
Ransomware Attack Shuts 300 Yum! Brands UK Restaurants
Ransomware attack on yum brands inc closes 300 restaurants in the uk – Ransomware attack on Yum! Brands Inc. closes 300 restaurants in the UK – a headline that sent shockwaves through the UK restaurant industry and beyond. This massive cyberattack crippled operations, leaving hundreds of KFC, Pizza Hut, and Taco Bell locations shuttered and raising serious questions about cybersecurity preparedness in the fast-food sector. The incident highlights the devastating financial and reputational damage a successful ransomware attack can inflict, leaving us to wonder about the long-term effects on both Yum! Brands and the UK’s hospitality landscape.
The scale of the disruption is staggering. Imagine 300 restaurants suddenly unable to serve customers, employees left without work, and a massive disruption to the supply chain. The financial losses are likely to be substantial, impacting not just Yum! Brands’ bottom line but also the livelihoods of countless individuals. This event serves as a stark reminder of the increasingly sophisticated and dangerous world of cybercrime.
Impact on Yum Brands Inc.
The ransomware attack that crippled Yum Brands Inc.’s UK operations, resulting in the temporary closure of 300 restaurants, delivered a significant blow to the company’s bottom line and operational efficiency. The immediate financial consequences were substantial, extending beyond the direct costs of remediation and ransom payments (if any were made) to encompass a wider range of operational and reputational damages.The closure of 300 restaurants across various brands caused immediate and substantial operational disruptions.
Lost revenue from sales, staff wages paid during closures, and the costs associated with restoring systems and regaining operational capacity all contributed to significant short-term financial losses. Furthermore, the disruption to supply chains, the need to dispose of perishable goods, and the potential for damage to food preparation equipment added further complexities and expenses.
Financial Consequences of the Ransomware Attack
The immediate financial impact included lost revenue from sales, which can be estimated based on average daily sales per restaurant and the duration of the closure. Additional costs arose from paying staff during the closure, remediation efforts involving IT specialists and cybersecurity consultants, and potential legal fees. The longer the disruption lasted, the more substantial these losses became.
For example, a closure lasting a week for a restaurant averaging £5,000 in daily sales would represent a direct loss of £35,000, not accounting for other associated costs. The overall financial impact would depend on factors like the length of the closure, the specific brands affected, and the success of mitigation strategies.
Operational Disruptions from Restaurant Closures
The closure of 300 restaurants disrupted not only sales but also the entire operational ecosystem. Supply chains were affected, leading to potential spoilage of perishable goods and disruption to delivery schedules. Restaurant staff faced uncertainty about their employment and income during the closure. Furthermore, the reputational damage impacted future bookings and customer confidence. Reopening restaurants required thorough checks of systems and equipment, adding further delays and costs.
This ripple effect across the entire operational framework underscores the severity of the impact.
Long-Term Effects on Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
The ransomware attack’s long-term effects on brand reputation and customer loyalty are difficult to quantify immediately but could be substantial. Negative media coverage and customer concerns about data security could erode trust in the affected brands. This could lead to a decline in customer visits, even after restaurants reopen. Yum! Brands will need to invest significantly in rebuilding customer trust through transparent communication, enhanced cybersecurity measures, and possibly loyalty programs to counteract the negative effects.
The long-term impact will depend on the company’s response to the crisis and its success in regaining customer confidence.
Estimated Losses Across Restaurant Brands
The precise financial losses are difficult to determine without internal Yum! Brands data, but a hypothetical breakdown provides insight into the potential scale of the impact. This table uses estimated average daily sales figures and assumes a one-week closure for simplification. Actual losses could be significantly higher or lower depending on numerous factors.
| Restaurant Brand | Estimated Number of Closed Restaurants | Estimated Average Daily Sales (£) | Estimated Weekly Loss (£) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KFC | 150 | 4000 | 6,000,000 |
| Pizza Hut | 75 | 3000 | 1,575,000 |
| Taco Bell | 75 | 2500 | 1,312,500 |
The Ransomware Attack Itself
The ransomware attack on Yum Brands Inc., resulting in the closure of 300 UK restaurants, highlights the significant vulnerabilities present even in large, established corporations. Understanding the specifics of the attack is crucial for learning from this incident and improving cybersecurity practices across the industry. While the exact details may not be publicly available for some time, we can analyze likely scenarios based on common ransomware attack vectors and the impact observed.The likely type of ransomware used was a sophisticated, multi-stage attack, rather than a simple file-encrypting program.
