
How FTC Revised Safeguards Rule Impacts Auto Dealerships
How FTC revised safeguards rule impacts auto dealerships? That’s the burning question for every car lot owner right now. The Federal Trade Commission’s updated safeguards rule is shaking things up, forcing dealerships to re-evaluate their data security practices and potentially invest heavily in upgrades. This isn’t just about fines – it’s about protecting customer data and maintaining trust in an increasingly digital world.
Let’s dive into what this means for your business.
This post breaks down the key changes in the FTC’s revised rule, focusing on how they specifically affect auto dealerships. We’ll cover everything from the updated requirements for data breach notification and consumer consent to the financial implications and necessary technological adaptations. We’ll also look at practical steps you can take to ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties.
FTC Safeguards Rule Revision Overview: How Ftc Revised Safeguards Rule Impacts Auto Dealerships
The Federal Trade Commission’s (FTC) revised Safeguards Rule, impacting how businesses protect consumer data, has significant implications for auto dealerships. This rule, significantly updated after decades, necessitates a thorough understanding of its changes and the resulting responsibilities for dealerships. Failure to comply can lead to substantial penalties.
Key Changes Introduced by the Revised Safeguards Rule
The revised rule strengthens data security requirements for businesses, including auto dealerships, that collect, receive, or maintain consumer information. Key changes focus on enhancing risk assessments, implementing robust security programs, and improving incident response capabilities. The rule moves away from a more generalized approach to a more risk-based framework, demanding a more proactive and tailored approach to data security depending on the specific vulnerabilities and sensitivities of the data handled.
This shift requires dealerships to thoroughly evaluate their systems and processes, identify potential weaknesses, and implement appropriate safeguards to mitigate identified risks. The rule also places a greater emphasis on the role of senior management in overseeing data security practices.
Timeline of the Revision Process
The FTC initiated the revision process in 2020, responding to the evolving digital landscape and increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Several public comment periods and stakeholder consultations were held throughout 2021 and 2022. The final rule was published in June 2022, with a compliance deadline of December 9, 2023. Key milestones included the release of the proposed rule, the analysis of public comments, and the finalization and publication of the revised rule in the Federal Register.
Objectives and Intended Outcomes of the Revised Rule
The primary objective of the revised Safeguards Rule is to enhance the security of consumer information held by businesses. The intended outcome is a reduction in data breaches and consumer harm resulting from data security failures. By mandating more robust risk assessments, comprehensive security programs, and effective incident response plans, the FTC aims to create a more secure environment for consumer data.
The rule also aims to increase accountability for businesses and to provide consumers with greater confidence in the security of their personal information. For example, a dealership’s failure to implement strong encryption could result in a breach exposing sensitive customer financial data, leading to identity theft and financial losses for customers and significant fines for the dealership.
Comparison of Old and New Safeguards Rules
The following table highlights significant differences between the old and new Safeguards Rules and their impact on auto dealerships:
| Feature | Old Rule | New Rule | Impact on Dealerships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment | General assessment of risks | Comprehensive, risk-based assessment tailored to specific vulnerabilities | Requires dealerships to conduct more thorough risk assessments, identifying specific vulnerabilities and implementing targeted security controls. |
| Security Program | General security measures | Detailed security program addressing all identified risks, including data encryption, access controls, and employee training | Dealerships must develop and implement a detailed security program that goes beyond basic measures, incorporating advanced security technologies and employee training. |
| Incident Response | Limited requirements | Comprehensive incident response plan, including detection, containment, and notification procedures | Dealerships must develop and regularly test a detailed incident response plan to handle data breaches effectively and comply with notification requirements. |
| Management Oversight | Limited accountability | Stronger management oversight and accountability for data security | Dealerships’ senior management must take a more active role in overseeing and ensuring the effectiveness of the data security program. |
Impact on Auto Dealership Data Security Practices
The revised FTC Safeguards Rule significantly raises the bar for data security practices across all industries, and auto dealerships are no exception. This updated rule demands a more proactive and comprehensive approach to protecting sensitive consumer information, impacting everything from employee training to the implementation of advanced security technologies. Failure to adapt could result in substantial financial penalties and reputational damage.The implications for auto dealerships are far-reaching, requiring a fundamental shift in how they handle customer data.
