
The Intersection of Digital Commerce and EDI
The intersection of digital commerce and EDI is a fascinating space where the speed and convenience of online marketplaces meet the structured efficiency of electronic data interchange. It’s a powerful combination that’s transforming how businesses operate, streamlining processes, and boosting profitability. This post dives deep into the synergy between these two crucial elements of modern business, exploring the benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping this dynamic landscape.
We’ll unpack the core concepts of digital commerce and EDI, examining how their integration leads to significant efficiency gains and cost reductions. We’ll also tackle the challenges involved, including security concerns and legacy system integration, offering practical solutions and best practices. Finally, we’ll look ahead to the future, considering the impact of emerging technologies like blockchain and AI on the continued evolution of EDI within the digital commerce ecosystem.
Defining Digital Commerce and EDI Integration

Digital commerce and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) are increasingly intertwined, forming the backbone of efficient and scalable business operations in today’s global marketplace. Understanding their individual components and how they synergistically work together is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chains and enhance customer experiences.
Core Components of Digital Commerce
Digital commerce encompasses all aspects of buying and selling goods or services online. Key components include e-commerce websites, online marketplaces, digital payment gateways, inventory management systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and order fulfillment processes. These components work together to provide a seamless online shopping experience for customers and efficient back-end operations for businesses. A robust digital commerce strategy relies on the effective integration of all these elements.
Functionalities of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
EDI is the electronic exchange of business documents in a standardized format between trading partners. It automates the transmission of documents such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and payment instructions. Key functionalities include standardized data formats (like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT), secure transmission protocols, automated data processing, and reduced manual intervention. EDI eliminates the need for paper-based transactions, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Commerce Leveraging EDI
Traditional commerce relies heavily on manual processes, paper-based documents, and often involves significant delays in communication and data exchange. Digital commerce, augmented by EDI, streamlines these processes. Instead of manually processing orders and invoices, EDI automates these tasks, reducing errors and speeding up the entire transaction cycle. This leads to faster order fulfillment, improved inventory management, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
The table below summarizes the key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Commerce | Digital Commerce with EDI |
|---|---|---|
| Order Processing | Manual, paper-based, prone to errors | Automated, electronic, accurate and fast |
| Invoice Processing | Manual, time-consuming, susceptible to delays | Automated, immediate, reduces payment cycle times |
| Inventory Management | Manual tracking, potential for inaccuracies | Real-time inventory updates, optimized stock levels |
| Communication | Slow, reliant on phone calls and emails | Instantaneous data exchange, improved collaboration |
Data Flow in a Digital Commerce System Using EDI
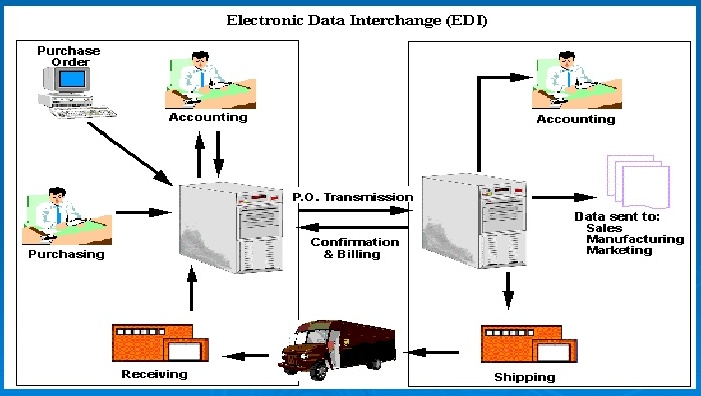
The following flowchart illustrates the typical data flow in a digital commerce system leveraging EDI:
A simplified representation of the data flow: Customer places order on e-commerce website -> Order information is sent to the company’s order management system -> Order data is translated into EDI format -> EDI message is sent to the supplier via a secure network -> Supplier processes the order and sends an acknowledgement in EDI format -> Supplier ships the goods and sends shipping notification in EDI format -> Company updates inventory and notifies the customer -> Payment information is exchanged via EDI.
