MSP Guide Safeguarding Clients from Ransomware
Msp guide how to safeguard your clients during a ransomware attack – MSP Guide: Safeguarding Clients from Ransomware – that’s the burning question, right? Ransomware attacks are terrifying, not just for the data loss, but for the crippling disruption to business. This guide isn’t just another checklist; it’s your battle plan. We’ll cover everything from building an impenetrable fortress before the attack to calmly navigating the chaos afterward, ensuring your clients can get back on their feet quickly.
We’ll look at practical strategies, real-world tools, and even how to communicate effectively during a crisis. Let’s dive in and equip you with the knowledge to protect your clients.
This guide breaks down the process into manageable steps, from pre-attack preparation, focusing on preventative measures and robust data backup strategies, to the critical incident response phase, detailing how to contain the attack and mitigate the damage. We’ll explore data recovery methods, post-incident reviews, and the crucial aspects of client communication and legal considerations. The aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how to handle a ransomware attack effectively, minimizing disruption and protecting your clients’ valuable data and reputation.
Pre-Attack Preparation
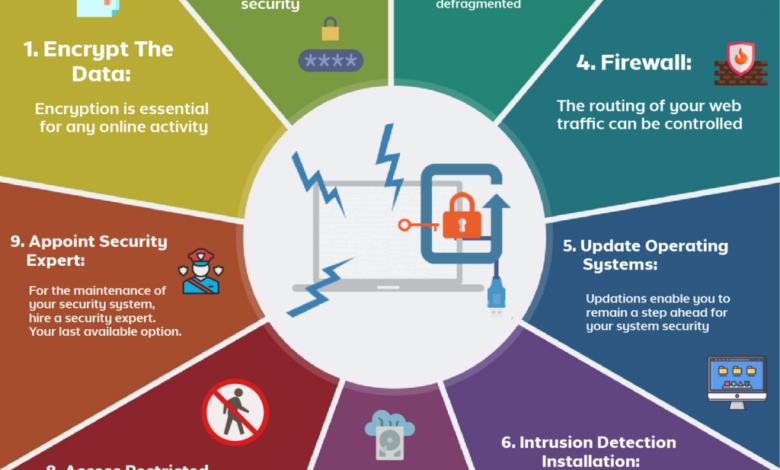
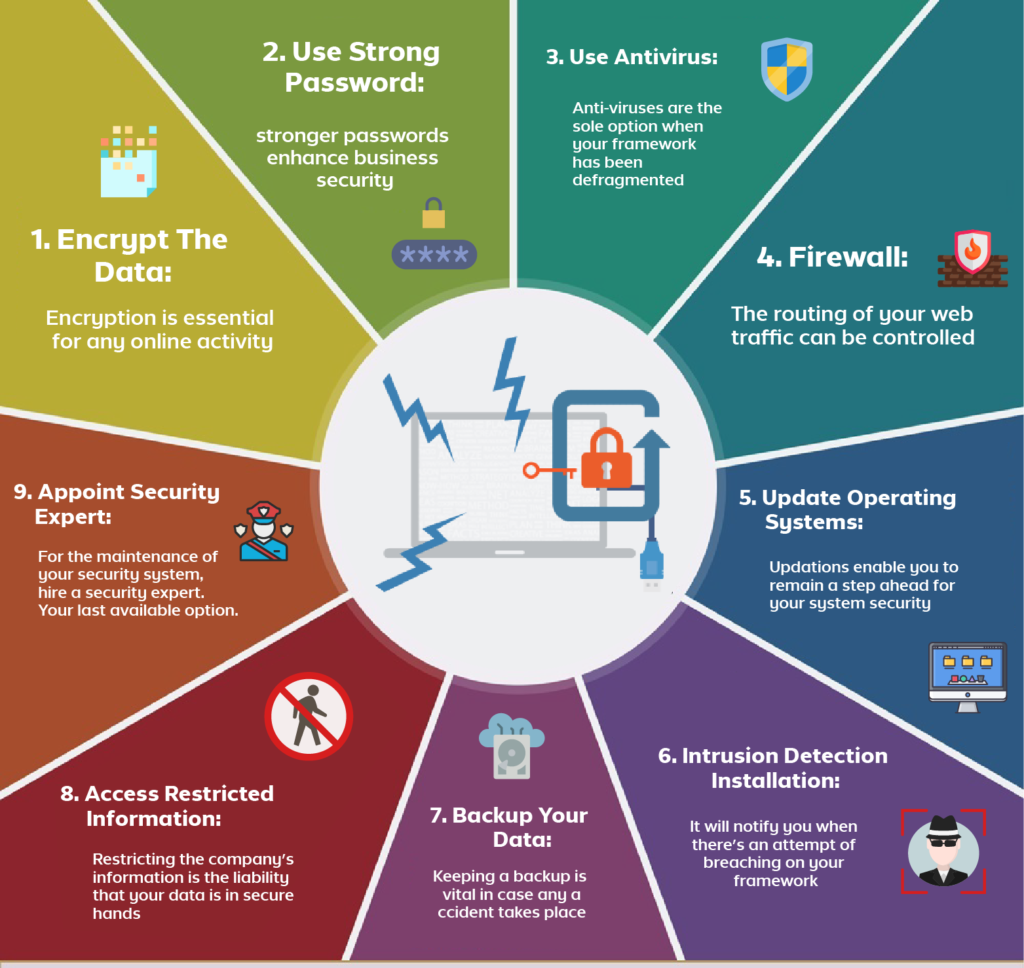
Proactive cybersecurity is paramount for MSPs looking to protect their clients from the devastating impact of ransomware. A robust, multi-layered defense is far more effective and cost-efficient than reactive remediation. This section Artikels essential preventative measures to significantly reduce the risk of a successful ransomware attack.
