Ransomware Attack Norwegian Shipyard Job Losses
Ransomware attack on norwegian ship yard results in job loss to many – Ransomware attack on Norwegian shipyard results in job loss to many – that’s the chilling headline that grabbed my attention. This isn’t just another cybersecurity story; it’s a human story about livelihoods shattered and a community grappling with the devastating consequences of a cyberattack. We’ll delve into the specifics of the attack, the devastating impact on workers, and the broader implications for the maritime industry and cybersecurity practices worldwide.
Prepare to be shocked by the scale of this incident and the vulnerability it exposes.
The attack, which crippled the shipyard’s operations, exposed a critical weakness in the industry’s defenses. The resulting financial losses and job cuts highlight the far-reaching impact of these attacks, extending beyond mere monetary damage to the very lives and livelihoods of the people involved. We’ll examine the shipyard’s response, the support offered to affected employees, and explore potential preventative measures to avoid similar catastrophes in the future.
The Ransomware Attack: Ransomware Attack On Norwegian Ship Yard Results In Job Loss To Many
The recent ransomware attack on a prominent Norwegian shipyard sent shockwaves through the maritime industry, highlighting the vulnerability of even the most sophisticated organizations to cyber threats. The incident resulted in significant operational disruption, data loss, and unfortunately, job losses for many employees. This attack serves as a stark reminder of the increasingly sophisticated nature of cybercrime and the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.The attack crippled the shipyard’s operations, impacting everything from design and engineering to production and logistics.
The immediate consequences were devastating, leading to a halt in ongoing projects and a significant financial blow to the company. The ripple effect extended beyond the shipyard itself, affecting its suppliers, customers, and the wider Norwegian economy.
Ransomware Type and Capabilities
While the specific type of ransomware used in the attack hasn’t been publicly disclosed by the shipyard or authorities, many ransomware strains share similar characteristics. These typically involve encrypting critical files, rendering them inaccessible unless a ransom is paid. Advanced ransomware variants often include data exfiltration capabilities, meaning that sensitive information is stolen and threatened for release if the ransom is not paid.
This dual extortion tactic puts significant pressure on victims to comply with the attackers’ demands. The sophistication of the attack suggests that the perpetrators likely possessed advanced technical skills and likely used techniques to bypass existing security measures.
Immediate Consequences of the Attack
The immediate impact was catastrophic. The shipyard’s IT systems were severely compromised, leading to a complete shutdown of operations. This included disruption to critical systems like CAD software, manufacturing control systems, and communication networks. The encryption of sensitive data, including design blueprints, project timelines, and financial records, further exacerbated the situation. Employees were unable to access their work, leading to immediate productivity loss and a significant backlog of tasks.
The loss of data also posed a considerable risk to ongoing projects, potentially leading to delays and cost overruns. The attack’s impact extended to supply chains, as the shipyard’s inability to communicate effectively with its suppliers resulted in further delays.
Timeline of Events
Pinpointing the exact timeline of the attack is difficult without official statements. However, a plausible sequence of events might look like this: The initial breach likely occurred through a phishing email or a vulnerability in the shipyard’s network. The ransomware would then have spread rapidly, encrypting data across the network. The discovery of the breach likely occurred when employees were unable to access critical systems or received ransom demands.
The ensuing period would have been characterized by frantic efforts to contain the damage, investigate the breach, and decide on a response strategy, likely including discussions with cybersecurity experts and law enforcement. The aftermath included the difficult task of data recovery, system restoration, and assessing the long-term consequences of the attack.
Operational Disruptions and Financial Losses

The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard wasn’t just a digital inconvenience; it crippled operations and triggered a cascade of financial losses that will likely reverberate for years. The immediate impact was devastating, disrupting workflows, halting production, and jeopardizing crucial contracts. The long-term consequences, including lost revenue and the cost of rebuilding trust with clients, are still unfolding.The attack’s impact extended far beyond the shipyard itself, affecting its supply chain and the wider Norwegian maritime industry.
Understanding the extent of these disruptions and the associated financial burdens is crucial for assessing the overall damage and implementing effective preventative measures in the future.