Its capabilities likely included lateral movement within the network, data exfiltration before encryption, and potentially even the deployment of additional malware to hinder recovery efforts. The scale of the disruption – 300 restaurant closures – suggests a wide-reaching infection affecting critical systems, likely beyond simple file servers. This points towards a ransomware strain with advanced features and capabilities designed for maximum impact.
Ransomware Infiltration Methods
Attackers likely employed a multi-pronged approach to infiltrate Yum Brands Inc.’s systems. Phishing emails targeting employees, exploiting known vulnerabilities in outdated software, or even compromising third-party vendors are all plausible entry points. The attackers may have leveraged social engineering tactics to gain initial access, followed by exploiting vulnerabilities to achieve broader network access. Once inside, they likely moved laterally, mapping the network and identifying high-value targets – such as point-of-sale systems, financial records, and customer databases – before deploying the ransomware payload.
A successful attack of this scale requires meticulous planning and execution, indicative of a highly organized and skilled threat actor.
Data Encryption and Ransom Demand
After gaining sufficient access, the attackers likely initiated the encryption process. This would have involved deploying the ransomware payload to target specific file types and systems crucial to Yum Brands’ operations. The encryption algorithm used would likely be highly robust, making decryption without the decryption key extremely difficult. The ransom demand itself would have likely been communicated through a note left on affected systems, possibly including a deadline and instructions for payment in untraceable cryptocurrency.
The attackers may have also threatened to leak exfiltrated data if the ransom wasn’t paid, further increasing the pressure on Yum Brands. This tactic, known as double extortion, is becoming increasingly common among ransomware gangs.
Vulnerabilities in Yum Brands’ Security Infrastructure
Several potential vulnerabilities could have allowed the attack. Outdated software, lacking regular security patching, is a common weakness. Inadequate network segmentation could have allowed the ransomware to spread rapidly across the network. Insufficient employee security awareness training might have made phishing attacks more effective. A lack of robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) could have allowed attackers to maintain access even after compromising initial credentials.
Finally, insufficient monitoring and detection capabilities might have allowed the attackers to operate undetected for a considerable period, enabling them to achieve widespread infection before detection. A thorough investigation will be needed to pinpoint the exact vulnerabilities exploited in this attack.
Response and Recovery Efforts

The ransomware attack on Yum Brands Inc. forced a swift and comprehensive response to mitigate damage, restore operations, and maintain customer and stakeholder trust. Their actions involved a multi-pronged approach encompassing immediate containment, data recovery, and transparent communication. The scale of the disruption necessitated a highly coordinated effort across various departments and external specialists.The initial response focused on isolating affected systems to prevent further spread of the ransomware.
This involved immediately disconnecting affected UK restaurant networks from the wider Yum Brands infrastructure. Simultaneously, forensic experts were brought in to analyze the attack, identify the source, and determine the extent of data compromise. This critical first step was vital in limiting the long-term impact of the attack.
Data Restoration and System Recovery
Following the containment phase, Yum Brands prioritized restoring data and systems. This involved a complex process of data recovery from backups, reinstallation of software, and rigorous security testing to ensure the integrity and safety of the restored systems. The process was likely challenging, given the number of affected restaurants and the potential for data loss. It’s probable that they employed a phased approach, prioritizing critical systems and data before moving to less essential aspects of their operations.
The use of specialized ransomware recovery tools and expertise from cybersecurity firms would have been crucial in this stage.
Communication Strategy
Open and transparent communication was key to managing the crisis. Yum Brands likely implemented a comprehensive communication plan to keep customers, employees, and stakeholders informed. This would have involved issuing press releases, updating their website, and directly contacting affected employees and franchisees. Maintaining a consistent and accurate flow of information helped to mitigate public panic and maintain trust.
Transparency about the incident and the steps being taken to address it likely helped to limit negative publicity and potential legal repercussions.
Timeline of Key Events
While the exact timeline wasn’t publicly released in detail, a likely sequence of events might look something like this:* Day 1-3: Initial ransomware attack, system isolation, forensic investigation initiated, initial communication to key stakeholders.
Day 4-7
Data recovery efforts begin, assessment of the extent of the damage, coordination with law enforcement and cybersecurity firms.
Day 8-14
Phased restoration of systems, employee training on updated security protocols. Further communication updates provided to the public.
Day 15-21
Most restaurants begin reopening, ongoing system monitoring and security enhancements implemented.
