Ultimate Guide 15 Critical CDP Facts Every Marketer Should Know
Ultimate guide 15 critical cdp facts every marketer should know – Ultimate Guide: 15 Critical CDP Facts Every Marketer Should Know – Ever felt overwhelmed by the sheer volume of marketing data? Lost in a sea of customer information, struggling to make sense of it all? You’re not alone. This guide cuts through the noise, delivering 15 essential facts about Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) that every marketer needs to know.
We’ll explore what CDPs are, how they work, and why they’re crucial for building personalized, effective marketing campaigns that drive results. Get ready to unlock the power of your customer data!
We’ll dive deep into the core functionalities of a CDP, comparing it to other marketing tools like CRMs and DMPs. We’ll uncover how CDPs seamlessly integrate data from various sources, creating a unified customer view. This unified view then fuels highly personalized marketing campaigns, targeted audience segmentation, and powerful analytics dashboards that show you exactly what’s working (and what’s not).
We’ll even cover crucial aspects like data security, choosing the right CDP for your needs, and implementing it successfully. Prepare for a journey into the world of data-driven marketing success!
Introduction: Ultimate Guide 15 Critical Cdp Facts Every Marketer Should Know
In today’s hyper-connected world, understanding your customers is paramount to marketing success. This is where Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) come into play. They’re becoming increasingly crucial for businesses aiming to deliver personalized experiences and drive meaningful engagement. But what exactly
is* a CDP, and how does it differ from other marketing tools?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a unified system designed to collect, organize, and activate first-party customer data. Its core functionality revolves around creating a single, comprehensive view of each customer, consolidating information from various sources – website interactions, CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and more – into a unified customer profile. This holistic view empowers marketers to personalize their messaging, improve customer segmentation, and optimize their campaigns for maximum impact.
Think of it as a central hub for all your valuable customer information, making it readily accessible and actionable.
CDP vs. Other Marketing Technologies
CDPs are often confused with other marketing technologies, particularly CRMs and DMPs. However, there are key distinctions. A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system primarily focuses on managing interactions and relationships with customers, often prioritizing sales and customer service aspects. While a CRM might hold customer data, it typically lacks the sophisticated capabilities for data unification and real-time activation that a CDP provides.
Conversely, a Data Management Platform (DMP) handles third-party cookie-based data for audience targeting and advertising. This is valuable for reaching broader audiences, but CDPs focus on the valuable first-party data that you own and control, offering a more detailed and actionable understanding of your individual customers. In essence, a CDP is more focused on understanding
- individual* customers, while a DMP is focused on building
- audience* segments.
A Brief History of CDPs
The concept of a CDP emerged in response to the growing complexity of marketing data and the need for a more unified approach. Early attempts to solve this problem involved complex integrations and custom-built solutions. However, the emergence of dedicated CDP vendors in the early 2010s marked a significant shift. These vendors offered pre-built platforms designed to simplify the process of unifying customer data and enabling personalized marketing.
The rise of big data and the increasing importance of first-party data further fueled the adoption of CDPs, making them an essential tool for modern marketers navigating the ever-changing digital landscape. The market has seen significant growth, with numerous vendors offering a variety of features and functionalities to cater to different business needs and sizes. For example, early CDPs often focused on email marketing personalization, but today’s CDPs incorporate advanced analytics, AI-powered insights, and seamless integration with a wide range of marketing technologies.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are transforming how marketers understand and engage with their audiences. A key element of their power lies in their ability to integrate and unify data from various sources, creating a holistic view of each customer. This allows for more personalized, effective, and efficient marketing campaigns. Understanding the intricacies of data integration within a CDP is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Data Integration Process within a CDP, Ultimate guide 15 critical cdp facts every marketer should know
A CDP’s core function is to ingest, harmonize, and activate customer data. This process involves collecting data from numerous sources, transforming it into a usable format, and resolving inconsistencies. Data sources can range from CRM systems and marketing automation platforms to website analytics, e-commerce platforms, and social media channels. The integration methods employed vary depending on the CDP and the specific data source, but common approaches include APIs, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and direct database connections.
A robust CDP will handle both real-time and batch data integration, ensuring a continuously updated customer profile. For example, a fashion retailer might integrate data from their website (browsing history, purchases), CRM (customer demographics, purchase history), and email marketing platform (email engagement) to build a comprehensive customer profile.
