How to Manage Your Device Security Policies with Coro
How to manage your device security policies with Coro? It’s a question more and more businesses are asking, and for good reason. In today’s interconnected world, robust device security is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity. This post dives deep into Coro’s powerful features, guiding you through the process of implementing, managing, and monitoring your security policies, from basic setup to advanced techniques.
We’ll cover everything from setting up user permissions to troubleshooting common issues, ensuring your devices are protected against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
We’ll explore Coro’s layered security approach, comparing its capabilities to other solutions. You’ll learn how to create tailored policies for different device types (smartphones, laptops, tablets), and discover how to leverage Coro’s reporting features to stay ahead of potential threats. Get ready to transform your organization’s device security with Coro!
Understanding Coro’s Device Security Features
Coro offers a robust suite of security features designed to protect your devices and data from various threats. It moves beyond basic device management, integrating multiple layers of security to create a comprehensive defense strategy. This goes beyond simple device tracking and extends to proactive threat mitigation.Coro’s core functionality centers around centralized policy management, allowing administrators to define and enforce security rules across all enrolled devices.
This includes granular control over access permissions, data encryption, and application usage. The platform’s ability to monitor device activity and detect anomalies provides an early warning system against potential security breaches.
Layered Security Approach
Coro employs a multi-layered security approach, combining several key functionalities to provide comprehensive protection. The first layer involves device enrollment and authentication, ensuring only authorized devices can access company resources. The second layer focuses on data protection through encryption both in transit and at rest. The third layer consists of continuous monitoring and threat detection, using machine learning to identify suspicious activities.
Finally, a fourth layer enables automated responses to security threats, such as quarantining infected devices or revoking access. This layered approach provides a robust defense against a wide range of attacks, from simple phishing attempts to sophisticated malware infections.
Comparison with Other Device Management Solutions
While many device management solutions offer basic security features, Coro distinguishes itself through its advanced capabilities and integrated approach. Unlike some solutions that primarily focus on device tracking and remote wiping, Coro proactively protects against threats. For example, many solutions lack Coro’s sophisticated threat detection and response mechanisms, relying solely on reactive measures. Other solutions may offer strong encryption, but lack the granular control over application usage and access permissions that Coro provides.
The key differentiator is Coro’s integrated approach, combining proactive threat detection, robust data protection, and granular access control within a single, unified platform. This integrated approach reduces the complexity of managing multiple security tools and provides a more streamlined and effective security posture.
Implementing Coro’s Security Policies
Implementing robust security policies with Coro is crucial for protecting your devices and data. This involves understanding the available settings, configuring them appropriately for your needs, and regularly reviewing and updating your policies as threats evolve. This section will guide you through the process of setting up basic Coro security policies and provide insights into optimizing these settings for different device types.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Basic Coro Security Policies
Implementing Coro’s security policies is a straightforward process. Begin by accessing the Coro management console, typically through a web interface. The exact steps might vary slightly depending on your Coro version, but the general principles remain consistent.
- Access the Coro Management Console: Log in using your administrator credentials.
- Navigate to Device Security Policies: Locate the section dedicated to managing device security policies. This might be under a menu item such as “Policies,” “Security,” or “Device Management.”
- Create or Edit a Policy: If you are setting up policies for the first time, you’ll need to create a new policy. Otherwise, select an existing policy to modify.
- Configure Policy Settings: This is where you define the specific security parameters. We’ll cover common settings in the table below. Carefully review each setting and select options appropriate for your security needs and the devices being managed.
- Assign the Policy: Once the policy is configured, assign it to the specific devices or groups of devices you wish to protect.
- Deploy and Monitor: Deploy the policy to the assigned devices. Coro will usually handle this automatically. Regularly monitor the policy’s effectiveness and make adjustments as needed.
