Perfecting Email Deliverability Sender Reputation
Perfecting email deliverability sender reputation is crucial for any business relying on email marketing. It’s not just about getting your emails into the inbox; it’s about ensuring they’re seen, read, and acted upon. This involves understanding the intricate dance between your email practices, your sender reputation, and the ever-evolving algorithms of email providers. We’ll explore the key elements, from authentication and list hygiene to content optimization and performance monitoring, to help you master the art of email deliverability and build a stellar sender reputation.
This journey involves mastering several key areas. First, we’ll dive into the technical aspects of email authentication, ensuring your emails are verifiable and trustworthy. Then, we’ll discuss building a positive sender reputation through consistent best practices and engaging content. We’ll also cover essential list management techniques, analyzing email performance data, and troubleshooting common deliverability problems. Finally, we’ll discuss choosing the right email sending infrastructure to support your email strategy and growth.
Understanding Email Deliverability
Getting your emails delivered to the inbox, not the spam folder, is crucial for any email marketing strategy. Email deliverability is the art and science of ensuring your messages reach their intended recipients successfully. It’s more than just hitting “send”; it’s about building a positive reputation with email providers and adhering to best practices that help your emails bypass spam filters.
Factors Influencing Email Deliverability, Perfecting email deliverability sender reputation
Numerous factors contribute to whether your emails land in the inbox or the spam folder. These factors can be broadly categorized into sender reputation, email content, and technical aspects of your email sending practices. A poor sender reputation can single-handedly sink your deliverability, while poor email content or technical issues can contribute to a negative reputation.
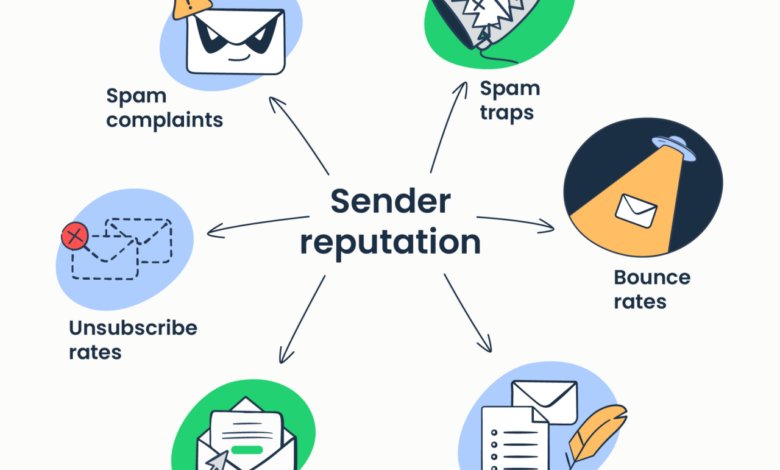
Sender Reputation’s Impact on Deliverability
Your sender reputation is arguably the most significant factor influencing email deliverability. It’s a score, often invisible to you, that email providers (like Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook) use to assess the trustworthiness of your email sending practices. A high sender reputation signifies that your emails are consistently legitimate, engaging, and not associated with spam. Conversely, a poor reputation flags your emails as potentially unwanted, leading to higher chances of landing in spam folders or even being blocked entirely.
This reputation is built over time based on various factors, including your email authentication, complaint rate, engagement rate, and the content of your emails. A single large-scale spam complaint can severely damage your reputation.
Setting Up Proper Email Authentication (SPF, DKIM, DMARC)
Proper email authentication is essential for establishing trust with email providers and improving your sender reputation. It helps verify that your emails are actually sent from your domain, preventing spoofing and phishing attempts. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): This DNS record specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. Setting this up involves adding a TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings. The record lists the IP addresses or domains of your authorized sending servers. For example, a simple SPF record might look like this:
v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.1 ip4:10.0.0.1 ~all.This record allows emails from the specified IP addresses. The
~allqualifier means that emails from other sources will be treated as soft fails (not necessarily blocked, but flagged). - DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): This method uses public-private key cryptography to digitally sign your emails, verifying their authenticity. You’ll need to generate a key pair (public and private) and add the public key as a TXT record to your DNS. The private key is used by your email sending server to sign each email. This adds an extra layer of verification to your emails.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance): DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM, providing instructions to email providers on how to handle emails that fail authentication. It allows you to specify a policy (reject, quarantine, or none) for emails that don’t pass SPF and DKIM checks. This helps protect your domain from email spoofing and phishing attempts. You’ll need to add a TXT record to your DNS specifying your DMARC policy.
