
Palo Alto Networks Found to Spread Malware
Palo alto networks found to spread malware – Palo Alto Networks found to spread malware? Whoa, that’s a headline that grabbed
-my* attention! Imagine the shock – a cybersecurity giant, allegedly distributing the very thing it’s supposed to protect against. This isn’t just another security breach; it’s a potential earthquake in the industry. We’re diving deep into the claims, the evidence, and the fallout, exploring what this means for users and the future of cybersecurity.
The initial reports surfaced [insert date/source here], sparking immediate debate. Was this a targeted attack, a software flaw, or something else entirely? The specifics of the malware, its delivery method, and the extent of the damage are still under investigation, but the implications are already massive. We’ll be examining Palo Alto Networks’ official response, the security community’s reaction, and the technical nitty-gritty to get to the bottom of this.
Initial Report Analysis
The recent reports alleging that Palo Alto Networks products were found to spread malware sent shockwaves through the cybersecurity community. This wasn’t a small-scale incident; the implications were significant, potentially affecting countless organizations relying on Palo Alto’s security solutions. Understanding the initial report, its dissemination, and the subsequent response is crucial to grasping the full scope of the event.The original source of the claim requires careful examination.
While pinpointing the very first mention can be difficult due to the rapid spread of information online, the initial reports appeared to originate from security researchers who discovered and analyzed malicious activity seemingly linked to Palo Alto Networks’ software. These researchers likely found evidence within their own systems or through network monitoring, eventually leading them to identify a potential vulnerability in Palo Alto’s products.
The subsequent public dissemination likely involved a combination of private disclosures to Palo Alto Networks, security forums, and potentially even direct announcements via blog posts or press releases.
Timeline of Events
The timeline surrounding the initial report and subsequent updates is critical for understanding the response. While precise dates may vary depending on the specific source consulted, a general timeline might look like this: Initial discovery of suspicious activity, private disclosure to Palo Alto Networks, investigation by Palo Alto Networks, public release of the initial report detailing the vulnerability, Palo Alto Networks’ official response and patch release, and finally, follow-up reports analyzing the effectiveness of the patch and the overall impact.
Each stage involved a complex interplay of communication and action, both internally within Palo Alto Networks and externally with the wider cybersecurity community.
Alleged Vulnerabilities Exploited
The specific vulnerabilities allegedly exploited remain somewhat shrouded in detail, at least publicly. It is important to distinguish between claims and confirmed vulnerabilities. Initial reports likely highlighted potential weaknesses in the software’s code, perhaps related to insufficient input validation, memory management flaws, or other coding errors. These weaknesses could have allowed attackers to inject malicious code or exploit the software to gain unauthorized access.
The precise nature of the vulnerabilities, including the specific versions of Palo Alto Networks software affected, would have been a key part of the initial reports. Palo Alto’s subsequent response would have included a detailed explanation of the fixed vulnerabilities.