Benefits of Integrating Digital Commerce and EDI
Integrating digital commerce platforms with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) offers significant advantages for businesses of all sizes. This synergy streamlines operations, reduces costs, and improves overall supply chain efficiency, ultimately leading to increased profitability and a stronger competitive edge. The benefits extend across various aspects of the business, from order processing to inventory management and beyond.
Efficiency Gains from EDI Integration
The integration of EDI into digital commerce leads to substantial efficiency improvements across the entire business process. Automated data exchange eliminates manual data entry, reducing the risk of errors and significantly speeding up order processing, invoicing, and payment cycles. This automation frees up valuable employee time, allowing staff to focus on higher-value tasks such as strategic planning and customer relationship management.
For example, a company using EDI to manage orders might see a reduction in order processing time from several hours per order to just minutes, resulting in faster delivery times and increased customer satisfaction. The speed and accuracy of EDI also allow for better inventory management, preventing stockouts and overstocking, which directly impacts profitability.
Reduction in Operational Costs Through EDI
EDI significantly reduces operational costs associated with digital commerce. The elimination of manual data entry translates directly into lower labor costs. Reduced errors mean fewer costly corrections and rework. Furthermore, EDI streamlines communication with suppliers and customers, minimizing the need for phone calls, emails, and faxes. This reduction in administrative overhead can lead to substantial savings, particularly for businesses handling high volumes of transactions.
For instance, a large retailer might save hundreds of thousands of dollars annually by switching to EDI for order processing alone, due to reduced labor costs and minimized error rates.
Improved Supply Chain Visibility
One of the most significant benefits of integrating digital commerce and EDI is the enhanced visibility it provides across the entire supply chain. Real-time data exchange allows businesses to track orders, inventory levels, and shipments with greater accuracy. This improved visibility enables proactive problem-solving, allowing businesses to address potential delays or disruptions before they impact customers. For example, if a shipment is delayed, the business can be immediately notified via EDI, allowing them to proactively communicate with the customer and potentially find alternative solutions.
This level of transparency strengthens relationships with suppliers and customers, building trust and fostering collaboration.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Improvements Across Business Sizes, The intersection of digital commerce and edi
The following table illustrates the potential cost savings and efficiency improvements that businesses of different sizes can achieve by integrating EDI into their digital commerce operations. These figures are illustrative and will vary based on specific circumstances and industry.
| Business Size | Cost Savings (Annual Estimate) | Efficiency Improvement (Percentage) | Specific Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business (1-10 employees) | $5,000 – $15,000 | 15-25% | Reduced order processing time by 20%, freeing up employee time for sales and marketing. |
| Medium Business (11-50 employees) | $15,000 – $50,000 | 25-40% | Automated invoicing and payment processing reduced administrative overhead by 30%. |
| Large Business (50+ employees) | $50,000+ | 40%+ | Improved inventory management reduced stockouts by 15%, leading to increased sales and reduced waste. |
Challenges in Implementing EDI in Digital Commerce
Integrating Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) into a modern digital commerce environment offers significant advantages, but it’s not without its hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges requires careful planning, robust security measures, and a deep understanding of both EDI protocols and the intricacies of your existing systems. Failure to address these issues can lead to costly delays, data breaches, and ultimately, a failed integration.
Security Risks Associated with EDI Data Exchange
EDI transactions involve the exchange of sensitive business data, making security a paramount concern. Unauthorized access or manipulation of this data can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Common threats include unauthorized access to EDI systems through weak passwords or vulnerabilities in software, interception of data during transmission (especially if unencrypted), and malicious software attacks targeting EDI infrastructure.
Robust security measures, including encryption of all data in transit and at rest, multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and the implementation of firewalls and intrusion detection systems, are crucial to mitigating these risks. Furthermore, adhering to established security standards like AS2 and utilizing secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL are essential. A well-defined security policy and regular employee training on security best practices are also vital components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Complexities of Integrating Legacy Systems with Modern Digital Commerce Platforms
Many businesses operate with legacy systems that weren’t designed for seamless integration with modern digital commerce platforms. These legacy systems often lack the flexibility and APIs necessary for efficient EDI communication. The integration process can be complex and time-consuming, requiring significant customization and potentially the development of custom interfaces or middleware to bridge the gap between the old and new systems.