Building a strong cybersecurity posture requires a holistic approach, encompassing various technical and procedural safeguards. This involves not only implementing advanced security technologies but also fostering a security-conscious culture within your clients’ organizations. Regular reviews and updates are crucial to ensure the effectiveness of these measures against evolving threats.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
A comprehensive backup and recovery plan is the cornerstone of ransomware resilience. This plan should detail various backup types, their frequency, secure storage locations, and robust verification methods. Regular testing of the recovery process is vital to ensure its effectiveness in a real-world scenario. Failure to adequately test your recovery plan can lead to significant data loss and business disruption during an attack.
| Backup Type | Frequency | Storage Location | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Weekly | Offsite Cloud Storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage) | Regular restoration testing to a separate environment |
| Incremental Backup | Daily | Offsite Cloud Storage (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage) | Verification of backup size and successful completion |
| Differential Backup | Daily | Locally encrypted storage, rotated offsite weekly | Comparison against previous backups and spot checks of critical data |
| Image-Level Backup | Monthly | Offsite Cloud Storage (different cloud provider from incremental backups) | Boot from backup image and verification of system functionality |
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error remains a leading cause of ransomware infections. Comprehensive employee training is crucial in mitigating the risk of phishing attacks, social engineering scams, and other malicious activities. Regular training sessions should be conducted, and the content should be updated to reflect the latest threat landscape.
- Phishing and Email Security Awareness: Recognizing and reporting suspicious emails, avoiding clicking on unknown links, and understanding the importance of email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Social Engineering Tactics: Identifying and resisting manipulative techniques used by attackers to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
- Password Security Best Practices: Creating strong, unique passwords, utilizing password managers, and understanding the importance of password hygiene.
- Safe Web Browsing Habits: Avoiding unsafe websites, using reputable anti-malware software, and understanding the risks of downloading files from untrusted sources.
- Recognizing and Reporting Security Incidents: Knowing how to identify suspicious activity, report security incidents promptly, and follow established incident response procedures.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication to access systems and accounts. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if credentials are compromised. Implementing MFA across all client systems and accounts should be a top priority for any MSP aiming to enhance its clients’ security posture. This includes not only employee accounts but also access to critical systems and applications.
Examples of MFA methods include using a combination of a password, a security token, and a biometric scan (fingerprint or facial recognition). The specific MFA method implemented will depend on the client’s specific needs and risk tolerance. However, the importance of deploying MFA cannot be overstated in today’s threat landscape.
Incident Response
Ransomware attacks are a brutal reality for businesses of all sizes, and a swift, effective incident response is crucial to minimizing damage and restoring operations. For MSPs, this means not only protecting your own infrastructure but also guiding your clients through the crisis. This section details the critical steps to take when a ransomware attack is detected on a client’s system.
The initial moments following the discovery of a ransomware attack are critical. Quick action can significantly reduce the impact and limit the spread of the malicious software. Procrastination can lead to irreversible data loss and substantial financial repercussions. Remember, the goal is containment, mitigation, and recovery.
Initial Steps Upon Discovering a Ransomware Attack
Immediate actions are paramount. First, isolate the affected system(s) to prevent further infection. Then, initiate a thorough investigation to determine the extent of the compromise. Finally, begin the process of communicating with the client and relevant stakeholders. Failure to act decisively in these early stages can significantly complicate recovery efforts.
