New Cybersecurity Reports Retraining & Vulnerability Management 2
New cybersecurity reports point to increased need for retraining and vulnerability management 2, and it’s a wake-up call for businesses everywhere. The sheer volume of sophisticated attacks, coupled with a persistent skills gap in the cybersecurity workforce, is creating a perfect storm. We’re facing a critical juncture where outdated practices and a lack of skilled professionals are leaving organizations dangerously exposed.
This isn’t just about patching software; it’s about fundamentally shifting how we approach security.
The recent surge in ransomware attacks, sophisticated phishing campaigns, and the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities highlights the urgent need for a multi-pronged approach. This means investing heavily in employee training, implementing robust vulnerability management programs, and embracing cutting-edge technologies to stay ahead of the curve. The consequences of inaction are simply too severe to ignore – we’re talking financial losses, reputational damage, and potential legal repercussions.
The Growing Cybersecurity Threat Landscape

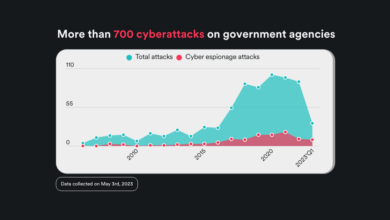
The cybersecurity threat landscape is evolving at an alarming rate, with increasingly sophisticated attacks targeting individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Recent reports paint a grim picture, highlighting a surge in ransomware attacks, supply chain compromises, and state-sponsored espionage. The sheer volume and complexity of these threats necessitate a proactive and adaptive approach to security, emphasizing both robust vulnerability management and continuous employee retraining.
Key Vulnerabilities Exploited in Recent Attacks
Three key vulnerabilities frequently exploited in recent attacks are Log4j, unpatched software, and phishing. Log4j, a widely used Java logging library, suffered a critical vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) allowing remote code execution. Its widespread use meant attackers could easily compromise systems globally. Unpatched software, in general, represents a vast attack surface. Many organizations fail to keep their software updated, leaving them vulnerable to known exploits.
Phishing attacks, often involving deceptively realistic emails or websites, continue to be incredibly effective, tricking users into revealing sensitive credentials or downloading malware. The impact of these vulnerabilities ranges from data breaches and financial losses to operational disruptions and reputational damage.
Real-World Incidents Illustrating Inadequate Vulnerability Management
The consequences of neglecting vulnerability management are clearly evident in several high-profile incidents. The 2020 SolarWinds supply chain attack saw malicious code embedded in a widely used software update, infecting thousands of organizations. This highlighted the devastating impact of vulnerabilities within the software supply chain. The Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 crippled a major fuel pipeline, demonstrating the potential for ransomware to disrupt critical infrastructure.
Finally, the numerous data breaches targeting healthcare providers underscore the severe consequences of inadequate security practices, resulting in the exposure of sensitive patient information and significant financial penalties.
Comparison of Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Vulnerability scanning tools are crucial for identifying and mitigating security risks. Different tools offer varying capabilities and levels of effectiveness. The following table compares three popular tools:
| Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nessus | Comprehensive vulnerability scanning, extensive plugin library, good reporting | Can be complex to configure, may produce false positives | Subscription-based, varying costs |
| OpenVAS | Open-source, cost-effective, regularly updated | Steeper learning curve than Nessus, may require more manual configuration | Free |
| QualysGuard | Cloud-based, easy to use, integrates well with other security tools | Can be expensive, may not be as comprehensive as Nessus | Subscription-based, varying costs |
The Need for Retraining in Cybersecurity: New Cybersecurity Reports Point To Increased Need For Retraining And Vulnerability Management 2
The cybersecurity landscape is evolving at an alarming rate, with new threats and attack vectors emerging constantly. This rapid change creates a significant skills gap in the cybersecurity workforce, leaving organizations vulnerable to increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. The lack of adequately trained professionals is a major contributor to the rising number of successful breaches and data leaks, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive retraining initiatives.The skills gap in cybersecurity is multifaceted.
It’s not simply a matter of a shortage of professionals; it’s also a mismatch between the skills possessed by the existing workforce and the skills required to combat modern threats. Many current cybersecurity professionals lack the expertise in areas like cloud security, artificial intelligence (AI) security, and the security of the Internet of Things (IoT). This gap is exacerbated by the rapid advancement of technologies used by attackers, who are constantly developing new and more effective methods of breaching security systems.
