Inside the Unified Cloud Security Enterprise Buyers Guide
Inside the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide, we embark on a journey to navigate the complexities of securing your cloud infrastructure. This guide dives deep into the nuances of unified cloud security, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the specific needs of enterprise buyers. We’ll dissect the crucial factors influencing purchasing decisions and illuminate the key players involved in the process.
This in-depth guide provides a comprehensive overview of unified cloud security, comparing it to traditional security models and highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each. We will examine the unique considerations of large organizations adopting cloud services, covering their specific security concerns and the steps involved in implementing a robust unified cloud security solution. We will also break down the buying process into manageable stages, illustrating the key activities, stakeholders, and decision criteria involved.
Defining Unified Cloud Security
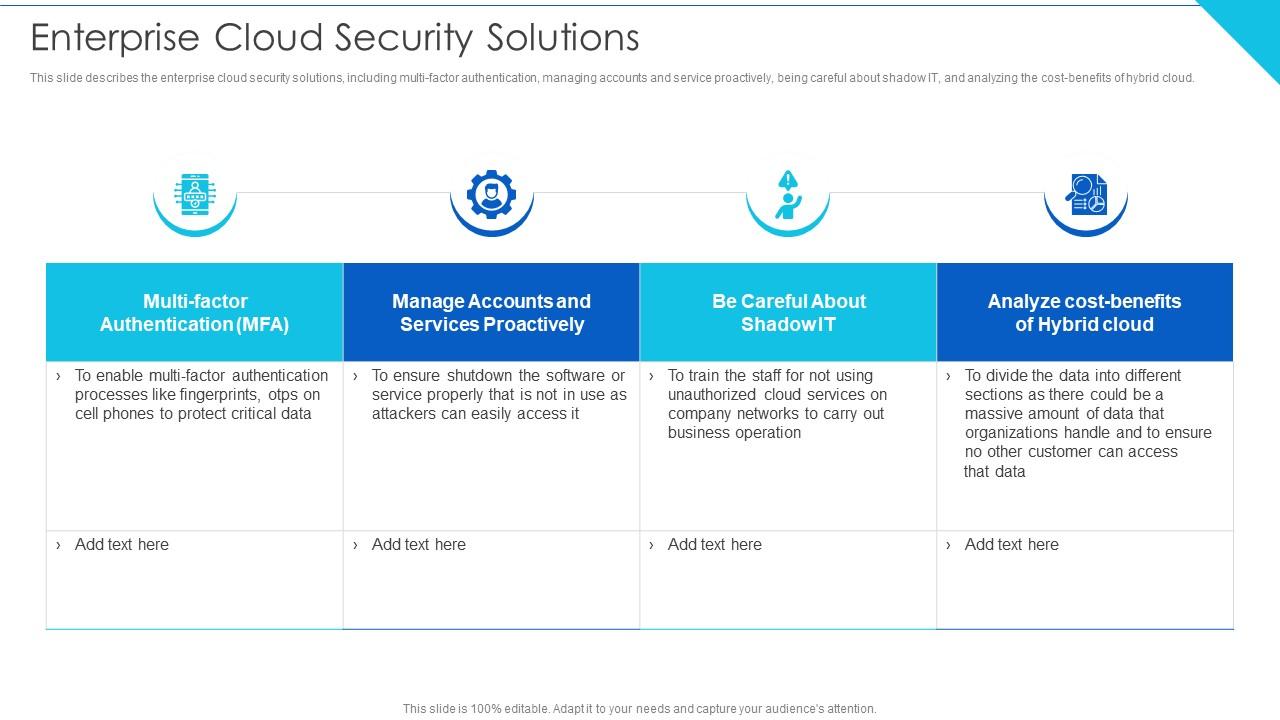
Unified cloud security is a crucial element in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape. It represents a paradigm shift from the traditional, siloed approach to cloud security, offering a more integrated and comprehensive strategy for protecting sensitive data and applications deployed in the cloud. This approach aims to streamline security operations, reduce vulnerabilities, and improve overall security posture.Unified cloud security integrates various security tools and technologies into a cohesive platform.
