Help Desks Under Siege Bolstering Cyber Defenses
Help desks under siege bolstering cyber defenses – Help desks under siege: bolstering cyber defenses is more critical than ever. The modern help desk faces a relentless barrage of sophisticated cyberattacks, ranging from simple phishing attempts to highly targeted intrusions. This isn’t just about IT; it’s about protecting the entire organization from data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. We’ll dive into the escalating threats, explore vulnerabilities, and discover strategies to strengthen your help desk’s defenses, ensuring your team can continue providing essential support without compromising security.
The sheer volume and complexity of support requests are increasing exponentially, while cybercriminals are constantly developing new and more effective attack vectors. This creates a perfect storm, leaving help desks vulnerable and overwhelmed. Understanding the landscape of these threats and implementing proactive security measures is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for survival in today’s digital world.
The Increasing Pressure on Help Desks
The modern help desk is facing unprecedented challenges. The sheer volume of support requests, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks targeting these crucial support channels, is creating a perfect storm of pressure on IT teams. This pressure manifests not only in increased workload but also in heightened security risks, potentially leading to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.The rising volume and complexity of support requests are driven by several factors.
The proliferation of remote work has exponentially increased the number of devices and applications requiring support. Users are increasingly reliant on technology for their daily tasks, leading to a higher frequency of requests for assistance. Furthermore, the complexity of modern IT infrastructures, with their diverse range of hardware, software, and cloud services, makes troubleshooting significantly more challenging.
This complexity often necessitates specialized expertise, putting a strain on already stretched help desk resources.
Evolving Cyber Threats Targeting Help Desks
Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting help desks as a primary attack vector. Help desks, by their nature, possess privileged access to sensitive company data and systems. Compromising a help desk agent can provide attackers with a backdoor into the entire organization’s infrastructure. The attacks are becoming more sophisticated, moving beyond simple phishing attempts to include advanced techniques like social engineering, malware distribution, and the exploitation of vulnerabilities in help desk software.
Common Attack Vectors Against Help Desks
Attackers employ various methods to compromise help desks. Phishing emails, often disguised as legitimate support requests or password resets, remain a common tactic. These emails may contain malicious attachments or links that download malware onto the agent’s computer. Another prevalent attack vector is the use of social engineering techniques, where attackers manipulate help desk agents into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
Finally, vulnerabilities in help desk software itself can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access. For example, outdated or improperly configured software can contain security flaws that attackers can leverage.
Examples of Help Desk Attacks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
| Attack Type | Impact | Mitigation Strategies | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Data breach, malware infection, account compromise | Security awareness training, multi-factor authentication (MFA), email filtering | An email appearing to be from a legitimate software vendor requests a password reset, leading to account takeover. |
| Social Engineering | Unauthorized access, data disclosure, system compromise | Employee training on social engineering tactics, strict access control policies | An attacker impersonates a user needing urgent assistance, tricking the agent into revealing sensitive information or granting access. |
| Malware Infection | Data theft, system disruption, ransomware attacks | Regular software updates, robust antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) | A malicious attachment in an email infects the agent’s computer, enabling the attacker to steal data or deploy ransomware. |
| Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities | Unauthorized access, data breach, system compromise | Regular software updates, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing | An attacker exploits a known vulnerability in the help desk software to gain access to the system and its data. |
Vulnerabilities Exploited in Help Desk Attacks
Help desks, often the first point of contact for users needing technical assistance, are unfortunately prime targets for cyberattacks. Their crucial role in accessing and managing systems, combined with the often less stringent security measures compared to other IT departments, makes them vulnerable to a variety of sophisticated attacks. Understanding these vulnerabilities is critical for strengthening defenses and preventing breaches.The success of many help desk attacks hinges on exploiting weaknesses in both the systems and the human element.
Attackers leverage common vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access, often using a combination of technical exploits and social engineering techniques. The consequences can range from data breaches and financial losses to complete system compromise and reputational damage.
Phishing and Social Engineering in Help Desk Compromises
Phishing and social engineering attacks are incredibly effective against help desks. Attackers often craft convincing emails or messages that appear to be from legitimate sources, such as internal IT staff or trusted vendors. These messages might request sensitive information, such as passwords, account credentials, or access codes, under the guise of troubleshooting or account verification. Successful phishing attacks can provide attackers with the initial foothold needed to compromise the entire system.
