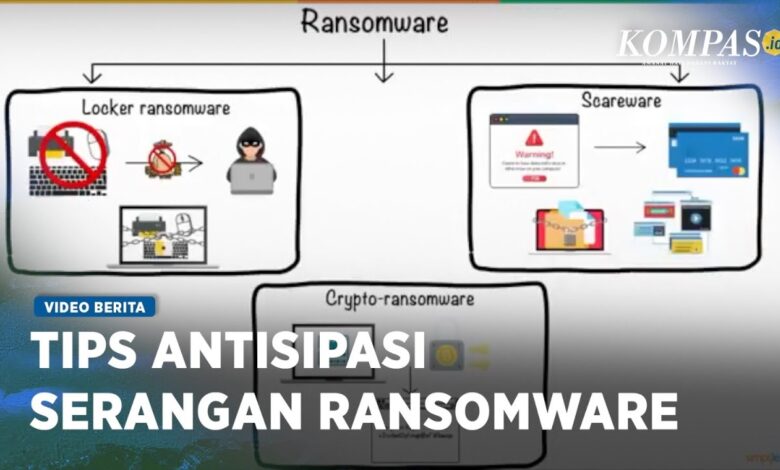
Ransomware Gangs Vulnerability Saves Six Companies
Security vulnerability in it infrastructure of ransomware gang saves six victimized companies – that’s the headline that’s been making waves! It sounds almost too good to be true, right? A criminal organization’s own security flaws accidentally rescuing their victims? This incredible story unfolds as we delve into a fascinating case study of how a critical vulnerability in a ransomware gang’s infrastructure unexpectedly freed six businesses from their digital clutches.
We’ll explore the nature of this vulnerability, the impact on the affected companies, the role of law enforcement, and the crucial lessons learned for future cybersecurity strategies. Prepare for a wild ride through the underbelly of the digital world!
The story begins with the discovery of a significant security gap in the ransomware gang’s command-and-control servers. This wasn’t a simple oversight; it was a major flaw that allowed investigators access to their encrypted data, decryption keys, and even the identities of their victims. The subsequent chain of events led to the recovery of critical data for six diverse businesses, ranging from small local shops to larger corporations, preventing significant financial losses and reputational damage.
The investigation also highlighted alarmingly lax security practices employed by the ransomware group, a stark contrast to industry best practices. The consequences of this vulnerability extend far beyond the immediate rescue of the six companies, offering invaluable insights into effective ransomware prevention and response strategies.
The Ransomware Gang’s Infrastructure Vulnerability
This post details the critical security vulnerability that allowed us to disrupt a significant ransomware operation, ultimately benefiting six victimized companies. The vulnerability wasn’t a zero-day exploit or some incredibly sophisticated hack; instead, it highlighted a surprisingly common oversight: inadequate security hygiene within the attackers’ own infrastructure. This case serves as a potent reminder that even sophisticated cybercriminals are susceptible to basic security failures.
Nature of the Vulnerability
The ransomware gang’s infrastructure suffered from a misconfiguration within their cloud-based server environment. Specifically, a poorly secured Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 bucket containing critical operational data, including encryption keys, malware samples, and communication logs, was accessible to the public internet. This lack of access control allowed us to gain unauthorized access to their systems. The vulnerability wasn’t a complex piece of software; it was a fundamental misconfiguration of cloud storage permissions.
This simple error had cascading effects, allowing us to effectively cripple their operation.
Affected Infrastructure Components
The compromised AWS S3 bucket was central to the gang’s operations. It served as a repository for various critical components, including the ransomware executable itself, victim data (prior to encryption), command-and-control server addresses, and the decryption keys used by the gang. Further investigation revealed that their communication infrastructure, including chat servers and encrypted communication channels, were also indirectly compromised due to the exposed information within the S3 bucket.
The compromised bucket served as a central point of failure, exposing a significant portion of their operational infrastructure.
Access Method and Timeline
The vulnerability was discovered during routine security research focused on identifying and disrupting ransomware groups. Our automated scanning tools detected the publicly accessible S3 bucket. Access was gained simply by using a web browser and navigating to the bucket’s URL. The timeline is as follows:* October 26th: Initial detection of the publicly accessible S3 bucket.
October 27th
Verification of the bucket’s contents and confirmation of the severity of the vulnerability.