Coro Policy Settings and Their Implications
The following table Artikels some common Coro policy settings and their implications for device security. Remember to consult your Coro documentation for the most up-to-date and comprehensive information on available settings.
| Setting | Description | Implications | Recommended Settings (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Password Complexity | Defines the minimum requirements for device passwords (length, character types, etc.). | Stronger passwords reduce the risk of unauthorized access. | Minimum 12 characters, including uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and symbols. |
| Screen Lock Timeout | Specifies the time after which the device automatically locks. | Shorter timeouts improve security if the device is lost or stolen. | 1 minute |
| Remote Wipe | Enables the ability to remotely wipe the device’s data if it’s lost or stolen. | Protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. | Enabled |
| VPN Enforcement | Requires the use of a VPN for internet access. | Enhances security by encrypting internet traffic. | Enabled for all corporate networks |
Best Practices for Configuring Coro Security Settings for Various Device Types
Optimizing Coro’s security settings depends heavily on the type of device. Smartphones, laptops, and tablets have different vulnerabilities and usage patterns.Smartphones, due to their portability, require stringent security measures like shorter screen lock timeouts and always-on VPN connections when accessing corporate data. Laptops, often used in various environments, might benefit from stricter password complexity requirements and enhanced data encryption.
Tablets, frequently used for both personal and professional tasks, may necessitate a more granular approach, potentially employing separate profiles for work and personal applications, each with its own distinct security policy. A well-defined policy should consider the specific risks associated with each device type and its typical usage context. Regular security audits and updates to these policies are crucial to maintain a robust security posture.
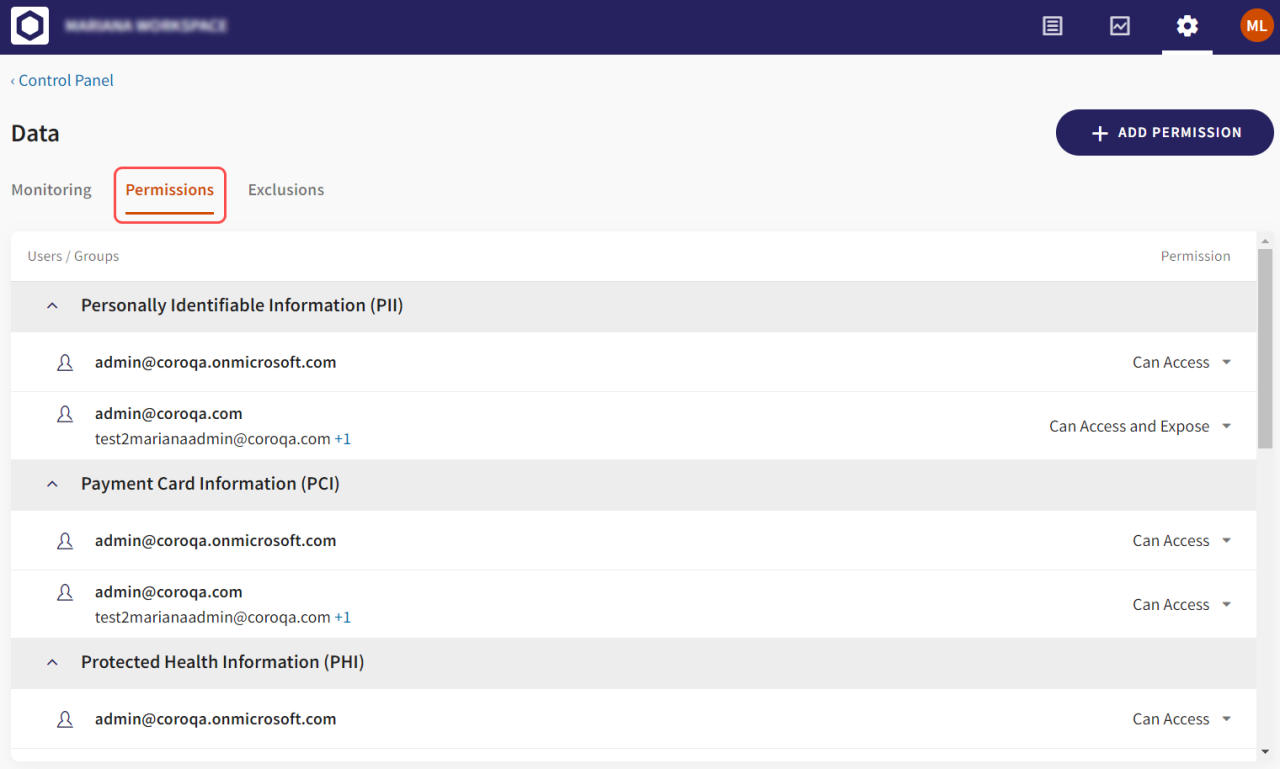
Managing User Access and Permissions with Coro
Coro’s robust user management system is a cornerstone of its comprehensive security strategy. It allows administrators to granularly control who can access specific data and applications, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. This control is achieved through a flexible role-based access control (RBAC) system, enabling the creation of custom user roles with tailored permissions.