This allows for centralized management, automated responses, and a holistic view of the entire security environment. This approach is becoming increasingly important as organizations rely more heavily on cloud services for their operations.
Core Principles of Unified Cloud Security
Unified cloud security is built on several core principles. These principles guide the design, implementation, and management of a unified security strategy. Centralized management is key, enabling administrators to manage security policies and configurations across all cloud environments from a single console. Automation is another critical component, enabling the automated detection and response to security threats. Integration is vital, ensuring that different security tools and technologies work seamlessly together.
Finally, a unified approach emphasizes a proactive security posture, focusing on preventing threats rather than simply reacting to them.
Key Components of Unified Cloud Security
Unified cloud security solutions typically incorporate several key components. These components work together to provide a robust security framework. Identity and access management (IAM) systems are essential for controlling user access to cloud resources. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools help prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. Security information and event management (SIEM) systems provide a centralized platform for monitoring and analyzing security events.
Vulnerability management tools help identify and remediate security vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure. Finally, threat intelligence feeds provide real-time information about emerging threats.
Benefits of Unified Cloud Security
Adopting a unified cloud security approach offers numerous benefits. Reduced operational costs are a significant advantage, stemming from the streamlined management of security tools and the automation of tasks. Improved security posture is another key benefit, achieved by reducing vulnerabilities and improving the overall security of cloud environments. Enhanced visibility and control over cloud resources is achieved through centralized management.
Faster response times to security incidents are also possible, thanks to the automation and integration capabilities of unified solutions.
Comparison with Traditional Siloed Security Models
Traditional, siloed security models often rely on separate security tools for different cloud environments. This approach can lead to fragmented security policies, difficulty in coordinating responses to security threats, and a lack of centralized visibility. Unified cloud security addresses these shortcomings by providing a more integrated and comprehensive approach to cloud security. The result is a more effective and efficient security posture.
Diving into the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide, it’s crucial to understand potential vulnerabilities within specific cloud services. One critical area is Azure Cosmos DB, where security concerns like those detailed in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details demand careful consideration. Ultimately, this knowledge is vital for informed decisions when structuring a robust cloud security strategy within the guide.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Unified Cloud Security
Implementing unified cloud security solutions can present certain challenges. Integration complexities can arise when combining various security tools and technologies. The cost of implementing and maintaining a unified solution can be significant. Vendor lock-in is a potential drawback, as migrating away from a unified platform can be challenging. Finally, the complexity of managing a unified solution may require specialized expertise.
Digging into the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide is revealing some interesting insights. One key consideration, as you’ll find throughout the guide, is navigating the complexities of data security in today’s interconnected world. For example, the recent Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions policy highlights the importance of compliance. Ultimately, understanding these evolving legal landscapes is crucial for any enterprise considering a cloud security solution, as detailed in the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide.
Unified Cloud Security Solutions
| Solution Name | Key Features | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) | Identifies and assesses misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance issues in cloud environments. | Provides a comprehensive view of security posture, enabling proactive remediation. | Can be complex to implement and requires expertise. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Collects, analyzes, and correlates security events across different cloud environments. | Provides centralized security monitoring and threat detection. | Requires significant data storage and processing capacity. |
| Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) | Controls and monitors access to cloud applications and data. | Enforces security policies across cloud applications. | May require additional configuration and integration with existing systems. |
| Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) | Provides granular access control to cloud resources, based on user identity and context. | Reduces the attack surface by restricting access to only authorized users. | Requires significant infrastructure changes and expertise to implement. |
Understanding Enterprise Buyers

Enterprise buyers in the cloud security landscape are a complex mix of factors. They’re not just looking for a product; they’re seeking solutions that address intricate security challenges and seamlessly integrate into their existing infrastructure. Their purchasing decisions are deeply rooted in a desire for robust protection, seamless integration, and demonstrable ROI. Understanding these drivers is crucial for any vendor hoping to successfully navigate the enterprise market.Enterprise cloud security buyers are driven by a multitude of factors, and their needs extend beyond simply choosing a product.
Digging into the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide, it’s clear that robust security measures are crucial. A key aspect of this, often overlooked, is the need to deploy AI code safety tools like those discussed in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed. This proactive approach to code security is increasingly vital for organizations looking to bolster their cloud defenses within the guide’s framework.