Comparison of Email Authentication Methods
| Method | Description | Impact on Deliverability | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPF | Verifies sending server IP addresses | Improves deliverability by preventing spoofing | Relatively easy |
| DKIM | Digitally signs emails to verify authenticity | Significantly improves deliverability and builds trust | Moderate |
| DMARC | Defines policy for handling authentication failures | Further enhances deliverability and protects against spoofing | Moderate to High |
Building a Positive Sender Reputation
Your sender reputation is the lifeblood of your email marketing efforts. It’s the invisible scorecard that determines whether your emails land in the inbox or the spam folder. Building a strong reputation takes time and consistent effort, but the rewards – higher open rates, increased engagement, and ultimately, better ROI – are well worth the investment. A positive sender reputation is built on trust and reliability, proving to email providers that you’re a legitimate sender delivering valuable content.Building a positive sender reputation requires a multi-faceted approach.
It’s not just about avoiding spammy practices; it’s about actively demonstrating to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and email clients that your emails are wanted and valuable. This involves careful list management, authentic content, and consistent monitoring of your email metrics. Neglecting these aspects can have severe repercussions, leading to decreased deliverability and significant financial losses.
Consequences of a Poor Sender Reputation
A damaged sender reputation translates directly into fewer emails reaching the inbox. Email providers, like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook, employ sophisticated algorithms to filter out unwanted or suspicious emails. If your sender reputation is poor, your emails will be flagged as spam, landing in the spam folder or even being blocked entirely. This results in a dramatic drop in open and click-through rates, diminishing your marketing campaign’s effectiveness.
For businesses relying heavily on email marketing, a poor sender reputation can significantly impact revenue and customer acquisition. Imagine a scenario where only 10% of your marketing emails reach your target audience – a substantial loss of potential engagement and conversions. Furthermore, rebuilding a tarnished reputation is a lengthy and challenging process, often requiring significant effort and investment.
Strategies for Improving Email Engagement
Improving email engagement, specifically open and click-through rates (CTR), is crucial for building a positive sender reputation. High engagement signals to email providers that your subscribers actively want to receive your emails. This can be achieved through several key strategies. First, ensure your subject lines are compelling and relevant to the recipient. Use A/B testing to determine which subject lines perform best.
Second, personalize your emails as much as possible. Using the recipient’s name and tailoring the content to their interests dramatically improves engagement. Third, focus on providing valuable and relevant content. Avoid generic or promotional emails; instead, offer insightful information, exclusive deals, or helpful resources that genuinely benefit the subscriber. Finally, regularly clean your email list to remove inactive or unengaged subscribers.
Sending emails to inactive addresses can negatively impact your sender reputation.
Checklist for Maintaining a Positive Sender Reputation
Proactive measures are vital to avoid damaging your sender reputation. This checklist summarizes key actions to take:
- Authenticate your emails: Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify your sender identity and prevent spoofing.
- Maintain a clean email list: Regularly remove inactive or bounced email addresses.
- Avoid spam triggers: Refrain from using excessive capitalization, excessive exclamation points, or deceptive subject lines.
- Get explicit consent: Ensure all subscribers have explicitly opted in to receive your emails.
- Monitor your email metrics: Track open rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates to identify areas for improvement.
- Provide a clear unsubscribe option: Make it easy for subscribers to unsubscribe from your emails.
- Segment your audience: Send targeted emails to specific groups based on their interests and behavior.
- Use a reputable email service provider (ESP): Choose an ESP with a strong track record of deliverability.
Following these guidelines will significantly contribute to building and maintaining a positive sender reputation, ultimately leading to improved email deliverability and a more effective email marketing strategy.
Email List Hygiene and Management
Maintaining a clean and healthy email list is paramount for achieving optimal email deliverability and maximizing your marketing ROI. A list cluttered with inactive, invalid, or unengaged email addresses can significantly harm your sender reputation, leading to your emails being flagged as spam and ultimately hindering your ability to reach your intended audience. Regular list hygiene practices are essential for preventing this.
Effective email list management goes beyond simply collecting addresses. It involves proactive strategies to ensure your list remains relevant, engaged, and free from problematic entries. This, in turn, improves your email deliverability rates and strengthens your relationship with your subscribers.
