Foundational Security The Enterprises Weakest Link
Foundational security is the enterprises weakest link – Foundational security is the enterprise’s weakest link, and it’s a problem far bigger than most companies realize. We often focus on flashy, new-fangled cybersecurity solutions, forgetting the bedrock principles that should be the foundation of any robust security posture. This oversight leaves organizations vulnerable to a surprisingly wide range of attacks, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated, targeted breaches.
Let’s dive into why this is such a critical issue and what we can do to shore up our defenses.
From inadequate access controls and outdated technology to insufficient security awareness training, the gaps in foundational security are numerous and often surprisingly easy to exploit. The consequences can be devastating, leading to data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. Understanding these weaknesses is the first step towards building a truly secure organization. We’ll explore common vulnerabilities, effective mitigation strategies, and the crucial role of human factors in this often-overlooked area of cybersecurity.
Defining Foundational Security Weaknesses
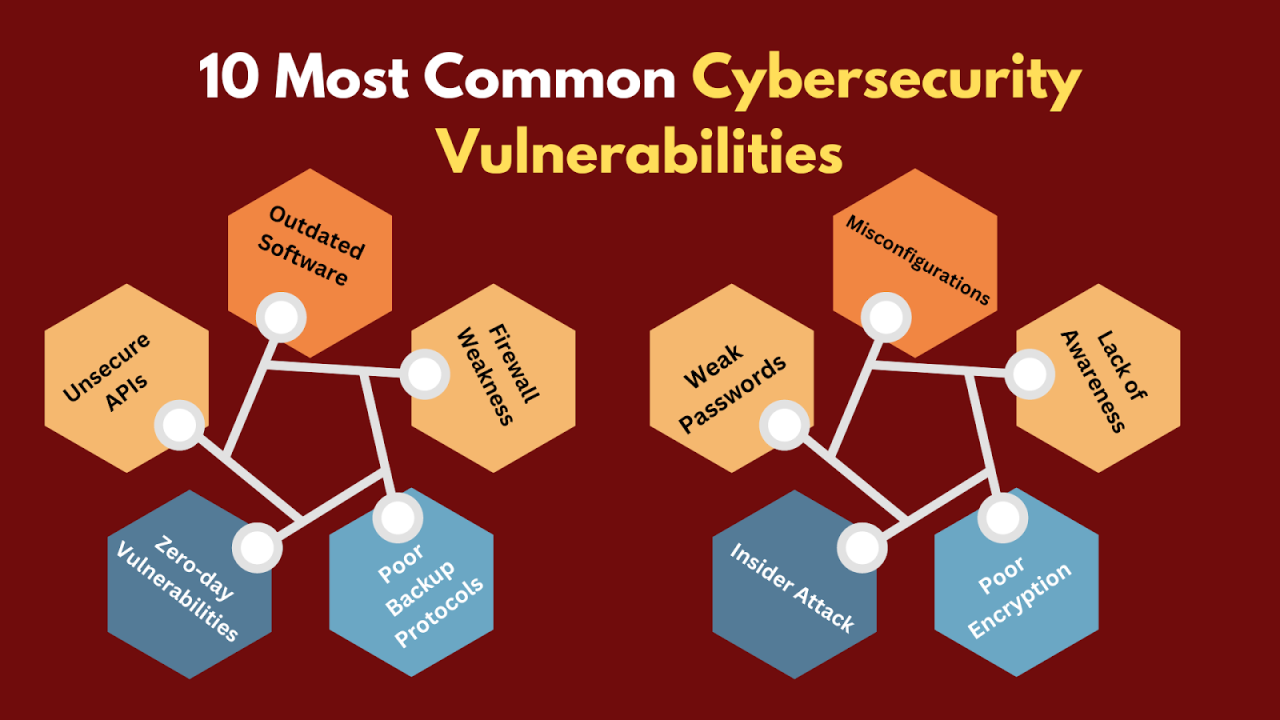
Foundational security, the bedrock upon which all other security measures are built, is often the weakest link in an enterprise’s defenses. Neglecting these fundamental aspects leaves organizations vulnerable to a wide range of attacks, resulting in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Let’s delve into some of the most prevalent foundational security weaknesses.
