
Protecting Municipalities from Ransomware
How municipal governments could protect against ransomware is crucial in today’s digital landscape. Municipalities, often with limited cybersecurity resources, face a significant threat from sophisticated ransomware attacks. These attacks can cripple essential services, damage reputations, and cause substantial financial losses. This article delves into practical strategies to bolster defenses and build resilient cybersecurity practices within local governments.
Understanding the various types of ransomware targeting municipalities, along with the motivations and tactics of attackers, is the first step. Successful and unsuccessful attack examples highlight the importance of proactive measures and the need for customized security strategies.
Understanding Ransomware Threats
Ransomware attacks are a growing concern for municipal governments, posing significant financial and reputational risks. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks, encrypting data and demanding payment for its release. Understanding the different types, tactics, and motivations of attackers is crucial for developing effective defense strategies.
Different Ransomware Types Targeting Municipalities
Municipal governments, with their diverse systems and interconnected networks, face a range of ransomware threats. These threats vary in sophistication and impact. Some common types include:
- File-encrypting ransomware: This is the most prevalent type, targeting sensitive data like financial records, personnel files, and operational documents. Attacks often involve encrypting entire systems, demanding payment for decryption keys, and potentially causing significant disruption to essential services.
- Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS): This model allows even less sophisticated actors to launch attacks. RaaS platforms provide tools and infrastructure, reducing the technical barriers to entry and enabling a wider range of attackers to target municipalities.
- Supply chain attacks: These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software or hardware vendors, potentially impacting multiple municipalities that rely on the compromised vendor.
- Double extortion attacks: Beyond encrypting data, attackers may also threaten to publicly leak sensitive information if the ransom isn’t paid. This adds another layer of pressure and potential damage.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Attacks
Numerous municipalities have fallen victim to ransomware attacks, highlighting the diverse impacts and vulnerabilities. Successful attacks often result in substantial financial losses and operational disruptions, while unsuccessful attacks can still have a considerable impact on resources and confidence.
- Successful attacks: The city of Baltimore in 2019 experienced a significant disruption to its services due to a ransomware attack, impacting 911 services and other critical operations. The city spent millions in recovery efforts.
- Unsuccessful attacks: Some municipalities may be targeted but successfully resist payment demands or recover data without paying. These cases illustrate the importance of robust backup and recovery plans.
Motivations and Tactics of Ransomware Actors
Ransomware actors have various motivations, including financial gain, political disruption, or simply testing their capabilities. Their tactics often involve exploiting known vulnerabilities, social engineering techniques, and phishing campaigns.
- Motivations: Profit maximization is a primary driver, with attackers aiming to receive the highest ransom payment possible. In some cases, attacks may be motivated by political agendas or a desire to demonstrate capabilities.
- Tactics: Phishing emails are a common tactic, tricking employees into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments. Exploiting known software vulnerabilities is another common approach. Compromised credentials are also commonly leveraged.
Potential Financial and Reputational Damage
The consequences of a ransomware attack can extend far beyond the initial ransom payment. Financial losses include the ransom itself, recovery costs, and lost productivity. Reputational damage can erode public trust and hinder future partnerships.
- Financial Damage: The ransom itself can be substantial, and recovery efforts can cost millions. Lost revenue and decreased operational efficiency also contribute to financial losses.
- Reputational Damage: A ransomware attack can damage a municipality’s reputation and erode public trust. Citizens may lose confidence in the municipality’s ability to protect their data and services.
Varying Levels of Technical Sophistication and Preparedness
Municipalities vary significantly in their technical sophistication and preparedness against ransomware attacks. Some may have robust cybersecurity defenses, while others may be less equipped to handle such threats.
- Varying preparedness: Resources dedicated to cybersecurity vary significantly. Smaller municipalities may have limited budgets and personnel to dedicate to cybersecurity efforts, leading to higher vulnerabilities.
