How to Spot Phishing Sites in 4 Simple Steps
How to spot phishing sites in 4 simple steps sets the stage for this essential guide, equipping you with the knowledge to protect yourself from online scams. Phishing attacks are constantly evolving, but understanding the tactics used by cybercriminals is the first step towards safeguarding your sensitive information. Learn to identify suspicious emails, scrutinize website URLs, and check for security indicators to stay one step ahead.
This guide will walk you through four crucial steps to recognize and avoid phishing attempts. From email headers to website security protocols, we’ll explore the key elements that distinguish legitimate sites from deceptive ones. By understanding these simple steps, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to phishing scams.
Introduction to Phishing: How To Spot Phishing Sites In 4 Simple Steps
Phishing is a deceptive online practice where attackers impersonate legitimate entities, like banks or social media platforms, to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or personal data. This fraudulent activity often involves crafting convincing emails, messages, or websites that mimic genuine platforms, making them difficult to distinguish from the real thing. Understanding the various tactics and motivations behind phishing is crucial for protecting yourself from falling victim to these sophisticated scams.Phishing attacks are typically driven by financial gain, identity theft, or malicious intent.
Attackers often target individuals’ accounts and personal information to access sensitive data, enabling them to make unauthorized transactions, steal identities, or even spread malware. The common goals behind phishing attempts are almost always to exploit vulnerabilities and manipulate users into releasing valuable information.
Knowing how to spot phishing sites is crucial, especially with the rise of sophisticated online scams. Learning four simple steps to identify fraudulent websites can protect you from potential harm. This is especially important now, as AI’s increasing role in software development necessitates vigilance in checking code for vulnerabilities. That’s why deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed, like those discussed in this helpful guide Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed , is a must for developers to keep their code safe from exploits.
So, armed with this knowledge, remember those four simple steps to protect yourself from phishing sites.
Common Goals of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks aim to exploit vulnerabilities and manipulate users into releasing valuable information. This information can be used for various malicious purposes, including financial gain, identity theft, or the distribution of malware.
- Financial Gain: Attackers frequently target bank accounts, credit cards, and online payment systems to steal money. They may attempt to gain access to online banking accounts, leading to unauthorized transactions and financial losses for the victim.
- Identity Theft: Phishing can lead to the theft of personal information, including names, addresses, social security numbers, and dates of birth. This stolen data can be used to open fraudulent accounts, apply for loans, or file tax returns in the victim’s name.
- Malware Distribution: Some phishing attempts are designed to install malicious software, such as viruses, spyware, or ransomware, on the victim’s computer. This can compromise the system, allowing attackers to steal data, control the device, or use it for further criminal activities.
Types of Phishing Scams
Phishing scams come in various forms, each designed to exploit specific vulnerabilities or situations. Understanding the different types helps in recognizing and avoiding them.
- Deceptive Phishing: This is the most common type, involving the creation of fake websites or emails that mimic legitimate services. The goal is to trick the recipient into entering their credentials on the fraudulent site, thus gaining access to their account.
- Spear Phishing: Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations, often using personalized information gathered from social media or other online sources. This makes the scam appear more authentic and increases the chances of success. This often involves knowing details about the target, making it a more sophisticated attack.
- Whaling: A more advanced form of spear phishing, whaling targets high-profile individuals, such as CEOs or other executives. The goal is to obtain sensitive information or gain control of valuable accounts.
- Clone Phishing: This technique involves creating a near-perfect copy of a legitimate email or message. The attackers often use a similar subject line and format to the original, but with malicious intent. This often involves subtle changes that are hard to detect for the untrained eye.
Importance of Recognizing Phishing Attempts
Recognizing phishing attempts is paramount for protecting yourself from financial losses, identity theft, and other detrimental consequences. The ability to distinguish legitimate communications from fraudulent ones is essential in today’s digital landscape.By understanding the common characteristics of phishing scams, you can significantly reduce the risk of becoming a victim. Vigilance and a healthy dose of skepticism are key components of online safety.
Recognizing Suspicious Email Headers
Phishing emails often rely on deceiving recipients with convincing subject lines and seemingly legitimate sender information. Critically examining the email header is crucial in identifying these attempts. Paying attention to details like the sender’s email address, subject line, and the overall tone of the message can help you discern between genuine and fraudulent communications.
Suspicious Email Header Characteristics
Phishing emails frequently exhibit inconsistencies that betray their fraudulent nature. These inconsistencies can manifest in various forms, making it essential to scrutinize each element carefully. The sender’s email address, the subject line, and the overall tone of the email should be assessed for any discrepancies or red flags.