The result is a widening chasm between the capabilities of defenders and the sophistication of attackers, leaving organizations exposed.
Types of Retraining Programs Needed
Addressing the cybersecurity skills gap requires a multi-pronged approach involving various retraining programs tailored to different skill levels and career paths. Entry-level programs should focus on foundational cybersecurity concepts, such as networking, operating systems, and basic security principles. Mid-career professionals might benefit from specialized training in areas like incident response, penetration testing, or cloud security. Advanced programs could focus on emerging threats like AI-powered attacks or the security implications of quantum computing.
These programs should be delivered through a variety of formats, including online courses, boot camps, and apprenticeships, to cater to different learning styles and schedules. A significant portion of these programs should focus on practical, hands-on experience to ensure that professionals can apply their knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios. For example, a program focusing on incident response might involve simulated attack scenarios and exercises in analyzing and mitigating real-world incidents.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
The cybersecurity field is in a constant state of flux. New threats, technologies, and regulations emerge regularly, demanding continuous learning and professional development from cybersecurity professionals. Organizations should encourage their employees to participate in ongoing training and certification programs to stay abreast of the latest developments. This could involve attending industry conferences, participating in online courses, or pursuing advanced certifications like the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH).
Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous learning within an organization is crucial; this includes providing access to relevant resources, encouraging knowledge sharing, and rewarding employees for their commitment to professional development. For instance, offering mentorship programs pairing experienced professionals with newer ones can accelerate skill development and knowledge transfer.
Best Practices for Designing Effective Cybersecurity Training Programs
Effective cybersecurity training programs should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of the participants. A program designed for network administrators will differ significantly from one designed for security analysts or incident responders. The training should be engaging and interactive, utilizing a variety of methods such as simulations, case studies, and hands-on labs. Furthermore, assessments should be integrated throughout the training process to gauge understanding and identify areas needing further attention.
Regular reviews and updates of the training materials are crucial to ensure that the content remains relevant and addresses the latest threats and vulnerabilities. For example, a program for incident responders might include simulated ransomware attacks, requiring participants to analyze logs, identify the source of the attack, and implement remediation steps. The effectiveness of the program could then be measured by assessing the speed and accuracy of the participants’ responses.
Vulnerability Management Best Practices
Effective vulnerability management is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s interconnected world. A robust framework is crucial for organizations of all sizes to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate potential security threats before they can be exploited by malicious actors. This proactive approach significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.A comprehensive vulnerability management framework involves a cyclical process of continuous improvement and adaptation.
It’s not a one-time fix but a sustained effort requiring ongoing monitoring and adjustments based on evolving threat landscapes and technological advancements. This framework necessitates a well-defined strategy, clear responsibilities, and the right tools to ensure effectiveness.
Identifying Vulnerabilities
Identifying vulnerabilities requires a multi-pronged approach combining automated scanning with manual penetration testing. Automated vulnerability scanners, such as Nessus or OpenVAS, can quickly assess a large number of systems and applications for known weaknesses. However, these tools are limited in their ability to detect zero-day vulnerabilities or custom-developed weaknesses. Therefore, manual penetration testing, performed by skilled security professionals, is essential to uncover more subtle and complex vulnerabilities.
This combination of automated and manual techniques provides a more comprehensive picture of the organization’s security posture. Regular scheduled scans, coupled with penetration testing at least annually, are recommended.
Assessing Vulnerabilities
Once vulnerabilities are identified, they must be assessed to determine their severity and potential impact. This assessment involves considering factors such as the likelihood of exploitation, the potential consequences of a successful attack (e.g., data breach, system downtime), and the availability of mitigation strategies. A common scoring system used for this purpose is the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), which provides a standardized numerical score based on the vulnerability’s characteristics.
Prioritization is key; vulnerabilities with higher CVSS scores and greater potential impact should be addressed first.
Mitigating Vulnerabilities
Mitigation strategies vary depending on the nature of the vulnerability. Options include patching software, implementing security controls (e.g., firewalls, intrusion detection systems), configuring security settings, and implementing compensating controls to reduce the risk if a complete fix isn’t immediately feasible. The chosen mitigation strategy should be documented and tracked, ensuring that the vulnerability is effectively addressed and its impact minimized.