Inadequate Access Control
Inadequate access control mechanisms are a significant contributor to enterprise vulnerabilities. This involves failing to properly restrict access to sensitive data and systems based on the principle of least privilege. Employees often have broader access than necessary, increasing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized modifications. For example, a junior employee with access to sensitive customer databases poses a risk if their account is compromised.
Furthermore, a lack of robust authentication and authorization procedures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), allows unauthorized individuals to gain access. The impact is magnified when access controls are poorly implemented, allowing lateral movement within the network once an initial breach occurs.
Insufficient Security Awareness Training
Insufficient security awareness training leaves employees susceptible to phishing attacks, social engineering, and other forms of malicious activity. Employees who lack awareness of security best practices are more likely to click on malicious links, download infected files, or inadvertently reveal sensitive information. A lack of regular, engaging training, coupled with a failure to reinforce key security concepts, creates a significant vulnerability.
The consequences can be severe, ranging from minor data breaches to significant financial losses and reputational damage. Consider the impact of a single employee falling prey to a phishing scam that grants access to the company’s financial systems.
Outdated Security Technologies
Relying on outdated security technologies is another critical foundational weakness. This includes using legacy systems, unpatched software, and unsupported hardware. These outdated technologies often lack the necessary security features to protect against modern threats. For instance, using an outdated firewall with known vulnerabilities exposes the organization to a variety of attacks. Similarly, failing to update operating systems and applications leaves systems vulnerable to exploits.
The consequences can range from data breaches and system outages to complete system compromise and ransomware attacks. The cost of remediation after an attack often far exceeds the cost of proactive updates and maintenance.
Impact of Foundational Security Weaknesses on Data Breaches
| Weakness | Impact | Likelihood | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inadequate Access Control | Data theft, unauthorized modifications, system compromise | High | Implement least privilege access, robust authentication (including MFA), regular access reviews |
| Insufficient Security Awareness Training | Phishing attacks, social engineering, malware infections, data leaks | High | Regular, engaging security awareness training, simulated phishing campaigns, clear security policies |
| Outdated Security Technologies | Exploits, vulnerabilities, system outages, data breaches, ransomware attacks | Medium to High | Regular software and hardware updates, patching, vulnerability scanning, security information and event management (SIEM) |
Vulnerabilities Stemming from Weak Foundations

A strong security posture isn’t built overnight; it requires a solid foundation. Ignoring fundamental security practices creates vulnerabilities that ripple throughout an organization, leaving it exposed to a wide range of threats. This section explores how weak foundational security directly contributes to significant security risks.Poor network security and inadequate endpoint protection are two major areas where weak foundations manifest, leading to significant vulnerabilities.
The interconnected nature of modern systems means a single point of failure can cascade into a larger breach.
The Relationship Between Poor Network Security and Foundational Weaknesses
Weak network security directly stems from a lack of foundational security best practices. This includes failing to implement robust firewalls, neglecting intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and employing outdated or poorly configured network devices. For example, a network lacking proper segmentation allows a compromised device to easily spread malware throughout the entire network. Similarly, a failure to implement strong authentication mechanisms opens the door to unauthorized access and lateral movement.
This lack of basic network hygiene creates an environment ripe for exploitation. A simple denial-of-service attack, easily mitigated with proper firewall rules and network monitoring, could cripple operations if foundational security is neglected.
Insufficient Endpoint Protection Exacerbates Security Risks
Endpoints – laptops, desktops, mobile devices – are often the first line of defense (or lack thereof) against attacks. Insufficient endpoint protection, a direct consequence of weak foundational security, leaves these devices vulnerable to malware, ransomware, and other threats. Outdated antivirus software, a lack of patch management, and failure to implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures all contribute to this risk.
A single compromised endpoint can serve as a gateway for attackers to gain access to sensitive data and internal networks. Imagine a scenario where an employee clicks a malicious link in a phishing email. Without up-to-date endpoint protection, this could lead to a full-blown system compromise, potentially exposing the entire company’s data.
