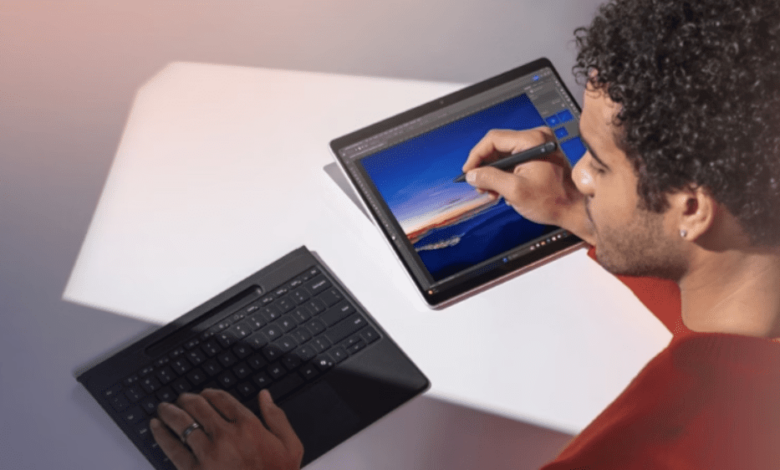
Microsoft to Roll Out AI-Powered PCs Concerningly in Coming Years
Microsoft to roll out ai powered pcs concerningly in coming years – Microsoft to roll out AI-powered PCs concerningly in coming years – that headline alone sparks a whirlwind of questions, doesn’t it? Will these supercharged computers revolutionize our lives, or will they usher in an era of unforeseen privacy concerns and ethical dilemmas? The integration of artificial intelligence into our personal computers is poised to be a monumental shift, impacting everything from how we work and play to the very fabric of our digital security.
This post dives into the exciting possibilities and the potentially unsettling implications of this technological leap.
We’ll explore the market’s potential reaction, the technological hurdles and breakthroughs, the implications for software and applications, and most importantly, the critical issues of security and privacy. Are we ready for a future where our PCs are not just tools, but intelligent partners – or even watchful overseers? Let’s find out.
Market Impact of AI-Powered PCs
The integration of artificial intelligence into personal computers represents a potential paradigm shift in the computing landscape, promising to redefine how we interact with technology and accomplish everyday tasks. This transition, however, is not without its challenges, presenting both exciting opportunities and potential pitfalls for manufacturers, consumers, and the broader tech industry.The market disruption caused by AI-powered PCs will be multifaceted.
We can expect to see a surge in productivity tools, personalized user experiences, and enhanced security features. Imagine software that anticipates your needs, automatically organizes your files, and proactively addresses potential system issues. This level of automation and personalization will redefine the user experience, potentially making computing more accessible and efficient for a wider range of users. However, concerns regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential displacement of certain jobs will undoubtedly need to be addressed.
Consumer Response to AI-Powered PCs
Consumer adoption of AI-powered PCs will likely follow a pattern of initial cautious optimism, followed by a period of gradual integration. Early adopters, typically tech-savvy individuals and professionals, will embrace the new technology, driving initial market growth. However, broader adoption will depend on factors such as price, ease of use, and the demonstrable benefits offered by AI features. Concerns about data security and privacy are likely to be significant barriers to adoption for a portion of the population.
Addressing these concerns through transparent data handling practices and robust security measures will be crucial for widespread acceptance. Furthermore, the level of sophistication and usefulness of the AI features will be a key determinant of consumer satisfaction and subsequent word-of-mouth marketing. A poorly implemented or overly intrusive AI system could quickly sour potential buyers. Conversely, a genuinely helpful and intuitive AI assistant could become a powerful selling point.
Projected Market Share of AI-Powered PCs
Predicting market share with complete accuracy is inherently difficult, but based on current trends and expert analysis, we can offer a plausible projection for the next five years. The following table illustrates a potential scenario, assuming a steady increase in AI capabilities and a gradual decrease in consumer apprehension:
| Year | AI PC Market Share | Traditional PC Market Share | Market Growth Rate (AI PCs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 5% | 95% | 20% |
| 2025 | 12% | 88% | 140% |
| 2026 | 22% | 78% | 83% |
| 2027 | 35% | 65% | 59% |
| 2028 | 50% | 50% | 43% |
This projection assumes a relatively rapid but still gradual adoption rate. Real-world market penetration will depend on a variety of factors including technological advancements, economic conditions, and the overall effectiveness of marketing campaigns highlighting the benefits of AI-powered PCs. For instance, if the cost of AI-powered components falls more rapidly than expected, or if a “killer app” emerges that dramatically showcases the advantages of AI integration, the adoption rate could accelerate significantly.
