Enhancing Cybersecurity Awareness A Comprehensive Guide
Enhancing cybersecurity awareness a comprehensive guide – Enhancing Cybersecurity Awareness: A Comprehensive Guide – We live in a digital world where our personal and professional lives are increasingly intertwined with technology. This makes understanding cybersecurity more crucial than ever. From everyday phishing scams to large-scale data breaches, the risks are real and the consequences can be devastating. This guide dives deep into practical strategies and essential knowledge to help you navigate the ever-evolving landscape of online threats and protect yourself and your data.
We’ll explore common vulnerabilities, effective prevention methods, and the importance of building a strong security mindset. Whether you’re a tech novice or a seasoned professional, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools and knowledge to bolster your cybersecurity defenses and stay one step ahead of the bad actors. Get ready to take control of your digital safety!
Understanding the Cybersecurity Landscape

The digital world, while offering unparalleled convenience and connectivity, presents a constantly evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats. Understanding these threats, their impact, and effective prevention methods is crucial for individuals and organizations alike. Ignoring cybersecurity best practices can lead to devastating consequences, from financial losses to reputational damage and even legal repercussions.The Current Threat Environment and its ImpactCyberattacks are no longer limited to large corporations; they increasingly target individuals and small businesses.
Sophisticated threat actors leverage advanced techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks, aiming to steal data, disrupt operations, or extort money. The impact of successful cyberattacks can be far-reaching and long-lasting, affecting not only financial stability but also personal privacy, national security, and public trust.Real-World Cybersecurity Incidents and Their ConsequencesNumerous real-world incidents highlight the severity of cyber threats.
The NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, for example, caused billions of dollars in damages worldwide by crippling critical infrastructure and businesses. The Equifax data breach in 2017 exposed the personal information of millions of individuals, resulting in significant financial and reputational harm for the company and lasting consequences for the affected individuals. These incidents demonstrate the far-reaching consequences of inadequate cybersecurity measures.Cyber Threat ComparisonThe following table compares different types of cyber threats, outlining their descriptions, impact, and prevention methods.
| Threat Type | Description | Impact | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Deceptive attempts to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communication. | Identity theft, financial loss, data breaches. | Employee training on phishing recognition, multi-factor authentication, email filtering. |
| Malware | Malicious software designed to damage or disable computers and computer systems. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, and ransomware. | Data loss, system crashes, operational disruption, financial loss. | Antivirus software, regular software updates, secure network configurations, data backups. |
| Ransomware | A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and demands a ransom payment for decryption. | Data loss, financial loss, business disruption, reputational damage. | Regular backups, strong passwords, employee training, robust security software, network segmentation. |
| Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks | Attempts to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. | Service disruption, loss of revenue, reputational damage. | Network security measures, intrusion detection systems, DDoS mitigation services. |
Identifying Personal Vulnerabilities
We all use technology daily, making us potential targets for cyberattacks. Understanding our own digital habits and weaknesses is the first step towards strengthening our online security. This section focuses on common vulnerabilities and offers practical strategies to mitigate them. Ignoring these vulnerabilities can lead to significant consequences, from identity theft to financial loss.
Common User Behaviors Increasing Cybersecurity Risks
Many seemingly harmless actions can significantly increase our vulnerability to cyber threats. For instance, clicking on suspicious links in emails or messages, downloading files from untrusted sources, and using weak or easily guessable passwords are all common pitfalls. Using public Wi-Fi without a VPN exposes our data to interception. Failing to update software leaves us susceptible to known vulnerabilities.
Finally, sharing personal information carelessly on social media platforms provides attackers with valuable intel for social engineering attacks. These behaviors, while seemingly insignificant individually, collectively create a significant security risk.
Creating Strong and Unique Passwords
Strong passwords are the cornerstone of personal cybersecurity. A strong password is long (at least 12 characters), complex (combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols), and unique to each account. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or pet names. Instead, consider using a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords. A password manager can help you create unique, strong passwords for every online account without the need to remember them all.
Imagine a password manager as a digital vault, keeping your passwords safe and organized, preventing the catastrophic effects of a single compromised password impacting multiple accounts.
