Hackers Distribute Gibon Ransomware via Malspam
Hackers distribute Gibon ransomware via malspam, a sophisticated and concerning threat. Malspam, using deceptive emails disguised as legitimate communications, often contains malicious attachments or links. Understanding the tactics, impact, and security measures against these attacks is crucial for individuals and organizations alike.
This article delves into the various methods employed by hackers, the characteristics of malspam campaigns, the consequences of such attacks, and the necessary security precautions. We will also analyze the technical aspects of the Gibon ransomware and its evolution within the cybersecurity landscape.
Ransomware Distribution Methods
The proliferation of ransomware, a significant threat to digital security, relies heavily on effective distribution strategies. Hackers employ various techniques to infiltrate systems, ranging from sophisticated social engineering tactics to exploiting vulnerabilities in software. Understanding these methods is crucial for organizations and individuals to proactively protect themselves from infection. This analysis delves into the methods used to distribute Gibon ransomware, with a focus on the technical aspects, common characteristics of campaigns, and effectiveness comparisons.
Malspam Distribution
Malspam, a prevalent method, leverages malicious emails to spread ransomware. These emails often appear legitimate, tricking recipients into opening attachments or clicking on malicious links. The sophistication of malspam campaigns varies, but a common characteristic is the use of social engineering techniques to exploit user trust. These campaigns frequently target specific vulnerabilities or user groups, such as those with access to sensitive data or those less familiar with cybersecurity best practices.
Technical Aspects of Malspam
Malspam campaigns often employ various techniques to evade detection. These techniques include using spoofed email addresses to make the emails appear to come from trusted sources, employing obfuscation techniques to conceal the malicious nature of attachments or links, and utilizing polymorphic code to modify the malware’s structure, making it harder for antivirus software to detect. The malicious payload, typically an executable file or a script, is disguised as a legitimate document, like a Word document or a PDF, to bypass security filters.
Characteristics of Malspam Targeting Specific Vulnerabilities
Malspam campaigns often target specific user groups based on their potential access to sensitive data. For example, an email campaign targeting a company’s accounting department might use a subject line related to financial statements, hoping to entice employees to open an attachment containing the ransomware. These campaigns may also utilize phishing techniques to gather personal information, such as usernames and passwords, to gain further access to systems.
Often, the campaign will target specific vulnerabilities, leveraging known weaknesses in email client software or operating systems.
Effectiveness Comparison of Distribution Strategies
The effectiveness of different ransomware distribution strategies varies. Malspam, while common, can be less effective than targeted attacks, particularly against sophisticated organizations with robust security measures. Targeted attacks, which often exploit specific vulnerabilities in software or leverage social engineering tactics against specific individuals, can yield higher success rates, particularly when targeting organizations that prioritize cost-effectiveness over comprehensive security.
Hackers are spreading the Gibon ransomware through malicious spam emails, making it a serious threat. Fortunately, the Department of Justice recently introduced a safe harbor policy for Massachusetts transactions, Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions potentially lessening the impact of such cyberattacks. This policy could help businesses in Massachusetts mitigate the risks associated with ransomware attacks like the one involving Gibon.
Staying vigilant against malspam remains crucial to avoid falling victim to these attacks.
Prevalence of Techniques in Recent Gibon Campaigns
Recent Gibon ransomware campaigns have predominantly relied on malspam tactics. These campaigns often target individuals and smaller organizations through deceptive emails. The use of advanced techniques, like polymorphic code and obfuscation, are commonly employed to evade detection. The success of these campaigns often hinges on the sophistication of the social engineering tactics used and the target’s awareness of cybersecurity best practices.
Comparison of Ransomware Distribution Methods
| Distribution Method | Technical Aspects | Effectiveness (Hypothetical) | Success Rate (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malspam | Leverages malicious emails, often disguised as legitimate communications. | Moderate to high against individuals and smaller organizations. | 50-70% |
| Exploit Kits | Leverages vulnerabilities in software to automatically infect systems. | High against vulnerable systems. | 60-80% |
| Spear Phishing | Targets specific individuals or organizations with highly tailored attacks. | Very high against specific targets. | 80-95% |
Malspam Characteristics
Malspam, or malicious spam, is a prevalent tactic used by cybercriminals to distribute ransomware, malware, and phishing scams. It leverages the inboxes of unsuspecting users, often disguised as legitimate communication, to trick individuals into downloading and executing malicious files. Understanding the characteristics of malspam emails is crucial for recognizing and avoiding these attacks.