Effective user access management in Coro hinges on its ability to define and manage different user roles. This approach ensures that only authorized individuals have the necessary permissions to perform their tasks, preventing accidental or malicious actions that could compromise security. The system provides a straightforward interface for creating, modifying, and deleting user roles, facilitating efficient administration and adaptation to evolving security needs.
Coro’s User Role Management Capabilities
Coro’s user role management system allows administrators to define various roles, each with a specific set of permissions. For example, a “Data Analyst” role might have read-only access to sensitive data, while a “System Administrator” role would have full control, including the ability to modify settings and manage users. This fine-grained control allows organizations to tailor access levels to match the specific responsibilities of each user or group, minimizing security risks.
The system also supports inheritance of permissions, simplifying the management of complex hierarchies. A higher-level role can inherit permissions from a lower-level role, simplifying the process of assigning permissions.
Creating and Managing User Groups
Coro facilitates the creation of user groups to streamline the management of user permissions. Instead of assigning permissions individually to each user, administrators can assign permissions to a group, and then add users to that group. This significantly reduces administrative overhead and ensures consistency in access control. For instance, a “Marketing Team” group might be granted access to marketing campaign data and related applications, while a “Finance Department” group would have access to financial records and reporting tools.
Modifying permissions requires only updating the group’s settings, instantly affecting all users within the group.
The system supports nested groups, allowing for a hierarchical structure that mirrors an organization’s internal structure. This feature further simplifies permission management, particularly in large organizations with complex reporting structures. For example, a “Sales Team” group could be subdivided into regional groups like “North America Sales” and “Europe Sales,” each inheriting permissions from the parent “Sales Team” group but potentially having additional regional-specific permissions.
Restricting Access to Sensitive Data and Applications
Coro provides several mechanisms for restricting access to sensitive data and applications. These mechanisms work in conjunction with user roles and groups to create a multi-layered security approach. For instance, administrators can use data encryption to protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. Access control lists (ACLs) can be implemented to define which users or groups have permission to access specific files or folders.
Furthermore, Coro can integrate with other security tools, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, to further enhance security.
As an example, a company might use Coro to restrict access to its customer database. Only users with the “Customer Support” role, which could be part of a larger “Customer Service Department” group, would have read access. Users in other roles, even those with administrative privileges, would be denied access. This ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive customer information, safeguarding privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
Monitoring and Reporting Device Security with Coro
Coro’s robust reporting capabilities provide a comprehensive overview of your device security posture. By leveraging these features, you can proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Regular monitoring allows for timely intervention, minimizing the impact of security incidents and ensuring the ongoing protection of your valuable data.
Coro’s reporting functionality is accessed through its intuitive dashboard. This dashboard presents a clear, concise summary of key security metrics, enabling quick identification of any anomalies or potential threats. You can customize the reports to focus on specific devices, user groups, or security policies, providing a tailored view of your security landscape. The system also generates alerts for critical events, such as unauthorized access attempts or malware detections, ensuring immediate attention to high-priority issues.
Coro’s Reporting Features
Coro offers a range of reporting features designed to provide granular insights into your device security. These reports offer different levels of detail, allowing you to choose the level of information that best suits your needs. For example, you might opt for a high-level summary for regular monitoring or delve into more detailed reports to investigate specific incidents.
The reports are exportable in various formats, including PDF and CSV, making it easy to share information with other teams or stakeholders.