For example, an attacker might impersonate a senior manager requesting immediate access to a specific system for an urgent matter, exploiting the help desk’s desire to be helpful and responsive. The pressure of urgency often overrides careful scrutiny of the request.
Impact of Weak Passwords and Access Controls
Weak passwords and inadequate access controls are significant vulnerabilities. Help desk staff often manage numerous accounts with varying levels of privilege. If these accounts use easily guessable passwords or if access controls are poorly configured, attackers can easily gain unauthorized access. A compromised help desk account can provide access to sensitive data, customer information, and critical systems. The use of default credentials, or passwords that are shared amongst multiple users, further exacerbates this risk.
A recent example highlighted the significant damage caused when a help desk employee reused a password across multiple accounts, allowing attackers to gain access to the company’s entire network after initially compromising a less sensitive account.
A Typical Help Desk Phishing Attack: A Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart illustrating a typical help desk phishing attack. The process would begin with the attacker crafting a convincing phishing email, perhaps mimicking an urgent request from a known executive. This email is sent to a help desk employee. If the employee falls for the phishing email, they might be tricked into revealing their credentials or granting the attacker access to a system.
The attacker then uses these credentials to escalate privileges and gain access to more sensitive data or systems. Finally, the attacker may exfiltrate data or install malware, leading to a significant breach. This visual representation clearly shows the ease with which a well-crafted phishing attack can compromise a help desk. Each step, from initial email to data exfiltration, represents a critical point of failure that needs to be addressed through robust security measures.
Strengthening Help Desk Cyber Defenses: Help Desks Under Siege Bolstering Cyber Defenses

Help desks are the frontline of many organizations’ IT security, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. A robust defense strategy is no longer optional; it’s essential for maintaining operational continuity and protecting sensitive data. This requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing technology, processes, and employee training. Neglecting any of these areas significantly weakens overall security.
Strengthening help desk defenses involves a layered approach, combining technical safeguards with robust security policies and employee awareness. This layered approach aims to create multiple obstacles for attackers, making it significantly harder for them to breach defenses and access sensitive information.
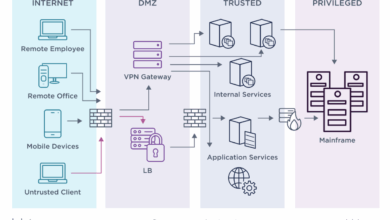
Securing Help Desk Systems and Infrastructure
Best practices for securing help desk systems and infrastructure involve a combination of technical controls and procedural safeguards. This includes implementing strong password policies, regularly patching software and operating systems, and using robust antivirus and anti-malware solutions. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also crucial for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses. Furthermore, segmenting the help desk network from other organizational networks limits the impact of a successful breach.
For example, isolating the help desk’s remote access tools from internal systems prevents attackers from pivoting to other critical resources after compromising the help desk. Finally, employing strong access control mechanisms ensures only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems and data.
Security Technologies for Help Desk Defense
Several security technologies can significantly bolster help desk defenses. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords, making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) monitor network traffic for malicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats in real-time. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of security events across the organization.
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools monitor data movement to prevent sensitive information from leaving the network without authorization. Finally, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities on individual workstations, helping to contain and remediate attacks quickly.
Employee Training and Awareness Programs, Help desks under siege bolstering cyber defenses
Employee training and awareness programs are paramount in preventing help desk attacks. Phishing attacks, for example, often exploit human error. Training should cover identifying and reporting phishing emails, recognizing social engineering tactics, and understanding safe browsing practices. Regular security awareness campaigns, incorporating simulated phishing exercises, help reinforce these concepts and keep employees vigilant. The training should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of help desk staff, focusing on the types of threats they are most likely to encounter.
For instance, help desk personnel handling remote access requests should receive specific training on verifying user identities and recognizing suspicious activity. A successful program should be ongoing, with regular updates and refresher courses to keep employees informed about evolving threats.