Unification of Customer Data
Once data is ingested, the CDP’s unification capabilities take center stage. This involves matching and merging data points from different sources to create a single, unified customer profile. This process often requires sophisticated matching algorithms to handle inconsistencies and duplicates across various data sources. For instance, a customer might be identified by an email address in one system and a phone number in another.
The CDP uses its matching logic to identify these as the same individual, combining the data into a single record. The result is a 360-degree view of the customer, providing marketers with a complete understanding of their behaviors, preferences, and interactions. This unified view eliminates data silos and allows for a more personalized and targeted approach to marketing.
Comparison of Data Integration Strategies
Different CDPs utilize various data integration strategies. Some CDPs rely heavily on APIs for real-time data synchronization, offering immediate updates to customer profiles. Others might employ batch processing, where data is integrated periodically. The choice of strategy depends on factors like the volume of data, the real-time requirements of the marketing campaigns, and the technical capabilities of the CDP and the data sources.
Some CDPs offer a hybrid approach, combining real-time and batch processing to optimize data integration. Furthermore, some CDPs provide pre-built connectors for common data sources, simplifying the integration process, while others might require custom integrations. The selection of the most appropriate strategy depends heavily on the specific needs and technical capabilities of the organization.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers

Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are revolutionizing marketing by providing a unified view of customer data, enabling marketers to create highly personalized and effective campaigns. This unified view eliminates data silos and allows for a more holistic understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This understanding is the key to unlocking truly effective personalization.
Data Activation and Personalization Through CDPs
CDPs don’t just collect and unify data; they activate it, transforming raw information into actionable insights that power personalized marketing. This activation involves leveraging the unified customer profile to tailor messaging, offers, and experiences across various channels. The result is a more relevant and engaging customer journey, leading to improved conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
Methods of Data Activation
Effective data activation within a CDP utilizes several key methods. Real-time personalization, for instance, allows marketers to dynamically adjust website content, email messaging, or ad creative based on a customer’s real-time behavior and preferences. Imagine a customer browsing your website for running shoes; a CDP can instantly personalize the displayed products and messaging based on their past purchases, browsing history, and even their location.
This immediacy creates a highly relevant and engaging experience.Segmentation, another crucial method, involves grouping customers based on shared characteristics and behaviors. A CDP can automatically segment customers into groups like “high-value customers,” “lapsed customers,” or “potential churners,” enabling targeted campaigns tailored to each segment’s unique needs. For example, a company could offer exclusive discounts to high-value customers, re-engagement emails to lapsed customers, or personalized support to those at risk of churning.
Hypothetical Marketing Campaign: Personalized Email Series
Let’s imagine a hypothetical e-commerce business selling handcrafted jewelry. Using a CDP, they could create a personalized email series triggered by customer actions. A new customer purchasing a necklace might receive an email suggesting matching earrings or a bracelet, building on their initial purchase. A customer who browses the website but doesn’t purchase might receive a follow-up email with a discount code or a reminder of their abandoned cart.
A loyal customer celebrating a birthday could receive a personalized email with a special birthday discount and a thank you message. This level of personalization, enabled by the CDP, fosters stronger customer relationships and drives sales. The data collected from each interaction further refines the customer profile, enabling continuous improvement of the personalization strategy. The result is a significantly improved customer experience and increased return on investment for the marketing efforts.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are revolutionizing marketing, offering unparalleled capabilities for understanding and engaging customers. This guide explores 15 critical facts every marketer should know, focusing on how CDPs empower data-driven decision-making and improve marketing ROI. This section delves into the power of CDPs for audience segmentation and targeting.
Audience Segmentation & Targeting
Effective audience segmentation is crucial for personalized marketing campaigns. CDPs excel at this by unifying customer data from various sources, enabling marketers to create highly granular and accurate segments. This allows for more targeted messaging, leading to improved engagement and conversion rates. By analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and demographics, CDPs help marketers identify distinct customer groups and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly.
This significantly increases the effectiveness of marketing campaigns compared to generic, mass-market approaches.
Here are some examples of effective audience segmentation strategies leveraging CDP capabilities:
- Segmenting by Purchase History: A retailer might segment customers based on their purchase frequency, average order value, or the types of products they frequently buy. This allows for targeted promotions of complementary products or loyalty programs tailored to high-value customers.
- Segmenting by Website Behavior: Analyzing website activity, such as pages visited, time spent on site, and abandoned carts, allows marketers to identify potential leads or customers who need further nurturing. For example, customers who abandoned their carts can receive targeted email reminders with special offers.