Data mapping and transformation are also crucial aspects, as data formats and structures may differ significantly between legacy and modern systems. Careful planning, including a thorough assessment of existing systems and their capabilities, is essential to determine the best approach to integration, whether it involves phased migration, system replacement, or the implementation of a robust middleware solution. Thorough testing is also critical to ensure data integrity and system stability throughout the integration process.
Common Integration Challenges and Solutions
Several common challenges arise during EDI integration in digital commerce. These include difficulties in mapping data between different systems, ensuring data accuracy and consistency across platforms, managing exceptions and errors during data exchange, and maintaining compatibility with various trading partners’ EDI standards. Solutions involve utilizing robust data mapping tools to facilitate the transformation of data between different formats, implementing comprehensive error handling mechanisms to address exceptions gracefully, and leveraging EDI translation software to manage compatibility issues with different trading partner systems.
Investing in a centralized EDI management system can simplify the process, providing a single point of control for managing all EDI transactions and monitoring their status. Establishing clear communication channels and collaboration between IT teams and business stakeholders is also crucial for successful integration.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Integrity and Security in EDI Transactions
Maintaining data integrity and security in EDI transactions within a digital commerce environment requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to control access to EDI systems, utilizing encryption protocols to protect data during transmission, and employing digital signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of EDI messages. Regular backups of EDI data are crucial for disaster recovery, while rigorous testing and validation of EDI messages ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as HIPAA or GDPR, is paramount. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities and improve overall security posture. Finally, a well-defined incident response plan is essential to address any security breaches or data integrity issues effectively and minimize their impact.
EDI Standards and Protocols in Digital Commerce
The seamless exchange of data between trading partners is crucial for efficient digital commerce. This relies heavily on Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards and protocols, which dictate the format and transmission of business documents electronically. Choosing the right combination significantly impacts speed, security, and cost-effectiveness.EDI Standards and Protocols play a vital role in structuring and transmitting business documents electronically.
Different standards define the structure and content of the documents, while protocols determine how these documents are transmitted securely. A deep understanding of these elements is essential for successful digital commerce integration.
EDI Standards: ANSI X12 and EDIFACT
ANSI X12 and EDIFACT are the two most prevalent EDI standards globally. ANSI X12 is predominantly used in North America, while EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport) enjoys broader international adoption. Both define standardized formats for various business documents like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. However, they differ in their structure and syntax. ANSI X12 uses a segmented approach, with data organized into segments and elements, while EDIFACT uses a more hierarchical structure based on data elements and composites.
The choice between them often depends on the geographical location of trading partners and their existing systems. For example, a company trading primarily within North America might favor ANSI X12, while a multinational corporation would likely utilize EDIFACT for global reach.
EDI Communication Protocols: AS2 and FTP/S
Several protocols facilitate secure and reliable EDI data transmission. AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) is a widely accepted standard that provides security, non-repudiation, and message integrity through encryption and digital signatures. FTP/S (File Transfer Protocol Secure) offers a simpler, more readily available alternative, leveraging SSL/TLS for encryption. However, AS2 generally provides more robust security features and better tracking capabilities compared to FTP/S.
The selection depends on the level of security required and the technical capabilities of the trading partners. A high-security transaction, such as exchanging sensitive financial data, would benefit from AS2’s advanced security features. A less sensitive transaction, perhaps involving less critical inventory data, might suffice with the simpler implementation of FTP/S.
Data Mapping in EDI
Mapping involves transforming data from one system’s format into the format required by the EDI standard and the recipient’s system. This is a crucial step, as different systems utilize varying data structures and terminologies. Mapping can be achieved through manual coding, specialized mapping software, or a combination of both. Consider a scenario where a company uses a custom ERP system that doesn’t natively support EDI.