They need solutions that address the intricate security challenges inherent in migrating to and operating within the cloud environment. They require solutions that are not only secure but also integrate seamlessly with their existing IT infrastructure, minimizing disruption and maximizing efficiency.
Specific Needs and Priorities
Enterprise buyers prioritize security posture, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. They demand solutions that not only protect their sensitive data but also align with industry regulations and standards. Scalability and flexibility are paramount; solutions must adapt to evolving business needs and accommodate future growth. Cost-effectiveness is also a significant concern, with buyers seeking solutions that offer a compelling return on investment (ROI) within their budget constraints.
Security Concerns and Challenges
Large organizations adopting cloud services face numerous security challenges. Data breaches, regulatory compliance issues, and the complexity of managing hybrid cloud environments are common concerns. Ensuring the security of sensitive data and maintaining control over access permissions are crucial. Compliance with industry regulations like GDPR and HIPAA is often a major hurdle. Maintaining visibility across a multi-layered and distributed cloud infrastructure is also challenging.
The security posture of third-party cloud providers also plays a significant role in overall risk assessment.
Factors Influencing Purchasing Decisions, Inside the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide
Several factors influence enterprise purchasing decisions for unified cloud security solutions. These include the overall security posture of the organization, the specific cloud services utilized, and the regulatory environment. The need for seamless integration with existing security tools and infrastructure is paramount. Demonstrable ROI, robust vendor support, and clear communication from vendors are also key considerations. Case studies and testimonials from other similar organizations often play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Roles and Stakeholders Involved
The enterprise cloud security buying process involves multiple roles and stakeholders. These include CIOs, CISOs, security architects, IT managers, compliance officers, and potentially legal representatives. Each stakeholder brings a unique perspective and set of priorities to the table, and understanding these perspectives is essential. The decision-making process often requires close collaboration and consensus building amongst these various parties.
Decision-Making Process
| Stage | Key Activities | Stakeholders | Decision Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needs Assessment | Identifying security gaps, defining requirements, and researching potential solutions. | CIO, CISO, Security Architects, IT Managers | Alignment with business objectives, compliance requirements, budget constraints, and integration capabilities. |
| Solution Evaluation | Comparing different solutions based on technical specifications, vendor support, and pricing. | Security Engineers, IT Managers, CISOs | Security features, scalability, integration capabilities, vendor reputation, and cost-effectiveness. |
| Vendor Selection | Evaluating vendor capabilities, negotiating contracts, and finalizing the purchase. | CIO, CISO, Legal Representatives, Procurement | Vendor reliability, support services, contract terms, and future roadmap alignment. |
| Implementation and Deployment | Integrating the solution into the existing infrastructure, training personnel, and monitoring performance. | IT Staff, Security Engineers, System Administrators | Ease of integration, user experience, support availability, and ongoing maintenance. |
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the unified cloud security enterprise buyers guide provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of cloud security within an enterprise setting. By understanding the core principles, benefits, challenges, and the specific needs of enterprise buyers, organizations can make informed decisions about implementing a unified cloud security solution. This guide serves as a valuable resource for all stakeholders involved in the cloud security buying process.
FAQ Explained: Inside The Unified Cloud Security Enterprise Buyers Guide
What are the key components of a unified cloud security solution?
Key components typically include identity and access management (IAM), data loss prevention (DLP), security information and event management (SIEM), and threat detection and response (TD&R) tools, all integrated to provide a holistic security posture.
What are some common security concerns for enterprises adopting cloud services?
Common concerns include data breaches, compliance violations, lack of visibility into security posture, and potential vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure and applications. Managing access to sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations are also critical concerns.
How does unified cloud security differ from traditional security models?
Traditional security models often rely on disparate, siloed tools for different aspects of security. Unified cloud security integrates these tools, providing a centralized platform and improved visibility, response, and management of security threats across the entire cloud environment.
What are some potential drawbacks of unified cloud security solutions?
Potential drawbacks include the complexity of integrating disparate systems, the need for significant upfront investment, and the potential for vendor lock-in. Careful consideration of the specific needs and existing infrastructure is crucial before implementation.