For instance, a high-severity vulnerability in a critical system might require immediate patching, while a low-severity vulnerability in a less critical system could be addressed during a scheduled maintenance window. Regular verification is vital to ensure that implemented mitigations remain effective.
Implementing a Vulnerability Management Program
Implementing a successful vulnerability management program requires a structured approach.
- Define Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the systems and applications to be included in the program, and set measurable objectives for reducing vulnerabilities.
- Establish a Vulnerability Management Team: Assign roles and responsibilities to individuals or teams responsible for different aspects of the program.
- Select and Implement Tools: Choose appropriate vulnerability scanning and management tools based on the organization’s needs and budget.
- Develop a Vulnerability Assessment Schedule: Create a regular schedule for vulnerability scans and penetration testing.
- Establish a Vulnerability Remediation Process: Define clear procedures for prioritizing, remediating, and verifying the resolution of vulnerabilities.
- Develop Reporting and Metrics: Track key metrics such as the number of vulnerabilities identified, the time taken to remediate vulnerabilities, and the overall effectiveness of the program.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and improve the program based on lessons learned and evolving threat landscapes.
Vulnerability Management Methodologies
Several methodologies exist for vulnerability management, each with its strengths and weaknesses. A risk-based approach prioritizes vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. This is often the most effective approach, as it allows organizations to focus their resources on the most critical vulnerabilities. In contrast, a compliance-based approach focuses on meeting regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
While compliance is important, a purely compliance-based approach may not address all potential vulnerabilities. A hybrid approach, combining risk-based and compliance-based methodologies, is often the most comprehensive and effective. The choice of methodology depends on the organization’s specific needs and risk tolerance.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Security
The modern cybersecurity landscape is incredibly complex, demanding sophisticated tools and strategies to effectively manage vulnerabilities and mitigate threats. Fortunately, technological advancements are providing powerful solutions to bolster our defenses, automating tasks, enhancing detection capabilities, and ultimately strengthening our overall security posture. This section will explore the crucial role technology plays in achieving this improved security.Automation is revolutionizing vulnerability management and threat detection.
Instead of relying solely on manual processes, which are time-consuming and prone to human error, organizations can leverage automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities, prioritize remediation efforts, and even automatically patch systems. This significantly reduces the window of opportunity for attackers and allows security teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. Automated threat detection systems continuously monitor network traffic and system logs for suspicious activity, triggering alerts and initiating responses far more quickly than human analysts could manage alone.
This speed is critical in containing breaches before they cause significant damage.
Automation in Vulnerability Management and Threat Detection
Automated vulnerability scanners continuously assess systems for known weaknesses, providing detailed reports that highlight critical vulnerabilities requiring immediate attention. This allows security teams to prioritize patching efforts based on risk level, focusing resources where they are most needed. Automated response systems can even automatically patch identified vulnerabilities, minimizing downtime and reducing the risk of exploitation. Sophisticated threat intelligence platforms correlate data from various sources to identify emerging threats and predict potential attacks, enabling proactive security measures.
For example, an automated system might detect a surge in login attempts from an unusual geographic location, triggering an immediate alert and potentially blocking access to prevent a brute-force attack.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Cybersecurity
Three emerging technologies significantly improving cybersecurity posture are Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Zero Trust Security, and Blockchain technology. XDR consolidates security data from various endpoints and sources, providing a unified view of the threat landscape and improving incident response. Zero Trust security operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring authentication and authorization for every user and device attempting to access resources, regardless of location.
Blockchain technology, known for its immutability, can be leveraged to enhance data security and improve the integrity of digital identities. Imagine a system where sensitive data is stored on a blockchain, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to alter or access it. The transparency and auditability of blockchain transactions also add an extra layer of security.
AI and Machine Learning in Threat Detection and Response
AI and machine learning (ML) are transforming threat detection and response. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of security data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity that might be missed by traditional security tools. This includes detecting sophisticated attacks like advanced persistent threats (APTs) that often evade traditional signature-based detection methods. AI-powered systems can also automate incident response, taking actions like isolating infected systems or blocking malicious traffic, significantly reducing the time it takes to contain a breach.