Email List Cleaning and Maintenance Methods
Regularly cleaning your email list is crucial for maintaining a healthy sender reputation. This involves identifying and removing inactive, invalid, and unengaged email addresses. Several methods can facilitate this process. These include employing email verification services to identify bad email addresses, analyzing bounce rates to identify consistently failing addresses, and segmenting your list to identify inactive subscribers based on their engagement levels (e.g., no opens or clicks in the past six months).
Removing these addresses prevents them from negatively impacting your sender score. Furthermore, employing automated processes, like suppressing bounced emails automatically, simplifies this maintenance.
Removing Inactive or Invalid Email Addresses
The importance of removing inactive or invalid email addresses cannot be overstated. These addresses contribute to higher bounce rates, a key indicator of poor sender reputation. High bounce rates signal to email providers that your list is unreliable, leading to your emails being classified as spam. Regularly purging your list of inactive subscribers—those who haven’t engaged with your emails for a specified period—is crucial.
Similarly, consistently removing hard bounces (permanently undeliverable addresses) and soft bounces (temporarily undeliverable addresses that persist after multiple attempts) improves your sender reputation and prevents further damage to your deliverability. For example, if you have a 20% bounce rate, that means for every 100 emails sent, 20 fail to reach the inbox. Removing these addresses significantly reduces that percentage, improving deliverability.
Double Opt-in Procedures for Building a Legitimate List
Implementing a double opt-in procedure is a best practice for building a legitimate and engaged email list. This method requires subscribers to confirm their email address after initially signing up. They receive a confirmation email containing a link that they must click to verify their subscription. This two-step process ensures that only genuinely interested individuals are added to your list, significantly reducing the likelihood of spam complaints and improving your sender reputation.
This verification process helps build a more targeted and responsive audience, ultimately improving your email campaign performance. For example, a company implementing a double opt-in procedure might see a significant decrease in unsubscribe rates compared to a company using a single opt-in procedure.
Effective Email List Segmentation Strategies
Segmenting your email list allows you to send more targeted and relevant messages, leading to higher engagement rates and improved deliverability. By dividing your subscribers into smaller, more homogeneous groups based on shared characteristics, you can tailor your email content to their specific interests and needs. This personalization increases the likelihood of opens, clicks, and conversions, all of which positively impact your sender reputation.
- Segmenting by demographics: Dividing your list based on age, location, gender, or other demographic data allows for highly targeted messaging.
- Segmenting by purchase history: Targeting customers based on their past purchases allows for personalized product recommendations and targeted promotions.
- Segmenting by engagement level: Separating highly engaged subscribers from less engaged ones allows for tailored communication strategies, potentially re-engaging inactive subscribers.
- Segmenting by website behavior: Tracking website activity and segmenting based on pages visited or products viewed enables highly personalized recommendations and offers.
Monitoring and Analyzing Email Performance
Maintaining optimal email deliverability requires consistent monitoring and analysis. By tracking key metrics and interpreting the data effectively, you can proactively identify and resolve potential issues before they significantly impact your sender reputation and campaign success. This proactive approach is crucial for ensuring your emails reach the inbox consistently.
Key Metrics for Email Deliverability and Sender Reputation
Tracking the right metrics provides a clear picture of your email performance. Understanding these metrics allows for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement. Key metrics fall into several categories: deliverability, engagement, and bounce rates.
- Delivery Rate: The percentage of emails successfully delivered to recipients’ inboxes. A low delivery rate signals potential deliverability problems.
- Open Rate: The percentage of recipients who opened your email. Low open rates might indicate issues with subject lines, sender reputation, or content relevance.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of recipients who clicked a link in your email. Low CTR suggests problems with your call to action, email content, or overall campaign relevance.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of emails that were not delivered. High bounce rates indicate problems with your email list hygiene or technical issues.
- Spam Complaint Rate: The percentage of recipients who marked your email as spam. A high spam complaint rate significantly damages your sender reputation.
- Unsubscribe Rate: The percentage of recipients who unsubscribed from your email list. While some unsubscribes are inevitable, a high rate might point to issues with content relevance or email frequency.