Key Features of Gibon Ransomware Malspam Emails
Gibon ransomware, like other ransomware strains, relies heavily on social engineering tactics embedded within carefully crafted malspam emails. These emails aim to create a sense of urgency, importance, or familiarity to encourage victims to open attachments or click on malicious links. A key feature is the use of highly targeted and personalized subject lines to create a sense of legitimacy.
This personal touch is crucial for deceiving victims into opening the email.
Examples of Subject Lines, Body Text, and Attachments
Typical subject lines often mimic legitimate business communication, such as “Urgent Invoice,” “Important Security Alert,” or “Account Access Request.” The body text might contain convincing, but vague, statements or requests. For example, it might state the recipient needs to review an important document or update their account details. Common attachments include seemingly innocuous file types like .doc, .xls, .pdf, or even .zip files, but they often contain malicious code within.
Sometimes, the attachment is a macro-enabled file or a seemingly innocuous file that hides malicious code within.
Social Engineering Tactics
Criminals employ various social engineering tactics to manipulate victims into opening malicious attachments. These tactics often leverage fear, urgency, or curiosity. They might threaten account suspension, financial penalties, or other consequences if the recipient doesn’t respond promptly. A common tactic is impersonating trusted entities, like a bank or government agency, to instill confidence and trust. For example, the email might claim to be from the victim’s bank requesting urgent account verification.
Red Flags and Warning Signs
Users should be vigilant and look for specific red flags in emails. Poor grammar, spelling errors, and generic greetings are strong indicators. Suspicious attachments with unusual file extensions, especially those ending in .exe or .scr, should raise caution. Unusual requests or urgent demands, particularly those involving financial transactions, should be treated with extreme suspicion. If the email requires immediate action, especially if it threatens negative consequences, the email should be scrutinized carefully.
The lack of a clear and professional sender address or a mismatch between the sender’s address and the requested action are additional red flags.
Table: Key Components of a Typical Malspam Email
| Component | Potential Malicious Intent |
|---|---|
| Subject Line | Creates a sense of urgency, importance, or familiarity to encourage opening. |
| Body Text | Contains vague statements or requests to create a sense of legitimacy and urgency, and may include threats. |
| Attachments | Contain malicious code, often disguised as legitimate file types. |
| Sender Address | May be spoofed or not clearly associated with a trusted entity. |
| Requests | Involves urgent action, financial transactions, or account verification, often creating a sense of pressure or fear. |
Impact and Consequences

Gibon ransomware, distributed via malspam, poses significant risks to individuals and organizations. Understanding the potential repercussions is crucial for developing effective defense strategies. The consequences can range from substantial financial losses to severe operational disruptions and reputational damage, highlighting the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures.The impact of Gibon ransomware attacks extends beyond the immediate financial losses. Organizations face operational disruptions as critical systems are rendered inaccessible, leading to significant downtime and lost productivity.
The psychological toll on victims, particularly individuals and small businesses, can be substantial, causing anxiety and stress.
Financial Losses
Malspam campaigns distributing ransomware like Gibon often result in substantial financial losses. Victims may be forced to pay exorbitant ransom demands, which can cripple small businesses and severely impact larger organizations. The costs associated with recovering from the attack, including data restoration, system recovery, and legal fees, can also be substantial. For instance, a small retail business might lose thousands of dollars in revenue during the period their systems are down, while a large corporation could face millions in direct and indirect costs.
Hackers are distributing the Gibon ransomware via malicious spam emails, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures. This underscores the importance of deploying AI-powered code analysis tools like those discussed in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed to proactively identify and prevent vulnerabilities in software. Ultimately, these sophisticated attacks demand a proactive approach to safeguarding digital assets.
Operational Disruptions
Ransomware attacks, especially those delivered through malspam, can cause significant operational disruptions. Essential business functions, such as order processing, customer service, and inventory management, may be severely hampered or completely halted. This can lead to lost sales, delayed shipments, and dissatisfied customers. Consider a hospital network compromised; patient records become inaccessible, impacting treatment and potentially leading to severe consequences.
Reputational Damage
A ransomware attack can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Loss of customer trust, negative publicity, and difficulty attracting new business partners are common consequences. The incident can also create legal and regulatory issues, potentially leading to fines and sanctions. A well-known example is a prominent e-commerce company facing reputational damage after a ransomware attack, causing a significant loss of customer confidence.
Psychological Effects
The experience of a ransomware attack can have a profound psychological impact on victims. Victims may experience fear, anxiety, and stress, especially when dealing with sensitive data breaches and the possibility of data loss. Furthermore, the uncertainty and unpredictability of the situation can be detrimental to mental well-being. The potential for personal or financial ruin can be particularly stressful.