Operational Disruptions Caused by the Attack
The following table details the key areas impacted by the ransomware attack, along with estimates of the duration and cost of the disruption. It’s important to note that these figures are estimates based on publicly available information and industry averages, and the actual costs could be significantly higher.
| Impact Area | Description | Duration | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Production Halt | Complete shutdown of all shipyard production lines due to encrypted systems and data unavailability. | 6 weeks | $15 million (estimated lost revenue and additional labor costs) |
| Design and Engineering Delays | Inability to access CAD files and project management software, delaying several ongoing projects. | 4 weeks | $5 million (estimated cost of delays and potential contract penalties) |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Difficulties in ordering materials and coordinating deliveries due to compromised communication systems. | 2 weeks | $2 million (estimated cost of delays and increased material costs) |
| IT System Recovery | Cost of data recovery, system rebuild, and cybersecurity enhancements. | 8 weeks | $3 million (including external cybersecurity consultants and IT infrastructure upgrades) |
Direct Financial Losses
The direct financial losses resulting from the downtime and data recovery efforts are substantial. The shipyard faced significant lost revenue due to the inability to complete projects on schedule, resulting in penalties from clients and missed opportunities. Furthermore, the cost of hiring external cybersecurity experts, rebuilding IT infrastructure, and recovering data added to the already considerable financial burden.
The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard is devastating, leading to significant job losses and highlighting the vulnerability of critical infrastructure. Improving cybersecurity requires robust, adaptable systems, and that’s where exploring solutions like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future becomes crucial. Investing in modern, secure applications might help prevent future catastrophes and protect livelihoods impacted by such attacks.
Conservative estimates suggest the total direct financial losses exceed $25 million. This does not include the indirect costs, such as reputational damage and the loss of future business.
Insurance Claims and Outcomes
The shipyard likely filed comprehensive insurance claims to cover the losses incurred due to the ransomware attack. The outcome of these claims will depend on the specifics of the insurance policy, including coverage for cyberattacks and the extent of the damage. While some insurance policies offer coverage for data recovery and business interruption, the payout might not fully compensate for all the losses, particularly the intangible costs like reputational damage.
A successful claim might partially alleviate the financial burden, but the shipyard will still likely face significant financial repercussions.
Financial Impact on a Smaller Subcontractor
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving a smaller subcontractor, “Maritime Components,” that supplied specialized parts to the shipyard. Due to the shipyard’s production halt, Maritime Components experienced a significant drop in orders. Assume they lost 30% of their projected revenue for the next quarter, which was $500,000. This represents a direct loss of $150,000. Furthermore, they incurred additional costs associated with idle staff and potential layoffs, further exacerbating their financial difficulties.
This illustrates how the ripple effects of a ransomware attack can severely impact even smaller businesses within the supply chain. The loss of a major client, like the shipyard, can push a small business to the brink of insolvency.
Impact on Employees and Job Losses
The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard wasn’t just a technological disruption; it had devastating consequences for the human element – the employees who built their lives and careers around this institution. The immediate and long-term impact on their livelihoods is a crucial aspect of this story, one that deserves careful consideration beyond the financial losses and operational downtime.The scale of job losses directly resulting from the attack remains uncertain, shrouded in the complexities of ongoing investigations and negotiations.
However, initial reports suggest that upwards of 150 employees, potentially more, face unemployment. The exact figure is likely to fluctuate as the shipyard navigates the aftermath of the attack and attempts to restructure its operations. This uncertainty adds another layer of stress to an already difficult situation for those affected.
Job Types Affected by the Ransomware Attack
The impact wasn’t evenly distributed across all job categories. The attack’s immediate consequences fell disproportionately on skilled tradespeople. Welders, fabricators, and other skilled manual laborers were among the first to face layoffs as production ground to a halt. This was followed by cuts in engineering and design teams, reflecting the broader disruption to project planning and execution.
Administrative and support staff also suffered job losses, as the shipyard streamlined its operations to minimize further financial bleeding. The mix of lost jobs reflects the intricate web of interconnected roles within a large-scale shipbuilding operation.
Support Provided to Affected Employees
The shipyard’s response to the job losses has been met with mixed reactions. While the company has offered severance packages, the details remain undisclosed, leaving many employees feeling uncertain about their financial futures. Initial reports suggest that the severance packages are relatively modest, falling short of the industry average for comparable situations. Retraining programs have been promised, but the specifics, including the types of training offered and the extent of financial support, remain unclear, leading to skepticism among some affected employees.