Ransomware Attack Vectors
A comparison of common ransomware attack vectors helps illustrate the various points of entry.
| Attack Vector | Description | Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Tricking users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments | Human error, lack of security awareness |
| Exploiting Vulnerabilities | Targeting known software flaws | Outdated software, lack of patching |
| Supply Chain Attacks | Compromising a vendor to gain access to multiple municipalities | Vendor vulnerabilities, weak security practices |
| Malicious Insider Actions | Employees intentionally introducing malware | Lack of access controls, insufficient monitoring |
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies: How Municipal Governments Could Protect Against Ransomware
Municipal governments face a significant threat from ransomware attacks, jeopardizing essential services and public trust. A proactive approach to risk assessment and mitigation is crucial to safeguarding critical infrastructure and maintaining operational continuity. This requires a multifaceted strategy encompassing comprehensive risk assessment, vulnerability identification, and robust preventative measures.Effective ransomware protection involves a comprehensive understanding of potential vulnerabilities within a municipal network, coupled with the implementation of preventive measures and incident response plans.
Municipal governments need a robust defense against ransomware attacks. A key element in that defense is proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in their systems. This involves more than just patching software; it’s crucial to understand the potential for malicious code to slip through. By deploying AI-powered tools like those described in Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed , municipalities can gain a crucial edge in proactively scanning code for potential threats.
This approach will greatly improve the overall security posture of their systems and make them more resilient to future ransomware attacks.
Regular security audits and updates are also essential to maintain a strong defense against evolving threats. Implementing the right security tools can significantly reduce the attack surface and enhance the resilience of the network.
Comprehensive Risk Assessment Framework
A robust risk assessment framework is vital for identifying potential vulnerabilities and prioritizing mitigation efforts. This framework should systematically evaluate all aspects of the municipal IT infrastructure, from network devices and software to employee access controls and data backups. It should include a detailed inventory of all systems and applications, outlining their criticality and potential impact in the event of a compromise.
Regular reviews and updates of the framework are crucial to address evolving threats and changing operational needs.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Municipal IT Infrastructure
Municipal networks often present unique vulnerabilities due to their complex systems and diverse user base. These vulnerabilities can include outdated software, inadequate security controls, insufficient employee training, and weak passwords. Furthermore, the interconnectedness of different systems, such as water management systems or traffic control systems, can create pathways for ransomware attacks to spread. The potential for human error and phishing attacks also poses a substantial threat.
Preventative Measures to Reduce the Likelihood of Ransomware Attacks
Implementing strong preventative measures is essential to deter ransomware attacks. These measures include regularly updating software and operating systems to patch known vulnerabilities. Multi-factor authentication should be implemented for all sensitive accounts. Regular security awareness training for employees can significantly reduce the risk of phishing attacks. Restricting access to critical systems based on the principle of least privilege is also important.
Regular penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities is highly recommended.
Incident Response Plans for Ransomware Attacks
Developing a comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for mitigating the impact of a ransomware attack. This plan should detail steps to contain the attack, restore systems, and minimize data loss. It should Artikel roles and responsibilities for personnel involved in the response process, including IT staff, legal counsel, and public relations representatives. The plan should also include communication protocols for notifying affected parties and the public.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Updates
Regular security audits and updates are essential to maintain a strong security posture. These audits should assess the effectiveness of existing security controls, identify vulnerabilities, and recommend improvements. Updates should be applied promptly to address known vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of the system. Security audits should include a review of employee access privileges, backup procedures, and incident response plans.
Recommended Security Tools for Municipal Governments
Implementing appropriate security tools is critical to strengthen the defense against ransomware attacks. These tools should include intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), anti-malware software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions. Email security gateways, secure web gateways, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools can further enhance protection. Cloud security solutions should also be considered.
