Cyber Security Website CAPTCHAs Vulnerable to Attacks
Cyber security website captchas are vulnerable to cyber attacks. It’s a shocking truth, isn’t it? We trust those wobbly letters and distorted images to keep our data safe, but the reality is, sophisticated bots are constantly finding ways to crack them. This post dives deep into the vulnerabilities of CAPTCHAs, exploring how attackers bypass these supposed security measures and the devastating consequences that follow.
We’ll uncover the sneaky tactics used to defeat these digital gatekeepers and discuss ways to bolster your website’s defenses.
From simple text-based CAPTCHAs to the more complex reCAPTCHA systems, we’ll dissect each type, revealing their weaknesses and highlighting the common attack vectors used to exploit them. We’ll examine how automated tools, employing techniques like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and machine learning, effortlessly bypass these seemingly impenetrable barriers. Think of it as a digital arms race, where attackers constantly refine their methods, forcing CAPTCHA technology to evolve in a never-ending game of cat and mouse.
Types of CAPTCHAs and their Vulnerabilities
CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) are a common security measure used to prevent automated bots from accessing websites and services. However, even on cybersecurity websites, which should be particularly robust against such attacks, CAPTCHAs are not immune to vulnerabilities. This discussion explores the common types of CAPTCHAs and their respective weaknesses.
You know, those pesky website captchas? Turns out, they’re not as bulletproof as we think against sophisticated cyberattacks. It highlights the need for robust, comprehensive security solutions, and that’s where platforms like Bitglass come in; check out this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to see how they address these gaps.
Ultimately, even with advanced tools, the fight against cyber threats requires constant vigilance and adaptation, as the vulnerabilities of even seemingly simple security measures like captchas demonstrate.
Text-Based CAPTCHAs
Text-based CAPTCHAs present distorted text characters to the user, requiring them to accurately transcribe the text. These are among the oldest forms of CAPTCHAs, but their simplicity makes them vulnerable to various attacks.
A major vulnerability stems from the fact that distorted text can be relatively easily deciphered by sophisticated OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software. Advances in machine learning have significantly improved the accuracy of OCR, rendering many text-based CAPTCHAs ineffective against determined attackers. Furthermore, automated solvers can be trained on large datasets of CAPTCHA examples, improving their success rate over time.
The relative simplicity of the challenge also allows for brute-force attacks, where numerous attempts are made until a correct solution is found.
Image-Based CAPTCHAs
Image-based CAPTCHAs require users to identify specific objects or features within an image. These can range from simple tasks like selecting all images containing traffic lights to more complex scenarios involving identifying distorted images or solving visual puzzles.
While more complex than text-based CAPTCHAs, image-based CAPTCHAs still suffer from vulnerabilities. Sophisticated image recognition algorithms, powered by deep learning techniques, can effectively bypass many of these challenges. Attackers can also use crowdsourcing techniques, paying humans to solve the CAPTCHAs for them, effectively undermining the security measure. Furthermore, the creation of high-quality, diverse image CAPTCHAs that are difficult for both bots and humans to solve is a complex challenge.
reCAPTCHA
reCAPTCHA, developed by Google, is a more advanced CAPTCHA system that uses a combination of risk analysis and challenge-response mechanisms. It often involves selecting images containing specific objects or verifying that you are not a robot.
While reCAPTCHA is generally considered more robust than simpler CAPTCHA implementations, it is not invulnerable. Sophisticated attacks targeting reCAPTCHA’s underlying risk assessment algorithms have been reported. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in how reCAPTCHA analyzes user behavior and can sometimes lead to successful circumvention. Additionally, similar to image-based CAPTCHAs, crowdsourcing remains a potential threat.