Conversely, if concerns about privacy or security remain unaddressed, or if the technology proves less user-friendly than anticipated, adoption could lag behind these projections.
Technological Advancements and Challenges

The rise of AI-powered PCs represents a significant leap forward in personal computing, driven by converging technological advancements. However, this integration also presents considerable challenges, ranging from practical limitations to complex ethical considerations. Understanding both the opportunities and the hurdles is crucial for navigating this technological shift responsibly.The development of AI-powered PCs hinges on several key technological breakthroughs.
Firstly, advancements in deep learning algorithms have enabled more sophisticated AI models capable of performing complex tasks directly on the device, reducing reliance on cloud connectivity. Secondly, the dramatic increase in processing power offered by new generations of CPUs and GPUs, particularly those designed with AI acceleration in mind, provides the computational muscle necessary to run these demanding algorithms efficiently.
Thirdly, the miniaturization of hardware components allows for the integration of powerful AI processors into increasingly compact and energy-efficient devices. Finally, improvements in memory technologies, such as high-bandwidth memory, ensure that the AI models have access to the data they need quickly and effectively.
Power Consumption and Thermal Management
Integrating powerful AI processing capabilities into PCs presents significant challenges in power consumption and thermal management. AI models, especially deep learning networks, are computationally intensive, demanding significant processing power and leading to increased energy consumption and heat generation. This necessitates innovative cooling solutions and efficient power management strategies to prevent overheating and extend battery life, especially in portable devices.
For example, the development of more efficient AI accelerators and the exploration of alternative computing architectures like neuromorphic computing are crucial for mitigating these challenges. Existing solutions like advanced thermal paste and improved heat sinks are continuously being improved, but these are often not sufficient for the next generation of AI-powered PCs.
Privacy Concerns and Data Security
The deployment of AI in PCs raises significant privacy concerns. AI models require vast amounts of data to train and operate effectively. This data, often including personal information, needs to be stored and processed securely to prevent unauthorized access and misuse. Ensuring data encryption both in transit and at rest, along with robust access control mechanisms, are critical to mitigating these risks.
Furthermore, the potential for AI models to infer sensitive information from seemingly innocuous data requires careful consideration and the implementation of privacy-preserving AI techniques. For instance, differential privacy methods can add noise to the data to protect individual privacy while still allowing for useful AI model training. Failure to address these concerns could lead to significant breaches of personal privacy and erode user trust.
Ethical Implications of Widespread AI Integration
The widespread integration of AI into personal computing devices presents a number of complex ethical implications. It’s crucial to proactively address these concerns to ensure responsible development and deployment.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI models are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the AI system will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For example, a facial recognition system trained primarily on images of white faces might perform poorly on individuals with darker skin tones.
- Job Displacement: The automation potential of AI-powered PCs could lead to job displacement in various sectors, requiring proactive measures for retraining and reskilling the workforce.
- Transparency and Explainability: Many AI models, particularly deep learning networks, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to identify and correct errors or biases.
- Accountability and Responsibility: Determining responsibility when an AI system makes a mistake or causes harm is a complex legal and ethical challenge. Clear guidelines and frameworks are needed to address accountability in the event of AI-related incidents.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: The potential for AI-powered PCs to collect and analyze vast amounts of user data raises concerns about surveillance and monitoring. Safeguards are needed to prevent misuse of this data and protect user privacy.
Software and Application Integration
AI-powered PCs represent a significant leap forward in computing, promising to revolutionize how we interact with software and applications. The integration of AI isn’t just about adding a few smart features; it’s about fundamentally changing the way applications are designed and used, leading to increased efficiency, enhanced user experience, and entirely new possibilities. This integration will impact everything from simple productivity tools to complex professional software.The potential for AI integration across various software applications is vast.
Imagine software that anticipates your needs, proactively assists with tasks, and learns from your workflow to optimize its performance. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality we’re rapidly approaching.
Examples of AI-Enhanced Software Applications, Microsoft to roll out ai powered pcs concerningly in coming years
Several software categories stand to gain immensely from AI integration. For example, image and video editing software could utilize AI for automated background removal, object recognition for precise selection tools, and intelligent upscaling to enhance resolution without artifacts. Similarly, writing and coding applications could benefit from AI-powered grammar and style checkers, code completion tools that understand context, and even AI-driven suggestions for improving code efficiency.
Finally, professional design software could leverage AI for automated layout generation, intelligent asset management, and the creation of variations on existing designs.