Isolating Infected Systems
Preventing the spread of ransomware is the immediate priority. A methodical approach to isolating infected systems is vital.
Here’s a step-by-step procedure:
- Disconnect from the Network: Immediately disconnect the infected system(s) from the network, both physically (by unplugging the Ethernet cable) and logically (by disabling network adapters). This prevents the ransomware from spreading to other devices via network shares or vulnerabilities.
- Power Down (If Necessary): In extreme cases, where the infection is rapidly spreading or exhibiting disruptive behavior, powering down the affected system(s) may be necessary to halt its activity. This is a last resort, as it can lead to data loss in some instances.
- Identify Affected Systems: Conduct a thorough network scan to identify any other potentially compromised systems. Look for unusual network activity, slowed performance, or signs of encryption on other devices.
- Implement Network Segmentation: If the network isn’t already segmented, consider implementing this as a proactive measure to limit the impact of future attacks. Segmentation isolates different parts of the network, preventing a single breach from compromising the entire system.
- Document Everything: Meticulously document every step taken, including timestamps, actions performed, and observations made. This detailed record will be invaluable during the investigation and recovery phases.
Communication Plan, Msp guide how to safeguard your clients during a ransomware attack
Open and honest communication is vital throughout the incident response process.
A well-defined communication plan includes:
- Immediate Notification to the Client: Inform the client immediately about the attack, outlining the steps being taken to contain it. Be transparent and avoid technical jargon.
- Regular Updates: Provide regular updates to the client on the progress of the investigation and recovery efforts. Keep them informed about any potential impact on their business operations.
- Stakeholder Communication: Depending on the severity of the attack, communication may also be necessary with law enforcement, legal counsel, and insurance providers.
- Public Relations (If Necessary): If the attack is significant or impacts a large number of individuals, a public relations strategy may be necessary to manage the situation and mitigate reputational damage.
Identifying Ransomware and Assessing Damage
Identifying the specific ransomware variant and assessing the extent of the damage is crucial for effective remediation.
Several tools and techniques can be employed:
- Malware Analysis Tools: Utilize tools like VirusTotal, Hybrid Analysis, or other sandbox environments to analyze samples of the ransomware and identify its type and capabilities. This information helps determine the appropriate recovery strategy.
- Network Monitoring Tools: Analyze network traffic logs to identify the entry point of the ransomware, the affected systems, and any lateral movement within the network. Tools like Wireshark or tcpdump can be useful.
- Disk Imaging and Forensics: Create forensic images of affected hard drives to preserve evidence and facilitate a thorough investigation. This is particularly important if legal action is being considered.
- Data Recovery Tools: Explore the use of data recovery tools, if applicable, to recover encrypted files. The success of data recovery depends on the type of ransomware and the encryption method used.
Data Recovery and Restoration: Msp Guide How To Safeguard Your Clients During A Ransomware Attack
Getting your business back online after a ransomware attack isn’t just about paying the ransom (which we strongly advise against unless absolutely necessary and under expert guidance). The real work begins with data recovery and restoration – the process of bringing your systems and data back to a pre-attack state. This is crucial for minimizing downtime, preventing further financial losses, and maintaining business continuity.
A well-defined recovery plan, tested regularly, is your best defense against prolonged disruption.
Restoring Data from Backups: Various Scenarios
The success of data restoration hinges on the quality and accessibility of your backups. Different scenarios require different approaches. A partial data loss, for example, might only necessitate restoring specific files or folders from a recent backup. Conversely, a complete system failure requires a full bare-metal restore, reinstalling the operating system and then restoring the data. Regularly testing your backups is critical to ensuring they are both accessible and recoverable when needed.
Think of a scenario where a critical server is hit – you need to be able to restore it quickly and efficiently. A weekly full backup with daily incremental backups allows for a faster restoration, minimizing downtime.
Comparison of Data Recovery Methods
Several methods exist for restoring data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. A bare-metal restore involves reinstalling the operating system and then restoring the entire system image from a backup. This is ideal for complete system failures, ensuring a clean and consistent environment. Image-based recovery is similar but might involve restoring to different hardware, requiring careful consideration of compatibility.
Finally, file-level recovery allows for the selective restoration of individual files or folders, useful for partial data loss scenarios. The choice of method depends on the extent of the damage and the available backups. For example, if only a few user files were encrypted, file-level recovery is sufficient; however, if the entire server was compromised, a bare-metal restore is necessary.
Validating Data Integrity After Recovery
After restoring your data, it’s crucial to validate its integrity. This ensures that the restored data is identical to the original data before the attack. This involves checksum verification – comparing the checksum (a unique digital fingerprint) of the restored files with the checksums of the original files (if available pre-attack). Discrepancies indicate potential data corruption during the attack or the recovery process.