CAPTCHA Comparison Table
The following table summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of different CAPTCHA types and suggests mitigation strategies.
| CAPTCHA Type | Vulnerability | Attack Method | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text-Based | Easily deciphered by OCR software | OCR, brute-force | Use more complex distortion techniques, implement adaptive difficulty |
| Image-Based | Vulnerable to advanced image recognition algorithms, crowdsourcing | Deep learning, crowdsourcing | Use more complex and diverse images, incorporate puzzles or complex tasks |
| reCAPTCHA | Vulnerable to attacks targeting risk assessment algorithms | Exploiting vulnerabilities in risk analysis | Regular updates to algorithms, improved risk assessment models |
Automated CAPTCHA Solving Techniques
The seemingly simple CAPTCHA, designed to distinguish humans from bots, is constantly challenged by sophisticated automated techniques. These techniques leverage advancements in computer vision, machine learning, and distributed computing to crack even the most complex CAPTCHAs, highlighting the ongoing arms race between security measures and automated attacks. Understanding these methods is crucial for developers to design more robust security systems.Automated bots and scripts employ a variety of methods to bypass CAPTCHAs.
It’s crazy how easily some website captchas can be bypassed; even sophisticated ones are vulnerable. Building truly secure systems requires a more robust approach, and that’s where advancements like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future become crucial. Ultimately, stronger security measures are needed to combat increasingly sophisticated cyber attacks targeting even the simplest website defenses, like those pesky captchas.
These methods range from simple brute-force attacks to highly sophisticated techniques utilizing artificial intelligence. The effectiveness of these methods depends on the type of CAPTCHA being used and the resources available to the attacker. The common thread is the automation of tasks that would normally require human intervention.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Image Processing
OCR technology is a cornerstone of automated CAPTCHA solving. Attackers use OCR software to interpret the distorted text or numbers presented in image-based CAPTCHAs. Advanced OCR engines can handle various fonts, distortions, and noise levels. These engines often combine image preprocessing techniques like noise reduction, image enhancement, and skew correction to improve accuracy. The processed image is then fed into the OCR engine, which attempts to recognize the characters.
The accuracy of OCR depends heavily on the complexity of the CAPTCHA. Simple CAPTCHAs with clear, easily recognizable characters are vulnerable to this technique. More sophisticated CAPTCHAs utilize techniques like font obfuscation and image distortion to make OCR less effective.
Machine Learning Techniques, Cyber security website captchas are vulnerable to cyber attacks
Machine learning (ML) algorithms, particularly deep learning models like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have significantly improved the accuracy of automated CAPTCHA solving. These algorithms are trained on massive datasets of CAPTCHA images and their corresponding solutions. The training process involves feeding the algorithm thousands or even millions of CAPTCHA examples, allowing it to learn patterns and features that distinguish between characters and noise.
Once trained, the model can accurately predict the solution for new, unseen CAPTCHAs. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are also used to handle CAPTCHAs that require understanding the sequence of characters. The effectiveness of ML-based approaches hinges on the size and quality of the training dataset. Larger and more diverse datasets lead to more robust and accurate models.
Crowdsourcing and Human-in-the-Loop Systems
For particularly challenging CAPTCHAs, attackers often resort to crowdsourcing. They utilize platforms like Amazon Mechanical Turk or other online labor markets to hire humans to solve CAPTCHAs for them. These platforms provide a large pool of workers willing to solve CAPTCHAs for a small fee. This approach is particularly effective against CAPTCHAs that require complex visual reasoning or human-like judgment.
This approach, while costly, bypasses the technological limitations of automated solutions. The efficiency of crowdsourcing depends on the price paid for solving the CAPTCHAs and the availability of workers.
Examples of CAPTCHA Solving Tools and Techniques
The following examples illustrate specific tools and techniques used for automated CAPTCHA solving. It’s important to note that the details of many of these tools are kept secret by those who develop and use them.
- OCR Software: Tesseract OCR is a popular open-source OCR engine that can be adapted to solve simple CAPTCHAs. Attackers often enhance its capabilities with custom preprocessing scripts to handle specific CAPTCHA designs.
- Machine Learning Libraries: Libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch provide the tools to build and train deep learning models for CAPTCHA solving. These libraries offer pre-trained models and various optimization techniques that can significantly improve accuracy.