Day 22 onwards
Full restoration of operations, continued investigation and analysis to prevent future incidents.This timeline is an approximation based on similar large-scale ransomware attacks. The actual timeline would depend on the specific technical challenges and logistical complexities involved in Yum Brands’ response. The speed and effectiveness of their response were likely critical factors in minimizing the overall impact of the incident.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
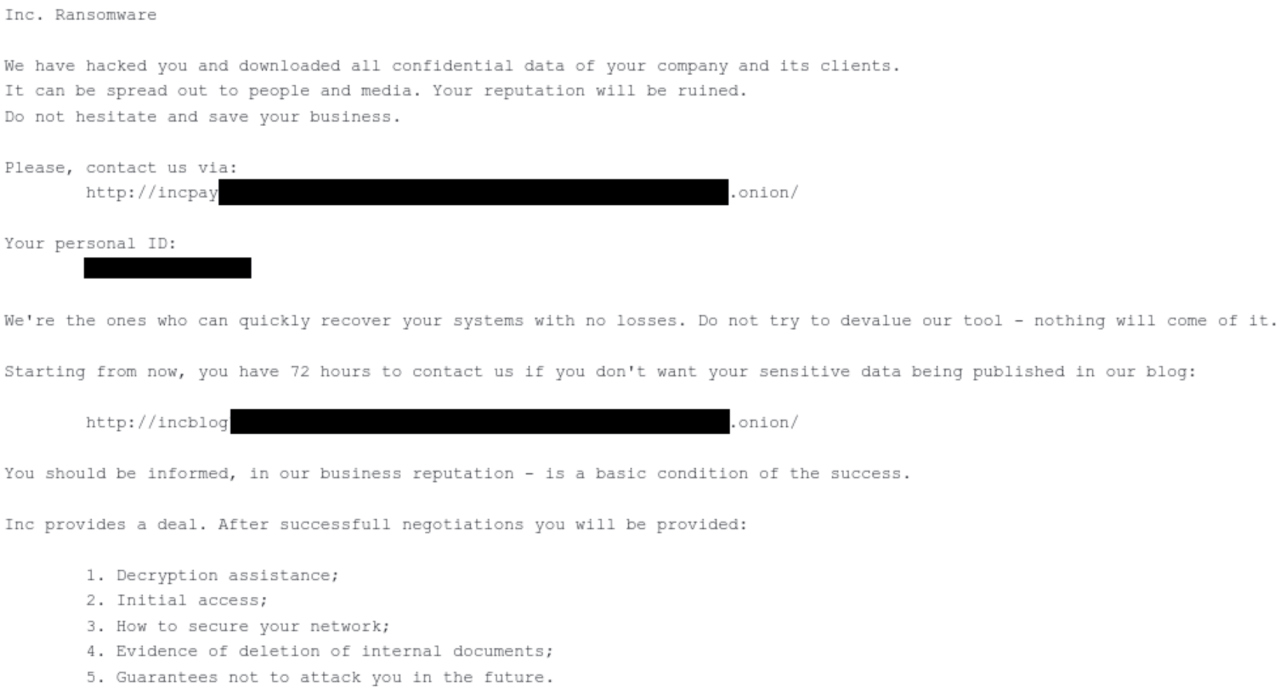
The ransomware attack on Yum Brands Inc., resulting in the closure of 300 UK restaurants, carries significant legal and regulatory ramifications for the company. The potential liabilities extend beyond financial losses to encompass substantial legal battles and penalties related to data breaches and regulatory non-compliance. Understanding these implications is crucial for assessing the long-term consequences of this incident.
Potential Legal Liabilities for Yum Brands Inc., Ransomware attack on yum brands inc closes 300 restaurants in the uk
Yum Brands Inc. faces several potential legal liabilities stemming from the ransomware attack. These liabilities could arise from various sources, including claims from customers, employees, and business partners who experienced data breaches or suffered financial losses due to the disruption of services. Furthermore, the company may face lawsuits alleging negligence in data security practices, leading to the attack and subsequent damages.
The scale of the incident, impacting hundreds of restaurants and potentially thousands of individuals, amplifies the potential for extensive litigation. The legal costs associated with defending against these claims could be substantial, adding to the overall financial burden.
Data Privacy Regulations Potentially Violated
The attack likely violated several key data privacy regulations, most notably the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. The GDPR mandates stringent data protection measures and imposes significant penalties for non-compliance. If the attack resulted in the unauthorized access or disclosure of personal data of customers or employees, Yum Brands Inc. could be in violation of GDPR’s provisions concerning data security, notification obligations, and data subject rights.