The rule’s emphasis on risk assessment, robust security measures, and comprehensive incident response plans necessitates a reevaluation of existing security protocols and a commitment to ongoing improvement. Dealerships must move beyond simply complying with minimum standards and embrace a culture of data security that permeates all aspects of their operations.
Areas Requiring Improvement in Compliance
The revised rule highlights several areas where auto dealerships often fall short. These include inadequate employee training on data security best practices, insufficient monitoring and detection of security breaches, and a lack of comprehensive incident response plans. Many dealerships may also lack the necessary technical expertise to implement and maintain advanced security technologies, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Furthermore, many lack a robust system for regularly assessing and mitigating risks associated with data security.
Best Practices for Data Security in the Automotive Industry
Implementing robust data security measures requires a multi-faceted approach. Dealerships should prioritize employee training programs that cover topics such as phishing awareness, password management, and the importance of data confidentiality. Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of existing security controls. Furthermore, the implementation of strong access controls, data encryption, and multi-factor authentication can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive customer information.
A comprehensive incident response plan should be in place, detailing the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach, including notification procedures and remediation strategies. Finally, regular review and updates of security policies and procedures are vital to maintain compliance with the evolving threat landscape.
Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with the revised FTC Safeguards Rule can result in significant penalties. The FTC has the authority to impose substantial fines, ranging from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the violation and the number of affected individuals. Beyond financial penalties, non-compliance can lead to reputational damage, loss of customer trust, and legal challenges. For example, a dealership that experiences a data breach due to inadequate security measures could face lawsuits from affected customers, further exacerbating the financial and reputational consequences.
The FTC can also impose corrective actions, such as requiring dealerships to implement specific security measures or undergo independent security assessments. These penalties can significantly impact a dealership’s financial stability and long-term viability.
Customer Data Privacy and the Revised Rule
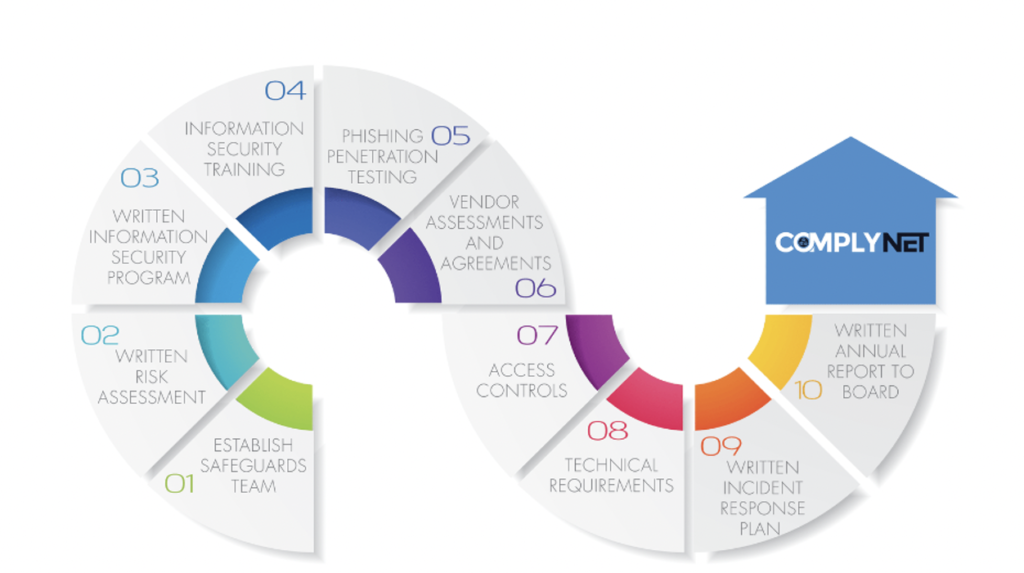
The FTC’s revised Safeguards Rule significantly impacts how auto dealerships handle customer data, placing a greater emphasis on robust security practices and transparent data handling. This heightened focus on privacy aims to protect consumers from data breaches and misuse of their personal information. The rule’s implications are far-reaching, affecting everything from data collection and storage to breach notification and consumer consent.