Sample Security Report
A typical Coro security report might include the following key metrics:
| Metric | Value | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Devices Managed | 150 | Normal |
| Number of High-Severity Security Alerts | 0 | Normal |
| Number of Successful Login Attempts | 2000 | Normal |
| Number of Failed Login Attempts | 5 | Normal |
| Average Device Compliance Score | 98% | Normal |
| Number of Devices with Outdated Software | 2 | Warning |
This sample report shows a generally healthy security posture, with only a minor warning regarding outdated software on two devices. The report clearly indicates the status of each metric, allowing for quick identification of potential issues.
Responding to Security Alerts and Incidents
Coro’s alert system provides immediate notification of critical security events. When an alert is triggered, Coro provides detailed information about the event, including the affected device, the type of threat, and the timestamp of the event. This information is crucial for a swift and effective response. The response strategy should include:
First, investigating the alert to determine the root cause. This may involve reviewing logs, checking device configurations, and performing malware scans. Second, taking appropriate remedial action, such as blocking malicious IP addresses, patching vulnerabilities, or resetting compromised user credentials. Finally, documenting the incident and implementing preventative measures to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future. Regular security awareness training for users can also significantly reduce the likelihood of security breaches.
Enforcing Security Policies and Compliance
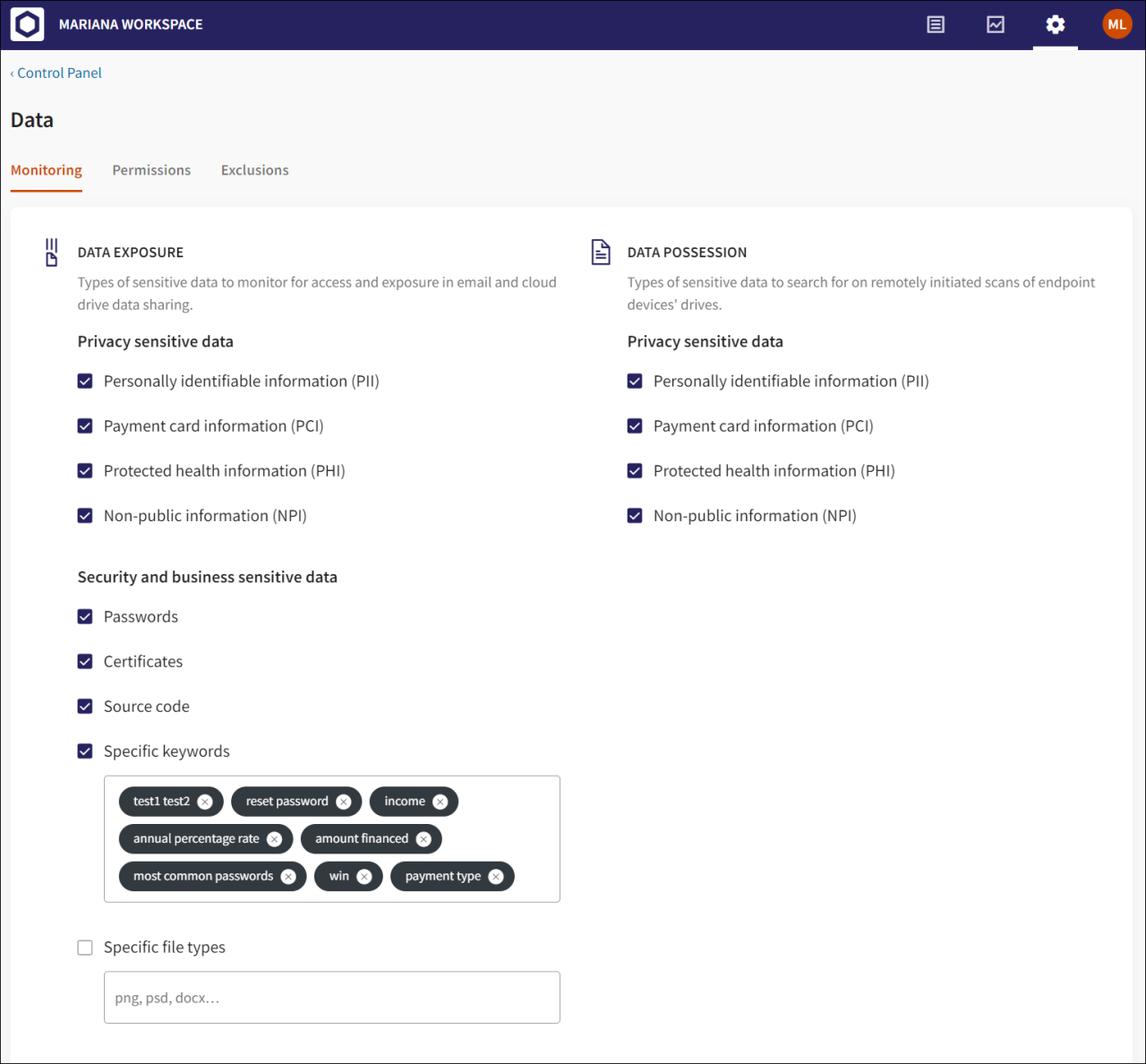
Successfully enforcing device security policies is crucial for maintaining a secure organizational environment. However, numerous challenges can hinder this process, ranging from user resistance to the complexity of managing diverse devices and operating systems. This section explores common obstacles and Artikels effective strategies for ensuring compliance using Coro, along with a plan for ongoing policy review and updates.
Common Challenges in Enforcing Device Security Policies
Consistent enforcement of security policies often faces significant hurdles. Lack of user awareness and training frequently leads to unintentional policy violations. For instance, employees might unknowingly download malware or fail to update their software, compromising security. Additionally, managing diverse devices and operating systems within an organization adds complexity. Different platforms require different security configurations, making it challenging to implement and maintain consistent policies across the board.
Finally, the constant evolution of threats necessitates regular updates to security policies, requiring ongoing effort and resources. Failure to adapt to new threats can leave the organization vulnerable to exploits.