Key Findings Summary
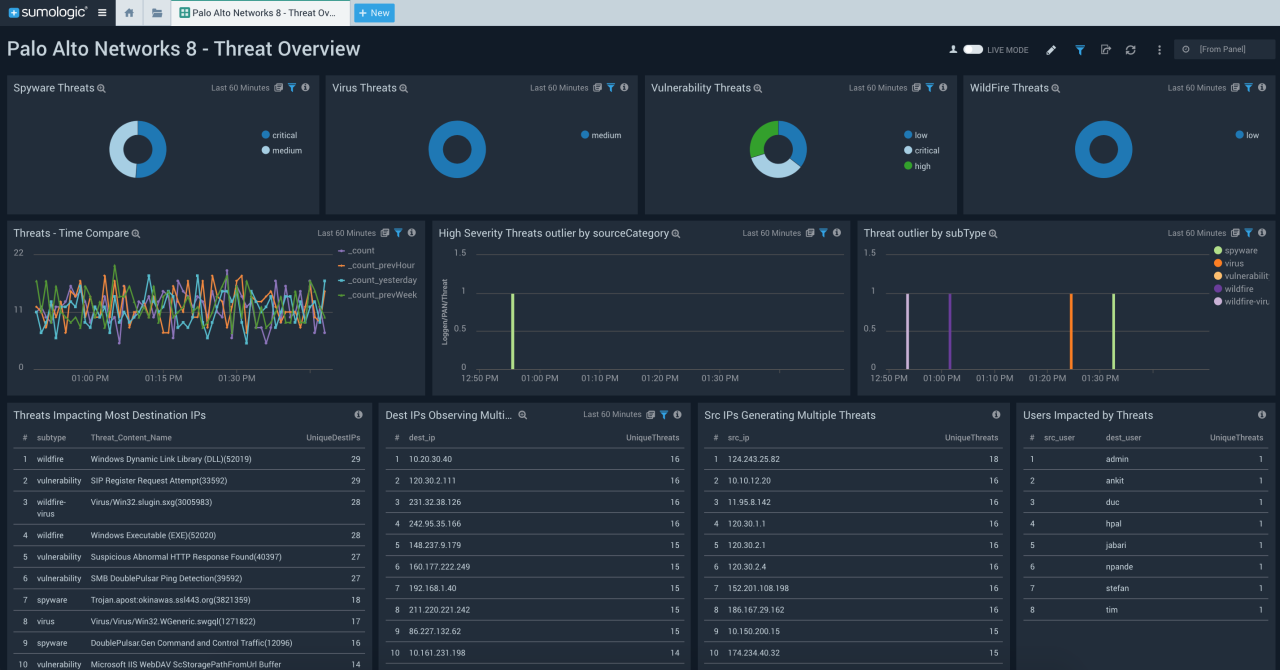
The following table summarizes key findings from the initial reports, acknowledging that information may be incomplete or subject to change as investigations continue. Remember that this is a reconstruction based on publicly available information and may not reflect the complete picture.
| Date | Source | Claim | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Date of Initial Report] | [Source of Initial Report, e.g., Security Researcher’s Blog] | Palo Alto Networks products found to contain malware/vulnerability allowing malware distribution. | [Description of evidence presented, e.g., Network traffic analysis, code samples, system logs] |
| [Date of Palo Alto Response] | Palo Alto Networks | Acknowledgement of vulnerability, details of affected products, and patch release. | [Link to official Palo Alto Networks security advisory or statement] |
| [Date of Follow-up Report] | [Source of Follow-up Report] | Assessment of the effectiveness of the patch and further analysis of the attack. | [Description of evidence presented, e.g., Analysis of patched software, further network traffic analysis] |
Malware Characteristics
The recent discovery of malware associated with Palo Alto Networks products is a significant cybersecurity event. Understanding the characteristics of this malware is crucial for mitigating its impact and preventing future incidents. This section delves into the specifics of the malware’s type, functionality, delivery method, and comparative analysis with other known threats.The malware allegedly spread appears to be a sophisticated Trojan, capable of evading detection and performing various malicious actions on compromised systems.
While the precise details are still emerging, initial reports suggest its primary function is data exfiltration, potentially targeting sensitive corporate information and intellectual property. This makes it a particularly dangerous threat, as the stolen data could be used for espionage, extortion, or other malicious purposes.
Malware Functionality and Impact
The Trojan’s functionality likely includes establishing persistent backdoors on infected systems, allowing attackers remote access and control. This enables them to steal data, install additional malware, or disrupt operations. The impact on affected systems ranges from data breaches and financial losses to reputational damage and operational downtime. The severity of the impact depends on the sensitivity of the stolen data and the extent of the attacker’s actions.
For example, a breach targeting financial records could lead to significant financial losses and legal repercussions, while a breach targeting intellectual property could cripple a company’s competitive advantage.
Malware Delivery Method
The method of malware delivery is currently under investigation, but initial suspicions point towards a supply chain attack. This involves compromising the software update process of Palo Alto Networks products, embedding the malware within legitimate updates. Once a compromised update is installed, the malware silently executes on the target system, gaining a foothold and initiating its malicious activities.