Email Performance Dashboard Visualization
A well-organized dashboard provides a clear, at-a-glance view of your email performance. This allows for quick identification of trends and potential problems. Below is a suggested HTML table structure for such a dashboard:
| Metric | Current Value | Previous Period Value | Trend | Target |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Rate | 95% | 92% | Up 3% | 98% |
| Open Rate | 20% | 18% | Up 2% | 25% |
| Click-Through Rate | 5% | 4% | Up 1% | 8% |
| Bounce Rate | 2% | 3% | Down 1% | 1% |
| Spam Complaint Rate | 0.1% | 0.2% | Down 0.1% | 0.05% |
| Unsubscribe Rate | 1% | 1.2% | Down 0.2% | 0.8% |
Interpreting Email Deliverability Reports
Different email service providers (ESPs) offer varying levels of detail in their deliverability reports. However, common elements include bounce rate breakdowns (hard vs. soft bounces), spam complaint rates, and recipient engagement metrics. For example, a high hard bounce rate suggests invalid email addresses on your list, while a high soft bounce rate might indicate temporary server issues. A detailed analysis of these reports is essential for identifying the root causes of deliverability problems.
Consider reviewing reports from your ESP, as well as using third-party deliverability tools for a more comprehensive view.
Identifying and Addressing Deliverability Issues
Analyzing your email performance data allows you to identify and address deliverability problems effectively. For instance, a consistently high bounce rate indicates a need for list hygiene improvements, such as removing invalid email addresses. A high spam complaint rate might require refining your email content, subject lines, or sender authentication. Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- List Cleaning: Regularly remove invalid or inactive email addresses from your list.
- Authentication: Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify your email’s authenticity.
- Content Optimization: Ensure your email content is engaging, relevant, and complies with best practices.
- Sender Reputation Management: Build a positive sender reputation through consistent email sending practices and engagement.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Continuously monitor your metrics and adjust your strategies based on the data.
Handling Email Deliverability Problems: Perfecting Email Deliverability Sender Reputation
Maintaining a healthy sender reputation is crucial for successful email marketing. However, even with the best practices in place, challenges can arise, impacting your email deliverability. Understanding these challenges and having a plan to address them is vital for keeping your emails reaching the inbox. This section Artikels common problems, solutions, and a recovery process.
Common Email Deliverability Challenges and Their Solutions
Several factors can negatively affect email deliverability. These range from technical issues to content-related problems. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach focusing on both technical infrastructure and email content.
- Low Engagement Rates: High unsubscribe rates, low open rates, and minimal click-through rates signal to ISPs that your emails are unwanted. Solution: Improve email content relevance, personalize messages, segment your audience effectively, and use compelling subject lines.
- Spam Traps and Complaint Filters: Sending emails to spam traps (email addresses designed to catch spam) or triggering complaint filters (users marking your emails as spam) significantly damages your sender reputation. Solution: Maintain a clean email list, regularly remove inactive subscribers, and ensure your content complies with anti-spam regulations.
- Authentication Issues: Lack of proper authentication methods like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC makes it easier for ISPs to identify your emails as fraudulent. Solution: Implement and verify all three authentication protocols. This proves your email’s authenticity and protects against spoofing.
- IP Address Reputation: If your IP address has been associated with spam in the past, your emails are more likely to be flagged. Solution: Use a reputable email sending service with a clean IP reputation. Avoid sending bulk emails from free or shared email accounts.
- Content-Related Issues: Using excessive spam triggers (e.g., excessive use of ALL CAPS, misleading subject lines, or excessive links) can lead to your emails being filtered as spam. Solution: Follow email best practices for content, avoiding spam trigger words and phrases. Ensure your content is relevant and engaging.
Appealing to ISPs After Being Blacklisted
Being blacklisted by an ISP is a serious setback, but not necessarily insurmountable. A structured approach is crucial.
- Identify the Blacklist: Determine which blacklist(s) have flagged your IP address or domain. Several online tools can help identify this.
- Analyze Your Sending Practices: Thoroughly review your email sending practices, focusing on the points discussed above (engagement, authentication, etc.). Identify any potential issues.
- Prepare a Remediation Plan: Artikel the steps you’ve taken to correct the identified problems. This should include data showing improved authentication, engagement, and list hygiene.
- Contact the ISP: Contact the relevant ISP’s abuse department. Clearly explain the situation, the steps you’ve taken to remedy the problem, and request delisting. Provide supporting evidence.