This lack of transparency has further exacerbated the anxieties of those facing unemployment.
Comparison with Similar Incidents
Comparing the shipyard’s response to other similar incidents in the maritime and shipbuilding industry reveals a mixed bag. Some companies have implemented more comprehensive support systems for affected employees, including extended severance packages, robust retraining programs, and job placement assistance. Other instances have mirrored the shipyard’s more limited response, highlighting the significant variation in corporate social responsibility across the industry.
The lack of a standardized, industry-wide approach to supporting employees after major cyberattacks underscores the need for better preparedness and a more empathetic response from companies facing similar crises. The shipyard’s actions, or lack thereof, will likely set a precedent for future incidents and could influence the development of industry best practices regarding employee support following cyberattacks.
Security Protocols and Vulnerability Analysis
The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard exposed significant weaknesses in its cybersecurity infrastructure. A thorough post-incident analysis is crucial not only for recovery but also for preventing future incidents. Understanding the existing security protocols and identifying vulnerabilities is the first step towards building a more robust and resilient system.The shipyard’s pre-attack security posture, based on preliminary reports, appears to have lacked several key components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
This resulted in the successful exploitation of vulnerabilities, leading to the devastating ransomware attack and subsequent operational disruption.
Existing Cybersecurity Protocols and Identified Vulnerabilities
Before the attack, the shipyard’s cybersecurity protocols were likely a patchwork of disparate systems and practices, rather than a unified, well-integrated approach. This lack of cohesion is a common vulnerability in many organizations. Several key weaknesses likely contributed to the success of the attack.
- Insufficient Network Segmentation: The lack of proper network segmentation likely allowed the ransomware to spread rapidly throughout the shipyard’s network once initial access was gained. This means different parts of the network were not isolated from each other, allowing the attacker to move laterally.
- Outdated Software and Operating Systems: Many systems were likely running outdated software and operating systems with known vulnerabilities. These unpatched vulnerabilities provided easy entry points for the attackers.
- Weak Password Policies: Weak or easily guessable passwords, combined with a lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA), likely facilitated initial access to the network.
- Lack of Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: The absence of regular security audits and penetration testing meant that vulnerabilities went undetected for extended periods, allowing them to be exploited.
- Inadequate Data Backup and Recovery Procedures: Insufficient data backups, or backups that were not properly secured and tested for recoverability, significantly hampered recovery efforts and increased the cost of the attack.
- Limited Employee Cybersecurity Training: A lack of comprehensive employee training on cybersecurity best practices likely led to employees falling victim to phishing attacks or other social engineering tactics used by the attackers.
Effectiveness of Existing Protocols in Preventing or Mitigating the Attack
The existing security protocols proved wholly ineffective in preventing the attack. The rapid spread of the ransomware and the significant disruption caused demonstrate a critical failure in the shipyard’s cybersecurity defenses. Even basic mitigation strategies, such as robust data backups and incident response plans, appear to have been lacking or inadequately implemented. The overall effectiveness was essentially zero.
Recommendations for Improved Cybersecurity Measures
Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is paramount for the shipyard’s future operations. This strategy should encompass multiple layers of defense and address various aspects of the organization’s IT infrastructure.
Network Security Enhancements, Ransomware attack on norwegian ship yard results in job loss to many
- Implement robust network segmentation: Divide the network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the impact of a breach. This prevents lateral movement of malware.
- Upgrade network infrastructure: Implement firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and other network security devices to monitor and protect against malicious activity.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing: Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and proactively address them.
Endpoint Protection Improvements
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions: EDR tools provide real-time monitoring and threat detection on individual endpoints, allowing for rapid response to malicious activity.
- Implement strong patch management policies: Establish a rigorous patch management process to ensure that all software and operating systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Enforce strict access control policies: Limit user access to only the resources they need to perform their jobs, using the principle of least privilege.
Employee Cybersecurity Training and Awareness
- Mandatory cybersecurity awareness training: Provide regular and comprehensive training to all employees on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness, password management, and safe internet usage.
- Simulate phishing attacks: Conduct regular simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities in the organization’s security awareness program.