A Hypothetical AI-Powered Productivity Suite
Let’s envision a hypothetical AI-powered productivity suite called “Synapse.” Synapse would integrate a word processor, spreadsheet application, presentation software, and email client, all seamlessly connected through a central AI assistant. Key features would include:* Contextual Understanding: Synapse would understand the context of your work across different applications. For instance, it could automatically extract data from a spreadsheet to populate a presentation, or summarize key points from an email into a concise action item list in your task manager.
Predictive Assistance
The AI would anticipate your needs, suggesting relevant files, contacts, or information based on your current task. It could also proactively schedule meetings or flag potential conflicts in your calendar.
Intelligent Automation
Microsoft’s AI-powered PC rollout in the coming years is definitely something to watch, and not just because of the tech itself. It makes me wonder about the future of app development, and how platforms like Domino will adapt. Learning more about domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , is crucial to understanding how we might build apps for this new AI-driven landscape.
Ultimately, the impact of these AI-powered PCs will depend on how developers respond to the challenges and opportunities they present.
Repetitive tasks like formatting documents, generating reports, or managing emails could be automated using AI, freeing up users to focus on more creative and strategic work.
Personalized Workflow Optimization
Synapse would learn your individual work habits and preferences over time, adapting its functionality and interface to optimize your productivity. This could involve customizing keyboard shortcuts, suggesting alternative phrasing, or prioritizing tasks based on their importance and urgency.
Comparison of AI-Powered and Traditional Software
The table below compares the performance and capabilities of AI-powered applications versus their traditional counterparts.
| Application | AI Version Features | Traditional Version Features | Performance Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Word Processor | Grammar & style suggestions, automated formatting, content summarization, AI-powered writing assistance | Basic text editing, formatting tools, spell check | AI version significantly improves writing quality, speed, and efficiency. |
| Spreadsheet | Automated data analysis, predictive modeling, intelligent data visualization, anomaly detection | Basic calculations, charting, data sorting | AI version offers deeper insights and allows for more complex analysis with less manual effort. |
| Email Client | Intelligent inbox management (prioritization, spam filtering, automated responses), smart scheduling, contact suggestions | Basic email composition, sending, and receiving | AI version reduces email overload and improves communication efficiency. |
Security and Privacy Implications
The integration of AI into personal computers presents a fascinating new frontier, but it also introduces significant security and privacy challenges. The very capabilities that make AI-powered PCs so useful – their ability to learn from user data and adapt to individual needs – also create vulnerabilities and raise ethical concerns about data protection. Understanding these implications is crucial for both developers and users to ensure responsible innovation and deployment.AI-powered PCs collect and process vast amounts of user data, creating potential risks that demand careful consideration.
This data, ranging from browsing history and typing patterns to voice recordings and facial recognition scans, can be valuable to malicious actors if compromised. Equally important is the potential for misuse of this data by the companies developing and deploying the AI systems themselves.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation Strategies
AI algorithms, like any software, are susceptible to attacks. A compromised AI model could lead to data breaches, system malfunctions, or even malicious actions. For example, an adversary could manipulate the AI’s training data to introduce biases or vulnerabilities, causing the system to behave unpredictably or make incorrect decisions. Furthermore, the increased reliance on cloud-based AI services introduces additional attack vectors, such as data interception during transmission.
Mitigation strategies include robust encryption of data both in transit and at rest, regular security audits of AI models and underlying software, and implementation of strong access controls to prevent unauthorized access or modification. Implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly updating software are also critical. Finally, employing techniques like differential privacy can help protect user data while still enabling the AI to function effectively.
Privacy Implications of AI Data Collection and Processing
The collection and processing of user data by AI-powered PCs raise serious privacy concerns. Regulations like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California place strict requirements on how personal data is collected, used, and protected. AI systems, by their nature, often process sensitive information, including personal preferences, health data (if health tracking apps are integrated), and financial details.
The potential for unintended data leakage or misuse is high, especially if the data is not anonymized or aggregated effectively. This raises the possibility of profiling, discrimination, and targeted advertising based on personal characteristics. Furthermore, the lack of transparency in some AI algorithms makes it difficult for users to understand how their data is being used and what inferences are being drawn from it.
Therefore, clear and understandable explanations of data usage are essential for building user trust.
Hypothetical Privacy Policy for an AI-Powered PC
This hypothetical privacy policy Artikels the data handling practices of a fictional AI-powered PC, “AI-Assist.”
This policy explains how AI-Assist collects, uses, and protects your personal data. We are committed to protecting your privacy and complying with all applicable data protection regulations.