The Importance of Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Even if your password is compromised, MFA requires a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone or email, or a biometric scan (fingerprint or facial recognition), before granting access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if your password is stolen or guessed.
Think of MFA as a security checkpoint – even if someone gets past the first gate (your password), they’ll still need to navigate a second, more secure barrier to gain access to your accounts. Implementing MFA across all your important accounts is a crucial step towards improving your overall online security.
Personal Cybersecurity Practices Checklist, Enhancing cybersecurity awareness a comprehensive guide
This checklist helps assess your current security practices and identify areas for improvement.
- Do I use strong, unique passwords for all my online accounts?
- Do I use a password manager to securely store my passwords?
- Have I enabled multi-factor authentication on all my important accounts?
- Do I regularly update my software and operating systems?
- Do I avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from untrusted sources?
- Do I use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi?
- Do I regularly review my online accounts for any unauthorized activity?
- Do I practice good social media security habits, avoiding oversharing personal information?
- Do I have a plan in place for what to do if I suspect my accounts have been compromised?
- Do I understand the security implications of the different devices I use (phones, laptops, tablets)?
Recognizing and Avoiding Phishing Attacks: Enhancing Cybersecurity Awareness A Comprehensive Guide
Phishing attacks are a pervasive threat in the digital world, designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, or social security numbers. Understanding the common tactics employed by phishers is crucial for effective protection. This section will equip you with the knowledge to identify and avoid these deceptive attempts.
Phishing attacks rely on social engineering principles, manipulating users into taking actions they wouldn’t normally take. They often leverage urgency, fear, or a sense of trust to bypass your critical thinking.
Key Characteristics of Phishing Emails and Websites
Phishing emails and websites share several common characteristics. Recognizing these patterns is the first step in avoiding a successful attack. These characteristics often work in concert to create a convincing facade of legitimacy.
Suspicious emails frequently display poor grammar and spelling, contain generic greetings (e.g., “Dear Valued Customer”), and use threatening or urgent language to pressure you into immediate action. Look for inconsistencies between the sender’s email address and the organization they claim to represent. Legitimate organizations typically use professional-looking email addresses that match their domain name.
Similarly, phishing websites often mimic the look and feel of legitimate websites, but with subtle differences. They might have slightly altered URLs, incorrect logos, or unprofessional design elements. Inspect the website’s URL carefully; look for misspellings or unusual characters. A secure website will typically begin with “https” and display a padlock icon in the address bar.
Examples of Different Phishing Techniques
Phishers employ a variety of techniques to increase their success rate. Understanding these diverse approaches helps you stay vigilant.
One common tactic is spoofing, where phishers disguise their email address or website to appear as if it’s from a trusted source. For example, an email might appear to be from your bank, but the sender’s address is slightly altered. Another common technique is the use of urgent requests, such as an email claiming your account has been compromised and requiring immediate action to prevent account suspension.
This creates a sense of panic and urgency, pushing you to act without thinking critically.
Spear phishing targets specific individuals or organizations, using personalized information to increase the likelihood of success. This approach might involve researching the target’s interests and activities to tailor the phishing attempt. Finally, smishing uses SMS text messages to deliver phishing attempts, while vishing leverages voice calls to trick victims.
So, you’re diving into enhancing cybersecurity awareness – a comprehensive guide is definitely needed these days! Building secure applications is key, and that’s where understanding the development process comes in. Check out this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future to see how modern development impacts security. Ultimately, a strong security posture starts with secure app design, feeding back into our comprehensive cybersecurity awareness journey.
Verifying the Authenticity of Emails and Websites
Several steps can help you verify the authenticity of emails and websites before clicking links or providing personal information.
Always hover over links before clicking to see the actual URL. This allows you to check if the link matches the expected destination. Never click links in unsolicited emails or messages. Instead, navigate directly to the website by typing the address into your browser. Contact the organization directly through a known phone number or official website to verify the authenticity of any suspicious communication.
Look for security certificates (HTTPS) and verify the website’s security features. Cross-reference information found in the email or website with information from the official website or other reliable sources.