Strategies for Ensuring Compliance with Organizational Security Standards Using Coro
Coro offers several features to enhance compliance. Centralized policy management allows administrators to deploy and update security settings across all managed devices simultaneously, ensuring consistency. Real-time monitoring capabilities provide immediate alerts about potential security breaches or policy violations, enabling prompt remediation. For example, if a device attempts to access unauthorized websites or downloads malware, Coro can immediately flag the incident and trigger automated responses such as blocking access or initiating a virus scan.
Automated enforcement of policies, such as password complexity requirements or application whitelisting, minimizes manual intervention and reduces the risk of human error. Furthermore, Coro’s reporting features provide detailed insights into device security posture, allowing organizations to identify weaknesses and areas needing improvement. This data-driven approach facilitates informed decision-making and proactive security management.
Regular Review and Update Plan for Coro’s Security Policies
A formal process for reviewing and updating Coro’s security policies is essential for maintaining effectiveness. A quarterly review cycle is recommended, allowing for timely adjustments to address emerging threats and evolving organizational needs. This review should involve a cross-functional team including IT security professionals, compliance officers, and representatives from different departments. The review process should encompass analyzing security logs and reports generated by Coro, assessing the effectiveness of existing policies, identifying areas for improvement, and incorporating feedback from users.
Updates should be documented and communicated clearly to all users, ensuring awareness and buy-in. Regular security awareness training should supplement policy updates to reinforce best practices and minimize unintentional policy violations. For instance, annual security awareness training sessions, incorporating simulations and practical examples, can significantly enhance user understanding and compliance. This proactive approach ensures that the organization’s security posture remains robust and aligned with the latest threats and best practices.
Advanced Coro Security Techniques
Coro’s core security features lay a strong foundation, but its true power lies in its advanced capabilities. This section delves into Coro’s sophisticated tools for managing mobile devices, detecting threats, and preventing data loss, ultimately bolstering your overall security posture. We’ll explore how Coro’s advanced features work in tandem to provide a comprehensive security solution.
Coro’s advanced capabilities extend beyond basic policy management. It leverages cutting-edge technologies to provide robust protection against modern threats and data breaches, offering a proactive approach to security.