Steps to Strengthen Network Security
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Conduct a thorough risk assessment of all IT systems. |
| 2 | Implement strong access controls and multi-factor authentication. |
| 3 | Regularly update software and operating systems. |
| 4 | Establish and test incident response plans. |
| 5 | Provide comprehensive security awareness training to all employees. |
| 6 | Implement robust data backup and recovery procedures. |
| 7 | Utilize appropriate security tools and technologies. |
| 8 | Establish a dedicated security team or designate a security officer. |
| 9 | Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing. |
| 10 | Maintain ongoing communication and collaboration with cybersecurity experts. |
Cybersecurity Training and Awareness
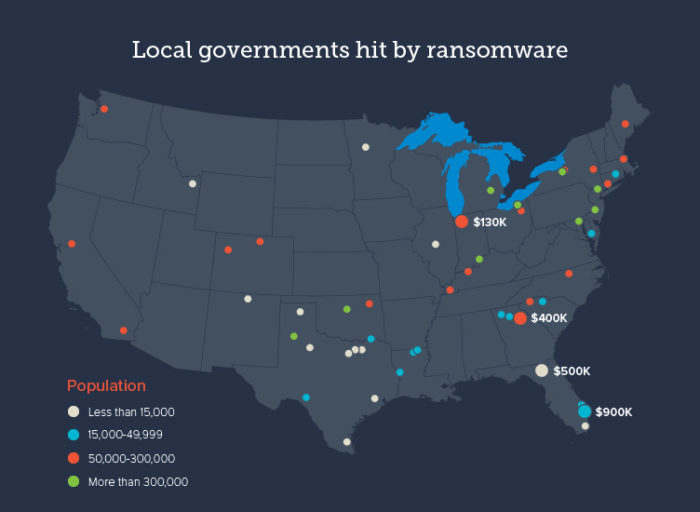
Municipal governments are critical infrastructure, making them prime targets for ransomware attacks. A robust cybersecurity strategy hinges on a well-trained workforce. Educating employees on recognizing and responding to threats is paramount to preventing breaches and mitigating the impact of attacks. This training must be ongoing and adaptable to evolving threats.Effective cybersecurity training equips municipal employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and report suspicious activities.
This proactive approach reduces the risk of successful attacks, protecting sensitive data and maintaining public trust. A culture of cybersecurity awareness fosters a shared responsibility for protecting the organization’s digital assets.
Municipal governments need robust cybersecurity measures to fend off ransomware attacks. One critical aspect is understanding vulnerabilities in cloud databases like Azure Cosmos DB, as detailed in Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details. By staying informed about these potential weaknesses, governments can strengthen their defenses and better protect sensitive data. This knowledge is key to developing proactive strategies against ransomware threats.
Importance of Cybersecurity Training for All Municipal Employees
Municipal employees, from front-line staff to senior administrators, must understand the importance of cybersecurity. Their actions directly impact the organization’s overall security posture. Training fosters a shared responsibility for data protection, reducing the likelihood of human error leading to successful attacks. This approach builds a resilient and informed workforce prepared to confront cyber threats effectively.
Effective Training Programs for Identifying Phishing Emails and Suspicious Links
Phishing attacks remain a significant threat. Comprehensive training programs should focus on recognizing phishing emails and suspicious links. Employees should learn to identify common indicators of fraudulent communications, such as poor grammar, generic greetings, and requests for urgent action. Training should include real-world examples of phishing attempts. Simulated phishing exercises are invaluable for testing employee awareness.
Municipal governments need robust cybersecurity measures to fend off ransomware attacks. Investing in advanced security systems and regular staff training is crucial. Plus, exploring options like the Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions could provide a valuable framework for navigating legal complexities. Ultimately, a layered approach encompassing prevention, detection, and response will strengthen their defenses against these increasingly sophisticated threats.