A Visual Guide Illustrating Common Phishing Tactics
Imagine a visual representation: Panel A depicts a seemingly legitimate email from your bank, with a slightly misspelled URL in the link. The sender’s email address is close, but not identical, to the bank’s official address. Panel B shows a website that mimics a popular online retailer, but with a slightly off-kilter logo and unprofessional design elements.
The URL is subtly altered, with an extra character inserted. Panel C shows a text message claiming a package delivery requires immediate action and includes a shortened URL that redirects to a malicious website. Panel D showcases a phone call from someone claiming to be from the IRS, demanding immediate payment to avoid legal consequences. Each panel highlights the subtle cues that indicate a phishing attempt.
The overall message is that paying attention to details can help you identify these attacks before they succeed.
Safeguarding Devices and Data
Protecting your devices and data is crucial in today’s digital world. A multi-layered approach, combining proactive measures with robust security software, is the most effective way to minimize your risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. This section will Artikel key strategies to secure your digital assets, both online and offline.
Regular Software Updates and Patches
Regular software updates are essential for maintaining a strong security posture. These updates often include critical security patches that address vulnerabilities exploited by malicious actors. Failing to update your software leaves your devices susceptible to malware infections, data theft, and other cyber threats. For example, neglecting to update your operating system could expose your computer to ransomware attacks that could encrypt your files and demand a ransom for their release.
Similarly, outdated apps on your phone could allow access to your personal information, including contacts and location data. Always enable automatic updates whenever possible, or set reminders to check for and install updates regularly.
Securing Mobile Devices
Mobile devices are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals. Strong passwords, or ideally, biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition), are crucial for access control. Enable device encryption to protect your data if the device is lost or stolen. Download apps only from official app stores and be cautious about granting excessive permissions to apps. Regularly review app permissions and revoke access to those you no longer need.
Consider using a mobile device management (MDM) solution for enhanced security and control, especially for work devices. For example, using a strong passcode and enabling device encryption will prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information stored on your phone, such as financial transactions or medical records.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Protecting sensitive data requires a multifaceted approach encompassing both online and offline practices. Online, utilize strong, unique passwords for each account and enable two-factor authentication whenever available. Be mindful of the websites and platforms you share your information with, ensuring they have robust security measures in place. Offline, store sensitive documents in a secure location, ideally a locked cabinet or safe.
Shred documents containing personal information before discarding them to prevent identity theft. Regularly back up your important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service, but ensure the backup is also secured with strong passwords and encryption. For instance, using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords can significantly improve your online security.
Similarly, physically securing sensitive documents prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data like bank statements or tax returns.
Recommended Security Software and Tools
Several security software and tools can enhance your overall protection.
Below is a list of examples, remember to research and choose options that best suit your needs and operating system:
| Software/Tool | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Antivirus Software (e.g., Norton, McAfee, Bitdefender) | Detects and removes malware, viruses, and other malicious software. |
| Firewall | Monitors and controls network traffic, blocking unauthorized access to your devices. Most operating systems include a built-in firewall. |
| Password Manager (e.g., LastPass, 1Password, Bitwarden) | Generates and securely stores strong, unique passwords for your online accounts. |
| VPN (Virtual Private Network) | Encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP address, providing enhanced privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Apps (e.g., Google Authenticator, Authy) | Adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts by requiring a second verification method, such as a code from an authentication app. |
Implementing Strong Security Practices
Building a robust cybersecurity defense isn’t just about reacting to threats; it’s about proactively implementing strong security practices that minimize vulnerabilities and protect your digital life. This involves a multi-layered approach, encompassing software, hardware, and, most importantly, smart user behavior. This section Artikels key practices to bolster your overall security posture.
Firewall and Antivirus Software Benefits
Firewalls act as gatekeepers, controlling network traffic entering and leaving your device or network. They examine incoming and outgoing data packets, blocking malicious traffic based on predefined rules. Antivirus software actively scans for and removes malware, viruses, and other harmful programs. Using both provides a powerful defense-in-depth strategy. A firewall prevents malicious connections from ever reaching your system, while antivirus software cleans up any threats that might slip through or originate internally.
Think of it like having a security guard at the door (firewall) and a cleaning crew inside (antivirus) to maintain a secure environment. The combined effect significantly reduces the risk of infection and data breaches.