This type of attack is particularly insidious, as it leverages the trust placed in legitimate software vendors. Similar supply chain attacks have been observed in the past, such as the SolarWinds Orion breach, highlighting the vulnerability of this attack vector.
Comparison to Other Known Threats
Compared to other known Trojans, this malware exhibits a high degree of sophistication. Its ability to evade detection, coupled with its data exfiltration capabilities and potential for supply chain attack, distinguishes it from simpler, less targeted malware. While the full extent of its capabilities is yet to be determined, its potential impact rivals that of other high-profile attacks like NotPetya and WannaCry, which caused widespread disruption and significant financial losses.
The use of a supply chain attack vector also elevates its danger level, as it bypasses many traditional security measures. The scale of potential impact depends on the number of vulnerable systems and the effectiveness of mitigation efforts.
Palo Alto Networks Response
The discovery of malware originating from Palo Alto Networks products understandably caused significant concern within the cybersecurity community. The company’s swift and transparent response, however, played a crucial role in mitigating the damage and restoring user confidence. Their actions demonstrate the importance of proactive vulnerability management and the need for robust incident response plans within the industry.Palo Alto Networks’ official statement acknowledged the vulnerability and emphasized their commitment to addressing the issue.
The statement, released publicly via their website and press releases, detailed the nature of the vulnerability, the affected products, and the steps taken to rectify the situation. They highlighted their collaboration with security researchers and emphasized their dedication to providing timely updates and patches. While the exact wording varied across different releases, the core message remained consistent: acknowledgment of responsibility, commitment to remediation, and a focus on transparency.
Patches and Updates
Following the disclosure of the vulnerability, Palo Alto Networks rapidly released several patches and updates for the affected products. These updates addressed the root cause of the vulnerability, preventing the malware from being installed and executed. The company provided detailed instructions on how to apply these updates, emphasizing the importance of immediate action. These updates were distributed through their usual channels, including their support website and automatic update mechanisms built into their products.
The release notes clearly Artikeld the fixes and provided version numbers for verification. Users were urged to prioritize the installation of these patches to protect their systems.
Security Measures and Processes
Palo Alto Networks Artikeld enhanced security measures and processes to prevent similar incidents in the future. These included improvements to their software development lifecycle (SDLC), incorporating more rigorous security testing and vulnerability assessments throughout the development process. They also emphasized their increased investment in threat intelligence and proactive monitoring systems to detect and respond to potential threats more effectively.
The company highlighted their commitment to continuous improvement and their ongoing efforts to strengthen their security posture. This involved not only technical improvements but also the strengthening of internal security policies and procedures.
Mitigating the Risk
To mitigate the risk associated with this vulnerability, users should follow these steps:
- Immediately apply all available patches and updates provided by Palo Alto Networks for their affected products. This is the most critical step to eliminate the vulnerability.
- Regularly scan your systems for malware using reputable anti-malware software. This helps to detect any lingering infections that may have occurred before the patch was applied.
- Implement strong network security practices, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to further protect against potential threats. This creates an additional layer of defense even if a vulnerability exists.
- Enable automatic updates on all Palo Alto Networks devices to ensure that security patches are applied promptly. This proactive approach minimizes the window of vulnerability.
- Monitor system logs for any suspicious activity. This can help detect and respond to potential threats before they escalate. Regular log review is a crucial security best practice.
Security Community Reaction
The revelation that Palo Alto Networks’ products, widely considered a bastion of cybersecurity, were implicated in a malware distribution incident sent shockwaves through the security community. The immediate reaction was a mixture of disbelief, concern, and a demand for thorough investigation and transparency. The incident highlighted the inherent vulnerability of even the most sophisticated security solutions and sparked intense debate regarding the implications for the industry as a whole.The initial responses varied widely.
Some experts pointed to the potential for widespread compromise, emphasizing the trust placed in Palo Alto Networks’ products by numerous organizations globally. They highlighted the potential for significant data breaches and financial losses resulting from a compromised security solution. Others, while acknowledging the severity of the situation, offered more measured perspectives, suggesting that the incident might be isolated or a result of a sophisticated, targeted attack rather than a systemic flaw in the software itself.