Other regulations, depending on the specific jurisdictions affected, may also apply, adding complexity to the legal landscape. For instance, California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) could be relevant if California residents’ data was compromised.
Potential Legal Actions Against Yum Brands Inc. or the Attackers
Several legal actions could be taken against Yum Brands Inc. These could include class-action lawsuits from affected customers alleging negligence and breach of contract. Regulatory bodies like the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK could also launch investigations, potentially leading to substantial fines. Furthermore, civil lawsuits from employees claiming damages due to data breaches or job losses are possible.
Separately, law enforcement agencies could pursue criminal charges against the attackers for offenses such as computer hacking, data theft, and extortion. The legal proceedings could be protracted and costly for all parties involved.
Potential Fines and Penalties for Yum Brands Inc.
The financial penalties Yum Brands Inc. might face are substantial and depend on several factors, including the extent of the data breach, the company’s compliance with data protection regulations, and the severity of the damage caused. Under the GDPR, fines can reach up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Similar hefty penalties could be imposed by other regulatory bodies depending on the applicable legislation.
In addition to regulatory fines, Yum Brands Inc. could face significant costs associated with legal fees, remediation efforts, and compensation to affected individuals. The total cost could easily run into millions, significantly impacting the company’s bottom line and reputation. For example, Marriott International faced a $124 million fine from the UK’s ICO for a data breach impacting millions of customers.
This serves as a stark reminder of the potential financial consequences of inadequate data security measures.
Cybersecurity Lessons Learned: Ransomware Attack On Yum Brands Inc Closes 300 Restaurants In The Uk

The ransomware attack on Yum Brands, resulting in the closure of hundreds of UK restaurants, serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities even large corporations face in the digital age. This incident highlights critical gaps in their cybersecurity posture and offers valuable lessons for other businesses, particularly in the food service industry. A thorough analysis reveals areas where preventative measures could have significantly reduced the impact of this attack.The attack on Yum Brands underscores the importance of proactive, multi-layered security.
While the specifics of the attack remain undisclosed, a combination of preventative measures and a robust incident response plan could have minimized the disruption. By comparing their response to similar incidents at other companies, we can identify best practices and develop a more comprehensive approach to cybersecurity risk management.
Key Cybersecurity Best Practices That Could Have Prevented the Attack
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to prevent ransomware attacks. Yum Brands could have benefited from several key practices. These include regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Furthermore, a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system would have added a significant layer of protection against unauthorized access. Employee training on cybersecurity best practices, particularly phishing awareness, is equally vital.
Finally, a robust and regularly updated endpoint detection and response (EDR) system could have detected and contained the ransomware before it could spread widely.
Mitigation of Future Ransomware Threats Through Improved Security Measures
Improved security measures could significantly mitigate future threats. A zero-trust security model, for instance, would limit access to sensitive data, even if an attacker compromises a single system. Regular software updates and patching are crucial to eliminate known vulnerabilities. Robust data backups, stored offline and regularly tested, ensure business continuity in the event of an attack. Implementing a security information and event management (SIEM) system would allow for real-time monitoring and threat detection, enabling quicker response times.
Finally, robust incident response planning, including regular drills and simulations, prepares the organization to effectively handle a future attack.
The ransomware attack on Yum Brands, shutting down 300 UK restaurants, highlights the vulnerability of even large corporations. Building robust, resilient systems is crucial, and that’s where exploring modern development approaches like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future becomes essential. Investing in secure, adaptable tech is the best defense against future disruptions caused by similar attacks.
The Yum Brands situation serves as a stark reminder of the importance of this.
Comparison of Yum Brands’ Response to Similar Ransomware Attacks
While the full details of Yum Brands’ response are not publicly available, comparing it to similar attacks on other large corporations reveals potential areas for improvement. For example, some companies facing similar incidents have prioritized rapid communication with stakeholders, including customers and regulatory bodies. Others have emphasized the importance of a swift and effective recovery plan, minimizing downtime and reputational damage.
A more transparent and proactive communication strategy during the crisis could have mitigated the negative publicity and public concern surrounding the closure of the restaurants.
Recommendations for Improving Cybersecurity Posture for Similar Organizations
The following recommendations can help organizations like Yum Brands improve their cybersecurity posture:
- Implement a comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training program for all employees.
- Regularly conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts.
- Deploy and maintain an effective endpoint detection and response (EDR) system.
- Develop and regularly test a robust incident response plan.
- Implement a zero-trust security model to limit lateral movement.
- Regularly back up critical data and store backups offline.
- Invest in a security information and event management (SIEM) system.