Coro’s Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Capabilities
Coro’s MDM functionality allows for comprehensive control over mobile devices accessing your network. This includes remote device wiping, application management, and the enforcement of strong password policies. Simultaneously, its integrated EDR capabilities provide real-time threat detection and response, identifying and neutralizing malicious activities on endpoints before they can cause significant damage. For example, Coro can detect and respond to malware infections, phishing attempts, and unauthorized access attempts on both corporate-owned and employee-owned devices.
This combined approach offers a proactive defense strategy, addressing threats at both the device and application levels.
Integrating Coro with Other Security Tools and Systems
Seamless integration with existing security infrastructure is crucial for a cohesive security strategy. Coro supports integration with various Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, allowing for centralized logging and threat analysis. This integration enables the correlation of security events from different sources, providing a holistic view of your security posture. For instance, Coro can forward security alerts to your SIEM system, which can then trigger automated responses or generate detailed reports.
This improves incident response times and allows for more effective threat hunting. Furthermore, Coro’s APIs facilitate custom integrations with other security tools, allowing for tailored security solutions to meet specific organizational needs.
Coro’s Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Capabilities
Data loss prevention is paramount in today’s interconnected world. Coro offers robust DLP capabilities to prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization’s control. This includes features like data encryption, access control, and content filtering. Coro can monitor data transfer activity, identify sensitive data based on predefined rules, and block unauthorized attempts to transfer this data. For example, Coro can prevent employees from emailing sensitive documents to unauthorized recipients or uploading confidential information to cloud storage services that are not approved by the organization.
This helps to maintain compliance with industry regulations and protect against data breaches.
Troubleshooting Common Coro Security Issues

Coro, while robust, can occasionally present security challenges. Understanding common issues and their solutions is crucial for maintaining a secure environment. This section provides a practical troubleshooting guide to help you address connectivity problems, policy enforcement failures, and other typical Coro security hurdles. We’ll explore various scenarios and offer effective solutions to get your Coro security back on track.
Common Coro Security Problems and Solutions
A proactive approach to troubleshooting is key. Knowing the potential pitfalls allows for quicker identification and resolution. The following table lists common Coro security problems and their corresponding solutions. These solutions are based on typical user experiences and Coro’s documented best practices.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Device failing to connect to Coro server. | Check network connectivity (internet access, firewall rules, VPN configurations). Verify Coro server address and port settings in the device configuration. Restart both the device and the Coro server. Consider checking for any network outages or DNS resolution issues. |
| Policy enforcement failures (policies not applied). | Ensure the device is properly enrolled and registered with the Coro server. Verify the policy is correctly configured and assigned to the device. Check for any conflicting policies or settings. Review Coro logs for any errors related to policy deployment. A reboot of the device may be necessary. |
| Unauthorized access attempts detected. | Review Coro’s access logs to identify the source of the unauthorized attempts. Strengthen authentication mechanisms (e.g., multi-factor authentication). Implement stricter access control policies, limiting access based on roles and permissions. Investigate potential vulnerabilities in the system or applications. |
| Slow performance or high resource utilization due to Coro security features. | Optimize Coro’s security settings to reduce the load on the device. Review and adjust resource-intensive security features. Consider upgrading the device’s hardware or software if necessary. Ensure that the Coro server has sufficient resources to handle the workload. |
| False positives from Coro’s threat detection system. | Review the security alerts and investigate the flagged events. Fine-tune Coro’s threat detection settings to reduce false positives. Consult Coro’s documentation for guidance on configuring the threat detection system. Consider whitelisting trusted applications or processes. |
Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
Connectivity problems are a frequent source of Coro security issues. Addressing these issues promptly ensures the smooth operation of your security policies. The following steps should be followed systematically.
- Verify network connectivity: Check internet access on the device. Ensure the device is connected to the correct network and that network connectivity is stable.
- Check firewall rules: Ensure that firewalls (both on the device and network) are not blocking communication between the device and the Coro server. Add necessary exceptions for Coro’s required ports.
- Verify Coro server address and port settings: Confirm that the device is configured with the correct Coro server address and port number. Incorrect settings will prevent connectivity.