- Segmenting by Engagement with Marketing Emails: CDPs can track email opens, clicks, and unsubscribes, allowing marketers to identify engaged and disengaged customers. This helps optimize email campaigns and personalize future communications based on individual preferences and engagement levels.
- Segmenting by Demographics and Firmographics: Combining demographic data (age, location, gender) with firmographic data (company size, industry) allows B2B marketers to target specific customer profiles with tailored messaging and content.
Key metrics used to evaluate the success of CDP-based segmentation and targeting include:
- Conversion Rates: Measuring the percentage of targeted customers who complete a desired action (e.g., purchase, signup).
- Click-Through Rates (CTR): Tracking the percentage of recipients who click on a link in a marketing email or ad.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Estimating the total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating the profitability of marketing campaigns based on the cost of the campaign versus the revenue generated.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Measuring the cost of acquiring a new customer through specific marketing channels.
The following table compares different segmentation techniques and their application in CDPs:
| Segmentation Technique | Description | CDP Application | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | Dividing customers based on observable characteristics like age, gender, location, income. | Targeting specific age groups with relevant product offers. | Targeting young adults (18-25) with trendy fashion items. |
| Behavioral | Grouping customers based on their past actions, such as website visits, purchases, and email engagement. | Sending personalized recommendations based on past purchases. | Recommending similar products to customers who recently purchased a specific item. |
| Psychographic | Segmenting customers based on their values, interests, lifestyle, and personality traits. | Creating targeted marketing campaigns aligned with specific customer values. | Targeting environmentally conscious consumers with eco-friendly products. |
| Firmographic (B2B) | Segmenting businesses based on company size, industry, revenue, and location. | Targeting large enterprises with enterprise-level software solutions. | Focusing marketing efforts on Fortune 500 companies in the tech industry. |
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Understanding your customer is paramount to successful marketing, and a Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a powerful tool to achieve this. But a CDP’s value isn’t just in data collection; it’s in the actionable insights gleaned from that data. Effective measurement and analytics are crucial for realizing the full potential of your CDP investment. This section delves into the importance of CDP analytics dashboards, key performance indicators (KPIs), and data interpretation for strategic optimization.
CDP Analytics Dashboards: Monitoring Performance and Campaign Effectiveness
CDP analytics dashboards provide a centralized view of your customer data and marketing campaign performance. These dashboards visualize key metrics, allowing marketers to quickly assess the health of their CDP implementation and the effectiveness of their campaigns. A well-designed dashboard should provide a clear, concise overview of essential data points, enabling rapid identification of trends and potential issues.
For example, a dashboard might display real-time customer engagement metrics, campaign conversion rates, and customer segmentation performance, all in one easily digestible view. This allows marketers to make data-driven decisions in real-time, optimizing campaigns on the fly and maximizing their return on investment. The ability to filter and drill down into specific data points further enhances the dashboard’s utility, providing a granular level of detail when needed.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring CDP ROI
Measuring the return on investment (ROI) of a CDP requires careful selection and monitoring of relevant KPIs. While the specific KPIs will vary depending on individual business goals, some common examples include:
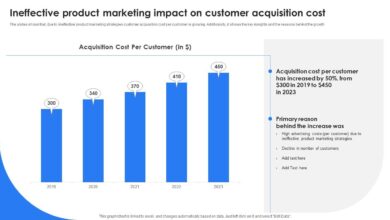
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This measures the cost of acquiring a new customer. A decrease in CAC after CDP implementation suggests improved targeting and personalization efforts.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This indicates the total revenue expected from a single customer throughout their relationship with the company. An increase in CLTV signifies the CDP’s effectiveness in fostering customer loyalty and engagement.
- Marketing ROI: This classic metric measures the return generated from marketing investments. A CDP should improve this by optimizing campaign targeting and personalization, leading to higher conversion rates and reduced wasted ad spend.
- Website Conversion Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action (e.g., making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter). Improved personalization enabled by the CDP should increase this rate.
- Email Open and Click-Through Rates: These metrics demonstrate the effectiveness of targeted email campaigns. Segmenting audiences within the CDP and personalizing email content should lead to higher open and click-through rates.
By tracking these KPIs over time, marketers can quantitatively assess the impact of their CDP investment and identify areas for improvement. For instance, if the CAC remains high despite increased marketing spend, it might indicate a need to refine targeting strategies within the CDP.