Thorough testing and validation are essential to confirm the functionality of restored systems and applications, preventing unexpected issues down the line. For example, you could run a database consistency check or application-specific tests to ensure everything functions as expected.
Data Recovery and Restoration Process Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps:
1. Assess the damage
Determine the extent of data loss and system compromise.
2. Identify the recovery method
Choose the appropriate method based on the assessment (bare-metal, image-based, or file-level).
3. Restore data from backups
Execute the chosen recovery method, restoring data to the affected systems.
4. Validate data integrity
Verify the integrity of restored data using checksums or other validation techniques.
5. System testing
Thoroughly test restored systems and applications to ensure functionality.
6. Security hardening
Implement enhanced security measures to prevent future attacks. This might include patching vulnerabilities, strengthening access controls, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
Post-Incident Activities

A ransomware attack, even with a successful recovery, leaves a trail of disruption and vulnerability. The true test of resilience isn’t just surviving the attack, but learning from it to build a stronger, more secure future. Post-incident activities are crucial for minimizing the impact of future attacks and improving overall security posture. This involves a thorough review of the incident, implementation of enhanced security measures, and rigorous documentation for future reference.The post-incident phase is not simply about returning to normal operations; it’s about transforming your security approach.
By systematically analyzing the attack, identifying weaknesses, and implementing improvements, you can significantly reduce your risk profile and better protect your clients’ valuable data. This proactive approach turns a negative experience into a valuable opportunity for growth and enhanced security.
Key Lessons Learned and Security Protocol Improvements
Analyzing the attack timeline, from initial infection to data recovery, is vital. We should identify specific vulnerabilities exploited by the attackers. For example, was it a phishing email, a software vulnerability, or a weak password? Identifying these weaknesses allows for targeted improvements. This could involve implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems, patching known vulnerabilities promptly, and conducting regular security awareness training for employees to reduce the likelihood of future phishing attacks.
A detailed report should be compiled, categorizing the lessons learned and mapping them to specific actionable improvements. For instance, if the attack exploited a known vulnerability in a specific software, upgrading that software to the latest version is a clear and immediate improvement. If employee negligence contributed, revised security awareness training should be implemented.
Post-Incident Review Meeting Agenda
A structured post-incident review meeting is essential. The agenda should include a chronological review of the attack, including the initial detection, the incident response actions taken, the data recovery process, and the overall business impact. The meeting should involve representatives from IT, security, legal, and potentially clients, depending on the scope of the attack and the nature of the client relationship.
Discussions should focus on both the technical aspects (e.g., the effectiveness of security tools and protocols) and the operational aspects (e.g., communication strategies and business continuity plans). The meeting should conclude with a clear action plan outlining the specific improvements to be implemented. A sample agenda could include: Review of timeline, identification of vulnerabilities, assessment of incident response effectiveness, review of data recovery process, discussion of communication strategies, definition of improvement actions, and assignment of responsibilities and deadlines.
Incident Response Process Documentation
Meticulous documentation is crucial. This should include a comprehensive record of the attack timeline, the steps taken during the incident response, the tools used, and the outcome of each action. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for future incident response efforts, allowing for quicker and more effective responses to similar events. It also aids in identifying patterns and trends in attacks, facilitating proactive security measures.
The documentation should be detailed enough to be useful for internal review and, if necessary, for external audits or legal proceedings. Consider using a standardized incident response template to ensure consistency and completeness. This template should include sections for initial discovery, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activity.
Forensic Analysis and Root Cause Determination
Forensic analysis is paramount to understand the root cause of the attack. This involves a deep dive into the systems affected by the ransomware, examining logs, network traffic, and other data to identify the attack vector and the methods used by the attackers. This detailed investigation goes beyond simply recovering data; it seeks to understand how the attack happened and prevent similar attacks in the future.
The findings from the forensic analysis should inform the improvements to security protocols and provide valuable insights for future security planning. For example, if the forensic analysis reveals that the attack originated from a compromised email account, this highlights the need for stronger password policies and enhanced email security measures. Similarly, if a software vulnerability was exploited, the analysis should identify the specific vulnerability and inform the necessary patching and mitigation strategies.
Client Communication and Legal Considerations
Open and honest communication with clients is paramount during and after a ransomware attack. Transparency builds trust, mitigates potential legal issues, and helps ensure a smoother recovery process. Failing to adequately communicate can severely damage your reputation and lead to costly legal battles. This section details best practices for client communication and the crucial legal considerations involved.