The revised rule compels auto dealerships to implement comprehensive security programs to protect customer data. This includes conducting risk assessments, implementing safeguards appropriate to the dealership’s size and complexity, and regularly monitoring and testing security measures. Failure to do so could result in significant penalties. The rule also introduces stricter requirements for data breach notification, demanding faster and more comprehensive disclosure to affected individuals and regulatory bodies.
Data Breach Notification Requirements
The revised rule mandates prompt notification of consumers in the event of a data breach. Dealerships are no longer afforded the same leeway in determining whether a breach necessitates notification. The rule specifies a timeframe for notification, emphasizing the need for swift action to mitigate potential harm. The notification must include specific details about the breach, including the types of data compromised and steps consumers can take to protect themselves.
Delays in notification can result in substantial fines and reputational damage. Furthermore, the rule clarifies the types of data considered sensitive and therefore subject to stricter notification protocols. For instance, a breach involving Social Security numbers or driver’s license information would necessitate immediate and comprehensive notification.
Consumer Consent and Data Transparency
The revised rule strengthens consumer rights regarding their personal data. Dealerships must be transparent about their data collection practices, obtaining explicit consent from consumers before collecting, using, or sharing their information. This means moving beyond simply having a privacy policy; dealerships must actively inform consumers about how their data is being used and obtain their affirmative agreement. This shift towards informed consent aligns with a broader trend towards data privacy and consumer empowerment.
The rule also provides consumers with greater control over their data, including the right to access, correct, and delete their information.
Sample Data Breach Notification Letter
The following is a sample data breach notification letter that complies with the revised rule’s requirements. Remember, this is a sample and specific wording should be adjusted based on the details of the actual breach.
Dear [Customer Name],We are writing to inform you of a recent data security incident that may have involved some of your personal information. On [Date], we discovered unauthorized access to our systems. While we have taken steps to secure our systems and prevent further unauthorized access, we have determined that the following information may have been accessed: [List of compromised data, e.g., name, address, driver’s license number, date of birth].We sincerely regret any inconvenience or concern this may cause. We are taking this matter very seriously and have implemented additional security measures to prevent future incidents. We recommend that you [List of recommended actions, e.g., monitor your credit reports, change your passwords].For more information or to report any suspicious activity, please contact us at [Phone number] or [Email address].Sincerely,[Dealership Name]
Financial Implications for Auto Dealerships
The revised FTC Safeguards Rule significantly impacts auto dealerships’ financial landscape, demanding investments in enhanced security measures and potentially leading to substantial costs if non-compliance penalties are incurred. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for dealerships to proactively manage risk and budget accordingly. This section will analyze the potential costs of compliance, explore cost-saving strategies, and compare the financial consequences of compliance versus non-compliance.
The costs associated with complying with the revised FTC Safeguards Rule are multifaceted. Dealerships will face expenses related to implementing new security technologies, conducting comprehensive risk assessments, providing employee training, and potentially hiring specialized cybersecurity personnel. These costs can vary widely depending on the size of the dealership, the existing security infrastructure, and the complexity of its data systems.
Smaller dealerships may find the initial investment particularly challenging, while larger dealerships with more extensive data holdings will likely face higher overall expenses.
Cost Breakdown of Compliance
The financial burden of compliance can be categorized into several key areas. First, there are costs associated with conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities in the dealership’s data security systems. This often requires hiring external cybersecurity consultants or investing in specialized risk assessment software. Secondly, implementing new security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and intrusion detection systems, will incur substantial costs.
The cost of purchasing and installing this technology, along with the ongoing maintenance and updates, represents a significant ongoing expense. Thirdly, training employees on the new security protocols and procedures is vital to ensure effective compliance. This includes the development and delivery of training materials, as well as time spent on employee training sessions. Finally, some dealerships may need to hire dedicated cybersecurity personnel to manage and oversee their security programs.
This can include salaries, benefits, and other associated employment costs. For example, a medium-sized dealership might expect to spend between $10,000 and $50,000 annually on compliance, depending on their existing infrastructure and chosen solutions. Larger dealerships with more complex systems could easily exceed $100,000.