- Monitor Your Reputation: After submitting your appeal, continue to monitor your sender reputation using online tools to ensure your emails are being delivered successfully.
Recovering From a Damaged Sender Reputation
Recovering from a damaged sender reputation takes time and consistent effort. Focus on regaining trust with ISPs and subscribers.
The process involves implementing the solutions Artikeld in the previous sections, and actively monitoring your email deliverability metrics. Consistent improvement in your email sending practices, coupled with proactive engagement with ISPs, is key to restoring your sender reputation. This is a long-term strategy requiring patience and persistent attention to detail.
Troubleshooting Deliverability Issues: A Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart where the starting point is “Email Deliverability Issue Detected?”. If yes, the next step is “Identify the Problem (low engagement, blacklist, etc.)?”. Following this, a decision point branches based on the identified problem: “Is it a technical issue (authentication, IP reputation)?” If yes, then “Implement solutions (SPF, DKIM, DMARC, IP warming)”. If no, then “Is it a content-related issue (spam triggers, irrelevant content)?” If yes, “Improve content relevance, remove spam triggers”.
If no, then “Is it a list hygiene issue?” If yes, “Clean email list, remove inactive subscribers”. Each of these branches eventually leads back to a final check: “Re-evaluate email deliverability metrics”. This loop continues until the issue is resolved.
Email Content and Deliverability
Your email’s content plays a surprisingly significant role in its ability to reach the inbox. Spam filters are sophisticated algorithms designed to identify and block unwanted emails, and they analyze various aspects of your email, including its content, to determine whether it’s legitimate or spam. Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing your email marketing campaigns and ensuring high deliverability rates.
Spam filters employ a complex set of rules and machine learning algorithms to analyze email content. They look for patterns and characteristics commonly associated with spam, such as excessive use of capital letters, suspicious links, and the presence of certain s. The more red flags an email raises, the higher the likelihood it will be flagged as spam and sent to the junk folder.
Spam Filter Analysis of Email Content
Spam filters examine various elements within your email to assess its legitimacy. This includes analyzing the text for spammy s, evaluating the image-to-text ratio, scrutinizing links for suspicious patterns, and assessing the overall structure and formatting of the email. A high proportion of images with little text, for instance, can trigger spam filters. Similarly, broken or misleading links are major red flags.
Perfecting email deliverability and sender reputation is crucial for any business. Building a strong reputation takes time and consistent effort, but the payoff is huge. Think of it like building a robust application – you need a solid foundation, much like the considerations discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , where architectural choices impact long-term success.
Ultimately, both require strategic planning and careful execution to achieve optimal results; a well-maintained sender reputation is as important as a well-designed application.
The algorithms constantly evolve, learning from new spam techniques and adapting their filtering criteria.
Techniques for Optimizing Email Content for Better Deliverability
Optimizing your email content is about minimizing the chances of triggering spam filters. This involves carefully crafting your email’s text, images, and links to create a message that appears legitimate and trustworthy to these filters. Key strategies include using a healthy text-to-image ratio, avoiding spammy s, and employing clear and concise language. Regularly testing and analyzing your email performance helps refine your approach and improve your deliverability over time.
Examples of Email Subject Lines Less Likely to Trigger Spam Filters
The subject line is often the first point of contact between your email and a spam filter. A poorly crafted subject line can instantly mark your email as suspicious. Therefore, using clear, concise, and relevant subject lines is crucial.
Here are a few examples of subject lines that are less likely to trigger spam filters:
- Order Confirmation #12345
- Your Weekly Newsletter
- Important Update Regarding Your Account
- Meeting Reminder: Project X Discussion
- Thank You for Your Recent Purchase
Notice these subject lines are straightforward, avoid using excessive capitalization or exclamation points, and clearly communicate the email’s purpose.
Choosing the Right Email Sending Infrastructure
Your email sending infrastructure is the backbone of your deliverability. Choosing the right one significantly impacts whether your emails land in the inbox or the spam folder. The platform you select dictates your sending capabilities, reputation management tools, and overall effectiveness in reaching your audience. This choice isn’t just about cost; it’s a strategic decision affecting your marketing ROI.
Several factors need careful consideration when selecting an email sending platform. These include the volume of emails you send, your budget, the level of technical expertise you possess, and the specific features you require for managing your email campaigns. Different platforms cater to different needs, from small businesses sending occasional newsletters to large enterprises managing millions of transactional emails daily.