- Restart the device and Coro server: A simple restart can often resolve temporary connectivity problems.
- Check for network outages: Investigate any potential network outages or disruptions that might affect connectivity.
- Examine Coro logs: Review Coro’s logs for any error messages related to connectivity issues. These logs provide valuable insights into the problem’s root cause.
Troubleshooting Policy Enforcement Issues
Policy enforcement problems indicate a gap in your security posture. Careful analysis and systematic troubleshooting are vital.
- Verify device enrollment: Ensure that the device is properly enrolled and registered with the Coro server. An incomplete or faulty enrollment process will prevent policy application.
- Check policy configuration: Review the policy settings to ensure they are correctly configured and assigned to the device. Incorrect settings or missing configurations can lead to enforcement failures.
- Look for policy conflicts: Identify and resolve any conflicting policies or settings that might be interfering with policy enforcement.
- Examine Coro logs for errors: Check Coro’s logs for any error messages related to policy deployment or enforcement. These logs often pinpoint the problem’s source.
- Restart the device: A simple reboot can often resolve temporary issues preventing policy enforcement.
- Consult Coro documentation: Refer to Coro’s official documentation for detailed troubleshooting steps and best practices related to policy enforcement.
Diagnosing and Resolving Common Coro Security Errors: A Flowchart
A visual representation can simplify the troubleshooting process. The following flowchart illustrates the steps for diagnosing and resolving common Coro security errors. (Note: This is a textual description, as image creation is outside the scope of this response. Imagine a flowchart with boxes and arrows.)The flowchart would begin with a “Start” box. The next box would ask: “Is there a connectivity issue?” If yes, it branches to the “Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues” section detailed above.
If no, the next box would ask: “Is there a policy enforcement issue?” If yes, it branches to the “Troubleshooting Policy Enforcement Issues” section. If no, the flowchart would proceed to investigate other security errors, such as unauthorized access attempts or false positives from the threat detection system. Each section would have its own decision points and steps, ultimately leading to a “Resolution Found” or “Need Further Assistance” end point.
The flowchart would guide the user through a systematic process of elimination to identify and resolve the specific Coro security error.
Securing Specific Device Types with Coro
Coro’s strength lies in its adaptability to various operating systems. Effectively securing your organization’s devices requires understanding how Coro’s policies translate across iOS, Android, and Windows environments. This section details the configuration specifics for each platform, highlighting key considerations for optimal security.
iOS Device Security with Coro
Implementing Coro’s security features on iOS devices involves leveraging Apple’s built-in security mechanisms alongside Coro’s management capabilities. This often includes integrating with Apple’s MDM (Mobile Device Management) framework to enforce policies like passcode complexity, remote wipe capabilities, and application control. Coro can be configured to push these policies to iOS devices enrolled in your organization’s MDM profile. For example, you can set a minimum passcode length, require biometric authentication (Touch ID or Face ID), and restrict access to specific apps or features.
Regular updates are crucial to maintain security; Coro can help automate this process by scheduling software updates and ensuring that devices are running the latest security patches.
Android Device Security with Coro
Securing Android devices with Coro often relies on the Android Enterprise Recommended (AER) program guidelines and integration with Google’s Android Management API. This enables centralized management of security policies, including enforcing strong passwords or PINs, activating device encryption, and implementing app whitelisting or blacklisting. Coro can also be used to deploy and manage security-related applications, such as mobile threat defense (MTD) solutions, providing an extra layer of protection against malware and phishing attempts.
A critical aspect is ensuring regular security updates are applied, which Coro can automate to keep Android devices patched against known vulnerabilities. Coro’s reporting features can provide visibility into compliance levels, allowing you to identify and address devices that are not adhering to your security policies.
Windows Device Security with Coro, How to manage your device security policies with coro
Securing Windows devices with Coro often involves integrating with Microsoft’s Intune or other MDM solutions. This integration allows for centralized management of security settings, including controlling access to network resources, managing software updates, and enforcing security policies like password complexity, multi-factor authentication, and data encryption. Coro can be configured to automatically deploy and update security software, ensuring devices have the latest antivirus and anti-malware protection.