Cost-Saving Measures
Several strategies can help dealerships mitigate the financial impact of compliance. One effective approach is to leverage existing technologies and resources whenever possible. This may involve upgrading existing security systems rather than completely replacing them, optimizing existing infrastructure to improve efficiency, and leveraging cloud-based solutions for enhanced scalability and cost-effectiveness. Another cost-saving measure is to prioritize security investments based on a thorough risk assessment.
By focusing resources on addressing the most critical vulnerabilities first, dealerships can maximize their return on investment and avoid unnecessary expenses. Finally, dealerships can explore partnerships with other businesses or industry associations to share best practices and potentially reduce the overall cost of compliance through collaborative efforts. For instance, a group of dealerships could jointly contract a cybersecurity firm for risk assessments or training, leading to cost savings for each individual participant.
Compliance Costs vs. Non-Compliance Costs
The potential costs of non-compliance significantly outweigh the costs of compliance. The FTC can impose substantial fines for violations of the Safeguards Rule, potentially reaching millions of dollars depending on the severity and extent of the non-compliance. Beyond financial penalties, a data breach resulting from inadequate security measures can lead to reputational damage, loss of customer trust, legal liabilities from affected customers, and significant operational disruptions.
These indirect costs can far exceed the upfront investment required for compliance. For example, a data breach involving sensitive customer information could result in legal fees, public relations expenses, and a significant loss of business, easily exceeding the costs associated with implementing robust security measures. The cost of non-compliance is ultimately a gamble with potentially devastating consequences.
Resources for Dealership Compliance
Dealerships can access various resources to aid their compliance efforts.
Several resources are available to assist dealerships in navigating the complexities of the revised FTC Safeguards Rule and ensuring compliance. These resources offer guidance, support, and tools to effectively manage data security and mitigate risks. Taking advantage of these resources can significantly improve a dealership’s ability to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive customer information.
- The FTC website: Provides comprehensive information on the Safeguards Rule, including FAQs, guidance documents, and enforcement actions.
- Industry associations: Organizations like the National Automobile Dealers Association (NADA) offer resources, training, and best practices specific to the automotive industry.
- Cybersecurity consultants: Experts can conduct risk assessments, recommend appropriate security measures, and assist with implementation.
- Software vendors: Many vendors offer security solutions tailored to the needs of auto dealerships, providing tools for data encryption, access control, and other security functions.
Employee Training and Awareness
The FTC’s revised Safeguards Rule significantly raises the bar for auto dealerships’ data security practices. A robust employee training program is no longer a “nice-to-have” but a critical component of compliance. Failing to adequately train employees leaves your dealership vulnerable to breaches, hefty fines, and reputational damage. This section details the importance of employee training and Artikels strategies for creating an effective program.The revised rule necessitates a shift in mindset.
Employees at all levels, from sales representatives to IT staff, must understand their roles in protecting customer data. This isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about fostering a culture of data security where every employee actively participates in protecting sensitive information. Effective training goes beyond simply presenting the rule; it must instill practical knowledge and reinforce the importance of compliance through ongoing education and reinforcement.
Effective Training Methods for Data Security Best Practices
Effective training employs a multi-faceted approach, combining various methods to cater to different learning styles. Dealerships should incorporate interactive elements, real-world scenarios, and regular refresher courses to ensure knowledge retention and adaptation to evolving threats. A blended learning approach, combining online modules with in-person workshops, is often the most effective. Online modules allow for self-paced learning and easy access to materials, while in-person workshops facilitate interaction, discussion, and practical exercises.
Examples of Training Materials for Auto Dealerships
Dealerships can utilize various training materials to educate employees. These include:
- Interactive online modules: These modules can present information in a concise and engaging manner, using quizzes and scenarios to test employee understanding.
- Videos and webinars: Short, focused videos demonstrating best practices, such as proper password management and phishing email recognition, can be highly effective.
- Role-playing exercises: Simulating real-life scenarios, such as responding to a phishing attempt or handling a data breach, can help employees develop practical skills.
- Checklists and quick reference guides: These provide easily accessible summaries of key data security procedures, reinforcing best practices in daily workflows.
- Case studies of data breaches: Analyzing real-world examples of data breaches can highlight the consequences of non-compliance and demonstrate the importance of proactive security measures. For example, a case study could focus on a dealership that suffered a significant financial loss and reputational damage due to a phishing attack.