Data Backups and Disaster Recovery Planning
Data loss can be catastrophic, impacting personal memories, financial records, and business operations. Regular backups are essential. This involves creating copies of your important files and storing them securely, ideally in multiple locations – one local and one offsite, like a cloud service or external hard drive. Disaster recovery planning goes beyond simple backups; it Artikels procedures to restore your data and systems in the event of a disaster, such as a hard drive failure, natural disaster, or cyberattack.
This plan should detail steps for data recovery, system restoration, and communication protocols. For example, a small business might have a plan that includes restoring data from a cloud backup and using a secondary server to resume operations within 24 hours of an outage.
Securing Home Networks
A secure home network is the foundation of online safety. Start by changing your router’s default password to a strong, unique one. Enable WPA2 or WPA3 encryption, the strongest available security protocols for Wi-Fi networks. Regularly update your router’s firmware to patch security vulnerabilities. Consider using a guest network to isolate visitors’ devices from your main network, limiting potential exposure.
Enable a firewall on your router and use strong passwords for all connected devices. Regularly scan your network for unauthorized devices to identify and remove any intruders. Imagine your home network as a physical house; you wouldn’t leave the doors unlocked, and you’d regularly check for any signs of intrusion. Applying these security measures provides a similar level of protection for your digital home.
Robust Password Management System Implementation
A strong password management system is crucial for online security. Begin by choosing a unique, strong password for each online account. Avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts; if one account is compromised, it won’t give attackers access to all your accounts. Use a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords. A password manager generates strong, unique passwords and auto-fills them when you log in, eliminating the need to remember them all.
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible, adding an extra layer of security. This requires a second verification method, such as a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password. Regularly review and update your passwords, especially if you suspect a security breach. Think of your passwords as keys to your digital life; managing them effectively is essential to protecting your valuable information.
A well-implemented password management system, including 2FA, is the best defense against brute-force attacks and credential stuffing.
Promoting a Culture of Cybersecurity Awareness
Building a strong cybersecurity posture isn’t solely about technology; it’s fundamentally about people. A culture of cybersecurity awareness, where employees understand and actively participate in protecting company data, is crucial for mitigating risks. This involves consistent education, engaging training, and ongoing reinforcement of best practices.
Strategies for Educating Employees About Cybersecurity Risks
Effective cybersecurity education needs to be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of employees. Generic training is often ineffective. Instead, focus on real-world scenarios relevant to their daily tasks. For example, a sales team might receive training emphasizing the risks of phishing emails containing client information, while the IT department would benefit from more in-depth sessions on vulnerability management.
The key is to make the training relatable and avoid overwhelming employees with technical jargon. Regular quizzes and interactive modules can help maintain engagement and reinforce learning.
Examples of Effective Cybersecurity Awareness Training Programs
Several approaches can successfully cultivate a cybersecurity-conscious workforce. Gamified training, incorporating interactive elements like quizzes and challenges, can significantly improve engagement and knowledge retention. Scenario-based training, presenting employees with realistic cybersecurity threats and allowing them to practice responses, is another highly effective method. For instance, a simulation might present an employee with a suspicious email and guide them through the process of identifying and reporting it.
Finally, incorporating real-world examples of data breaches and their consequences can underscore the importance of security practices. A case study of a company suffering a significant data breach due to employee negligence can serve as a powerful learning tool.
The Importance of Regular Cybersecurity Awareness Campaigns
Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, so regular awareness campaigns are essential to keep employees informed and updated. These campaigns shouldn’t be one-off events; rather, they should be integrated into the company’s overall communication strategy. Monthly newsletters, short training videos, or even posters around the office can all contribute to maintaining a high level of awareness. The frequency and format of these campaigns should be adjusted based on employee feedback and the evolving threat landscape.
For example, a surge in phishing attacks targeting specific industries might warrant a focused campaign addressing those particular threats.
Template for an Internal Cybersecurity Awareness Newsletter
Subject: Stay Safe Online: Your Monthly Cybersecurity Update
Headline: [Catchy headline related to the month’s focus, e.g., “Beware of Spooky Phishing Emails This Halloween!”]
Body:
[Brief overview of the month’s key cybersecurity threats and tips. Include a real-world example or case study.]