- Maintain up-to-date software and patches across all systems.
- Establish clear communication protocols for handling cybersecurity incidents.
Impact on the UK Restaurant Industry
The ransomware attack on Yum Brands Inc., resulting in the closure of 300 UK restaurants, sent shockwaves far beyond the immediate impact on the company itself. The incident highlighted the vulnerability of the UK restaurant sector to cyber threats and raised serious concerns about its overall confidence and stability. The ripple effects extended across the supply chain, employment, and consumer behavior, potentially reshaping the industry’s landscape for years to come.The closure of 300 restaurants, even temporarily, represents a significant blow to the UK’s vibrant food service sector.
This disruption underscores the interconnectedness of businesses and the fragility of supply chains in a globally connected world. The incident served as a stark reminder of the need for robust cybersecurity measures across the entire industry.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The sudden closure of so many restaurants created immediate disruptions to the supply chain. Suppliers who relied on Yum Brands for a significant portion of their business experienced immediate losses in revenue and potentially had to lay off staff. Farmers and producers supplying ingredients faced reduced demand, leading to spoilage and financial losses. This cascading effect highlights the systemic risk posed by large-scale cyberattacks to the entire food ecosystem.
For example, a dairy farmer supplying cheese to multiple Yum Brands locations might find themselves with a surplus of unsold product, resulting in significant financial strain. Similarly, logistics companies responsible for transporting ingredients and supplies to these restaurants faced reduced work and associated revenue losses.
Employment Impacts
The temporary closure of 300 restaurants directly resulted in the loss of thousands of jobs, at least temporarily. Employees, from chefs and servers to managers and support staff, faced uncertainty regarding their employment and income. This had a broader impact on the local economies where these restaurants were located, leading to decreased consumer spending and potential further job losses in related businesses.
The long-term consequences could include increased unemployment rates in specific regions and strain on social welfare systems. A hypothetical scenario could involve a significant number of these employees being unable to find comparable jobs within the industry, leading to a skills gap and longer-term economic hardship.
Consumer Behavior and Spending
The negative publicity surrounding the attack likely impacted consumer confidence and spending habits. Customers might have been hesitant to visit other restaurants in the Yum Brands network or even other establishments, fearing similar disruptions or data breaches. This decline in consumer spending could further strain the industry’s already fragile recovery from the pandemic. The perception of risk associated with eating out, fueled by the ransomware attack, could shift consumer preferences towards home-cooked meals or alternative dining options, impacting the overall revenue of the UK restaurant industry.
This shift in consumer behaviour might lead to some restaurants being forced to permanently close, leading to a consolidation of the market.
Hypothetical Long-Term Consequences
Imagine a scenario where the attack’s impact extends beyond the immediate recovery period. Increased insurance premiums for cyber liability, stricter regulations on data security, and a heightened awareness of cyber risks could lead to higher operating costs for restaurants. This could force smaller, independent establishments to close, leading to a less diverse and potentially less competitive restaurant industry.
Furthermore, the loss of consumer confidence could lead to a long-term decline in the industry’s growth, resulting in fewer job opportunities and a decreased contribution to the UK economy. This scenario highlights the systemic risk of large-scale cyberattacks and the need for proactive measures to mitigate future threats.
Final Review
The Yum! Brands ransomware attack underscores a critical need for robust cybersecurity measures across all industries. The closure of 300 restaurants serves as a potent symbol of the real-world consequences of neglecting digital security. Beyond the immediate financial impact, the long-term effects on brand reputation and customer trust are significant. This incident should serve as a wake-up call, prompting businesses to reassess their security protocols and invest in preventative measures to avoid similar catastrophes.
The recovery process will undoubtedly be lengthy and complex, highlighting the immense challenges businesses face in the wake of a successful ransomware attack. The ripple effect across the UK restaurant industry is also something to consider closely.
Common Queries
What type of ransomware was likely used?
The specific type of ransomware hasn’t been publicly revealed, but given the scale of the attack, it was likely a sophisticated and powerful variant capable of widespread encryption.
How long were the restaurants closed?
The duration of the closures varied depending on the restaurant and the speed of recovery efforts. Some may have been closed for days, while others might have taken longer.
Did Yum! Brands pay the ransom?
Whether or not a ransom was paid is typically not disclosed publicly by companies for security reasons.
What are the long-term effects on Yum! Brands’ brand image?
Long-term effects could include decreased customer trust, negative media coverage, and potential loss of market share, requiring significant rebuilding of brand reputation.