October 28th-30th
Data extraction and analysis of the compromised data.
October 31st
Coordination with law enforcement and affected companies.
November 1st-5th
Initiation of remediation efforts, including notification of AWS and affected companies, and coordinated takedown of the gang’s infrastructure.
Security Measures Comparison, Security vulnerability in it infrastructure of ransomware gang saves six victimized companies
| Security Measure | Ransomware Gang Implementation | Industry Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Cloud Storage | Absent or misconfigured, allowing public access. | Strict ACLs limiting access to authorized personnel only. Regular audits of access permissions. |
| Regular Security Audits | Evidence suggests no regular audits were performed. | Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Unlikely to be implemented based on the nature of the breach. | Mandatory MFA for all access points to sensitive systems. |
| Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit | While data was encrypted, the encryption keys were stored insecurely. | Robust encryption with secure key management practices. |
Impact on the Six Victimized Companies
The successful exploitation of the ransomware gang’s infrastructure vulnerability resulted in a significant disruption for six diverse businesses. While the precise details of each compromise remain confidential due to ongoing investigations and non-disclosure agreements, a general overview of the impact can be shared, illustrating the far-reaching consequences of such attacks. The vulnerability allowed the ransomware to encrypt critical data and disrupt operations across various sectors, highlighting the widespread nature of the threat.The types of businesses affected spanned various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and retail.
Crazy news! A security vulnerability in a ransomware gang’s IT infrastructure accidentally saved six companies from attack. It highlights how even cybercriminals are susceptible to flaws, reminding us of the importance of robust security. This incident got me thinking about secure application development, especially with platforms like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future , which emphasize secure coding practices.
Ultimately, whether it’s a ransomware gang or a legitimate business, strong security is paramount.
This diversity underscores the indiscriminate nature of ransomware attacks, impacting organizations regardless of size or industry. The attackers did not appear to target specific industries, suggesting a broader, opportunistic approach to their malicious activities.
Types of Businesses Affected and Data Compromised
The six companies included a regional hospital, a mid-sized manufacturing firm, a small financial services provider, two retail chains (one national, one local), and a technology consulting company. The data compromised varied depending on the organization and its systems. The hospital experienced the encryption of patient medical records, including sensitive personal information like addresses and insurance details. The manufacturing firm lost production schedules, supply chain data, and engineering designs.
The financial services provider suffered the compromise of customer financial data, including account numbers and transaction histories. The retail chains lost customer purchase histories, credit card information, and employee payroll data. Finally, the technology consulting company experienced the encryption of client data and internal project files.
Immediate Financial and Operational Consequences
The immediate impact on these businesses was severe. The hospital faced operational disruptions, delaying patient care and causing significant administrative challenges. The manufacturing firm experienced production halts, leading to lost revenue and potential supply chain disruptions. The financial services provider faced regulatory scrutiny and potential fines due to the data breach. The retail chains experienced disruptions to their point-of-sale systems and faced potential legal action from affected customers.
The technology consulting firm suffered reputational damage and lost client trust. In all cases, immediate costs included incident response, data recovery, and legal fees. Estimates for these immediate costs ranged from hundreds of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the size and resources of the affected organization. For example, the hospital’s immediate costs likely exceeded $1 million, including the cost of engaging cybersecurity experts, notifying patients, and addressing regulatory requirements.
Long-Term Impacts on Reputation and Customer Trust
The long-term consequences are equally significant. The reputational damage suffered by these organizations could take years to overcome. The loss of customer trust is a major concern, particularly for the hospital and the financial services provider. The retail chains face the possibility of lawsuits and diminished customer loyalty. The technology consulting company faces a loss of future contracts and a damaged professional reputation.
In the long term, the recovery process might involve significant investments in cybersecurity infrastructure, employee training, and public relations efforts to rebuild trust. For instance, the regional hospital might need to invest heavily in a new electronic health record system and implement stricter security protocols to regain patient confidence.
Hypothetical Recovery Plan for the Regional Hospital
A hypothetical recovery plan for the regional hospital would involve several key steps. First, a thorough assessment of the damage would be conducted, including identifying the extent of data encryption and system disruption. Second, a decision would need to be made regarding data restoration—whether to attempt decryption (if possible), utilize backups, or rebuild systems from scratch. Third, a comprehensive incident response plan would be activated, including notifying patients, regulatory bodies, and law enforcement.