Interpreting CDP Analytics Data to Optimize Marketing Strategies
CDP analytics data is not just for reporting; it’s a powerful tool for continuous optimization. Analyzing data from various sources – website activity, email engagement, CRM data, etc. – provides a holistic view of customer behavior. This allows marketers to identify patterns, segment customers effectively, and personalize their marketing efforts with greater precision.For example, if analytics reveal a high bounce rate on a specific landing page for a particular customer segment, marketers can use this insight to redesign the page, improve its content, or adjust their targeting criteria.
Similarly, if email open rates are low for a certain segment, it might indicate a need to re-evaluate the email subject lines, content, or even the segmentation strategy itself. By continuously analyzing data and iterating on marketing strategies, businesses can maximize the value of their CDP and achieve superior marketing results. The key is to establish a data-driven feedback loop, using insights from the CDP to inform and improve marketing campaigns over time.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Choosing the right Customer Data Platform (CDP) is crucial for marketers. Data is the lifeblood of effective marketing, and a CDP is the central nervous system that allows you to collect, unify, and activate that data for personalized campaigns. But with this power comes responsibility, particularly concerning the security and privacy of the customer data your CDP manages.
This section delves into the vital aspects of security and privacy within the CDP ecosystem.
CDP Security Measures and Privacy Protocols
Modern CDPs employ a multi-layered approach to security, recognizing the sensitive nature of the data they handle. These measures often include robust encryption both in transit and at rest, protecting data from unauthorized access. Access controls, based on roles and permissions, ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data sets. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Many CDPs also leverage advanced threat detection systems, using machine learning to identify and respond to anomalies that could indicate malicious activity. Furthermore, data masking and anonymization techniques can be employed to protect sensitive information while still allowing for analysis and use in marketing campaigns. For example, a CDP might mask email addresses while retaining customer segments for targeted advertising.
CDP Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is paramount for any CDP. CDPs must adhere to strict guidelines regarding data collection, storage, processing, and sharing. This includes providing consumers with transparency regarding data usage, obtaining explicit consent where required, and offering data access, correction, and deletion options. CDPs often incorporate features that automate compliance processes, such as consent management tools and data subject access request (DSAR) portals.
They also provide detailed documentation and reporting capabilities to demonstrate compliance to auditors. For example, a CDP designed for GDPR compliance might include a built-in consent management platform that tracks individual user consent across different channels and campaigns.
Best Practices for Data Security and Privacy in a CDP Environment
Maintaining a secure and privacy-compliant CDP environment requires a proactive and ongoing commitment. The following checklist Artikels key best practices:
- Regularly review and update security policies and procedures.
- Implement strong access controls and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
- Encrypt data both in transit and at rest.
- Utilize data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques where appropriate.
- Establish clear data governance policies and procedures.
- Ensure compliance with all relevant data privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.).
- Provide users with transparency and control over their data.
- Maintain comprehensive data logs and audit trails.
- Invest in employee training on data security and privacy best practices.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Choosing the right Customer Data Platform (CDP) is crucial for effective marketing. A poorly chosen CDP can lead to wasted resources and a failure to achieve marketing goals. Understanding the nuances of different vendors and their offerings is paramount to making an informed decision. This section will explore the key factors to consider when selecting a CDP and provide a framework for comparing different options.
Choosing the Right CDP: Vendor Comparison and Feature Analysis
The CDP market is crowded with vendors offering a range of features and pricing models. Understanding these differences is vital for selecting a platform that aligns with your specific business needs and budget. Key differences often lie in data integration capabilities, the level of customization offered, the sophistication of analytics tools, and the overall user experience. For instance, some CDPs excel at integrating with a wide array of marketing technologies, while others may specialize in specific industries or use cases.
Pricing models vary widely, from subscription-based fees with tiered pricing structures to more complex models that incorporate usage-based charges.
Key Factors in CDP Selection
Several key factors should guide your CDP selection process. These include:
- Data Integration Capabilities: Consider the number and types of data sources your CDP needs to integrate with (e.g., CRM, website analytics, email marketing platforms). A robust CDP should seamlessly integrate with your existing tech stack.
- Data Governance and Security: Data security and compliance are paramount. Ensure the CDP you choose complies with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and offers robust security features to protect customer data.
- Scalability and Performance: Choose a CDP that can handle your current data volume and scale to accommodate future growth. Performance is crucial for real-time data processing and efficient campaign execution.
- Analytics and Reporting Capabilities: The CDP should provide robust analytics and reporting tools to track campaign performance, gain customer insights, and optimize marketing strategies. Look for features such as custom dashboards, segmentation capabilities, and predictive analytics.