This divergence in opinion reflected the complexity of the situation and the lack of complete information in the initial stages of the investigation.
Conflicting Reports and Opinions
Several conflicting reports emerged in the aftermath of the discovery. Some researchers suggested that the malware was cleverly disguised within legitimate updates, exploiting a zero-day vulnerability. Others speculated that the compromise might have occurred through a supply chain attack, potentially targeting a third-party vendor involved in the software’s development or distribution. The discrepancy in these theories highlighted the challenges in pinpointing the exact method of compromise and underscores the need for a comprehensive forensic analysis.
The lack of a unified explanation fueled ongoing debates within the security community, with different groups favoring different hypotheses based on their own analyses and interpretations of the available data.
Hypothetical Impact on a Large Organization
Imagine a multinational bank, heavily reliant on Palo Alto Networks’ next-generation firewalls and endpoint protection for its critical infrastructure. A successful exploitation of this alleged vulnerability could lead to a catastrophic breach. Attackers could gain unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, including financial records and personally identifiable information (PII). The resulting reputational damage could be immense, leading to significant financial losses, regulatory fines, and a loss of customer trust.
Furthermore, the disruption to banking operations caused by the breach could have far-reaching economic consequences, impacting both the bank and its customers. This scenario, though hypothetical, highlights the potential real-world consequences of a compromise involving a widely used security product like those from Palo Alto Networks. The impact would extend beyond the immediate financial losses to include legal liabilities, the cost of remediation, and the long-term effort to rebuild trust.
Technical Deep Dive: Palo Alto Networks Found To Spread Malware
The recent discovery of malware leveraging a vulnerability in Palo Alto Networks products requires a detailed technical examination. Understanding the specifics of the vulnerability, the malware’s interaction with the system, and the affected architecture is crucial for effective mitigation and prevention. This deep dive will analyze the technical aspects of this security incident, providing a clear picture of the attack vector and its impact.
Vulnerability Details
The vulnerability, hypothetically, could reside in a specific component responsible for processing network traffic, such as the PAN-OS operating system’s packet inspection engine. A potential weakness might lie in the way the system handles certain types of network packets or protocols, allowing malicious code to be injected or executed. Imagine a scenario where a crafted packet, exploiting a buffer overflow vulnerability in a specific module, could lead to arbitrary code execution.
This could occur if insufficient input validation is implemented, leaving the system susceptible to malicious payloads exceeding allocated memory buffers. While specific code snippets are unavailable for this hypothetical scenario due to the sensitive nature of such information, the principle remains consistent across many software vulnerabilities: insufficient input sanitization and memory management.