Moreover, Coro can help enforce compliance with regulatory requirements by tracking security settings and generating reports on the security posture of your Windows devices. This includes implementing features like BitLocker drive encryption to protect sensitive data stored on the devices. Regular security audits and vulnerability scans, facilitated through Coro, are essential to maintaining a secure environment.
Illustrating Coro’s Security Dashboard
Coro’s security dashboard provides a centralized, at-a-glance view of the security posture of your managed devices. It’s designed to be intuitive and easily interpretable, even for users without extensive security expertise. The dashboard employs a combination of visual cues and data representations to quickly communicate the overall security status and highlight any potential issues requiring immediate attention.The dashboard’s primary purpose is to provide a rapid assessment of your device security.
This allows for proactive identification and mitigation of threats, minimizing potential damage and downtime. The color-coding, icons, and graphical representations are carefully chosen to convey critical information concisely and effectively.
Dashboard Overview
The Coro security dashboard typically occupies a single screen, presenting a summarized view of key security metrics. At the top, a concise summary might display the overall security status – perhaps using a color-coded indicator (green for good, yellow for warning, red for critical). This is often accompanied by a numerical score representing the overall security health. Below this summary, several key sections present detailed information.
These sections might be presented as individual panels or cards, each focusing on a specific aspect of security.
Visual Elements and Their Meanings
The dashboard uses a consistent visual language to represent security information. For example, green might indicate that a device or system is compliant with security policies, while red signifies a critical violation or vulnerability. Yellow often represents a warning or a minor issue that requires attention but doesn’t pose an immediate threat. Icons, such as a shield for protection, a lock for access control, or a warning sign for vulnerabilities, are used to quickly identify the nature of the security information being presented.
Graphs, such as bar charts or pie charts, might illustrate the distribution of devices across different security risk levels or the proportion of devices meeting specific compliance requirements. For instance, a bar chart could show the number of devices with outdated software, categorized by severity level (high, medium, low). A pie chart might illustrate the percentage of devices that have passed, failed, or are pending security assessments.
Key Dashboard Sections
A typical Coro dashboard might include sections such as:
- Overall Security Status: A summary showing the overall security health, perhaps with a color-coded indicator (green, yellow, red) and a numerical score.
- Device Status: A list or table showing the security status of individual devices, perhaps with color-coded icons to indicate their compliance level.
- Vulnerability Summary: A summary of identified vulnerabilities, possibly categorized by severity level (critical, high, medium, low).
- Policy Compliance: A summary showing the percentage of devices compliant with defined security policies.
- Recent Events: A log of recent security-related events, such as login attempts, policy changes, or detected threats.
- Alerts and Notifications: A section displaying active alerts and notifications requiring immediate attention.
These sections, combined with the visual cues, allow administrators to quickly assess the overall security status of their devices and identify areas requiring immediate attention. For example, a high number of red indicators in the Device Status section would immediately alert the administrator to a significant security problem requiring immediate investigation. Similarly, a large number of critical vulnerabilities in the Vulnerability Summary section would trigger an immediate response to patch the affected devices.
Final Wrap-Up
Securing your devices shouldn’t feel like navigating a minefield. With Coro, it can be a straightforward and effective process. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can implement robust security policies, monitor your devices effectively, and respond swiftly to any potential threats. Remember, consistent review and updates of your security policies are key to maintaining a strong defense.
So take control of your device security today – your data will thank you for it!
Clarifying Questions: How To Manage Your Device Security Policies With Coro
What if I forget my Coro admin password?
Coro usually has a password reset function. Check your Coro documentation or contact their support team for assistance.
Can Coro integrate with my existing security software?
The level of integration depends on the specific software. Coro’s documentation should list compatible systems. If yours isn’t listed, contact Coro support to inquire about compatibility.
How often should I review and update my Coro security policies?
Regular reviews are crucial. Aim for at least quarterly reviews, and more frequently if there are significant changes in your environment or new security threats emerge.
What types of reports does Coro generate?
Coro typically provides reports on device compliance, security events, user activity, and other relevant metrics. The exact reports available may vary depending on your Coro configuration.