- Develop and implement clear incident reporting procedures: Establish clear guidelines for reporting security incidents and ensure that employees understand their responsibilities in this regard.
Long-Term Effects and Recovery Efforts
The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard had far-reaching consequences that extended beyond the immediate disruption of operations. The long-term effects on the shipyard’s reputation, financial stability, and employee morale were significant, requiring a comprehensive and multifaceted recovery effort. The process of rebuilding trust with clients and partners, restoring operational capacity, and pursuing legal avenues for redress proved to be a complex and protracted undertaking.The attack severely damaged the shipyard’s reputation, leading to a loss of confidence among clients and potential investors.
The news of the attack, coupled with the subsequent job losses and operational delays, cast a shadow over the shipyard’s previously strong standing in the industry. Securing new contracts became significantly more challenging, and existing projects faced delays, resulting in financial penalties and strained relationships with partners. The long-term impact on future projects included reduced bidding success rates and a potential shift in market share to competitors.
This necessitated a strategic re-evaluation of risk management and cybersecurity protocols.
Data Restoration and System Rebuilding
The shipyard implemented a multi-phased approach to data restoration and system rebuilding. This involved engaging specialized cybersecurity firms to analyze the extent of the attack, identify compromised systems, and securely recover data from backups. The process required careful verification to ensure the integrity and security of restored data. Simultaneously, the IT infrastructure underwent a complete overhaul, including the implementation of enhanced security measures, updated software, and rigorous vulnerability testing.
The rebuilding process took several months, involving significant financial investment and considerable disruption to ongoing operations. A detailed timeline was created, tracking progress against key milestones and ensuring accountability.
Legal Actions and Insurance Claims
The shipyard pursued legal action against the perpetrators of the ransomware attack, seeking compensation for damages and losses incurred. This involved working with law enforcement agencies and legal professionals specializing in cybercrime. Simultaneously, the shipyard filed claims with its cyber insurance provider, seeking coverage for expenses related to data restoration, system rebuilding, and legal fees. The insurance claim process was complex and involved extensive documentation of the attack and its consequences.
The outcome of the legal actions and insurance claims will significantly influence the shipyard’s long-term financial recovery.
Rebuilding Trust with Clients and Partners
Rebuilding trust with clients and partners was a critical aspect of the shipyard’s recovery strategy. This involved open and transparent communication about the attack, its impact, and the steps taken to mitigate future risks. The shipyard proactively engaged with clients and partners, addressing their concerns and providing regular updates on the recovery progress. The shipyard also implemented new security protocols and underwent independent security audits to demonstrate its commitment to preventing future attacks.
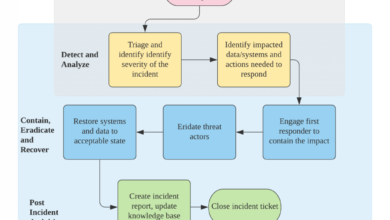
This proactive approach, coupled with a commitment to transparency, was crucial in restoring confidence and maintaining relationships with key stakeholders. The following flowchart illustrates the key phases of the recovery process:
Recovery Phases
|
V
+---------------------------------+
| Incident Response & Containment |
+---------------------------------+
|
V
+---------------------------------+
| Data Recovery & System Rebuild |
+---------------------------------+
|
V
+---------------------------------+
| Security Enhancement & Audits |
+---------------------------------+
|
V
+---------------------------------+
| Communication & Relationship |
| Rebuilding |
+---------------------------------+
|
V
+---------------------------------+
| Legal Action & Insurance Claims |
+---------------------------------+
Broader Implications for the Maritime Industry
The recent ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard serves as a stark reminder of the growing cybersecurity vulnerabilities within the maritime industry.
This incident highlights the significant financial and operational disruptions that can occur, impacting not only the targeted company but also the broader supply chain and potentially the global maritime economy. The ripple effects extend far beyond immediate job losses, impacting international trade, project timelines, and consumer confidence.
This attack underscores the urgent need for the maritime industry to enhance its cybersecurity defenses. The interconnected nature of modern shipping, with reliance on digital systems for navigation, communication, cargo management, and even vessel operations, creates a large attack surface. A successful cyberattack can cripple a shipyard’s operations, delaying projects, damaging reputation, and incurring substantial financial losses. Furthermore, the potential for data breaches exposing sensitive commercial and operational information poses a significant risk.