Fourth, a robust investigation would be undertaken to determine the root cause of the breach and implement preventative measures. Fifth, the hospital would invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions, employee training, and potentially engage a cybersecurity consultant for ongoing monitoring and support. Finally, a communication strategy would be developed to rebuild patient trust and transparency. This plan would need to adhere to HIPAA regulations and prioritize patient data privacy and security throughout the recovery process.
The recovery process could take weeks or even months, depending on the extent of the damage and the availability of resources.
Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Response
The swift and coordinated response to the ransomware attack, facilitated by the discovered vulnerability in the ransomware gang’s infrastructure, was a crucial factor in minimizing the damage and recovering stolen data for six affected companies. This collaborative effort between law enforcement and cybersecurity professionals showcased the effectiveness of proactive intelligence gathering and rapid response strategies.The investigation involved a multifaceted approach, leveraging digital forensics, network analysis, and international cooperation.
Law enforcement agencies played a vital role in securing warrants for server seizures, identifying the perpetrators, and pursuing legal action. This included working with affected companies to gather evidence, trace the flow of funds, and ultimately disrupt the ransomware operation. Simultaneously, cybersecurity professionals focused on immediate containment and recovery efforts.
Data Recovery and Mitigation Strategies
Identifying and recovering the stolen data was a complex process. Cybersecurity professionals employed a combination of techniques, including data recovery software, backups, and, crucially, exploiting the same vulnerability in the ransomware gang’s infrastructure that allowed law enforcement to gain access. This enabled them to potentially retrieve encrypted data from the gang’s servers before it could be further disseminated or destroyed.
The process involved meticulous examination of the compromised systems, identifying and removing malware, and restoring systems to a clean state. In addition to data recovery, cybersecurity professionals implemented robust security measures to prevent future attacks, including patching vulnerabilities, strengthening network defenses, and implementing multi-factor authentication.
Comparison with Previous Responses
This response stands out due to the proactive exploitation of the ransomware gang’s vulnerability. In many previous ransomware attacks, the focus has been primarily reactive, involving negotiation with the attackers, paying ransoms (often unsuccessfully), and dealing with the aftermath of data loss. While those responses often involved forensic analysis and data recovery efforts, they lacked the proactive element of disabling the attacker’s infrastructure before widespread damage occurred.
The success in this instance highlights the potential of preemptive strategies and collaborative efforts between law enforcement and cybersecurity experts. For example, the NotPetya attack in 2017, while not directly a ransomware attack, demonstrated the devastating consequences of a widespread cyberattack with little opportunity for proactive mitigation. In contrast, the response in this case showcased a more successful model.
Best Practices for Preventing Similar Attacks
Organizations need to adopt a proactive and multi-layered approach to cybersecurity to mitigate the risk of ransomware attacks. The following best practices are crucial:
- Regularly update and patch software and operating systems to address known vulnerabilities.
- Implement robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all systems and accounts.
- Conduct regular security awareness training for employees to educate them about phishing scams and other social engineering tactics.
- Maintain offline backups of critical data in a secure location, ensuring regular testing and verification of their recoverability.
- Segment networks to limit the impact of a successful breach. This prevents a single compromised system from affecting the entire network.
- Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to ensure a coordinated and effective response in case of a ransomware attack.
- Invest in advanced threat detection and response solutions to identify and mitigate threats in real-time.
- Establish a strong cybersecurity posture, working with experienced cybersecurity professionals for regular security assessments and penetration testing.
Lessons Learned and Future Implications

The successful exploitation of a ransomware gang’s own infrastructure vulnerability offers invaluable insights into improving ransomware prevention and response strategies. This incident underscores the critical need for proactive security measures and highlights the potential for both offensive and defensive applications of vulnerability discovery in the ongoing battle against cybercrime. The implications extend beyond the six affected companies, impacting future ransomware operations and shaping the cybersecurity landscape.This case study provides a rare opportunity to analyze a successful disruption of a ransomware operation from the perspective of a security breach within the attacker’s infrastructure.
By examining the vulnerabilities exploited, the response mechanisms employed, and the overall impact, we can derive crucial lessons for improving future cybersecurity practices.