For example, an AI system might detect a subtle pattern in network traffic that suggests an insider threat, flagging it for investigation before it escalates into a major security incident.
SIEM Systems and Improved Vulnerability Management, New cybersecurity reports point to increased need for retraining and vulnerability management 2
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems play a critical role in improved vulnerability management by collecting and correlating security logs from various sources. This provides a centralized view of security events across the organization, allowing security teams to quickly identify and respond to security incidents. By analyzing log data, SIEM systems can detect patterns of suspicious activity that may indicate vulnerabilities being exploited.
This allows for proactive remediation efforts, preventing potential breaches before they occur. Furthermore, SIEM systems can be integrated with vulnerability scanners to automatically correlate vulnerability data with security events, providing a more complete picture of the organization’s security posture. For example, a SIEM system might detect a series of failed login attempts originating from a specific IP address, then cross-reference this with vulnerability scan data to determine if that IP address is associated with a system containing known vulnerabilities.
This integrated approach allows for a much more effective and timely response to potential threats.
The Economic Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches
Cybersecurity breaches are no longer a hypothetical threat; they’re a costly reality for organizations of all sizes. The financial consequences extend far beyond the immediate costs of remediation, impacting long-term profitability and even survival. Understanding the full economic impact is crucial for effective risk management and proactive security investment.The financial consequences of data breaches and cyberattacks are staggering.
Direct costs include the expenses associated with incident response, such as hiring forensic investigators, legal counsel, and public relations firms. Organizations also face significant costs related to data recovery, system restoration, and notification of affected individuals. The cost of replacing compromised systems and data can run into millions, depending on the scale and complexity of the breach.
Consider the 2017 Equifax breach, which cost the company over $700 million in fines, legal fees, and remediation efforts. This serves as a stark reminder of the potentially devastating financial impact of a large-scale data breach.
Direct Costs of Cybersecurity Breaches
Direct costs represent the immediate and tangible expenses incurred as a direct result of a cybersecurity incident. These costs are often easily quantifiable and include:
- Incident response: Hiring cybersecurity experts to investigate the breach, contain the damage, and recover data.
- Legal and regulatory fees: Costs associated with complying with data breach notification laws and potential lawsuits.
- System restoration: The expense of rebuilding compromised systems and restoring data from backups.
- Data recovery: Costs involved in recovering lost or corrupted data.
- Notification costs: The expense of notifying affected individuals about the breach, as required by various regulations.
Indirect Costs of Cybersecurity Breaches
Beyond the direct financial losses, organizations also face significant indirect costs that can be harder to quantify but equally damaging to their bottom line. These indirect costs can significantly impact an organization’s long-term financial health.
- Reputational damage: A data breach can severely damage an organization’s reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and potential business opportunities. The negative publicity can persist for years, impacting future revenue streams.
- Loss of customer trust: Customers may lose confidence in an organization’s ability to protect their data, leading to a decline in sales and market share. This loss of trust can be particularly damaging for businesses that handle sensitive customer information.
- Business disruption: A cybersecurity breach can disrupt business operations, leading to lost productivity and revenue. This disruption can be particularly costly for organizations that rely on technology to operate.
- Increased insurance premiums: After a breach, insurance companies may increase premiums or even refuse to renew coverage, adding to the organization’s financial burden.
Factors Contributing to Increasing Breach Costs
Several factors contribute to the ever-increasing cost of cybersecurity breaches. These include:
- The sophistication of cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are constantly developing more sophisticated techniques to bypass security measures, making breaches more difficult and expensive to remediate.
- The growing volume of data: Organizations are collecting and storing more data than ever before, making them more attractive targets for cybercriminals and increasing the potential cost of a breach.
- Stricter regulations: Governments worldwide are enacting stricter regulations around data protection, leading to increased fines and penalties for organizations that fail to protect customer data.
- Increased regulatory scrutiny: Regulatory bodies are increasingly scrutinizing organizations’ cybersecurity practices, leading to higher costs associated with compliance and audits.
Strategies for Reducing the Financial Impact of Cybersecurity Incidents
Proactive measures are essential to mitigate the financial impact of cybersecurity incidents. A comprehensive approach is vital:
- Invest in robust cybersecurity infrastructure: Implementing strong security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention tools, can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of a breach.
- Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan: Having a well-defined plan in place can help organizations quickly contain and remediate a breach, minimizing the financial impact.
- Regularly back up data: Regular backups can help organizations quickly restore data in the event of a breach, reducing downtime and data loss.
- Provide cybersecurity awareness training to employees: Educating employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices can significantly reduce the risk of human error, a major cause of many breaches.
- Cybersecurity insurance: Securing cybersecurity insurance can help organizations offset some of the financial costs associated with a breach.
Improving Organizational Cybersecurity Culture
A strong cybersecurity culture isn’t just about policies and technology; it’s about embedding security awareness into the very fabric of an organization. It’s about fostering a mindset where every employee understands their role in protecting sensitive data and the company’s reputation. This requires a multifaceted approach that combines training, communication, and leadership commitment.Building a robust cybersecurity culture involves cultivating a shared understanding and responsibility for security across all levels of the organization.
This goes beyond simply complying with security protocols; it’s about actively engaging employees in the process of protecting the company’s assets. A successful approach requires clear communication, consistent reinforcement, and demonstrable leadership support.
Elements of a Strong Cybersecurity Culture
A strong cybersecurity culture is characterized by several key elements. Employees at all levels understand and actively participate in security practices. There’s a clear understanding of cybersecurity risks and the consequences of breaches. Reporting mechanisms are readily available and used without fear of retribution. Regular security awareness training is provided and actively engaged with.
Leadership actively champions security initiatives, demonstrating a commitment to security from the top down. Finally, a culture of continuous improvement is fostered, with regular reviews and updates to security practices.
Fostering a Culture of Security Awareness
Fostering a culture of security awareness requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. This involves implementing regular training programs tailored to different roles and responsibilities within the organization. It also means using a variety of communication channels, such as emails, posters, intranet articles, and even gamified training modules, to reach employees. Regular security awareness campaigns, highlighting current threats and best practices, are crucial.
These campaigns can include phishing simulations to test employee vigilance and provide valuable real-world training. Incentivizing secure behavior through rewards and recognition programs can further encourage participation. For example, recognizing employees who report near misses or security vulnerabilities can reinforce the importance of proactive security engagement.
Communicating Cybersecurity Risks and Best Practices
Effective communication is paramount in establishing a strong cybersecurity culture. Avoid technical jargon and instead use clear, concise language that everyone can understand. Regularly communicate the potential consequences of security breaches, emphasizing the impact on the organization and its employees. Provide practical examples of real-world cyberattacks and their consequences. Share best practices in a simple, easy-to-understand manner, focusing on actionable steps employees can take to protect themselves and the organization.
Use visuals, infographics, and short videos to enhance engagement and comprehension. For example, a short video demonstrating the dangers of clicking on suspicious links can be far more effective than a lengthy written policy.
Examples of Successful Cybersecurity Awareness Training Programs
Many organizations have implemented successful cybersecurity awareness training programs. One example is a program that uses a combination of online modules, interactive workshops, and gamified challenges to engage employees. Another effective approach is a tiered training system, offering customized training based on an employee’s role and responsibilities. For example, executives might receive training focused on high-level risks and strategic decision-making, while IT staff might receive more technical training.
A program that incorporates regular phishing simulations and rewards employees for reporting suspicious emails can significantly improve employee vigilance. Regular feedback mechanisms, such as surveys and focus groups, can help tailor training to the specific needs of the organization and its employees. Finally, a program that integrates security awareness into the onboarding process for new employees helps establish a strong security foundation from the start.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-increasing sophistication of cyber threats. Understanding future trends is crucial for organizations to proactively adapt their security strategies, invest in appropriate retraining programs, and effectively manage vulnerabilities. Failing to do so leaves businesses vulnerable to increasingly costly and damaging breaches.The following sections will explore three key trends shaping the future of cybersecurity, their impact on vulnerability management and retraining, and the challenges and opportunities they present.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
AI and ML are rapidly transforming cybersecurity, offering powerful tools for threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity, far exceeding the capabilities of human analysts alone. This leads to faster detection of threats and more efficient responses. However, the reliance on AI also introduces new challenges.