Effective communication requires a proactive and well-defined strategy. This involves pre-prepared templates, regular updates, and a designated point of contact to ensure consistent messaging. Legal compliance is equally important, requiring adherence to data privacy regulations and prompt reporting to relevant authorities where necessary.
Sample Communication Templates
Having pre-written communication templates ready significantly streamlines the response process during a crisis. These templates should be tailored to different stages of the incident. Below are examples for initial notification, progress updates, and resolution announcements.
Initial Notification Template:
Subject: Urgent Notification Regarding a Security Incident Affecting [Client Name]
Dear [Client Name],
We are writing to inform you of a security incident involving a ransomware attack that has impacted our systems and may have affected some of your data. We are taking immediate steps to contain the attack and recover your data. We will provide regular updates on our progress. A dedicated point of contact, [Name and Contact Information], is available to answer any questions you may have.
Sincerely,
[Your Company Name]
Progress Update Template:
Subject: Update on Security Incident Affecting [Client Name]
Dear [Client Name],
This is an update on the ransomware incident reported on [Date]. We have [briefly describe actions taken, e.g., isolated affected systems, engaged cybersecurity experts]. We are currently working on [describe current actions, e.g., data recovery, system restoration]. We anticipate [estimated timeline for resolution]. We will continue to provide updates every [frequency of updates].
Sincerely,
[Your Company Name]
Resolution Announcement Template:
Subject: Resolution of Security Incident Affecting [Client Name]
Dear [Client Name],
We are pleased to announce the successful resolution of the ransomware incident reported on [Date]. All affected systems have been restored, and your data has been recovered. We have implemented additional security measures to prevent future incidents. We appreciate your patience and understanding throughout this process.
Sincerely,
[Your Company Name]
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Ransomware attacks trigger various legal and regulatory obligations. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage. Understanding these obligations is crucial for MSPs.
- Data Breach Notification Laws: Many jurisdictions have laws requiring notification of affected individuals following a data breach. These laws vary in their requirements, including the timeframe for notification and the information that must be disclosed.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): If you handle personal data of EU residents, GDPR compliance is mandatory. This includes having robust security measures in place and promptly notifying authorities of data breaches.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): If you manage data protected under HIPAA (e.g., healthcare data), you must comply with its strict regulations regarding data breaches and security.
- State-Specific Regulations: Several US states have their own data breach notification laws, often with requirements that exceed federal standards.
- Contractual Obligations: Review your service level agreements (SLAs) with clients to understand your contractual obligations in the event of a security incident.
Maintaining Client Confidentiality
Protecting client confidentiality is paramount throughout the incident response process. This requires careful handling of sensitive data and adherence to strict privacy protocols.
Best practices include using secure communication channels, limiting access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only, and employing robust data encryption techniques. Regular security audits and employee training on data privacy best practices are essential. Furthermore, maintaining detailed records of all actions taken during the incident is crucial for demonstrating compliance and transparency.
Incident Reporting to Authorities
In some cases, reporting a ransomware attack to law enforcement and relevant regulatory bodies is mandatory. This is often required under data breach notification laws or if the attack involves critical infrastructure. Prompt reporting allows authorities to investigate the attack, potentially identify the perpetrators, and share information to prevent similar incidents.
The specific authorities to contact will vary depending on the jurisdiction, the nature of the attack, and the type of data involved. It’s crucial to understand your reporting obligations and act swiftly to comply.
Conclusive Thoughts
Successfully navigating a ransomware attack requires proactive planning and a well-defined response strategy. This guide has provided you with the essential tools and knowledge to protect your clients. Remember, prevention is key, but a robust response plan is equally crucial. By implementing the strategies Artikeld here, you can significantly reduce the impact of a ransomware attack and ensure the continuity of your clients’ businesses.
Stay vigilant, stay proactive, and stay ahead of the curve. The security landscape is constantly evolving, so continuous learning and adaptation are essential. Let’s work together to make the digital world a safer place.
User Queries
What is the most common way ransomware gets into a system?
Phishing emails are a primary vector. These often appear legitimate, tricking users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments.
Should I pay the ransom?
Generally, paying the ransom is NOT recommended. There’s no guarantee you’ll get your data back, and you’ll be encouraging further attacks. Focus on recovery from backups.
What if I don’t have backups?
Data recovery from an unbacked system is extremely difficult and expensive. Professional data recovery services may be needed, but success is not guaranteed.
How often should I test my backups?
Regular testing, at least monthly, is crucial to ensure your backups are functional and data is recoverable. Test both full and incremental backups.