Spotting Poor Grammar and Spelling Errors
Phishing emails often suffer from noticeable errors in grammar and spelling. These errors serve as a significant indicator of their fraudulent nature. Legitimate businesses, particularly those with established online presence, typically maintain high standards of communication. A high frequency of errors can raise serious doubts about the email’s authenticity. For instance, if an email from a bank or online retailer contains numerous typos, it strongly suggests a phishing attempt.
Comparing Legitimate and Phishing Email Headers
Understanding the differences between legitimate and phishing email headers is crucial in recognizing fraudulent attempts. A meticulous examination of these details will help you identify potentially malicious communications. The following table illustrates key differences:
| Feature | Legitimate | Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| Sender Email Address | The sender’s email address will typically match the company’s official website address or be from a recognized business email domain (e.g., @companyname.com). | The sender’s email address may use a similar-looking domain to the legitimate one, but with subtle variations (e.g., @compamyname.com), or be from a non-recognized or unusual domain. |
| Subject Line | Subject lines of legitimate emails are typically clear, concise, and relevant to the message’s content. They often use formal and professional language. | Phishing emails often use urgent or alarming subject lines to create a sense of urgency or fear (e.g., “Urgent Action Required,” “Your Account Has Been Compromised”). They may use informal or even aggressive language. |
| Tone | The tone of a legitimate email is professional, polite, and avoids aggressive or demanding language. | Phishing emails often employ a threatening or demanding tone, attempting to pressure the recipient into taking immediate action (e.g., clicking a link or providing personal information). |
Scrutinizing Website URLs
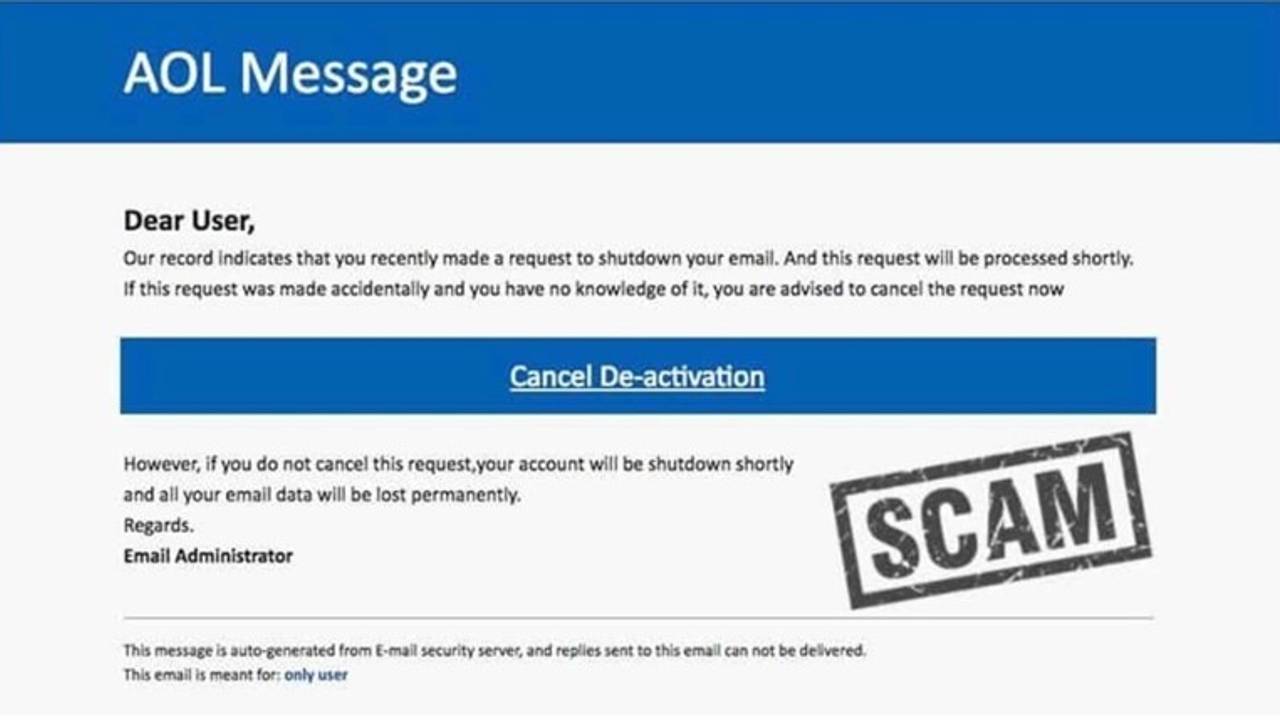
Spotting a phishing site often hinges on a keen eye for detail, especially when it comes to the website’s address. A seemingly legitimate URL can mask malicious intent, and a critical examination of the address is crucial to avoiding phishing traps. A seemingly minor difference can be the key to identifying a fraudulent site.The website URL is the digital storefront, and like a storefront, its appearance and address can reveal much about its true nature.