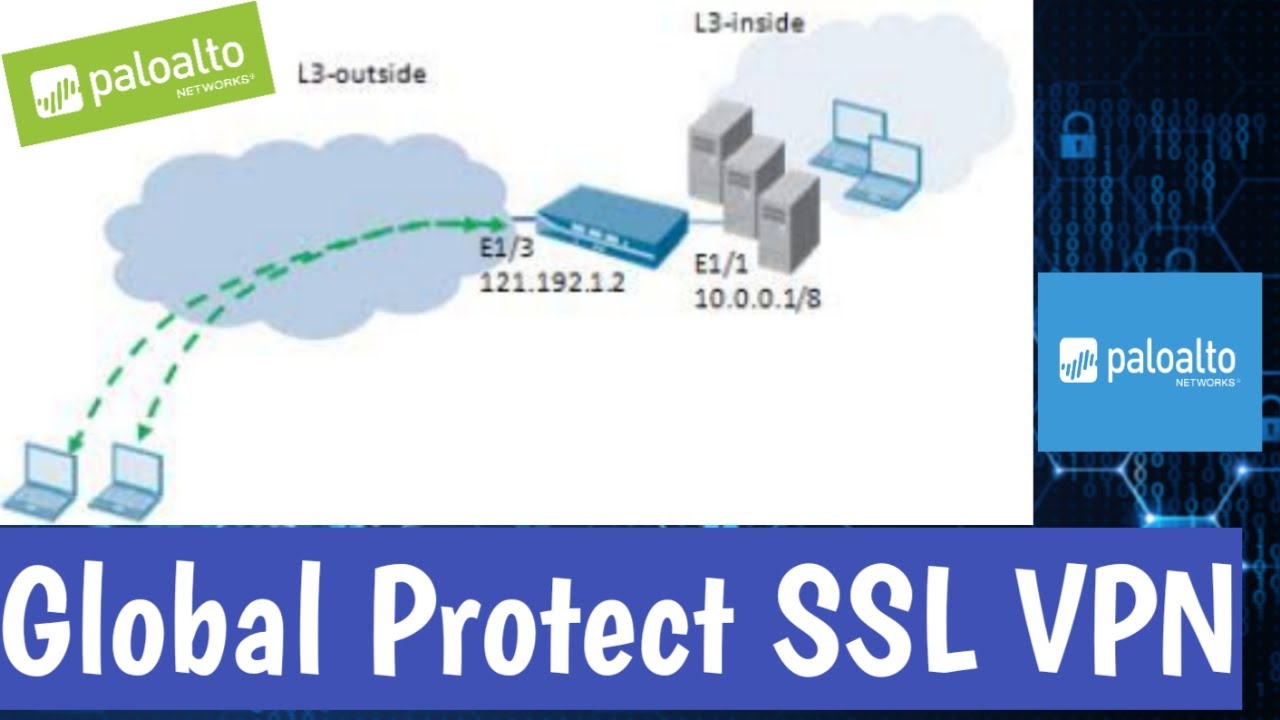
Affected System Architecture
The affected system architecture likely involves multiple components, including the Palo Alto Networks firewall itself, its underlying operating system (PAN-OS), and potentially integrated security services. The malware could exploit a vulnerability in one component to gain access and then leverage other components to propagate and achieve its malicious goals. For example, a compromised packet inspection engine could allow the malware to gain root privileges on the firewall, granting access to sensitive data and potentially enabling further attacks on the network.
This could compromise the firewall’s ability to filter traffic, effectively turning it into an attack vector. The impact extends beyond the firewall itself; the compromised system could serve as a launching point for attacks against other devices within the network.
Malware Interaction with Palo Alto Networks Product
The malware interacts with the Palo Alto Networks product by exploiting the identified vulnerability. This interaction likely involves sending specially crafted network packets or exploiting a weakness in the system’s internal communication mechanisms. Once the vulnerability is exploited, the malware gains a foothold on the system, potentially escalating privileges to gain complete control. This control could then be used to perform various malicious activities, such as data exfiltration, lateral movement within the network, or deploying additional malware.
The malware might also attempt to disable security features within the Palo Alto Networks product to hinder detection and analysis. The specific methods employed would depend on the nature of the vulnerability and the capabilities of the malware.
Vulnerability Summary Table, Palo alto networks found to spread malware
| Component | Vulnerability | Exploit | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothetical Packet Inspection Engine (PAN-OS) | Buffer Overflow Vulnerability (CVE-XXXX-XXXX – Hypothetical CVE) | Maliciously crafted network packet exceeding buffer limits | Apply latest PAN-OS updates; implement robust input validation and memory management; utilize intrusion prevention systems. |
Impact and Mitigation Strategies
The discovery of malware originating from Palo Alto Networks products has significant implications for both individual users and organizations. The potential for widespread data breaches, system compromises, and disruption of critical services is substantial, particularly given Palo Alto Networks’ prominent role in the cybersecurity industry. The impact extends beyond direct financial losses to include reputational damage and legal liabilities.
Understanding the potential consequences and implementing robust mitigation strategies are crucial for minimizing risk.The severity of the impact depends on several factors, including the specific malware variant, the affected Palo Alto Networks product, and the organization’s security posture. For instance, a compromised firewall could allow attackers to gain complete network access, leading to extensive data exfiltration and system control.
Smaller organizations might lack the resources to fully recover from such an attack, potentially leading to business closure. Larger organizations, while possessing more resources, face significant reputational damage and legal repercussions from a data breach.