Creating a Comprehensive Employee Training Program
A comprehensive program should include:
- Needs assessment: Identify specific data security risks faced by the dealership and tailor training to address these risks.
- Curriculum development: Create a training plan that covers all aspects of the revised Safeguards Rule, including data encryption, access control, employee responsibilities, incident response procedures, and vendor management.
- Delivery method selection: Choose a combination of online and in-person training methods to maximize engagement and knowledge retention.
- Assessment and evaluation: Implement regular quizzes, tests, and simulations to assess employee understanding and identify areas needing further training. Consider using a system for tracking completion and scores.
- Ongoing training and updates: Data security threats are constantly evolving. Dealerships must provide ongoing training and updates to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices. This could involve regular refresher courses, newsletters, or updates to online training modules.
Technological Adaptations Required
The FTC’s revised Safeguards Rule necessitates significant technological upgrades for auto dealerships to ensure robust data security. Failure to adapt could lead to hefty fines and reputational damage. Dealerships must invest in modernizing their systems to meet the heightened standards for protecting sensitive customer and employee information. This involves not only implementing new technologies but also integrating them seamlessly into existing workflows.
The revised rule demands a multi-faceted approach to data security, going beyond simple antivirus software. Dealerships need to assess their current infrastructure, identify vulnerabilities, and implement solutions to address those vulnerabilities. This includes upgrading hardware, software, and network security measures, as well as implementing robust data encryption and access control mechanisms.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Implementing strong data encryption is paramount. This involves encrypting data both at rest (on servers and storage devices) and in transit (when data is being transmitted over networks). Dealerships should utilize encryption protocols like AES-256 for maximum security. Access control measures, such as role-based access control (RBAC), limit access to sensitive data based on an individual’s role and responsibilities, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
For example, a service advisor might have access to customer contact information and service history, but not to financial data. This granular control reduces the potential impact of a security breach.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems
Modern intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) are essential for monitoring network traffic for malicious activity. These systems can identify and block attempts to access systems illegally, preventing data breaches before they occur. A robust IDPS continuously analyzes network traffic, looking for patterns indicative of attacks, such as denial-of-service attempts or unauthorized access attempts. Many IDPS solutions offer real-time alerts and reporting, allowing security personnel to respond quickly to threats.
For instance, a dealership might implement an IDPS that monitors for suspicious login attempts from unusual geographic locations, alerting security staff to potential phishing or brute-force attacks.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
A SIEM system consolidates security logs from various sources across the dealership’s IT infrastructure, providing a centralized view of security events. This allows security personnel to identify trends, detect anomalies, and respond effectively to security incidents. A SIEM system can correlate events from different sources to identify potential attacks or vulnerabilities that might otherwise go unnoticed. For example, a SIEM system might detect a pattern of failed login attempts followed by a successful login from an unusual IP address, indicating a potential compromise.
This centralized view streamlines incident response and allows for more efficient investigation of security events.
Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing, How ftc revised safeguards rule impacts auto dealerships
Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are crucial for proactively identifying and addressing security weaknesses. Vulnerability scanning automatically identifies known vulnerabilities in software and hardware, while penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of security controls. These processes help dealerships identify and fix security gaps before malicious actors can exploit them. For instance, a dealership might conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify outdated software versions with known security flaws, allowing them to update the software promptly and mitigate the risk of exploitation.
Penetration testing can further assess the effectiveness of these updates and identify any remaining vulnerabilities.
Implementation Steps
Implementing new technologies requires a phased approach. First, a thorough risk assessment should identify critical systems and data. Then, a plan should be developed, outlining specific technologies to be implemented, timelines, and responsibilities. Next, the chosen technologies should be procured and installed, followed by thorough testing and training for staff. Finally, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of the security measures.