Examples of Simulated Phishing Attacks to Test Employee Awareness
Simulated phishing attacks, delivered discreetly, are a critical component of training. These exercises should mimic real-world scenarios, using realistic subject lines and email content. Employees should be debriefed after each simulation, reviewing correct responses and identifying areas for improvement. Post-simulation feedback and guidance are essential for reinforcing learned concepts and improving overall awareness. For example, an email pretending to be from the IT department requesting login credentials would be a realistic exercise.
Elaboration on the Importance of Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication
Robust password policies and multi-factor authentication are crucial components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Strong passwords, incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, make accounts harder to crack. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity with multiple methods, such as a code sent to a mobile phone.
These measures significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Discussion of the Role of Awareness Campaigns in Raising Cybersecurity Consciousness
Regular awareness campaigns can significantly enhance cybersecurity consciousness. These campaigns should disseminate information through various channels, including newsletters, intranet announcements, and town hall meetings. Visual aids, such as posters and infographics, can further engage employees and promote a culture of vigilance. Regular reminders and updates keep cybersecurity top of mind.
Table of Different Training Modules for Municipal Staff
| Module | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing Awareness | Recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts. | All employees |
| Password Management | Creating and managing strong passwords. | All employees |
| Social Engineering Awareness | Understanding social engineering tactics. | All employees |
| Data Handling Procedures | Proper handling of sensitive data. | Specific staff with access to sensitive data |
| Incident Reporting Procedures | Reporting suspicious activity and incidents. | All employees |
Data Backup and Recovery

Municipal governments hold critical data, from citizen records to financial information. Protecting this data from ransomware attacks necessitates robust backup and recovery procedures. A well-designed strategy for data backup and recovery can significantly reduce the impact of a ransomware attack, ensuring business continuity and minimizing disruption to essential services.A comprehensive backup and recovery strategy is not merely a technical exercise; it’s a crucial component of a broader cybersecurity posture.
A well-implemented plan safeguards against data loss, enabling swift restoration after an attack, minimizing financial and reputational damage.
Strategies for Robust Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Effective backup and recovery procedures require a multi-layered approach. This includes not only the technical aspects of data replication but also the establishment of clear protocols and testing routines. Regularly scheduled backups, combined with off-site storage, are critical elements.
Importance of Off-Site Backups and Data Redundancy
Off-site backups are paramount for data redundancy. Storing backups at a geographically separate location minimizes the risk of data loss from physical disasters, like fires or floods, or cyberattacks targeting the primary data center. This geographical separation is crucial for ensuring business continuity, even in the event of a catastrophic incident. Multiple copies of data, stored in different locations, create redundancy, ensuring data availability.
Testing the Effectiveness of Backup and Recovery Plans
Regular testing of backup and recovery plans is essential to ensure their effectiveness. This involves simulating various failure scenarios and evaluating the restoration process. Regular testing exercises, using realistic attack scenarios, validate the backup and recovery plan’s resilience and identify potential vulnerabilities. These exercises should include testing restoration time and data integrity.
Different Backup Solutions for Municipal Data
Various backup solutions are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right solution requires careful consideration of factors such as data volume, budget constraints, and security requirements. Different solutions may be more appropriate for different types of municipal data.
Comparison of Backup Solutions
| Backup Solution | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based Backup | Data is stored and managed in a cloud environment. | Scalability, accessibility, disaster recovery | Security concerns, potential bandwidth limitations, vendor lock-in |
| On-Premise Backup | Data is stored on servers within the municipal facility. | Control over data, potentially faster restoration | Vulnerability to physical damage, limited scalability |
| Hybrid Backup | Combines cloud and on-premise storage. | Balances security and scalability, improved disaster recovery | Complexity of management, potential for increased costs |
Different backup solutions provide various advantages and disadvantages, with each best suited to specific needs and budgets. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for selecting the most appropriate strategy for a municipal government’s data protection.