- Automated CAPTCHA Solving Services: Several online services offer automated CAPTCHA solving capabilities. These services often employ a combination of OCR, machine learning, and crowdsourcing to achieve high success rates. The details of their algorithms are typically proprietary.
- Browser Extensions: Some malicious browser extensions are designed to automatically solve CAPTCHAs encountered during web browsing. These extensions might use a combination of techniques, including OCR and interaction with CAPTCHA solving services.
Evolution of CAPTCHA Technology
In response to these increasingly sophisticated attacks, CAPTCHA technology has evolved significantly. We’ve seen a shift from simple text-based CAPTCHAs to more complex challenges involving image recognition, puzzles, and even behavioral analysis. The goal is to create CAPTCHAs that are difficult for bots to solve while remaining easy for humans. However, this is an ongoing arms race, with attackers constantly developing new techniques to circumvent the latest security measures.
The development of more robust and adaptive CAPTCHA systems is crucial for maintaining online security.
The Impact of Vulnerable CAPTCHAs on Cybersecurity Websites

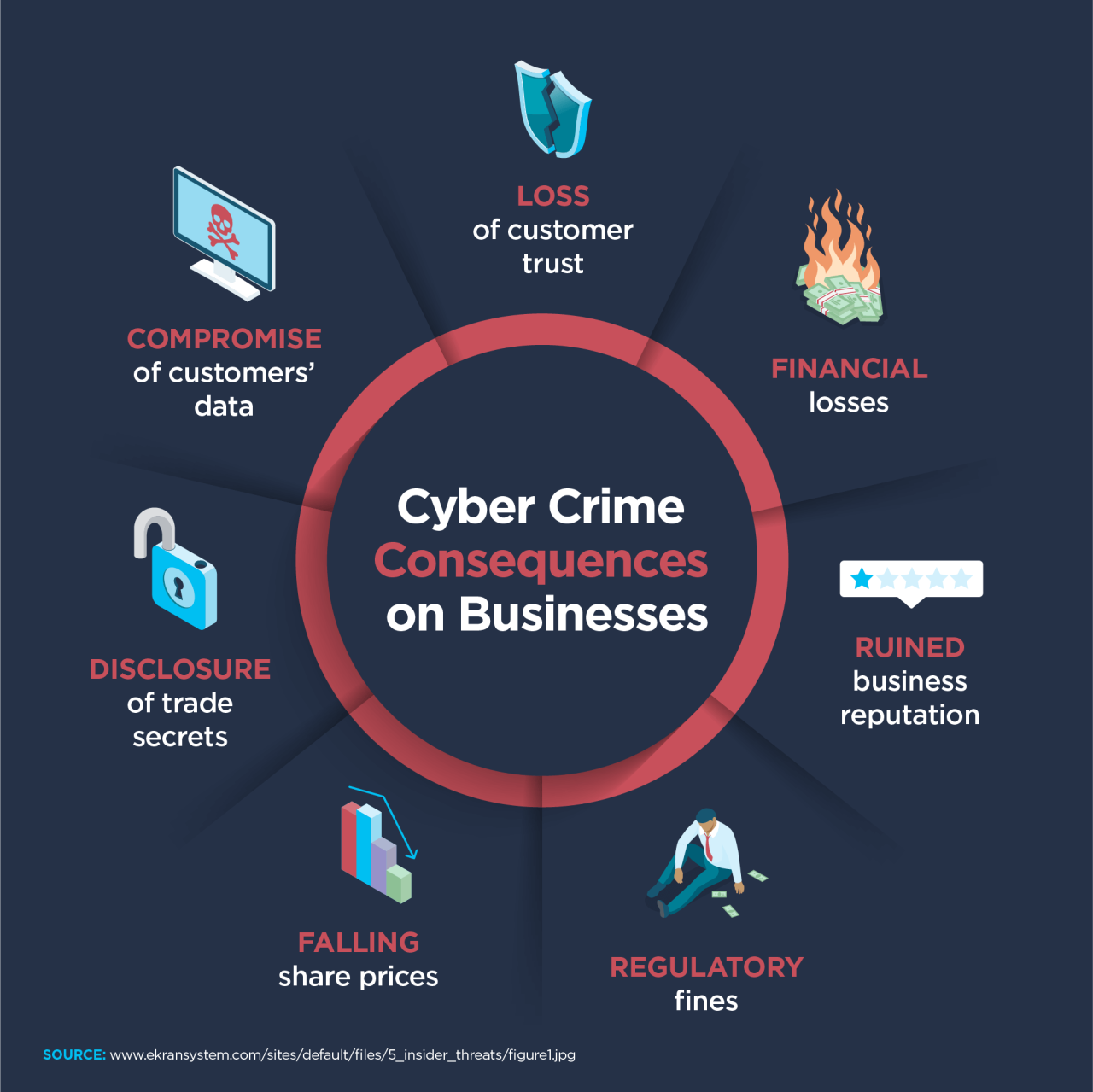
The seemingly simple CAPTCHA, designed to thwart automated bots, can ironically become a significant vulnerability for cybersecurity websites if compromised. A successful CAPTCHA bypass allows malicious actors to circumvent crucial security measures, leading to a cascade of negative consequences that can severely damage a company’s reputation and compromise sensitive data. The impact extends far beyond simple inconvenience; it represents a direct threat to the very security these websites are designed to protect.Successful CAPTCHA attacks on cybersecurity websites have far-reaching implications.
The consequences can range from minor inconveniences like inflated website traffic to catastrophic data breaches and complete system outages. The vulnerability of CAPTCHAs directly undermines the trust placed in these companies by clients and partners, potentially leading to significant financial losses and legal repercussions.
Data Breaches and Account Takeovers
A bypassed CAPTCHA provides malicious actors with a direct pathway to sensitive data. Automated scripts can then be used to harvest user credentials, personal information, and confidential client data. This can lead to large-scale identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational damage. For a cybersecurity firm, this is particularly damaging as it directly contradicts their core business of protecting sensitive information.