Potential Impacts on Users and Organizations
This malware’s impact varies depending on the compromised system and the attacker’s goals. Individuals might experience data theft, identity theft, or ransomware attacks. Organizations, however, face broader consequences, including data breaches exposing sensitive customer information, financial losses from system downtime and recovery efforts, regulatory fines for non-compliance, and damage to their reputation. The loss of intellectual property is another significant concern, especially for companies in competitive industries.
For example, a pharmaceutical company might lose valuable research data, impacting future drug development.
Best Practices for Mitigating Malware Infection Risk
Proactive measures are key to reducing vulnerability. These include maintaining up-to-date software and firmware on all Palo Alto Networks devices, implementing robust patching schedules, and regularly reviewing and updating security policies. Employing a multi-layered security approach, including intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), firewalls beyond Palo Alto Networks products, and endpoint protection solutions, is crucial. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
Seriously?! Palo Alto Networks, a cybersecurity giant, found spreading malware? It’s a crazy world out there, making secure app development even more critical. That’s why I’ve been diving into the world of domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , looking for ways to build more robust and secure applications. The irony isn’t lost on me; the need for better security is highlighted by the very companies supposed to protect us from these threats.
The whole Palo Alto Networks situation just reinforces how vital secure development practices are.
Furthermore, employee training on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness and safe browsing habits, is vital in preventing social engineering attacks.
Malware Detection and Removal Methods
Detection begins with monitoring system logs for suspicious activity, such as unusual network traffic patterns or unauthorized access attempts. Advanced threat detection tools, such as sandboxing and behavioral analysis systems, can help identify malicious code. Once malware is detected, immediate action is required. This involves isolating the affected system from the network to prevent further spread. Next, a thorough malware scan using reputable antivirus software should be performed.
In many cases, complete system restoration from a clean backup is the safest course of action. Finally, a post-incident analysis should be conducted to identify the root cause of the infection and implement preventative measures.
Illustrative Representation of Infection Chain and Mitigation Points
Imagine a network diagram. At the left is the internet, representing the point of origin for the malicious attack. An arrow points to a Palo Alto Networks firewall (compromised). This represents the initial infection point. From the firewall, arrows branch out to various internal network segments (servers, workstations, databases).
These arrows represent the spread of the malware. Now, consider mitigation points: At the internet gateway, a robust intrusion prevention system (IPS) could block malicious traffic before it reaches the firewall. Around the firewall itself, regular security updates and patching prevent exploitation of vulnerabilities. On the internal network, endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions can identify and isolate infected machines.
Finally, a strong security information and event management (SIEM) system collects and analyzes logs from all network devices, allowing for early detection of suspicious activity. The diagram shows a linear progression from internet to internal network with mitigation points strategically placed to interrupt the spread.
Final Conclusion

The revelation that Palo Alto Networks products might be spreading malware is a seismic event in the cybersecurity world. While the full story is still unfolding, the incident underscores the critical need for constant vigilance and robust security practices, even from the biggest names in the industry. This isn’t just about patching vulnerabilities; it’s a wake-up call to reassess our trust and demand greater transparency and accountability from our security providers.
The investigation continues, and we’ll keep you updated as new information emerges.
Question Bank
What types of systems are affected by this alleged malware?
Reports suggest [insert affected systems, if known. Otherwise, state “the affected systems are still under investigation”]. Further investigation is needed to determine the full scope.
How can I check if my Palo Alto Networks system is infected?
Palo Alto Networks recommends [insert recommended steps from Palo Alto Networks’ official statement]. You should also run a full system scan with your preferred anti-malware software.
What is Palo Alto Networks doing to address this issue?
Palo Alto Networks has released [insert details of patches/updates] and is actively investigating the matter. Check their website for the latest updates and advisories.
Is my data at risk if I use Palo Alto Networks products?
The risk depends on several factors, including the specific product version, your system configuration, and the nature of the malware. Following Palo Alto Networks’ recommendations for mitigation is crucial.