Incident Response Plan for Help Desk Security Breaches
A robust incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the damage caused by a help desk security breach. The plan should Artikel clear procedures for identifying, containing, eradicating, recovering from, and learning from security incidents.
- Incident Detection and Reporting: Establish clear procedures for detecting and reporting security incidents, including contact information for security personnel and escalation paths.
- Containment: Artikel steps to isolate affected systems and prevent further damage, such as disconnecting compromised workstations from the network.
- Eradication: Detail the process for removing malware and restoring affected systems to a secure state, including using backups and forensic analysis.
- Recovery: Define procedures for restoring systems and data, including testing and validation before bringing systems back online.
- Post-Incident Activity: Artikel steps for reviewing the incident, identifying vulnerabilities, and implementing corrective actions to prevent future incidents. This includes documenting the incident response process and conducting a post-incident review to identify areas for improvement.
The Role of Automation and AI in Help Desk Security
Help desks are increasingly becoming the target of sophisticated cyberattacks, making robust security measures crucial. Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI) offer powerful tools to enhance help desk security and efficiency, significantly reducing the risk of breaches and improving response times. By automating repetitive tasks and leveraging AI’s analytical capabilities, organizations can build a more resilient and proactive defense against cyber threats.AI-powered solutions can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity.
This proactive approach allows for early detection and prevention of attacks, minimizing damage and disruption. Furthermore, automation streamlines workflows, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues requiring human judgment and expertise.
Automation Improves Help Desk Efficiency and Security
Automation can significantly improve help desk security and efficiency by handling routine tasks such as password resets, account lockouts, and basic troubleshooting. This frees up human agents to focus on more complex issues and security incidents requiring human intervention. Automated systems can also enforce security policies consistently, ensuring that all users adhere to established protocols. For example, automated systems can verify user identities through multi-factor authentication, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
This consistent application of security policies is difficult to maintain manually and is a significant advantage of automation.
AI Detects and Prevents Cyber Threats
AI algorithms can analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify suspicious activities that might indicate a cyberattack. For example, an AI system might detect unusual login attempts from unfamiliar locations or a sudden surge in data exfiltration attempts. These anomalies, often missed by human analysts, trigger alerts, allowing security teams to investigate and respond promptly.
AI can also be used to predict potential threats based on historical data and emerging trends, enabling proactive security measures. Consider a scenario where an AI system detects a rise in phishing emails targeting a specific user group; it could then automatically update security protocols to filter these emails more effectively.
Comparison of AI-Powered Security Solutions
Several AI-powered security solutions are available for help desks, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some solutions focus on threat detection, using machine learning algorithms to identify malicious activity in real-time. Others prioritize threat prevention, using AI to block malicious emails, websites, and files before they reach users. Still others combine both detection and prevention capabilities, providing a comprehensive security solution.
The choice of solution depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization. For instance, a smaller organization might opt for a cloud-based solution offering a balance of features and affordability, while a larger enterprise might prefer a more customized, on-premise solution with advanced capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI in Help Desk Security
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Detection | Improved accuracy and speed of threat detection, identification of subtle anomalies | Potential for false positives, requiring human oversight; reliance on quality of training data |
| Threat Prevention | Proactive blocking of malicious activity, reduced risk of successful attacks | Potential for legitimate activities to be blocked, requiring careful configuration; cost of implementation and maintenance |
| Automation | Increased efficiency, reduced workload for human agents, consistent enforcement of security policies | Initial investment in infrastructure and training; potential for system failures to disrupt operations |
| Scalability | Ability to handle increasing volumes of data and users | Complexity of implementation and management in large organizations; need for skilled personnel |
Future Trends in Help Desk Security

The landscape of help desk security is constantly evolving, driven by increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks and the rapid adoption of new technologies. Predicting the future is inherently uncertain, but by analyzing current trends and emerging threats, we can anticipate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for help desk security professionals. This will involve a continuous adaptation of strategies and technologies to maintain a robust and resilient security posture.The increasing reliance on remote work and cloud computing presents both significant advantages and considerable security challenges for help desks.
These changes demand a proactive and flexible approach to security, encompassing not only technological advancements but also changes in operational practices and employee training.