Transactional vs. Bulk Email Services
Transactional emails, like order confirmations or password resets, require a different approach than bulk marketing emails. Transactional services prioritize reliability and speed, ensuring timely delivery of crucial information. Bulk email services, on the other hand, focus on campaign management, list segmentation, and analytics, allowing for targeted marketing efforts. Using the wrong service type can severely hamper your deliverability. Transactional emails sent through a bulk platform might trigger spam filters, while marketing emails sent via a transactional service lack the features for effective campaign management.
Transactional email services excel at individual, time-sensitive messages. They prioritize immediate delivery and often offer robust features for managing bounces and ensuring reliable delivery to individual recipients. Bulk email services, however, are designed for large-scale campaigns. They offer features such as list segmentation, A/B testing, and detailed analytics to optimize campaign performance. The choice depends entirely on your primary email sending needs.
Comparing Email Sending Platforms
The market offers a variety of email sending platforms, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some popular options include SendGrid, Mailchimp, Amazon SES, and Constant Contact. These platforms differ in pricing models (pay-as-you-go, subscription-based), features (automation, analytics, segmentation), and the level of technical expertise required.
For instance, SendGrid offers a robust and scalable infrastructure suitable for high-volume transactional and marketing emails. Mailchimp is known for its user-friendly interface and features geared towards small to medium-sized businesses. Amazon SES provides a cost-effective solution for large-scale email sending, but requires more technical expertise to set up and manage. Constant Contact is a popular choice for simpler marketing campaigns with a focus on ease of use.
The best choice depends on your specific requirements and resources.
The Importance of Choosing a Reputable Email Service Provider
Selecting a reputable Email Service Provider (ESP) is crucial for maintaining a positive sender reputation. A provider with a strong track record and robust infrastructure is less likely to have its IP addresses blacklisted, thus ensuring higher deliverability rates. A reputable ESP also provides tools and support to help you manage your sender reputation, such as authentication methods (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) and deliverability monitoring.
Reputable ESPs invest heavily in maintaining their infrastructure and ensuring compliance with industry best practices. This includes implementing measures to prevent their servers from being used for malicious activities, which directly contributes to the overall sender reputation and deliverability of their clients. Choosing an unreliable provider can lead to significant email deliverability problems, harming your brand’s reputation and marketing effectiveness.
Selecting an Email Sending Infrastructure Based on Specific Needs
Before choosing an email sending platform, carefully assess your needs. Consider your email volume, budget, technical expertise, and desired features. Start by defining your email marketing goals. Are you primarily sending transactional emails or marketing campaigns? What level of automation and analytics do you require?
What is your budget for email marketing software? Answering these questions will help narrow down the options.
For example, a small e-commerce business with a low email volume and limited technical expertise might opt for a user-friendly platform like Mailchimp. A large enterprise with a high email volume and a dedicated IT team might choose a more scalable and customizable solution like SendGrid or Amazon SES. A company focused solely on transactional emails might benefit from a specialized transactional email service.
The ideal solution will depend on the unique needs and resources of each organization.
Final Conclusion
Ultimately, perfecting email deliverability and sender reputation is an ongoing process, not a destination. By consistently implementing best practices, monitoring your performance, and adapting to changes in the email landscape, you can significantly improve your email deliverability and build a strong sender reputation. This leads to increased engagement, better ROI on your email marketing efforts, and ultimately, a healthier and more profitable business.
Remember, a healthy sender reputation isn’t just about avoiding the spam folder—it’s about building trust and fostering meaningful connections with your audience.
Common Queries
What happens if my sender reputation is damaged?
A damaged sender reputation can result in your emails being marked as spam, filtered out by ISPs, and ultimately failing to reach your intended recipients. This can severely impact your marketing campaigns and business growth.
How often should I clean my email list?
Regularly cleaning your email list is recommended, ideally at least quarterly, to remove inactive or invalid email addresses. The frequency depends on your email list size and growth rate.
What are some examples of email content that might trigger spam filters?
Excessive use of ALL CAPS, excessive use of exclamation points, suspicious links, and generic subject lines are common culprits.
Can I recover from being blacklisted?
Yes, but it requires a thorough investigation of the cause, implementing corrective measures, and submitting an appeal to the relevant ISPs. This process can take time and effort.
