cybersecurity. The FDA in the United States, for example, has guidelines and regulations aimed at ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices, including those with cybersecurity implications. Similarly, the European Union has directives and regulations related to medical devices, which often incorporate cybersecurity requirements.
Comparison of International Regulations and Standards
International regulations and standards for medical device cybersecurity exhibit variations in scope and stringency. Differences exist regarding the types of devices covered, the specific security requirements, and the enforcement mechanisms. Harmonization efforts are ongoing to create a more unified global approach to medical device cybersecurity, fostering greater interoperability and security across borders. These variations necessitate careful consideration when manufacturers operate across different jurisdictions.
Importance of Stakeholder Collaboration
Collaboration among stakeholders is vital in developing and implementing effective cybersecurity policies. This includes healthcare providers, device manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and cybersecurity experts. A collaborative approach ensures that the resulting policies address the multifaceted challenges of medical device cybersecurity in a comprehensive and adaptable manner. This collective effort leads to a more secure healthcare ecosystem, benefiting patients and providers alike.
Future Trends in Medical Device Cybersecurity
The ever-evolving digital landscape presents both opportunities and threats to the healthcare industry. Medical devices, increasingly interconnected and reliant on software, are becoming prime targets for cyberattacks. This necessitates proactive measures to safeguard these critical systems, and future trends will play a significant role in shaping effective strategies.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Medical Device Security
New technologies are emerging to fortify the defenses of medical devices against cyberattacks. These advancements offer promising avenues for bolstering security protocols and mitigating risks. Examples include incorporating robust encryption methods into the device’s firmware, and leveraging hardware security modules (HSMs) to protect sensitive data. This multi-layered approach can provide greater assurance in the face of evolving threats.
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing various sectors, and cybersecurity is no exception. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of potential cyberattacks. This proactive approach to threat detection can prevent attacks before they cause significant damage. For instance, AI-powered systems can detect unusual access attempts, unusual data patterns, or deviations in device performance, alerting administrators to potential breaches in real time.
Blockchain Technology for Secure Data Management
Blockchain technology, known for its decentralized and immutable nature, can significantly enhance the security and transparency of medical device data. By recording and storing data in a distributed ledger, blockchain can provide an auditable trail of data modifications, reducing the risk of tampering or unauthorized access. This approach can ensure data integrity and build trust in the healthcare system.
Mitigating Cyber Risks with Emerging Technologies
These emerging technologies can be effectively integrated into the design and operation of medical devices to mitigate cyber risks. For example, incorporating AI into medical device systems can automatically detect anomalies in device behavior and flag suspicious activity, allowing for swift intervention and prevention of potential harm. This proactive approach is crucial in preventing attacks and maintaining patient safety.
Future Challenges in Medical Device Cybersecurity
While these technologies offer promising solutions, significant challenges remain. One major hurdle is the need for standardization and interoperability across various medical device platforms. Ensuring that different devices can communicate and share information securely while maintaining a consistent level of security is a complex task. Another challenge is the ongoing need for skilled personnel to implement and maintain these complex security systems.
Last Point
In conclusion, the growing reliance on medical devices in healthcare necessitates a robust cybersecurity strategy. Addressing the vulnerabilities in these devices requires a multi-faceted approach involving device manufacturers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies. Ultimately, protecting patients from cyberattacks on medical devices demands proactive measures and ongoing vigilance. The future of secure medical technology depends on a collaborative effort to enhance security protocols and implement innovative solutions.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common types of medical devices vulnerable to cyberattacks?
Pacemakers, insulin pumps, imaging equipment, and medical monitoring devices are particularly vulnerable. Their interconnected nature and reliance on digital communication channels make them susceptible to various attack vectors.
How can healthcare providers protect themselves from these attacks?
Implementing robust security protocols, regularly updating software, and educating staff on security awareness are crucial steps. Strong encryption and secure communication channels are also essential.
What are the legal ramifications of a medical device cyberattack?
Depending on the severity and consequences, legal repercussions can include fines, lawsuits, and potential criminal charges. Healthcare providers and manufacturers could face significant financial and reputational damage.
What role do regulatory bodies play in medical device cybersecurity?
Regulatory bodies set standards and guidelines to ensure medical devices meet minimum security requirements. Their involvement is crucial for establishing and enforcing robust cybersecurity regulations.