The breach of client data could result in substantial financial penalties, legal action, and loss of client trust. Imagine a scenario where a sophisticated botnet, having bypassed the CAPTCHA, gains access to a security firm’s client database containing sensitive financial records and intellectual property. The resulting fallout would be devastating.
Denial-of-Service Attacks
Beyond data breaches, vulnerable CAPTCHAs can facilitate denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Malicious actors can leverage automated tools to flood a website with fake requests, overwhelming its servers and making it inaccessible to legitimate users. This is especially critical for cybersecurity firms, whose services rely on consistent uptime and availability. A successful DoS attack could cripple a firm’s ability to provide services to its clients, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
The impact could be amplified if the attack targets critical infrastructure within the firm’s network.
Real-world Examples of CAPTCHA Bypass Attacks
While specific details of successful CAPTCHA bypasses on cybersecurity firms’ websites are often kept confidential for security reasons, the general vulnerability is well-documented. Numerous academic papers and security reports detail successful attacks against various CAPTCHA implementations, demonstrating the effectiveness of sophisticated techniques like machine learning and deep learning to overcome these security measures. For instance, studies have shown that even advanced CAPTCHAs, like those incorporating image recognition or complex puzzles, can be bypassed with sufficient computational resources and well-crafted algorithms.
The impact of these attacks ranges from minor inconveniences to significant data breaches, highlighting the need for robust and constantly evolving security measures.
Hypothetical Scenario: CAPTCHA Bypass at a Security Firm
Let’s imagine a scenario where a sophisticated cybercriminal group targets “Fortress Security,” a leading cybersecurity firm. Their website, boasting robust security features, employs a custom-designed CAPTCHA. However, a vulnerability in the CAPTCHA’s implementation is discovered and exploited by the attackers. The attackers use a combination of machine learning and brute-force techniques to bypass the CAPTCHA. This allows them to automate the creation of thousands of fake accounts.