We collect data such as usage patterns, voice commands, and typing data to improve the functionality of AI-Assist. This data is anonymized and aggregated whenever possible. We may share anonymized data with our partners for research and development purposes. Users have the right to access, correct, or delete their data at any time. We will not sell your personal data to third parties.
We use industry-standard security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. For specific questions, please contact our data protection officer at [email protected]
User Experience and Accessibility: Microsoft To Roll Out Ai Powered Pcs Concerningly In Coming Years
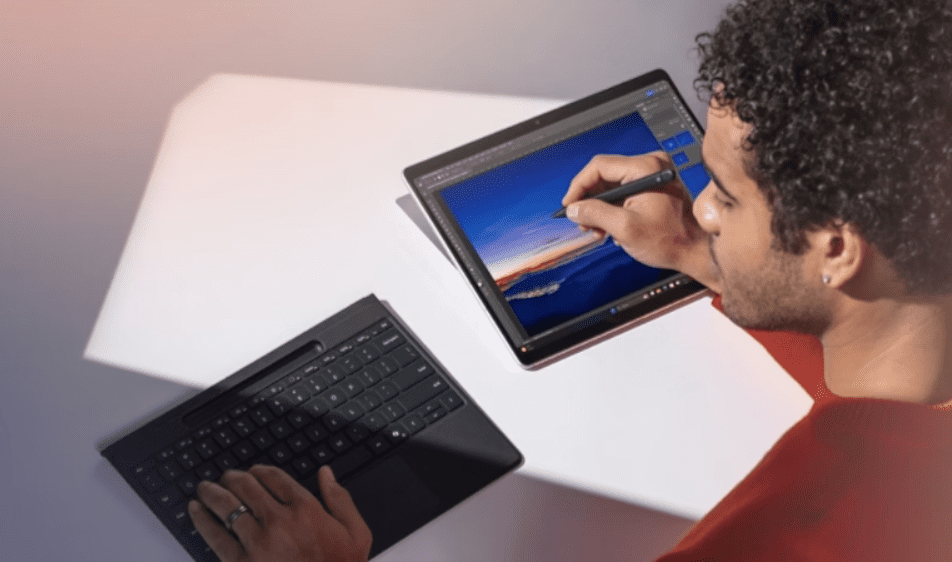

AI-powered PCs have the potential to revolutionize the user experience, moving beyond simple task automation to create truly personalized and accessible computing environments. This shift hinges on AI’s ability to learn individual user preferences and adapt the system accordingly, ultimately making technology more intuitive and inclusive for everyone.AI can significantly enhance the user experience through personalized features and improved accessibility.
Imagine a system that anticipates your needs based on your past behavior, proactively suggesting relevant applications, files, and information. This level of personalization extends to interface customization, adapting the visual layout, font sizes, and even color schemes to optimize comfort and efficiency. Furthermore, AI can streamline complex tasks, intelligently automating repetitive actions and providing helpful suggestions to improve workflow.
AI-Enhanced Personalization
AI algorithms can analyze user behavior patterns, such as frequently used applications, preferred file types, and typical working hours, to create a highly personalized computing experience. This could manifest in features like automatically launching preferred applications upon login, prioritizing relevant notifications, and even suggesting optimal screen brightness and sound settings based on the time of day and surrounding environment. For example, an AI could learn that a user consistently works on graphic design projects in the evenings and automatically adjust the display settings to reduce eye strain.
Similarly, it could preemptively open relevant software and files based on the user’s calendar appointments.
AI and Assistive Technologies for Users with Disabilities
AI-powered PCs offer significant potential for users with disabilities by seamlessly integrating assistive technologies and providing personalized support. For instance, AI can power advanced speech-to-text and text-to-speech functionalities with improved accuracy and natural language processing. This enables individuals with motor impairments to interact with their computers more effectively. Furthermore, AI can enhance screen readers by providing contextual information and simplifying navigation through complex interfaces.
Imagine an AI that automatically identifies and describes images, providing detailed audio descriptions for visually impaired users. Similarly, AI could offer real-time translation of text or speech, bridging communication barriers for users with hearing or language-related disabilities.
Ideal User Interface for an AI-Powered PC
The ideal user interface for an AI-powered PC would be highly customizable and adaptable, prioritizing intuitive navigation and accessibility features. Imagine a clean, uncluttered desktop with customizable widgets displaying frequently accessed information, such as calendar appointments, weather updates, and news headlines. These widgets could be resized, repositioned, and even customized with different color schemes to match individual preferences.
A central AI assistant, accessible via voice commands or a dedicated icon, would act as a control hub, allowing users to perform various tasks, from launching applications and searching for files to controlling smart home devices and managing notifications. The interface would offer adjustable font sizes, high contrast modes, and customizable keyboard shortcuts, catering to users with visual impairments.