The data needs to be extracted from the ERP, transformed into the required ANSI X12 format (for example, 850 Purchase Order), and then transmitted to the trading partner. The mapping process defines the rules and transformations to ensure accurate data conversion. This might involve changing data types, reformatting data fields, and handling data discrepancies between systems. A poorly executed mapping process can lead to data errors and rejected transactions.
Comparison of EDI Standards and Protocols
| Standard/Protocol | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitability for Digital Commerce |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANSI X12 | Widely used in North America, well-documented | Can be complex to implement, less internationally standardized | Suitable for North American businesses, but requires careful consideration for international trade. |
| EDIFACT | Internationally recognized, supports diverse business documents | Steeper learning curve, can be more complex to implement | Well-suited for global businesses and international trade. |
| AS2 | Secure, reliable, provides non-repudiation and message integrity | More complex to implement than FTP/S | Highly suitable for secure transactions involving sensitive data in digital commerce. |
| FTP/S | Simple to implement, widely available | Security less robust than AS2 | Suitable for less sensitive transactions or where simpler implementation is prioritized. |
Future Trends in Digital Commerce and EDI: The Intersection Of Digital Commerce And Edi

The intersection of digital commerce and EDI is poised for significant transformation, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving business needs. The future will see a much more automated, intelligent, and secure exchange of business documents, fundamentally altering how businesses interact with their supply chains and customers. This evolution will be shaped by emerging technologies, improved standards, and a greater focus on efficiency and data security.
The integration of emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) will redefine EDI’s capabilities within the digital commerce landscape. These technologies offer solutions to current challenges and unlock opportunities for unprecedented levels of efficiency and transparency.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies on EDI in Digital Commerce
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security and transparency, offers the potential to revolutionize EDI by creating a tamper-proof audit trail for all transactions. Imagine a scenario where every order, invoice, and shipment update is recorded on a distributed ledger, instantly verifiable by all parties involved. This significantly reduces the risk of fraud and disputes, streamlining the entire process. AI, on the other hand, can be leveraged to automate data entry, error detection, and even predict potential supply chain disruptions.
For example, an AI-powered system could analyze historical EDI data to identify patterns and alert businesses to potential delays or shortages before they impact operations. The integration of IoT devices allows for real-time tracking of goods, providing granular visibility into the supply chain and further enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of EDI data exchange.
Automation and Machine Learning in Streamlining EDI Processes
Automation and machine learning are key drivers in the evolution of EDI. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate repetitive tasks such as data mapping, translation, and error resolution, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets of EDI transactions to identify anomalies, predict future trends, and optimize processes. For example, machine learning can predict the likelihood of payment delays based on historical data and customer behavior, enabling businesses to proactively manage cash flow.
This level of automation leads to significant cost savings, reduced error rates, and improved overall efficiency.
Evolution of EDI Standards and Their Adaptation to New Technologies
EDI standards are constantly evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and changing business needs. The adoption of newer standards like ebXML and RosettaNet allows for greater interoperability and flexibility, enabling businesses to seamlessly integrate with a wider range of partners. These standards are being adapted to accommodate the requirements of new technologies such as blockchain and AI, ensuring that EDI remains relevant and effective in the digital age.
For instance, new standards are being developed to handle the unique data structures and security requirements of blockchain-based EDI transactions.
Predictions for the Future of EDI Integration in Digital Commerce
The future of EDI integration within digital commerce is bright, promising significant improvements in efficiency, security, and transparency. Here are some key predictions:
- Increased adoption of cloud-based EDI solutions: Cloud-based platforms offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them increasingly attractive to businesses of all sizes.
- Wider use of AI and machine learning for automation and predictive analytics: AI-powered systems will automate more EDI processes, reducing manual intervention and improving accuracy.
- Greater integration with other digital technologies: EDI will be seamlessly integrated with other technologies such as blockchain, IoT, and CRM systems, creating a more holistic and efficient digital ecosystem.
- Enhanced security and data privacy: Advanced security measures, such as blockchain-based encryption, will become increasingly important to protect sensitive EDI data.