Carefully scrutinizing the URL is an essential step in protecting yourself from phishing scams. By understanding the common characteristics of phishing URLs and how to spot subtle variations from legitimate sites, you can greatly reduce your risk of falling victim to these deceptive practices.
Importance of Examining Website URLs
Careful scrutiny of a website’s URL is paramount to identifying potential phishing attempts. Phishing sites often mimic legitimate websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information. This deceptive practice leverages the user’s trust in the familiar domain name, leading them to believe they are interacting with a legitimate entity. The URL itself can be a crucial piece of the puzzle in recognizing these fraudulent sites.
Knowing how to spot phishing sites is crucial these days. A quick way to avoid scams is by checking for suspicious emails and links. For example, if a transaction seems too good to be true, it likely is. Luckily, the Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions ( Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions ) can help in certain situations, but it doesn’t replace the need to be cautious.
Always verify the sender’s authenticity and look for typos in emails to further protect yourself from potential fraud. Following these steps can help keep your transactions safe.
Recognizing Suspicious Website URLs
Phishing websites often employ deceptive tactics to mask their true identity. These tactics frequently involve minor alterations to legitimate website URLs, creating a sense of familiarity and trust.
Common Phishing URL Characteristics
Phishing URLs often exhibit several key characteristics that distinguish them from legitimate counterparts. These include subtle variations in spelling, the use of subdomains, and unexpected domain names.
Identifying Subtle Variations in Legitimate and Phishing URLs
Legitimate and phishing websites may share significant similarities in their URLs. A critical eye and an understanding of these common characteristics are key to detecting subtle differences. These subtle variations can be crucial in discerning whether a site is genuine or fraudulent.
Table Comparing Legitimate and Phishing Website URLs
| Feature | Legitimate | Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| URL Structure | Follows a standard format, e.g., www.example.com/login | May use unusual characters or structure, e.g., www.exampl3.com/log1n |
| Domain Name | Uses a recognized and trusted domain name, e.g., www.paypal.com | May use a similar but slightly altered domain name, e.g., www.paypa1.com, or a completely unrelated domain. |
| Subdomain | Uses a recognized subdomain if applicable, e.g., secure.example.com | May use an unfamiliar or irrelevant subdomain, e.g., login.suspicioussite.net |
Checking for Security Indicators

Spotting a phishing attempt often comes down to recognizing the subtle signs of a fraudulent website. Beyond examining the email headers and scrutinizing URLs, a crucial step involves checking for security indicators. These visual cues can often be the difference between a legitimate site and a deceptive one. Understanding these indicators is essential for protecting yourself from falling prey to online scams.
HTTPS Certificates and Validity
Secure websites use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), a protocol that encrypts the communication between your browser and the website. This encryption protects your sensitive data, such as passwords and credit card information, from being intercepted by malicious actors. A critical part of HTTPS is the digital certificate, which verifies the website’s identity.Checking the certificate’s validity involves verifying the issuing authority and the certificate’s expiration date.
Reputable certificate authorities (CAs) are trusted entities that issue digital certificates. The validity period of a certificate is limited, so it’s crucial to ensure the certificate hasn’t expired. Modern browsers will often display warnings if a certificate is invalid or expired.
Importance of Locked Padlock Icons
A locked padlock icon in your browser’s address bar, typically near the beginning of the URL, is a strong visual indicator of a secure connection. This icon signifies that the website is using HTTPS and that your data is encrypted during transmission. If the padlock is absent or appears broken, it’s a significant red flag, suggesting a potential security risk.
It’s important to pay close attention to this visual cue, as it is a direct visual representation of the website’s security posture.
Importance of Secure Connections (HTTPS)
HTTPS is paramount for online security. It safeguards sensitive information from prying eyes. When a website uses HTTPS, all data exchanged between your browser and the server is encrypted, protecting your personal information from unauthorized access. Without HTTPS, data is transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and manipulation. Therefore, looking for the HTTPS protocol is an essential step in verifying the security of a website.
Ever wondered how to sniff out those sneaky phishing sites? It’s easier than you think! Just remember these four simple steps: check the URL for suspicious characters, look for poor grammar or formatting, be wary of urgent requests, and double-check the site’s security. Knowing how to identify these red flags is crucial, especially when dealing with sensitive information like those potentially exposed by a recent Azure Cosmos DB vulnerability.
For more detailed information on the specifics of the Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability, check out the comprehensive breakdown on this page: Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details. Following these simple steps will help you stay safe online, whether you’re just browsing or dealing with a recent security breach.