This iterative process allows for adjustments and improvements based on ongoing assessments and the evolving threat landscape. Regular updates and patches are vital to maintain the effectiveness of security software and systems.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations

The FTC’s revised Safeguards Rule carries significant legal weight for auto dealerships. Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties and reputational damage, impacting not only the dealership’s financial stability but also its standing within the community. Understanding the legal landscape and proactively implementing robust compliance measures is crucial for mitigating risk.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the revised Safeguards Rule exposes dealerships to a range of legal consequences. The FTC has the authority to impose substantial civil penalties, potentially reaching millions of dollars depending on the severity and nature of the violation. Beyond financial penalties, the FTC can also issue cease-and-desist orders, requiring dealerships to immediately halt non-compliant practices and implement corrective actions.
Furthermore, non-compliance can lead to consumer lawsuits, further increasing legal and financial burdens. A history of non-compliance can also negatively affect a dealership’s ability to secure loans or insurance, highlighting the pervasive impact of regulatory breaches. For example, a dealership failing to properly secure customer data leading to a data breach could face significant fines, legal action from affected customers, and damage to its reputation.
The Role of Legal Counsel in Ensuring Compliance
Engaging legal counsel specializing in data security and privacy regulations is paramount. Attorneys can provide guidance on interpreting the complex provisions of the revised rule, tailoring compliance programs to the specific operations of the dealership, and conducting regular audits to ensure ongoing compliance. They can also assist in developing incident response plans to effectively manage data breaches and minimize legal exposure.
A lawyer’s expertise is crucial in navigating the legal complexities, drafting necessary policies, and ensuring the dealership’s actions align with the evolving regulatory landscape. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of legal challenges and protect the dealership’s interests.
Potential Legal Challenges Dealerships Might Face
Dealerships might face legal challenges stemming from data breaches, inadequate security measures, failure to provide proper data breach notifications, or insufficient employee training. Class-action lawsuits from affected customers are a significant concern, particularly in cases involving widespread data compromises. The FTC itself can initiate enforcement actions, leading to investigations, fines, and mandated corrective actions. State attorneys general also have the authority to pursue legal action against dealerships violating state privacy laws, adding another layer of legal complexity.
These legal challenges can be costly and time-consuming, potentially impacting the dealership’s reputation and profitability. For example, a failure to implement multi-factor authentication could be cited as a cause of a data breach, resulting in legal liability.
Key Legal Terms and Definitions
The following list provides key legal terms relevant to the revised FTC Safeguards Rule:
- Safeguards Rule: The Federal Trade Commission’s rule requiring financial institutions to implement reasonable safeguards to protect customer information.
- Data Breach: Unauthorized access to, use of, or disclosure of sensitive customer information.
- Reasonable Security Measures: Security measures appropriate to the size and complexity of the dealership and the sensitivity of the data being protected.
- Risk Assessment: A process of identifying and analyzing potential threats and vulnerabilities to customer information.
- Data Encryption: The process of converting data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Incident Response Plan: A documented plan outlining steps to take in the event of a data breach.
- Consumer Financial Data: Information collected from customers relating to their financial status, including but not limited to personal identifying information, account numbers, and transaction details.
- Privacy Notice: A disclosure to consumers about how their data is collected, used, and protected.
Final Wrap-Up
The FTC’s revised safeguards rule presents significant challenges, but also opportunities, for auto dealerships. By proactively addressing data security vulnerabilities and implementing robust compliance measures, dealerships can not only avoid hefty fines but also strengthen customer trust and enhance their overall reputation. Don’t wait until a breach occurs – start reviewing your practices today and prepare for the changes ahead.
The future of data security in the automotive industry is here, and it’s time to adapt.
Expert Answers
What are the biggest changes in the revised FTC Safeguards Rule?
The revised rule strengthens requirements for data security, breach notification, and consumer consent. It emphasizes a risk-based approach to security and increases accountability for dealerships.
How much will compliance cost my dealership?
Costs vary depending on your current security infrastructure and the size of your operation. However, the costs of non-compliance (fines, lawsuits, reputational damage) far outweigh the costs of proactive compliance.
What kind of employee training is required?
Training should cover data security best practices, the revised rule’s requirements, and procedures for handling data breaches. Regular refresher courses are also recommended.
What happens if my dealership experiences a data breach?
You must promptly notify affected individuals and the FTC, following specific procedures Artikeld in the revised rule. Failure to do so can result in significant penalties.
Where can I find more information and resources?
The FTC website is an excellent starting point. You can also consult with legal counsel specializing in data security and privacy.