Adversaries are increasingly using AI to create more sophisticated and evasive attacks, leading to an arms race in AI-driven security. Retraining needs will shift towards specialized skills in AI/ML-based security tools and techniques, requiring cybersecurity professionals to understand both the defensive and offensive applications of these technologies. This includes developing expertise in AI model explainability, ensuring transparency and accountability in automated security decisions.
The Expanding Attack Surface Due to IoT and Cloud Computing
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and the increasing reliance on cloud computing significantly expand the attack surface for organizations. IoT devices, often lacking robust security features, represent easy targets for attackers, while cloud environments, while offering scalability and flexibility, introduce complexities in security management. Vulnerability management in this context requires a holistic approach, encompassing both on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure, as well as a diverse range of IoT devices.
Retraining is crucial to equip cybersecurity professionals with the skills needed to manage and secure these diverse environments. This includes expertise in cloud security architectures, IoT security protocols, and the implementation of effective access control mechanisms across these distributed systems. For example, the recent SolarWinds attack highlighted the vulnerability of supply chains and the need for robust security measures across the entire ecosystem, including third-party vendors and cloud service providers.
Quantum Computing’s Potential Impact on Cryptography
The development of quantum computing poses a significant threat to current cryptographic algorithms. Quantum computers, with their immense processing power, have the potential to break widely used encryption methods, rendering sensitive data vulnerable. This necessitates a shift towards post-quantum cryptography (PQC), which are algorithms designed to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers. Vulnerability management will need to incorporate the transition to PQC, requiring significant investment in upgrading infrastructure and retraining cybersecurity professionals in the implementation and management of these new algorithms.
The challenges include the complexity of PQC algorithms, the need for widespread adoption, and the potential for unforeseen vulnerabilities in these new cryptographic methods. The opportunities lie in developing and deploying robust PQC solutions, securing data against future quantum attacks.
Seriously, those new cybersecurity reports are stressing me out! The emphasis on retraining and proactive vulnerability management is crucial, especially considering how quickly tech evolves. To build secure, future-proof apps, understanding development approaches like those outlined in this insightful article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future is key. Ultimately, strong security hinges on both updated skills and robust development practices, so let’s all stay informed!
Projected Evolution of Cybersecurity Threats and Defenses (5-Year Projection)
Imagine a graph with time (0-5 years) on the x-axis and threat sophistication/defense capabilities on the y-axis. The threat curve starts at a moderate level at year 0, then rapidly increases, exhibiting a steeper incline from year 2 onwards, representing the escalating sophistication of AI-driven attacks and the expansion of the attack surface. The defense curve also increases, but at a slower rate initially, reflecting the time required for organizations to adapt to new threats and implement advanced security measures.
However, from year 3 onwards, the defense curve shows a more rapid increase, representing the increasing adoption of AI-driven security solutions and the transition to PQC. While the threat curve remains above the defense curve throughout the five years, the gap between them narrows towards year 5, suggesting a gradual improvement in the balance between threats and defenses, though continuous adaptation will remain critical.
This visualization illustrates the ongoing arms race between attackers and defenders and the importance of continuous investment in cybersecurity capabilities.
Last Point
In conclusion, the message from these new cybersecurity reports is clear: we can’t afford to be complacent. The evolving threat landscape demands a proactive, multi-faceted response. By investing in comprehensive retraining programs, strengthening vulnerability management strategies, and embracing new technologies, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile and build a more resilient security posture. It’s time to move beyond reactive measures and embrace a culture of continuous learning and proactive security.
The future of cybersecurity depends on it.
User Queries
What are the most common types of vulnerabilities being exploited?
Commonly exploited vulnerabilities include outdated software, weak passwords, and unpatched systems. Phishing attacks also remain a significant threat.
How much does retraining cost?
The cost of retraining varies greatly depending on the program, the number of employees, and the type of training. It’s an investment, but the cost of a data breach far outweighs the cost of prevention.
What are some examples of effective vulnerability management tools?
Many effective tools exist, from open-source options to commercial platforms. The best choice depends on your organization’s specific needs and budget. Research is key to finding the right fit.
How can I build a stronger cybersecurity culture in my organization?
Start by making cybersecurity a top priority, communicating risks effectively, and providing regular training. Encourage employees to report suspicious activity and reward responsible behavior.