Cloud-Based Versus On-Premise Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Both cloud-based and on-premise infrastructures are susceptible to vulnerabilities stemming from weak foundational security, but the nature of those vulnerabilities differs. On-premise infrastructure requires meticulous management of physical security, network configurations, and patching. A failure to adequately secure physical servers or implement robust access controls can lead to significant breaches. Cloud-based infrastructure, while offering many advantages, relies heavily on the security practices of the cloud provider and the organization’s own configuration.
Misconfigured cloud services, a lack of proper access controls, and inadequate monitoring can expose sensitive data stored in the cloud. Both environments necessitate strong foundational security practices, but the specific implementation and focus areas vary considerably.
Securing Remote Access Points with Weak Foundational Security
Securing remote access points is especially challenging when foundational security is weak. Organizations often rely on VPNs for remote access, but if the underlying network security is poor, the VPN itself becomes a vulnerable point. Weak passwords, inadequate authentication methods, and a lack of proper access controls can compromise the VPN and expose sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong password policies, and regular security audits are crucial for mitigating this risk, even in the face of weaker foundational security.
However, the ideal solution involves strengthening the overall foundational security to minimize vulnerabilities.
Hypothetical Data Breach Scenario
Imagine a small business that neglects to implement basic security measures. Their network lacks a firewall, their employees use weak passwords, and their endpoint protection is outdated. An attacker launches a phishing campaign, successfully compromising an employee’s computer. Due to the lack of network segmentation, the attacker gains access to the entire network, including the company’s database server.
The attacker exfiltrates sensitive customer data, leading to a significant data breach and potential regulatory fines. This scenario highlights how a single weak foundational security element can have cascading consequences, resulting in a major security incident.
Strengthening Foundational Security Measures
So, we’ve established that foundational security is often the weakest link. Now, let’s talk about fixing it. Strengthening your organization’s security posture requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on proactive measures and robust response planning. This isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of improvement and adaptation.
Multi-Factor Authentication Enterprise-Wide Implementation
Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across your entire enterprise is crucial for bolstering security. A phased rollout minimizes disruption and allows for thorough testing. First, prioritize high-risk accounts (administrators, executives, access to sensitive data) for immediate MFA implementation. Next, expand to other critical departments and gradually roll out to all employees. Choose MFA methods appropriate for your workforce, considering factors like cost, user experience, and security effectiveness.
Thorough training is vital to ensure user adoption and understanding. Regularly review and update your MFA strategy to adapt to evolving threats and technologies. For example, you might start with a combination of passwords and one-time codes via SMS, then transition to more robust methods like authenticator apps or hardware security keys as budgets and user comfort allow.
Regular Security Audits for Weakness Identification
Regular security audits are essential for identifying and addressing foundational weaknesses. These audits should encompass both technical and procedural aspects of your security infrastructure. Technical audits assess vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. Procedural audits evaluate the effectiveness of security policies, procedures, and employee training. Employ a combination of automated vulnerability scanning tools and manual penetration testing to gain a comprehensive view of your security posture.
Regular audits, ideally quarterly or biannually, allow for early detection and remediation of vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Document findings meticulously, prioritize remediation efforts based on risk level, and track progress toward resolution. The cost of a security audit is significantly less than the cost of a data breach.
Robust Incident Response Planning for Breach Mitigation
A robust incident response plan is crucial for mitigating the impact of breaches originating from weak foundations. This plan should Artikel clear procedures for detecting, containing, eradicating, recovering from, and learning from security incidents. The plan should include clearly defined roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and escalation procedures. Regular drills and simulations are vital for testing the plan’s effectiveness and ensuring team preparedness.
Consider involving external security experts in the development and testing of your incident response plan to ensure its thoroughness and adherence to best practices. For instance, simulating a phishing attack and evaluating the response time and effectiveness of containment measures can highlight areas for improvement.
Essential Security Policies and Procedures
A comprehensive set of security policies and procedures is the bedrock of a strong security posture. These policies should cover areas such as access control, password management, data security, incident response, and acceptable use of company resources. Policies should be clearly written, easily accessible to all employees, and regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology and threats.
Training programs should ensure that all employees understand and comply with these policies. Examples include a clear data classification policy defining the sensitivity of different data types and corresponding access controls, a strong acceptable use policy outlining appropriate behavior regarding company resources, and a comprehensive incident reporting procedure outlining steps for reporting and handling security incidents.