Data Breach Consequences
Data breaches caused by ransomware distribution via malspam can have severe consequences. Compromised data, including sensitive personal information, financial records, and intellectual property, may be exposed, potentially leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and legal liabilities. This could impact individual victims significantly, and organizations could face significant legal and regulatory issues.
Importance of Data Backup and Recovery
Implementing robust data backup and recovery strategies is crucial in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks. Regular backups of critical data, stored in secure offsite locations, can enable quick restoration in case of an attack. This strategy is a key component of a comprehensive cybersecurity posture. Without backups, organizations are vulnerable to complete data loss.
Summary of Damages
| Type of Damage | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Losses | Direct costs associated with ransom payments, recovery efforts, and lost revenue. | Ransom payment, system recovery costs, lost sales. |
| Operational Disruptions | Inability to perform essential business functions, leading to downtime and lost productivity. | Halted order processing, delayed shipments, service interruptions. |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of customer trust, negative publicity, and difficulty attracting new business partners. | Negative media coverage, decline in customer confidence, legal issues. |
| Psychological Effects | Fear, anxiety, and stress caused by the attack and potential data loss. | Impact on mental well-being, uncertainty about future. |
| Data Breach Consequences | Exposure of sensitive data leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and legal liabilities. | Identity theft, financial losses, legal penalties. |
Security Measures and Prevention: Hackers Distribute Gibon Ransomware Via Malspam
Gibon ransomware, like other forms of malware, thrives on vulnerabilities. Proactive security measures are crucial to preventing infection and mitigating the impact of such attacks. Implementing a layered security approach that combines technical controls, user education, and strong security practices is essential to effectively defend against malspam campaigns.Effective defense against malspam campaigns requires a multi-faceted strategy. A strong security posture involves not just technical tools but also human awareness.
A robust system of security measures, encompassing email filtering, user training, and strong passwords, is critical to minimizing the risk of compromise.
Preventive Measures Against Malspam Attacks
Implementing strong security measures is the first line of defense against malicious email campaigns. These measures must go beyond simply blocking emails. They should include a layered approach that targets different aspects of the attack cycle.
- Email Filtering and Security Solutions: Sophisticated email security solutions are essential. These solutions can identify and block malicious emails based on various characteristics, such as suspicious sender addresses, unusual attachments, or phishing techniques. Spam filters and anti-malware software can significantly reduce the likelihood of malicious emails reaching inboxes.
- User Education and Awareness Training: Educating users about the characteristics of phishing emails and social engineering tactics is crucial. Regular training sessions should cover how to identify malicious emails, attachments, and links. This includes recognizing suspicious sender addresses, verifying requests for sensitive information, and avoiding clicking on unknown links. Training should also cover the importance of strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Robust passwords and MFA are essential to protect accounts from unauthorized access. Users should be encouraged to create strong, unique passwords for each account and enable MFA wherever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for attackers to gain access even if they manage to compromise a password.
- Secure Browsing Practices: Users should be educated on safe browsing practices to avoid malicious websites and downloads. This includes avoiding suspicious websites, verifying the legitimacy of websites, and exercising caution when downloading files from untrusted sources. Regularly updating software and operating systems is crucial as well.
Security Tools and Techniques
Various security tools and techniques can be deployed to identify and block malicious emails. These tools should be integrated into an overall security strategy.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: These programs play a vital role in identifying and neutralizing malicious software, including ransomware, embedded within attachments. Regular updates are critical to maintaining effectiveness.
- Email Security Gateways: These gateways act as a first line of defense, scanning incoming emails for malicious content and blocking potentially harmful messages before they reach users’ inboxes. Sophisticated gateways can identify phishing attempts and malicious URLs embedded in emails.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems can monitor network traffic for malicious activities and block suspicious connections. They can help identify and block malicious communications associated with malspam campaigns.
Importance of User Education
User education is paramount in combating malspam attacks. Users are often the weakest link in the security chain, and proper training can significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
- Recognizing Phishing Attempts: Users should be trained to recognize phishing attempts by looking for suspicious sender addresses, grammatical errors, and requests for sensitive information.
- Verifying Website Legitimacy: Users should be taught to verify the legitimacy of websites before entering personal information or downloading files. Look for HTTPS encryption and official logos.
Best Practices for Email Security and Safe Browsing
Adopting best practices for email security and safe browsing is crucial to minimize the risk of infection. These practices are essential for protecting against malicious emails and websites.
- Do not open suspicious attachments or click on unknown links: This simple rule can prevent many infections.