Emerging Threats and Challenges
The future will likely see a rise in AI-powered attacks that can bypass traditional security measures with greater efficiency and sophistication. We can expect more targeted phishing campaigns designed to exploit specific vulnerabilities within help desk systems and employee knowledge. Furthermore, the increasing interconnectedness of systems will create more attack vectors, making it crucial to implement a holistic security approach rather than focusing on individual components.
The rise of deepfakes and other synthetic media technologies poses a new threat, potentially leading to sophisticated social engineering attacks that are difficult to detect. For example, a deepfake video of a supervisor instructing a help desk agent to perform a dangerous action could easily compromise a system.
With help desks facing relentless cyberattacks, efficient solutions are crucial. Streamlining processes is key, and that’s where faster app development comes in. Learning about domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , can significantly improve response times and bolster our defenses against these escalating threats. Ultimately, quicker development cycles mean faster deployment of security patches and improved help desk efficiency.
Impact of Remote Work and Cloud Computing
The widespread adoption of remote work has expanded the attack surface for help desks, as employees access company systems from diverse and potentially less secure locations. Cloud computing, while offering scalability and flexibility, introduces new security concerns related to data breaches, misconfigurations, and third-party vulnerabilities. The lack of physical security controls in remote work environments necessitates a greater emphasis on robust authentication mechanisms, secure access control, and comprehensive endpoint security solutions.
For example, a company might need to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all employees accessing the help desk system, regardless of location. Similarly, rigorous security policies and procedures need to be in place for accessing and managing cloud-based help desk applications and data.
Predictions for Future Help Desk Security Technologies and Practices
We can anticipate a significant increase in the adoption of AI and machine learning for threat detection and response within help desk environments. This will involve the implementation of sophisticated security information and event management (SIEM) systems capable of analyzing vast amounts of data to identify and mitigate threats in real-time. Zero Trust security models, which assume no implicit trust within the network, will become increasingly prevalent.
This means that every user and device will be authenticated and authorized before accessing resources, regardless of their location or network affiliation. Behavioral analytics will play a crucial role in identifying anomalies and potential insider threats. For instance, an unusual pattern of login attempts from a specific user’s account or an unusual access pattern to sensitive data might trigger an alert.
Hypothetical Future Scenario: A Highly Secure Help Desk
Imagine a future help desk operating within a highly secure environment. Access is granted only through multi-factor authentication, utilizing biometric verification and one-time passwords. The help desk system is fully integrated with a sophisticated SIEM system, leveraging AI to proactively detect and respond to threats. All communications are encrypted using end-to-end encryption, ensuring confidentiality. Employees receive regular security awareness training and participate in simulated phishing exercises to enhance their ability to recognize and report suspicious activity.
The help desk infrastructure is segmented, with critical systems isolated from less sensitive ones. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools monitor all data transfers, preventing sensitive information from leaving the network without authorization. This highly secure environment minimizes the risk of successful attacks, ensuring the continuous operation of the help desk and the protection of sensitive data.
Final Wrap-Up

In a world where cyber threats are evolving at an alarming rate, securing your help desk is paramount. By understanding the vulnerabilities, implementing robust security measures, and embracing the potential of automation and AI, organizations can significantly reduce their risk. Proactive strategies, coupled with employee training and a well-defined incident response plan, are crucial for building a resilient help desk capable of withstanding the relentless pressure of modern cyberattacks.
Remember, a strong help desk isn’t just about efficiency; it’s the first line of defense in protecting your entire organization.
Question & Answer Hub
What are some common signs of a compromised help desk?
Unusual login attempts, unauthorized access to sensitive data, unexplained system slowdowns, and reports of suspicious emails or links from support staff are all potential red flags.
How can we improve employee awareness of help desk security threats?
Regular security awareness training, phishing simulations, and clear communication about security protocols are essential. Make it a part of ongoing employee development.
What is the role of incident response in help desk security?
A well-defined incident response plan Artikels the steps to take in case of a security breach, minimizing damage and ensuring a swift recovery. This plan should be tested regularly.
How expensive is implementing robust help desk security measures?
The cost varies depending on the chosen solutions, but the cost of a data breach far outweighs the investment in prevention. Consider it an insurance policy against significant losses.