Using these accounts, they gain access to the company’s internal forum, downloading confidential client data and internal security documents. Further exploiting the breach, they initiate a distributed denial-of-service attack, crippling Fortress Security’s ability to respond to client emergencies. The resulting reputational damage and financial losses are immense, forcing Fortress Security to undergo a costly and time-consuming recovery process.
This scenario highlights the critical need for continuous monitoring and improvement of CAPTCHA security, especially for organizations in the cybersecurity industry.
Mitigation Strategies and Best Practices
Strengthening CAPTCHA security is crucial for protecting websites from automated attacks. While no CAPTCHA is perfectly invulnerable, implementing robust strategies and best practices significantly reduces the risk of compromise. This involves a multi-layered approach combining advanced CAPTCHA technologies, supplementary authentication methods, and careful consideration of risk factors.
Effective mitigation involves a proactive approach to security, combining technological solutions with careful planning and ongoing maintenance. Simply relying on a single CAPTCHA type is insufficient; a layered approach, incorporating diverse techniques and regular updates, is essential to staying ahead of evolving attack methods.
Advanced CAPTCHA Technologies
Employing more sophisticated CAPTCHA types beyond basic image-based tests is paramount. These include advanced CAPTCHAs that leverage machine learning to adapt to evolving attack strategies. For instance, reCAPTCHA v3 analyzes user behavior subtly in the background, without requiring explicit user interaction, scoring the likelihood of a bot interaction. Another example is using CAPTCHAs that incorporate multiple challenge types, such as puzzles, audio challenges, and behavioral analysis, making it significantly harder for automated bots to crack.
The use of adaptive CAPTCHAs, which adjust their difficulty based on user interaction patterns, further enhances security. This dynamic approach ensures that even if one challenge is bypassed, the overall system remains robust.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation
MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond CAPTCHAs. Even if a bot successfully bypasses the CAPTCHA, MFA requires the user to provide a second form of verification, such as a one-time code sent to their phone or email, or a biometric scan. This significantly reduces the chances of unauthorized access, even if the CAPTCHA is compromised. Implementing MFA is particularly crucial for high-security applications and sensitive user data.
For example, a banking website could utilize a CAPTCHA for initial access and then require a one-time password generated by an authenticator app for transactions.
Risk Assessment in CAPTCHA Selection
Choosing the right CAPTCHA is not a one-size-fits-all solution. A thorough risk assessment is vital. Factors to consider include the sensitivity of the data protected by the website, the frequency and sophistication of attacks experienced, and the level of user experience desired. For a website with low-risk data, a simple image-based CAPTCHA might suffice. However, for a financial institution handling sensitive financial information, a more robust multi-layered CAPTCHA system, potentially incorporating behavioral biometrics, is essential.
This approach ensures that the chosen CAPTCHA aligns with the specific security needs of the website.
Best Practices for CAPTCHA Implementation and Maintenance
Successful CAPTCHA implementation requires careful planning and ongoing maintenance. A proactive approach is crucial for maintaining robust security.
- Regularly update CAPTCHA libraries and algorithms to address newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Monitor CAPTCHA performance metrics, such as solve rates and error rates, to identify potential weaknesses.
- Implement robust logging and monitoring to detect and respond to suspicious activity.
- Use a variety of CAPTCHA types and challenge methods to avoid reliance on a single point of failure.
- Integrate CAPTCHA solutions with other security measures, such as web application firewalls (WAFs) and intrusion detection systems (IDS).
- Provide clear and user-friendly instructions to help users complete CAPTCHAs successfully.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Keep abreast of the latest CAPTCHA vulnerabilities and best practices through industry resources and security updates.
Future Trends in CAPTCHA Technology

The landscape of CAPTCHA technology is constantly evolving, driven by the relentless arms race between developers striving to create more robust security measures and attackers seeking to circumvent them. The future of CAPTCHAs lies in leveraging advanced technologies and incorporating user behavior analysis to create a more seamless and secure authentication experience. This shift necessitates a move away from traditional, easily automated methods towards more sophisticated and adaptive systems.