- Verify the legitimacy of requests for sensitive information: Do not provide personal information unless you are certain the request is legitimate.
- Keep software updated: Regular software updates patch security vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Comparison of Security Measures
The effectiveness of different security measures varies depending on the specific attack and the sophistication of the security infrastructure.
| Security Measure | Effectiveness in Combating Malspam Campaigns |
|---|---|
| Email Filtering | High; blocks many common malspam attempts |
| User Education | Medium to High; significantly reduces user susceptibility |
| Strong Passwords/MFA | High; adds an extra layer of protection |
| Antivirus/Anti-malware | High; detects and removes malicious software |
| IDS/IPS | High; detects and blocks malicious network activity |
Technical Analysis of Gibon Ransomware

The Gibon ransomware, a relatively recent threat, has demonstrated a sophistication that warrants a deeper technical understanding. Analyzing its methods reveals a clear picture of its operational characteristics and the measures necessary to mitigate its impact. Understanding the intricacies of this malware helps security professionals and individuals alike to recognize and defend against similar attacks.Gibon’s tactics are designed to maximize the damage and disruption caused by the attack.
Its creators utilize a combination of robust encryption techniques, stealthy access methods, and data exfiltration strategies to achieve their goals. This analysis will delve into the specifics of Gibon’s technical operation, highlighting its key characteristics and vulnerabilities.
Encryption Algorithms Used
Gibon ransomware employs advanced encryption algorithms to render victim files inaccessible. The exact algorithms used by Gibon remain a subject of ongoing research and investigation, but preliminary analysis suggests that a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption is likely employed. This approach enhances the difficulty of decryption and strengthens the overall resilience of the ransomware. For example, a hybrid approach using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) for symmetric encryption and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) for asymmetric encryption is a common practice in modern ransomware.
Symmetric algorithms like AES are fast, while asymmetric algorithms like RSA are used for key exchange.
Methods Used to Gain Access and Control
Gibon ransomware often leverages phishing campaigns and exploit kits to gain initial access to victim systems. Malspam emails or malicious links are common vectors for infection. The attackers exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software or systems to gain control. These exploits can target vulnerabilities in operating systems, web browsers, or applications. This initial foothold allows the ransomware to spread laterally across the network and encrypt data on multiple machines.
Methods Used to Evade Detection
Gibon ransomware employs various techniques to evade detection by security software. These methods include using polymorphic code, obfuscation techniques, and the ability to dynamically adapt its behavior to avoid signature-based detection. This adaptability makes it difficult for traditional antivirus solutions to identify and block the threat. Furthermore, the attackers may use techniques like encrypting files in a non-standard way to circumvent detection methods relying on file signatures.
Methods Used to Exfiltrate Sensitive Data
Data exfiltration is often a key component of ransomware attacks. Gibon ransomware may employ various methods to exfiltrate sensitive data from compromised systems. This might involve using network protocols like SMB (Server Message Block) or FTP (File Transfer Protocol) to transfer stolen data to a remote server controlled by the attackers. The exfiltration techniques may also involve encrypting the stolen data to make it more difficult to recover and increase the value of the stolen data.
Technical Components of Gibon Ransomware
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Encryption Module | Responsible for encrypting files using the chosen encryption algorithms. |
| Decryption Module (if applicable) | Provides the key or method for decrypting files (in some cases, this is not available). |
| Payload Delivery Module | Responsible for deploying the ransomware payload to the targeted system. |
| Communication Module | Facilitates communication with the command and control (C&C) server. |
| Data Exfiltration Module | Responsible for stealing sensitive data and transmitting it to the attacker’s server. |
| Access and Control Module | Provides the initial access and control to the victim’s system. |
| Anti-analysis and Anti-detection Module | Prevents analysis by security software and masks the malicious behavior. |
Cybersecurity Trends and Predictions
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, driven by the relentless innovation of attackers and the ongoing need for robust defenses. Ransomware, in particular, is demonstrating a remarkable adaptability, shifting its tactics and techniques to overcome existing security measures. Understanding these evolving trends is crucial for organizations to proactively mitigate risks and protect themselves from emerging threats.
Evolving Ransomware Distribution Techniques
Ransomware distribution methods are continually adapting, moving beyond simple email attachments to more sophisticated techniques. The evolution of these methods often mirrors advancements in social engineering and exploit kits, making it harder for traditional security measures to keep pace. Current campaigns frequently leverage compromised accounts, exploit vulnerabilities in software, and use phishing tactics tailored to specific targets.