Building a Resilient Cybersecurity Culture
A strong cybersecurity posture isn’t just about technical measures; it’s fundamentally about fostering a culture where security is a shared responsibility. This requires a shift in mindset, moving beyond compliance to proactive engagement and vigilance. Municipal governments need to create an environment where employees understand the importance of cybersecurity and are empowered to act responsibly. This involves not only establishing policies but also instilling a culture of continuous learning and improvement.Building a resilient cybersecurity culture requires a multifaceted approach.
It involves clearly defining roles and responsibilities, establishing robust communication channels, and fostering a sense of shared accountability among all employees. This culture needs to be nurtured from the top down, with leadership setting the tone and actively promoting security awareness.
Leadership’s Role in Promoting Cybersecurity Culture
Leadership plays a critical role in establishing a strong cybersecurity culture. Executives and managers must demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity by integrating it into decision-making processes and everyday operations. This includes actively participating in security awareness training, publicly promoting the importance of security, and rewarding employees who exhibit a proactive approach to security. Effective leadership fosters trust and empowers employees to report security concerns without fear of retribution.
Best Practices for Establishing Cybersecurity Policies
Effective cybersecurity policies are clear, concise, and easily understood by all employees. They should Artikel acceptable use of technology, procedures for handling sensitive data, and reporting protocols for security incidents. These policies should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving threats and best practices. A policy should also address penalties for non-compliance. Examples include explicit prohibitions on phishing scams, clear procedures for handling lost or stolen devices, and requirements for strong password management.
Importance of Regular Security Updates and Patches
Regular security updates and patches are crucial for mitigating vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals constantly develop new techniques to exploit weaknesses in software and systems. Keeping systems updated ensures that the latest security protections are in place, reducing the risk of successful attacks. Failure to apply updates can leave systems vulnerable to known exploits, which could be catastrophic. For example, a critical vulnerability in a city’s water management system could have disastrous consequences.
Collaboration with Other Agencies and Stakeholders
Collaboration with other agencies and stakeholders is essential for enhancing municipal cybersecurity. Sharing information about emerging threats, best practices, and incident response strategies can strengthen the collective defenses. This collaboration could include partnering with state and federal agencies, sharing information with private sector organizations, or even collaborating with neighboring municipalities.
Establishing Clear Communication Channels During a Ransomware Incident, How municipal governments could protect against ransomware
Establishing clear communication channels is critical during a ransomware incident. This includes designated individuals or teams responsible for handling communications and a plan for updating the public and affected stakeholders. A well-defined process for communicating with affected parties, law enforcement, and the media is essential.
Roles and Responsibilities in a Municipal Cybersecurity Team
A structured cybersecurity team is vital for effective incident response and prevention. This team should include individuals with specific roles and responsibilities, each playing a critical part in the overall security strategy.
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Officer | Oversees the overall cybersecurity program, develops and implements policies, and ensures compliance. |
| Incident Response Team Lead | Coordinates the response to security incidents, manages communications, and works with law enforcement. |
| Network Administrator | Monitors network activity, identifies and addresses vulnerabilities, and manages security tools. |
| Security Analyst | Analyzes security logs, investigates threats, and provides recommendations for improvement. |
| Data Protection Officer | Ensures compliance with data protection regulations and policies, and protects sensitive data. |
| Public Relations Officer | Communicates with the public about security incidents and updates. |
Financial and Legal Considerations
Ransomware attacks pose significant financial and legal challenges for municipalities. Beyond the immediate cost of ransom payments and recovery efforts, the long-term implications can cripple budgets and erode public trust. Understanding the financial ramifications and legal obligations is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.Municipalities face a complex web of financial and legal responsibilities when confronting ransomware. The cost of a successful attack extends far beyond the ransom itself, encompassing lost productivity, damage to reputation, legal fees, and the expense of restoring systems and data.
Furthermore, legal frameworks surrounding data security and breach notification create significant obligations that need careful consideration.