[Highlight a specific security practice, e.g., “Strong Password Practices,” with clear instructions and examples.]
[Include a short quiz or poll to test employee knowledge.]
[Link to relevant resources, such as company security policies or helpful online articles.]
Enhancing cybersecurity awareness is crucial, and a comprehensive guide should cover all aspects, from basic hygiene to advanced threats. Understanding cloud security is a big part of that, and that’s where tools like Bitglass come in; check out this article on bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management to learn more. Ultimately, a strong cybersecurity awareness program needs to address the evolving landscape of cloud-based threats for complete effectiveness.
Call to action: [Encourage employees to report suspicious activity or ask questions.]
Responding to Security Incidents
No one wants to think about it, but security incidents happen. Whether it’s a phishing scam, a malware infection, or a data breach, knowing how to respond effectively is crucial to minimizing damage and protecting your data. A proactive approach, including a well-defined incident response plan, is far more effective than reacting in a panic.A swift and organized response to a security incident is vital for limiting damage and maintaining business continuity.
The longer a breach goes undetected, the more extensive the potential harm. This includes financial losses, reputational damage, legal ramifications, and the loss of sensitive customer information. Having a pre-defined plan allows for a more efficient and effective response, reducing chaos and improving the chances of a successful resolution.
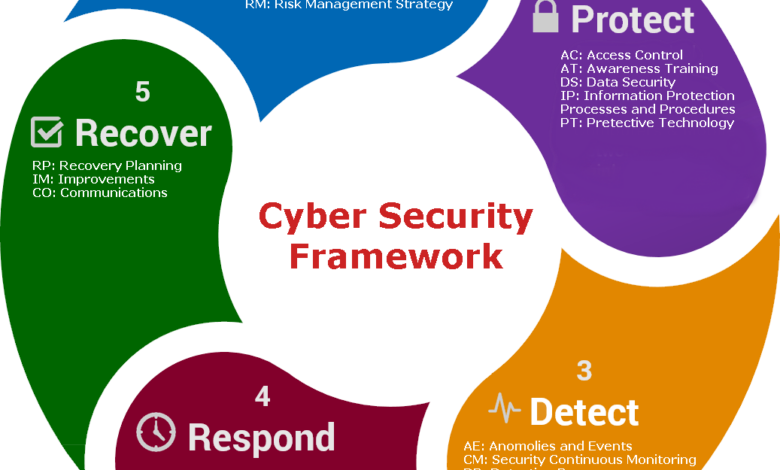
Incident Reporting and Response Planning
A robust incident response plan is the cornerstone of effective security. This plan should detail the steps to take from initial detection to recovery and post-incident analysis. It should clearly define roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and escalation procedures. Regular drills and simulations are crucial to ensure the plan is effective and that everyone understands their roles. For example, a plan might specify who is responsible for isolating infected systems, who communicates with law enforcement or affected parties, and who conducts the post-incident review.
This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology and threats.
Steps to Take When a Security Incident Occurs
The steps involved in responding to a security incident are generally iterative and may overlap. However, a structured approach is key.
- Preparation: This includes having a well-defined incident response plan, regularly updated, and practiced. This also involves having the necessary tools and resources in place, such as forensic software and secure communication channels.
- Detection and Analysis: This involves identifying the incident, determining its scope and impact, and gathering evidence. This could involve analyzing logs, network traffic, and system activity.
- Containment: This involves isolating the affected systems or networks to prevent further damage. This might include shutting down systems, disconnecting networks, or blocking malicious IP addresses.
- Eradication: This involves removing the threat from the affected systems. This could involve removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, or restoring systems from backups.
- Recovery: This involves restoring affected systems and data to their normal operational state. This might involve restoring data from backups, reinstalling software, and reconfiguring systems.
- Post-Incident Activity: This involves reviewing the incident, identifying lessons learned, and updating the incident response plan to prevent similar incidents in the future. This often involves documenting the entire process and creating a comprehensive report.
Best Practices for Handling Data Breaches
Data breaches require a particularly swift and thorough response. Transparency with affected individuals and regulatory bodies is paramount. Notification laws vary by jurisdiction, but prompt notification is generally required. Examples of best practices include:
- Immediately contain the breach to prevent further data loss.