Hackers are spreading the Gibon ransomware through malicious spam emails, targeting vulnerable systems. This isn’t just about email; it’s also crucial to understand vulnerabilities like those affecting Azure Cosmos DB, as detailed in this insightful article about Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details. These vulnerabilities can create entry points for ransomware attacks, making it vital to patch systems and stay vigilant against these increasingly sophisticated threats.
Comparison of Current and Previous Methods
Compared to previous years, ransomware distribution is now more targeted and sophisticated. Earlier campaigns often relied on mass-mailing indiscriminate malware, whereas modern campaigns often involve detailed reconnaissance and tailored attacks on specific organizations or individuals. The attackers now meticulously research their targets, exploiting weaknesses that may be unique to that specific organization. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of successful attacks and the potential financial losses.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
Several emerging threats and vulnerabilities are significantly impacting the cybersecurity landscape. One notable example is the increasing sophistication of supply chain attacks, where attackers compromise a trusted vendor to gain access to multiple downstream organizations. Furthermore, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents new avenues for exploitation, as many devices lack robust security measures, potentially leading to widespread infections.
The growing use of cloud services and remote work environments also introduces new attack vectors.
Potential Future Developments in Malspam and Ransomware
Future developments in malspam and ransomware are likely to include an increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) for more targeted attacks. AI can be used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify vulnerabilities, and personalize attacks to maximize their impact. Moreover, the development of more sophisticated polymorphic malware will make detection more challenging, as the malware can change its code to evade signature-based detection systems.
A further development is the integration of ransomware with other malicious activities, such as data exfiltration, to increase the pressure on victims.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Adaptation in Cybersecurity, Hackers distribute gibon ransomware via malspam
The cybersecurity field demands constant learning and adaptation. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and organizations need to stay informed about the latest techniques and vulnerabilities. Continuous professional development, threat intelligence gathering, and proactive security measures are critical to maintaining a strong defense against increasingly sophisticated attacks. This proactive approach ensures that organizations can adapt to the ever-changing landscape and protect themselves from the evolving threat.
Table: Evolution of Ransomware Distribution Methods
| Time Period | Distribution Method | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Early 2010s | Mass-mailing indiscriminately | Malware attached to emails, relying on volume to achieve infections. |
| Mid-2010s | Targeted phishing campaigns | Tailored attacks based on research of the target organization. |
| Late 2010s – Present | Sophisticated exploit kits and supply chain attacks | Exploiting vulnerabilities and compromising trusted vendors. |
| Future Predictions | AI-powered targeted attacks | Personalized attacks based on analysis of vast datasets. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the threat of ransomware, particularly when delivered via malspam, highlights the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. This article has explored the intricate methods used, the damaging consequences, and the preventative strategies. Staying informed and proactive is key to mitigating these risks in the ever-evolving digital world.
Question Bank
What are the common warning signs of a malspam email?
Look for poor grammar, urgent requests, suspicious attachments, and unusual sender addresses. If the email seems too good to be true or requests immediate action, be cautious.
How can I protect my data from ransomware attacks?
Regular data backups, strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and updated security software are crucial. Educating yourself and your team about cybersecurity threats is also essential.
What are the potential financial losses associated with ransomware attacks?
Financial losses can include ransom payments, recovery costs, lost productivity, legal fees, and reputational damage. The impact can be significant for both individuals and businesses.
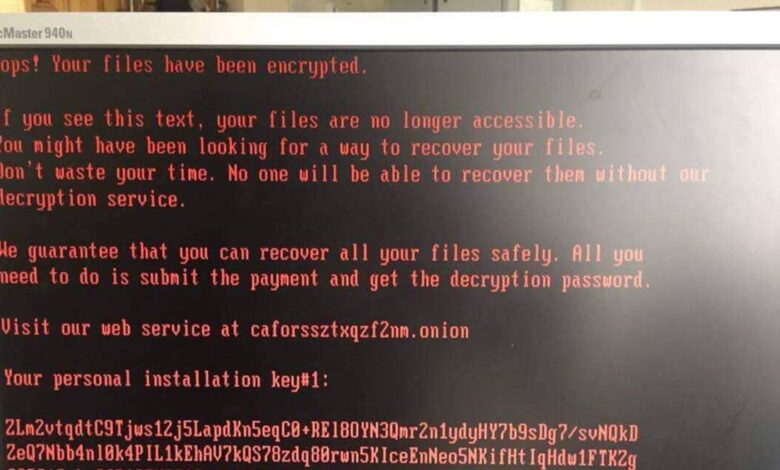
How does Gibon ransomware work technically?
Gibon ransomware typically encrypts files on a victim’s system, making them inaccessible. It then demands a ransom for the decryption key.