Financial Implications of Ransomware Attacks
Municipalities operate on tight budgets, and ransomware attacks can have a devastating financial impact. The direct costs include ransom payments, often substantial sums, and the cost of recovery efforts, such as data restoration, system rebuilding, and forensic analysis. Indirect costs, such as lost revenue from disrupted services, employee downtime, and damage to public image, can be equally significant and harder to quantify.
Legal Responsibilities of Municipalities Regarding Data Security
Municipalities have legal obligations regarding data security, often dictated by state and federal laws. These laws often mandate the implementation of reasonable security measures to protect sensitive data. Failure to meet these standards can lead to lawsuits, regulatory fines, and damage to the municipality’s reputation. Breach notification laws require municipalities to inform affected individuals or entities about a data breach promptly and accurately.
Compliance with these legal frameworks is paramount.
Importance of Cyber Insurance and Risk Transfer Strategies
Cyber insurance can play a critical role in mitigating the financial impact of ransomware attacks. It provides a financial safety net to cover the costs associated with a breach, including ransom payments, data recovery, legal fees, and public relations expenses. Insurance policies often include coverage for business interruption, regulatory fines, and reputational harm. Risk transfer strategies, such as carefully crafted contracts with vendors and service providers, are also essential for shifting some responsibility to other parties.
Comparison of Cyber Insurance Policies
| Policy Feature | Policy Type A (Broad Coverage) | Policy Type B (Limited Coverage) |
|---|---|---|
| Ransom Payment Coverage | Yes, up to policy limits | Yes, but with limitations on amount and/or conditions |
| Data Recovery Costs | Yes, including restoration and rebuilding | Yes, but potentially with deductibles and limitations |
| Legal Fees | Yes, for breach investigation and litigation | Yes, but with specific exclusions |
| Business Interruption | Yes, covering lost revenue and operational downtime | May or may not include this, often with specific conditions |
| Reputational Damage | Yes, for public relations and crisis management | May exclude or limit coverage for this |
| Policy Limits | Higher, tailored to municipal needs | Lower, more basic coverage |
Different cyber insurance policies cater to various needs and budgets. A comparison of policies highlights the critical distinctions in coverage levels and limitations. Understanding these differences is essential for municipalities to select appropriate insurance.
Examples of How Municipalities Have Handled Ransomware Attacks Financially
Several municipalities have faced ransomware attacks and demonstrated varying approaches to financial recovery. Some have negotiated with attackers to minimize immediate financial losses. Others have relied on cyber insurance to cover a portion of the costs associated with the incident. Effective crisis management and financial planning are essential during and after a ransomware attack. For instance, City X, faced with a significant ransom demand, utilized a combination of cyber insurance and a phased recovery plan to minimize disruption and financial strain.
City Y, on the other hand, relied solely on their insurance coverage to address the financial consequences of a ransomware attack, highlighting the varying strategies employed by municipalities.
Epilogue

In conclusion, securing municipal governments against ransomware requires a multifaceted approach. Robust risk assessments, comprehensive training programs, and dependable backup and recovery procedures are essential. A strong cybersecurity culture, nurtured by leadership and collaboration, is equally critical. By prioritizing proactive measures and fostering a culture of vigilance, municipalities can significantly reduce their vulnerability to ransomware attacks and safeguard essential services for their citizens.
Clarifying Questions
What are some common types of ransomware targeting municipalities?
Common ransomware types include encrypting ransomware, which encrypts critical data, and exfiltration ransomware, which steals sensitive data before encrypting it. Other threats involve denial-of-service attacks that disrupt operations.
What is the role of strong password policies and multi-factor authentication?
Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication are crucial in preventing unauthorized access to systems. These measures significantly reduce the risk of successful attacks.
How can municipalities effectively test employee awareness?
Simulating phishing attacks is an effective method to gauge employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities in their response. Regular testing allows for improvement in identifying suspicious emails and links.
What are some recommended security tools for municipal governments?
Recommended tools include endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and firewalls. These tools can help detect and prevent malicious activity before it impacts systems.