Creating and Enforcing a Strong Password Policy
A strong password policy is fundamental to preventing unauthorized access. This policy should mandate the use of complex passwords that meet specific length, character type, and complexity requirements. It should also include guidelines for password storage and rotation. Consider implementing password managers to help employees create and manage strong, unique passwords for different accounts. Regular password resets and the prohibition of password reuse are also crucial.
For example, a strong password policy might require passwords to be at least 12 characters long, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and prohibit the use of easily guessable information like birthdays or names. Regular audits should verify adherence to the password policy.
The Role of Human Factors in Foundational Security

Let’s face it: even the most robust technical security measures are vulnerable if the human element is neglected. Foundational security, while encompassing firewalls and encryption, ultimately hinges on the actions and awareness of the people within an organization. Human error, intentional or unintentional, remains a primary driver of security breaches, undermining even the strongest technical defenses.The impact of human error on foundational security is significant and far-reaching.
A single misplaced password, a careless click on a phishing link, or a failure to patch a known vulnerability can have catastrophic consequences, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. This isn’t about blaming individuals; it’s about acknowledging the inherent vulnerabilities in human behavior and designing security strategies that account for them.
Social Engineering Attacks Exploiting Weak Foundational Security
Social engineering attacks prey on human psychology, exploiting weaknesses in foundational security through manipulation and deception. These attacks often bypass technical controls by targeting individuals directly. A classic example is the phishing email, cleverly disguised to appear legitimate, prompting recipients to divulge sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or credit card details. Another common tactic involves pretexting, where attackers fabricate a scenario to gain access to information or systems.
For instance, an attacker might pose as a system administrator requesting login credentials to troubleshoot a problem. The success of these attacks often hinges on the lack of security awareness training and the absence of robust verification procedures. The seemingly simple act of verifying the caller’s identity through an independent channel can prevent a significant breach.
Security Awareness Training Programs
Security awareness training is paramount in mitigating human-related vulnerabilities. Effective training programs should go beyond simple compliance checklists. They need to engage employees, making them active participants in security rather than passive recipients of rules. Interactive modules, realistic simulations, and regular refresher courses are crucial for reinforcing key security concepts and best practices. The goal is to cultivate a security-conscious culture where employees understand the potential consequences of their actions and are empowered to identify and report suspicious activities.
Let’s be honest, foundational security is often the enterprise’s Achilles’ heel. We’re so focused on shiny new apps that we forget the basics. But building secure, scalable apps is crucial, which is why I’ve been diving into the world of domino app dev, the low-code and pro-code future , to see how it addresses these core security concerns.
Ultimately, though, even the most innovative development approach won’t help if we neglect foundational security practices; it remains the weakest link.
For example, a well-designed program might include scenarios demonstrating the dangers of clicking on suspicious links or revealing personal information to unauthorized individuals. Regular quizzes and assessments can further enhance knowledge retention and identify knowledge gaps within the workforce.
Best Practices for Promoting a Strong Security Culture
Cultivating a strong security culture requires a multi-faceted approach. It’s not just about providing training; it’s about embedding security into the very fabric of the organization.
- Lead by Example: Senior management must actively demonstrate commitment to security, setting the tone from the top down.
- Open Communication: Foster a culture of open communication where employees feel comfortable reporting security incidents without fear of retribution.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Clear Security Policies: Implement clear, concise, and easily accessible security policies that are regularly reviewed and updated.
- Incentivize Security: Recognize and reward employees who demonstrate strong security practices and report potential threats.
- Gamification: Incorporate gamification elements into security awareness training to make learning more engaging and interactive.
The Role of Employee Background Checks
Employee background checks play a crucial role in preventing insider threats and strengthening foundational security. Thorough background checks, including criminal history checks and verification of employment history and education credentials, can help identify individuals who may pose a risk to the organization. While not a foolproof solution, background checks are a valuable tool in reducing the likelihood of malicious insiders gaining access to sensitive information or systems.
The process should be conducted in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, ensuring fairness and protecting employee privacy. The results should be used to inform hiring decisions and access control policies, further reinforcing foundational security measures.