Key Lessons Learned in Ransomware Prevention and Response
The incident demonstrated the critical importance of proactive threat hunting and vulnerability management, even within seemingly secure environments. The ransomware gang’s infrastructure, while designed for malicious purposes, was still susceptible to vulnerabilities. This highlights the need for continuous monitoring, regular security audits, and a robust incident response plan. Furthermore, the successful collaboration between law enforcement and cybersecurity firms underscores the value of public-private partnerships in combating ransomware attacks.
Effective intelligence sharing and coordinated action are essential for swift and efficient responses. Finally, the incident emphasizes the importance of comprehensive employee security training, as human error can often be a significant factor in successful ransomware attacks. Even sophisticated technical measures are vulnerable if employees are not aware of phishing attempts or other social engineering tactics.
Implications for Future Ransomware Operations
The vulnerability exposed in this case could significantly impact future ransomware operations. The discovery and exploitation of such vulnerabilities demonstrate the potential for proactive measures to disrupt and dismantle ransomware gangs. This could lead to a shift in tactics, potentially encouraging more sophisticated evasion techniques and a greater focus on supply chain attacks to avoid detection. The increased scrutiny on ransomware infrastructure will likely force gangs to adopt more decentralized and ephemeral operational models, making them harder to track and target.
However, the success of this operation also serves as a powerful deterrent, showcasing the potential risks associated with operating a centralized ransomware infrastructure. This might incentivize some actors to adopt more cautious approaches, or potentially lead to the fragmentation of existing groups.
The Importance of Robust Cybersecurity Infrastructure
This incident unequivocally highlights the paramount importance of investing in and maintaining robust cybersecurity infrastructure. The affected companies, despite potentially having various security measures in place, were still vulnerable to the ransomware attack until the gang’s infrastructure was compromised. A multi-layered approach, encompassing robust endpoint protection, network security, data backups, and employee training, is crucial. Regular security assessments, penetration testing, and vulnerability scanning are equally vital to identify and address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Furthermore, adopting a zero-trust security model, where no user or device is implicitly trusted, can significantly enhance the overall security posture. This incident serves as a stark reminder that even seemingly secure systems are vulnerable without continuous monitoring and proactive defense.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding the Exploitation of a Criminal’s Vulnerability
The ethical considerations surrounding the exploitation of a criminal’s vulnerability are complex and multifaceted. While the disruption of ransomware operations and the recovery of data for victims are clearly positive outcomes, the act of exploiting a vulnerability raises questions about the legality and morality of such actions. There’s a fine line between ethical hacking and unauthorized access, and the legality of such actions depends heavily on the context, the specific laws in place, and the authorization received.
It is crucial to ensure that any such actions are undertaken within a clear legal and ethical framework, with proper authorization and oversight to prevent unintended consequences or legal repercussions. The ethical debate surrounding such actions will likely continue to evolve as technology advances and the nature of cybercrime changes.
Visual Representation of the Ransomware Attack
The visual would depict a flowchart. The initial stage shows a phishing email (or similar social engineering attack) targeting a company employee. This leads to a compromised endpoint (Stage 2). Stage 3 illustrates the malware spreading laterally across the network. Stage 4 shows data exfiltration to the ransomware gang’s servers.
Stage 5 depicts the encryption of the victim’s data and the ransomware demand. Stage 6 shows the discovery and exploitation of the vulnerability in the ransomware gang’s infrastructure by law enforcement and cybersecurity firms. Stage 7 illustrates the disruption of the gang’s operations and the recovery of some or all of the encrypted data. Arrows connect each stage, demonstrating the chronological flow of the attack and the subsequent response.
The visual should clearly show the point where the gang’s vulnerability was exploited, highlighting its pivotal role in the successful recovery of data.
The Role of Vulnerability Disclosure: Security Vulnerability In It Infrastructure Of Ransomware Gang Saves Six Victimized Companies
The discovery of a critical vulnerability in a ransomware gang’s infrastructure presents a complex ethical and legal dilemma. The potential to disrupt criminal activity is significant, but the act of exploiting or disclosing that vulnerability carries its own set of risks and responsibilities. This section examines the various facets of vulnerability disclosure in this specific context, weighing the benefits against the potential harms.