Emerging CAPTCHA technologies promise a significant leap forward in online security. The integration of behavioral biometrics, advanced AI, and machine learning techniques is transforming how we approach authentication, moving beyond simple image recognition to a more holistic understanding of user interactions.
Behavioral Biometrics in CAPTCHA Enhancement
Behavioral biometrics offer a powerful tool to enhance CAPTCHA effectiveness. By analyzing subtle variations in a user’s typing rhythm, mouse movements, and scrolling patterns, systems can build a unique behavioral profile. This profile acts as an additional layer of security, making it significantly harder for automated bots to mimic human behavior. For instance, a system might analyze the time taken to complete a CAPTCHA, the trajectory of mouse movements, and the pressure applied to the keys, comparing these against established user baselines.
Discrepancies would trigger a security alert. This approach offers a passive and frictionless method of authentication, enhancing security without significantly impacting user experience.
Challenges and Opportunities Presented by AI and Machine Learning Advancements
The advancements in AI and machine learning pose both challenges and opportunities for CAPTCHA technology. While AI-powered bots are becoming increasingly sophisticated at solving traditional CAPTCHAs, these same technologies can be harnessed to create more robust and adaptive CAPTCHA systems. The challenge lies in staying ahead of the curve, continuously developing new methods to outpace the evolving capabilities of AI-driven attacks.
Opportunities exist in developing CAPTCHAs that leverage AI to learn and adapt to new attack vectors, dynamically adjusting their difficulty based on the observed user behavior and potential threats.
A Futuristic CAPTCHA System: Adaptive Behavioral Authentication
Imagine a CAPTCHA system that seamlessly integrates behavioral biometrics with advanced AI. This futuristic system, which we’ll call “Adaptive Behavioral Authentication” (ABA), would operate without explicit challenges. Instead, it passively monitors user interactions throughout their session. The system would analyze various behavioral patterns, such as typing speed and rhythm, mouse movements, scrolling behavior, and even subtle variations in keystrokes.
This data would be compared against a baseline profile created during the user’s initial registration. Any significant deviation from this baseline, indicating potential automated activity, would trigger a secondary authentication step, perhaps involving a brief, context-sensitive challenge tailored to the identified anomaly. The system’s AI would continuously learn and adapt, identifying new attack patterns and refining its detection algorithms, making it highly resistant to automated attacks.
The ABA system would be nearly invisible to legitimate users, offering robust security without interrupting the flow of their online experience. Its adaptive nature would make it incredibly difficult for bots to predict and circumvent, ensuring sustained protection against evolving attack techniques.
Final Thoughts
The vulnerability of CAPTCHAs on cybersecurity websites is a serious concern, highlighting the constant need for adaptation and innovation in online security. While CAPTCHAs offer a layer of protection, they’re not a silver bullet. Relying solely on them leaves your website exposed. A multi-layered approach, combining robust CAPTCHAs with multi-factor authentication and a vigilant security posture, is essential to effectively protect your valuable data and user accounts.
The future of CAPTCHA technology lies in incorporating more sophisticated methods, leveraging behavioral biometrics and advanced AI to stay ahead of the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. The fight for online security is far from over, and the battle against CAPTCHA-cracking bots continues.
Key Questions Answered: Cyber Security Website Captchas Are Vulnerable To Cyber Attacks
What are the most common types of CAPTCHAs?
Common CAPTCHA types include text-based (identifying distorted text), image-based (selecting images matching a criteria), and reCAPTCHA (checking boxes or solving puzzles).
How much does a CAPTCHA breach cost a company?
The cost varies wildly depending on the scale of the breach, the type of data compromised, and the resulting legal and reputational damage. It could range from thousands to millions of dollars.
Can CAPTCHAs be completely bypassed?
While difficult, no CAPTCHA is completely unbreakable. Sophisticated attackers can utilize various methods to circumvent them, emphasizing the need for layered security.
Are there CAPTCHAs that are inherently more secure than others?
Generally, more complex CAPTCHAs, incorporating multiple challenge types or behavioral biometrics, offer better security than simpler text-based ones.