Summary of Security Indicators
| Indicator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| HTTPS | Indicates that the website uses a secure connection, encrypting data exchanged between your browser and the server. | https://www.examplebank.com |
| Padlock Icon | A visual cue in the browser’s address bar that typically appears next to the URL, indicating a secure connection. | |
| Domain Validation | Verification of the website’s identity by a trusted authority. | A green bar with the website name displayed below the address bar, or similar visual indicators provided by browsers. |
Taking Action After Identifying a Phishing Attempt
Phishing attempts, while often subtle, can have significant consequences if not addressed promptly. Knowing how to react when you suspect a phishing attempt is crucial for safeguarding your personal information and accounts. This section details the steps to take to mitigate potential harm and report suspicious activity effectively.Identifying a phishing attempt is just the first step. The next crucial phase involves taking appropriate action to prevent further damage and report the incident to the relevant authorities.
This section will Artikel the necessary steps to report suspected phishing attempts, protect your accounts, and understand what to do if you believe you’ve been a victim.
Appropriate Responses to Phishing Attempts
Recognizing a phishing attempt is the first step; reacting swiftly and decisively is equally important. Ignoring or interacting with a phishing attempt can lead to serious consequences. A swift and correct response can prevent significant damage to your accounts. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from suspicious emails or websites.
Reporting Suspicious Emails and Websites, How to spot phishing sites in 4 simple steps
Reporting suspicious emails and websites is essential to prevent others from falling victim to the same scam. Many email providers and web browsers offer mechanisms for reporting suspicious activity. This aids in preventing future scams and allows authorities to investigate the perpetrators.
- Email Providers: Most email clients have a “report spam” or “report phishing” option within the email client itself. Clicking on this option often allows you to flag the email and explain why it is suspicious.
- Web Browsers: Many web browsers have tools to report phishing websites. Look for options like “report this website” or “mark as unsafe” within the browser’s settings.
- Specialized Reporting Platforms: Some organizations, like your bank or credit card provider, have dedicated reporting portals for suspicious activity. These platforms often allow you to submit specific details about the incident.
Protecting Your Accounts from Potential Damage
Taking proactive steps to secure your accounts can minimize the risk of compromise. Changing passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and monitoring account activity are vital steps. Regular review of account statements for unusual transactions is also recommended.
- Change Passwords Immediately: If you suspect a phishing attempt has compromised your password, change the password for the affected account(s) immediately to prevent further access.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, like a code sent to your phone, beyond your password.
- Monitor Account Activity: Regularly review your account statements for any unauthorized transactions. This allows you to identify and address any suspicious activity promptly.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Reporting a Suspected Phishing Attempt
A systematic approach to reporting suspicious activity can greatly enhance the efficiency of the process. Following a clear process helps in gathering relevant information for a thorough investigation.
- Identify the Suspicious Element: Carefully examine the email, website, or other communication to pinpoint the suspicious aspect, noting any inconsistencies or alarming elements.
- Document the Details: Note the sender’s email address or website URL, the subject line, and any specific instructions or requests. Take screenshots of the message or website.
- Contact the Relevant Parties: Report the phishing attempt to the appropriate parties, such as your email provider, bank, or relevant authorities. Provide the details you collected.
- Follow Up: If necessary, follow up with the reporting parties to ensure your report has been received and investigated.
What to Do If You Think You’ve Been a Victim of Phishing
Taking swift action after realizing you’ve been a victim of a phishing attempt is essential. This includes immediately changing passwords, monitoring accounts for suspicious activity, and contacting your financial institutions to prevent further harm.
- Change Passwords: Change the passwords for all accounts you believe may have been compromised.
- Monitor Accounts: Monitor all affected accounts for any unauthorized activity and report any suspicious transactions immediately.
- Contact Financial Institutions: Immediately contact your bank, credit card company, or other financial institutions to report the incident and prevent unauthorized withdrawals or charges.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, protecting yourself from phishing attacks is a crucial aspect of online safety. By mastering the art of identifying suspicious emails, scrutinizing website URLs, and checking for security indicators, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling prey to these elaborate scams. Remember, vigilance and a proactive approach are your best defenses against phishing attempts. Now go forth and surf the web safely!
Top FAQs
What are some common characteristics of a phishing email header?
Phishing emails often have poor grammar or spelling errors, unusual sender email addresses, and urgent or threatening subject lines. They might also try to create a sense of urgency or pressure to act quickly.
How can I tell if a website is legitimate?
Look for a secure connection (HTTPS), a properly formatted URL, and the presence of a locked padlock icon in your browser’s address bar. Be cautious of sites with unusual or suspicious domain names or subdomains.
What if I think I’ve clicked on a phishing link?
Immediately change your passwords, monitor your accounts for suspicious activity, and report the phishing attempt to the appropriate authorities and the website itself. Contact your bank or financial institution if necessary.
What are some examples of suspicious website URL characteristics?
Look for misspellings of legitimate websites, unusual domain names, and URLs that don’t seem to match the site’s content. Shortened URLs can also hide the true destination.