- Conduct a thorough forensic investigation to determine the root cause and extent of the breach.
- Notify affected individuals and regulatory bodies as required by law.
- Offer credit monitoring and identity theft protection services to affected individuals.
- Cooperate fully with law enforcement investigations.
- Review and update security policies and procedures to prevent future breaches.
Incident Response Process Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart with six distinct boxes, connected by arrows.Box 1: Incident Detection (e.g., security alert, user report) -> Box 2: Incident Analysis (e.g., determine impact, gather evidence) -> Box 3: Containment (e.g., isolate affected systems) -> Box 4: Eradication (e.g., remove malware, patch vulnerabilities) -> Box 5: Recovery (e.g., restore systems and data) -> Box 6: Post-Incident Review (e.g., document findings, update security policies).
Each box would contain a brief description of the activities within that stage. The arrows represent the flow of the process. This visual representation provides a clear and concise overview of the incident response process.
Staying Updated on Cybersecurity Threats
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging daily. Staying informed about these threats is crucial for individuals and organizations alike to effectively protect themselves. Ignoring the latest vulnerabilities can leave you exposed to significant risks, including data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage. Proactive learning and a commitment to continuous improvement are essential components of a robust cybersecurity strategy.Cybersecurity is a dynamic field; what works today might be obsolete tomorrow.
Therefore, continuous learning and professional development are not merely recommended but absolutely necessary. This involves staying abreast of emerging threats, learning about new attack vectors, and familiarizing yourself with the latest security technologies and best practices. Regularly updating your knowledge ensures you can adapt your security measures to counter evolving threats effectively.
Reputable Cybersecurity News Sources and Blogs
Maintaining awareness requires consistent engagement with reliable sources. The following table lists several reputable cybersecurity news sources and blogs, categorized by their focus area, to help you stay informed about the latest threats and best practices. Remember to critically evaluate information from any source and verify details from multiple sources where possible.
| Resource Name | URL | Description | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| KrebsOnSecurity | https://krebsonsecurity.com/ | Brian Krebs’ blog, known for in-depth reporting on cybersecurity breaches and scams. | Breaking news, data breaches, malware analysis |
| The SANS Institute | https://www.sans.org/ | Provides cybersecurity training, certifications, and resources, including news and research. | Training, certifications, research, news |
| Threatpost | https://threatpost.com/ | Covers the latest threat intelligence, vulnerability disclosures, and security news. | Threat intelligence, vulnerability analysis, security news |
| SecurityWeek | https://www.securityweek.com/ | Offers news, analysis, and insights on various cybersecurity topics. | Broad cybersecurity news, analysis, and opinions |
| Dark Reading | https://www.darkreading.com/ | Provides in-depth coverage of security threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices. | Enterprise security, threat intelligence, vulnerability management |
| National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) | https://www.nist.gov/ | Provides standards, guidelines, and publications related to cybersecurity. | Standards, guidelines, publications, research |
Conclusive Thoughts
Ultimately, enhancing cybersecurity awareness isn’t just about installing software or changing passwords; it’s about cultivating a proactive and informed approach to digital safety. By understanding the threats, implementing strong security practices, and staying informed about the latest vulnerabilities, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect yourself from the ever-present dangers of the online world. Remember, your digital security is your responsibility – take charge and make it a priority!
General Inquiries
What is multi-factor authentication (MFA) and why is it important?
MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond just a password. It requires you to verify your identity using a second factor, like a code from your phone or a security key, making it much harder for unauthorized users to access your accounts, even if they have your password.
How often should I update my software and apps?
Software updates often include crucial security patches that fix vulnerabilities. Aim to update your operating system, apps, and antivirus software regularly, ideally as soon as updates are released.
What should I do if I think I’ve been a victim of a phishing attack?
Immediately change any passwords you suspect may have been compromised. Report the phishing attempt to the website or organization it impersonated. Monitor your accounts for any unusual activity and consider running a malware scan.
What are some good resources to stay updated on cybersecurity threats?
Websites like KrebsOnSecurity, Threatpost, and the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) website are excellent sources for up-to-date information on current threats and vulnerabilities.