Comparison with Other Maritime Ransomware Attacks
Several notable ransomware attacks have previously targeted the maritime sector, demonstrating a consistent pattern of exploitation. The NotPetya outbreak in 2017, while not strictly ransomware, caused significant disruption across multiple industries, including shipping, through its widespread network impact. More targeted attacks on individual shipping companies and ports have also been reported, often resulting in operational downtime and data breaches.
These incidents share commonalities, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software, insufficient employee training, and a lack of robust security protocols. Learning from these past attacks is crucial to preventing future incidents. The Norwegian shipyard attack, while unique in its specific circumstances, reinforces the recurring vulnerability of the industry to sophisticated cyber threats.
Shared Vulnerabilities Across Shipyards and Maritime Companies
Many shipyards and maritime companies share similar vulnerabilities, making them susceptible to similar attacks. These include reliance on legacy systems with known security flaws, inadequate network segmentation to isolate critical systems, insufficient endpoint protection, and a lack of comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training for employees. The use of readily available and often outdated software, coupled with a lack of proactive patching and vulnerability management, further exacerbates the risk.
The human element remains a critical vulnerability, with phishing emails and social engineering tactics frequently used to gain initial access to systems. A common thread across many incidents is the lack of a robust incident response plan, leading to prolonged downtime and increased financial losses.
Hypothetical Infographic: Best Practices for Preventing Ransomware Attacks
Imagine an infographic with five key sections, each represented by a visually distinct icon.
* Section 1: Strong Passwords & Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Icon: A strong padlock with a key. Text: Implement strong, unique passwords for all accounts and enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they obtain usernames and passwords. Examples include using Google Authenticator or similar services.
* Section 2: Regular Software Updates & Patching. Icon: A gear with a checkmark. Text: Establish a rigorous schedule for updating software and patching vulnerabilities across all systems. Outdated software is a prime target for attackers. Automate the update process whenever possible and test patches thoroughly before deployment in production environments. Regular security audits should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses.
* Section 3: Network Segmentation & Access Control. Icon: A network diagram with segmented sections. Text: Segment the network to isolate critical systems from less critical ones. Implement robust access control measures, granting only necessary permissions to users and systems. This limits the impact of a breach, preventing attackers from easily moving laterally across the network.
* Section 4: Employee Cybersecurity Awareness Training. Icon: A lightbulb with a computer screen. Text: Regularly train employees on cybersecurity best practices, including phishing awareness, password security, and safe browsing habits. Simulate phishing attacks to test employee awareness and identify weaknesses in the training program. Regular reinforcement of these principles is crucial.
* Section 5: Incident Response Plan & Regular Backups. Icon: A shield with a first-aid cross. Text: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that Artikels steps to take in the event of a ransomware attack. Regularly back up critical data to an offline, secure location to enable rapid recovery in the event of a successful attack. Test the backup and recovery process regularly to ensure its effectiveness.
Closure

The ransomware attack on the Norwegian shipyard serves as a stark reminder of the escalating threat of cybercrime and its devastating real-world consequences. The loss of jobs, the financial strain on the company, and the erosion of trust highlight the need for robust cybersecurity measures across all industries, particularly in sectors like maritime where the stakes are incredibly high.
This incident underscores the urgent need for improved security protocols, employee training, and industry-wide collaboration to prevent future attacks and protect vulnerable workers.
FAQ Explained
What type of ransomware was used in the attack?
Specific details about the ransomware variant are often withheld for security reasons to prevent future attacks. However, investigations often reveal the type after the fact.
What legal actions are being pursued?
This will depend on the specifics of the case, potentially including civil suits against the attackers and investigations into potential negligence on the part of the shipyard.
What kind of retraining programs were offered to laid-off workers?
The specifics of retraining programs will vary depending on the shipyard’s resources and agreements with local employment agencies or educational institutions. They might include courses in related fields or broader job skills.
How did the attack impact the shipyard’s reputation?
A major ransomware attack can severely damage a company’s reputation, impacting future contracts and investor confidence. Rebuilding trust requires transparency and a demonstrable commitment to enhanced security.