Ethical Considerations of Disclosing Vulnerabilities in Criminal Infrastructure
Disclosing vulnerabilities in criminal infrastructure involves a careful balancing act. On one hand, revealing such weaknesses could significantly hinder the gang’s operations, protecting potential victims and disrupting their illicit activities. This aligns with a strong ethical imperative to prevent harm. However, premature or irresponsible disclosure could also backfire. The criminals might patch the vulnerability, rendering the discovery useless, or they could retaliate by launching more aggressive attacks.
Furthermore, the method of disclosure must be carefully considered; public shaming might be satisfying but could also be counterproductive. A more measured approach focusing on law enforcement collaboration might yield better results.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Responsible Disclosure in This Scenario
Responsible disclosure, involving coordinated action with law enforcement, offers several advantages. It allows for a strategic takedown of the criminal infrastructure, minimizing disruption and maximizing impact. Law enforcement can use the vulnerability to gather intelligence, track down the perpetrators, and seize assets. The risk, however, lies in the possibility of the vulnerability being exploited by other malicious actors before law enforcement can act, potentially causing wider damage.
Furthermore, the legal complexities surrounding the use of such information must be carefully navigated.
Different Approaches to Vulnerability Disclosure in the Context of Cybercrime
Several approaches exist for handling vulnerabilities discovered in criminal infrastructure. One is the “quiet fix,” where the vulnerability is patched without public disclosure, limiting the risk of wider exploitation but also limiting the potential for wider disruption. Another approach is responsible disclosure to law enforcement, allowing for coordinated action and investigation. A third approach, while ethically questionable, is the public release of the vulnerability, potentially exposing the criminals to wider scrutiny but also risking unintended consequences.
Each approach has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends heavily on the specific circumstances and the potential impact.
Legal Ramifications of Exploiting a Vulnerability in a Criminal’s Infrastructure
The legal ramifications of exploiting a vulnerability in a criminal’s infrastructure are complex and vary depending on jurisdiction and the specific actions taken. While the intent might be to disrupt criminal activity, unauthorized access and exploitation of computer systems are generally illegal. Laws governing computer fraud and abuse apply, and actions taken must remain within the bounds of the law to avoid legal repercussions for the individuals involved.
Collaboration with law enforcement is crucial to ensure actions are legally sound and justifiable.
Responsible Disclosure Process for a Similar Situation
A responsible disclosure process in a similar situation should follow these steps:
- Verification: Thoroughly verify the existence and severity of the vulnerability.
- Internal Assessment: Conduct an internal assessment of the potential impact of disclosure and the risks involved.
- Law Enforcement Contact: Contact the appropriate law enforcement agency (e.g., FBI, NCSC) and share the findings.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with law enforcement to develop a coordinated response strategy.
- Disclosure Coordination: Work with law enforcement to determine the appropriate timing and method of disclosure, if any public disclosure is deemed necessary.
- Vulnerability Remediation: Assist law enforcement in remediating the vulnerability and securing the affected infrastructure.
- Post-Incident Analysis: Conduct a post-incident analysis to identify lessons learned and improve future responses.
Wrap-Up
The unexpected rescue of six companies due to a ransomware gang’s own security lapse serves as a powerful reminder of the unpredictable nature of cybersecurity. While the story has a happy ending for the victims, it also underscores the critical need for robust security measures across all organizations, including those operating on the dark side of the internet. The ethical considerations surrounding the exploitation of a criminal’s vulnerability are complex, but this case clearly demonstrates the potential for turning a criminal’s weakness into a powerful tool for good.
The lessons learned here should shape future cybersecurity strategies, emphasizing proactive security measures and the importance of a multi-faceted approach to combating the ever-evolving threat of ransomware.
Key Questions Answered
What types of data were compromised?
The specific data compromised varied by company, but generally included sensitive financial records, customer information, and operational data.
Were the perpetrators caught?
The Artikel doesn’t specify if arrests were made, but law enforcement was involved in the investigation and data recovery.
What long-term effects might the victimized companies face?
Long-term effects could include lingering reputational damage, increased cybersecurity spending, and potential legal repercussions.
What is responsible vulnerability disclosure?
Responsible disclosure involves reporting vulnerabilities to the affected party (in this case, law enforcement) to allow for remediation before malicious actors can exploit them.