- Standardization and interoperability improvements: New and improved EDI standards will ensure seamless integration between businesses and reduce the complexity of data exchange.
Case Studies
Real-world examples showcase the transformative power of EDI integration within digital commerce. These case studies highlight how businesses across various sectors have leveraged EDI to streamline operations, reduce costs, and boost profitability. Examining these successes offers valuable insights for organizations considering implementing or improving their EDI strategies.
EDI Implementation in the Retail Industry: A Clothing Retailer’s Success
A large clothing retailer implemented EDI to automate its order processing and inventory management. Previously, manual data entry was prone to errors and caused significant delays. With EDI, orders are transmitted electronically, reducing errors and speeding up the entire process. The company saw a significant reduction in order processing time, from an average of 7 days to just 2 days.
Inventory management also improved, leading to reduced stockouts and overstocking. This resulted in a considerable increase in sales and a significant reduction in operational costs. The improved efficiency also enhanced customer satisfaction due to faster order fulfillment.
EDI Integration in the Automotive Parts Supply Chain
An automotive parts supplier implemented EDI to improve communication and collaboration with its manufacturing clients. Before EDI, the supplier relied on manual paperwork, leading to delays and communication breakdowns. EDI enabled real-time order tracking and inventory updates, improving the efficiency of the supply chain. The supplier was able to meet client demands more effectively, reduce lead times, and minimize stockouts.
This resulted in increased sales, improved customer relationships, and a strengthened competitive position in the market. The reduction in manual processes also freed up staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
EDI and the Pharmaceutical Industry: Ensuring Traceability and Compliance
A pharmaceutical company integrated EDI to improve traceability and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. The company uses EDI to track and manage the movement of its products throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution. This enables the company to quickly and accurately respond to product recalls or other compliance issues. EDI also ensures that all transactions are accurately documented and auditable, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
The improved traceability and compliance helped the company maintain its reputation and avoid costly fines. The system’s reliability and accuracy also contributed to enhanced operational efficiency.
| Company | Industry | Success Factors | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Clothing Retailer | Retail | Automated order processing, improved inventory management, reduced order processing time, increased sales, reduced operational costs. | Thorough planning and employee training are crucial for successful EDI implementation. |
| Automotive Parts Supplier | Automotive | Real-time order tracking, improved supply chain efficiency, reduced lead times, increased sales, improved customer relationships. | Choosing the right EDI software and partner is essential for seamless integration. |
| Pharmaceutical Company | Pharmaceutical | Improved traceability, compliance with regulatory requirements, reduced risk of non-compliance penalties, enhanced operational efficiency. | Continuous monitoring and system maintenance are vital for long-term success. |
Wrap-Up
Ultimately, the successful integration of EDI into digital commerce strategies offers businesses a clear path to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved supply chain visibility. While challenges exist, the potential rewards are substantial, driving a continuous evolution towards a more streamlined and data-driven approach to business. By embracing the best practices and leveraging emerging technologies, companies can harness the full power of this powerful combination to thrive in today’s competitive market.
The future of digital commerce hinges on the effective utilization of EDI, and understanding this intersection is key to staying ahead of the curve.
Common Queries
What is the difference between EDI and API?
EDI uses standardized formats for exchanging structured data between systems, while APIs allow for more flexible data exchange using custom formats and protocols. EDI is typically used for high-volume, standardized transactions, whereas APIs are often used for more customized integrations.
How secure is EDI?
EDI security relies on various measures, including encryption, digital signatures, and secure communication protocols like AS2. However, robust security practices and regular audits are crucial to mitigate risks.
What are the common EDI mapping challenges?
Common challenges include data format discrepancies, differing data structures between systems, and the need for complex transformations to ensure accurate data exchange. Proper mapping software and experienced personnel are essential for successful implementation.
Is EDI suitable for small businesses?
While larger businesses often benefit most from EDI’s scalability, cloud-based EDI solutions and managed service providers are making it more accessible and cost-effective for small businesses to leverage its advantages.