Screen readers would be deeply integrated, providing comprehensive audio descriptions and context-aware navigation. Furthermore, the system would automatically adapt to different input methods, supporting voice control, eye tracking, and alternative input devices as needed. The overall aesthetic would be minimalist and uncluttered, focusing on clear visual hierarchy and intuitive information presentation. The color palette would be customizable, allowing users to choose schemes that are comfortable and accessible.
The system would provide feedback on all actions, ensuring users are aware of what the AI is doing and how it is responding to their inputs.
Economic and Societal Effects
The widespread adoption of AI-powered PCs promises a transformative impact on the global economy and society, bringing both significant opportunities and considerable challenges. The integration of AI into personal computing will reshape industries, alter job markets, and fundamentally change how we communicate, access information, and engage in education and professional development. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for navigating this technological shift effectively.The economic impact of AI-powered PCs will be multifaceted.
While some fear widespread job displacement due to automation, the reality is likely more nuanced. Certain roles heavily reliant on repetitive tasks may be automated, leading to job losses in sectors like data entry and basic customer service. However, the development, implementation, maintenance, and support of AI systems will create entirely new job categories requiring specialized skills in areas such as AI engineering, data science, and AI ethics.
The net effect on employment will depend on the speed of adaptation and the effectiveness of retraining and upskilling initiatives. For example, the rise of AI-powered design tools might displace some graphic designers, but it will also create demand for professionals skilled in using and optimizing these tools.
Job Displacement and Creation
The introduction of AI-powered PCs will undoubtedly lead to some job displacement, particularly in roles involving routine tasks. However, this will be counterbalanced by the creation of new jobs in areas directly related to AI development, implementation, and maintenance. The automotive industry provides a relevant example: the increasing automation of vehicle manufacturing has led to job losses in some areas, but it has also created new roles in software engineering, robotics, and AI-related fields.
Successful navigation of this transition will require proactive investment in education and training programs that equip workers with the skills needed for the jobs of the future. This includes fostering digital literacy and promoting lifelong learning.
Changes in Communication and Information Access
AI-powered PCs have the potential to revolutionize communication and information access. AI-driven tools can translate languages in real-time, facilitating global communication and collaboration. Personalized learning platforms can adapt to individual learning styles, providing customized educational experiences. AI-powered search engines can sift through vast amounts of data to provide users with highly relevant and accurate information, improving research and decision-making.
However, concerns around the spread of misinformation and the potential for AI to exacerbate existing biases in information access must be addressed. For instance, the development of AI algorithms that identify and flag fake news is crucial to maintain the integrity of online information.
Long-Term Effects on Education and Professional Development
AI-powered PCs are poised to significantly impact education and professional development. Personalized learning platforms can cater to individual student needs, optimizing learning outcomes and providing adaptive support. AI-powered tools can automate administrative tasks, freeing up educators to focus on student interaction and personalized instruction. In professional development, AI can provide customized training programs, enhancing employee skills and boosting productivity.
For example, AI-powered simulations can provide realistic training scenarios for surgeons, pilots, and other professionals requiring high levels of expertise. However, it is crucial to ensure equitable access to these technologies to avoid exacerbating existing educational and economic inequalities. Investment in digital infrastructure and training programs is essential to bridge the digital divide and ensure that everyone benefits from the transformative potential of AI-powered PCs.
Final Wrap-Up
The impending arrival of AI-powered PCs from Microsoft presents a complex and fascinating future. While the potential benefits – enhanced productivity, personalized experiences, and groundbreaking accessibility features – are undeniable, the ethical, security, and privacy concerns require careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. As we stand on the precipice of this technological revolution, thoughtful discussion and responsible development are paramount to ensure that this powerful technology serves humanity, rather than the other way around.
The journey ahead promises to be both exhilarating and challenging, and the choices we make today will shape the landscape of tomorrow’s digital world.
Expert Answers
What specific AI features can we expect in these new PCs?
While details are scarce, expect features like advanced voice assistants, intelligent predictive text, automated organization of files, and potentially AI-powered photo and video editing tools. The extent of these features will likely vary across different models and price points.
How will these AI-powered PCs impact jobs?
This is a complex question. While some jobs might be automated, new roles in AI development, maintenance, and ethical oversight will likely emerge. The overall impact will depend on how effectively society adapts to this technological shift and invests in retraining and education.
What about data security – will my personal information be safe?
This is a major concern. Microsoft will need to implement robust security measures to protect user data from breaches and misuse. Transparency about data collection practices and strong user privacy controls will be essential for building trust.