Emerging Threats and Foundational Security
The seemingly simple building blocks of IT security – strong passwords, updated software, and basic network hygiene – often form the weakest links in an enterprise’s defenses. Emerging threats are expertly exploiting these foundational vulnerabilities, pushing the boundaries of what we consider secure. Understanding these threats and their impact on foundational security is crucial for building resilient systems.
Three Emerging Threats Targeting Foundational Security Weaknesses
The convergence of several technological advancements has created a landscape where traditional security measures are insufficient. Three significant threats highlight this vulnerability. First, sophisticated phishing attacks, often employing AI-powered personalization and social engineering, bypass basic authentication controls. Second, the rise of supply chain attacks leverages vulnerabilities in third-party software and hardware to gain unauthorized access to an organization’s systems.
Third, the increasing prevalence of ransomware, often deployed through phishing or exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities, directly targets foundational security by encrypting critical data and demanding ransom payments. These threats underscore the need for a holistic approach to security, moving beyond simple perimeter defenses.
The Impact of Increasing IoT Device Usage on Foundational Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices dramatically expands the attack surface for any organization. These devices, often lacking robust security features, represent easy entry points for malicious actors. The sheer number of devices, coupled with their often-unpatched software and weak authentication mechanisms, creates a significant challenge for organizations attempting to maintain foundational security. A single compromised IoT device can serve as a foothold for a larger attack, potentially compromising sensitive data or disrupting critical operations.
For example, a compromised smart thermostat could be used as a gateway to access a company’s internal network, illustrating the pervasive nature of this threat.
Securing the Supply Chain and its Relationship to Foundational Security, Foundational security is the enterprises weakest link
Securing the supply chain is paramount to maintaining foundational security. Organizations rely on numerous third-party vendors for software, hardware, and services. A vulnerability in any part of this chain can compromise the entire system. The challenge lies in verifying the security practices of all involved parties and ensuring that all components meet a minimum security standard. This necessitates robust vetting processes, continuous monitoring, and incident response plans that encompass the entire supply chain.
The recent SolarWinds attack, where malicious code was inserted into the company’s software updates, serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of supply chain vulnerabilities.
Implications of AI-Powered Attacks on Foundational Security Measures
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape, presenting both opportunities and challenges. AI-powered attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of automating tasks like vulnerability scanning, phishing campaign creation, and malware development. These attacks can overwhelm traditional security measures, exploiting weaknesses in foundational security more effectively and at a much larger scale. For instance, AI can be used to generate highly personalized phishing emails, increasing the likelihood of success, or to identify and exploit zero-day vulnerabilities before they are patched.
A Hypothetical Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Targeting Weak Foundational Security
Imagine a sophisticated APT group targeting a manufacturing company. They begin by compromising a poorly secured IoT device on the factory floor, gaining initial access to the internal network. Exploiting known vulnerabilities in outdated software, they establish a persistent presence, silently exfiltrating sensitive data, including designs for new products and customer information, over an extended period. This data is then used for industrial espionage, providing a competitive advantage to the attackers while simultaneously causing significant financial and reputational damage to the victim.
The attack remains undetected for months, highlighting the devastating consequences of neglecting foundational security measures. The attackers’ success relies heavily on the company’s failure to implement basic security practices like regular software updates, strong password policies, and robust network segmentation.
Conclusion: Foundational Security Is The Enterprises Weakest Link
Ultimately, strengthening foundational security isn’t about adopting the latest technology; it’s about building a culture of security from the ground up. This requires a multifaceted approach that combines robust technology, well-defined policies, comprehensive training, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By addressing the fundamental weaknesses in our security practices, we can significantly reduce our risk profile and build organizations that are truly resilient against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Let’s make foundational security a priority, not an afterthought.
FAQ Explained
What is the biggest mistake companies make regarding foundational security?
Ignoring the human element. Technical security measures are crucial, but they’re useless if employees aren’t trained to recognize and avoid phishing attempts or follow basic security protocols.
How much does foundational security training cost?
The cost varies widely depending on the size of the organization, the type of training, and whether it’s delivered internally or externally. However, the cost of a data breach far outweighs the investment in proper training.
Can small businesses afford robust foundational security?
Absolutely. Many affordable and effective tools and practices are available, even for smaller organizations. Focusing on the basics – strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular software updates – can make a significant difference.