- Ease of Use and Implementation: A user-friendly interface and straightforward implementation process are essential. Consider the level of technical expertise required to manage the platform and the vendor’s support resources.
- Budget and Pricing Model: Evaluate the CDP’s pricing model and ensure it aligns with your budget. Consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance costs.
CDP Decision Matrix
A decision matrix can help you systematically compare different CDP options. The following table provides a framework. Remember to adjust the criteria and weighting based on your specific business priorities.
| CDP Vendor | Data Integration | Security & Compliance | Pricing | Overall Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | Excellent (integrates with 20+ platforms) | Good (GDPR and CCPA compliant) | $5,000/month | 8/10 |
| Vendor B | Good (integrates with 10+ platforms) | Excellent (ISO 27001 certified) | $3,000/month | 7/10 |
| Vendor C | Fair (integrates with 5 platforms) | Good (GDPR compliant) | $1,000/month | 5/10 |
| Vendor D | Excellent (highly customizable integrations) | Excellent (SOC 2 Type II certified) | $10,000/month | 9/10 |
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers
Implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning and execution. A successful implementation hinges on understanding the process, anticipating potential challenges, and having a clear roadmap. This section delves into the practical aspects of CDP implementation, integration, and the potential hurdles you might encounter.
CDP Implementation Process
The typical implementation process for a CDP can be broken down into several key phases. Effective planning is paramount before any technical work begins. This includes defining clear objectives, identifying data sources, and selecting the right CDP vendor. Data migration, the process of transferring customer data from disparate sources into the CDP, is often complex and requires careful consideration of data cleansing and transformation.
Thorough testing is crucial to ensure data accuracy and functionality before a full rollout. Ignoring any of these phases can lead to delays, budget overruns, and ultimately, a failed implementation.
Challenges in Integrating a CDP with Existing Marketing Technology Stacks
Integrating a CDP with existing marketing technology (martech) stacks presents several challenges. The complexity arises from the diverse range of systems involved, each with its own data structures and APIs. Data inconsistencies, security concerns, and the need for robust data governance protocols all contribute to the difficulty. For example, integrating a CDP with an email marketing platform might require mapping customer IDs and ensuring data synchronization to prevent duplicate messages.
Similarly, integrating with a CRM system necessitates a careful approach to avoid data conflicts and maintain data integrity. The lack of standardized APIs across different martech solutions further exacerbates these challenges.
Step-by-Step Guide to CDP Implementation
A successful CDP implementation follows a structured approach. Consider these key phases:
- Planning & Scoping: Define clear business objectives, identify key data sources and stakeholders, and select a suitable CDP vendor. This phase involves a thorough assessment of your existing marketing infrastructure and data landscape.
- Data Assessment & Preparation: Analyze the quality and consistency of your existing customer data. Identify and address data gaps, inconsistencies, and duplicates. This might involve data cleansing, standardization, and enrichment processes.
- Data Migration: Carefully plan and execute the migration of your customer data from various sources into the CDP. This often involves using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools and processes.
- Integration with Martech Stack: Integrate the CDP with other marketing technologies, such as CRM, email marketing platforms, and analytics tools. This requires careful configuration of APIs and data mapping.
- Testing & Validation: Thoroughly test the CDP’s functionality and data accuracy. This includes verifying data integrity, ensuring data flows correctly, and testing integrations with other systems. A robust testing phase helps identify and resolve any issues before the full launch.
- Deployment & Go-Live: Once testing is complete, deploy the CDP to your marketing team. This may involve training sessions and ongoing support to ensure smooth adoption.
- Monitoring & Optimization: Continuously monitor the CDP’s performance, data quality, and overall effectiveness. Regularly optimize the system to ensure it meets evolving business needs.
15 Critical CDP Facts for Marketers

This guide has explored the core functionalities and benefits of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs). Now, let’s look ahead to understand the evolving landscape and the future trends shaping the CDP ecosystem. The advancements in technology and the ever-increasing demand for personalized customer experiences are driving significant changes in how CDPs are developed, implemented, and utilized.
Future Trends in CDP Technology
The future of CDPs is inextricably linked to advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). We’re already seeing a significant shift towards AI-powered personalization, where CDPs leverage AI algorithms to analyze customer data and deliver highly targeted and relevant messaging across all touchpoints. Predictive analytics is another key area of growth, enabling marketers to anticipate customer behavior and proactively address their needs.
For example, a retailer might use predictive analytics within their CDP to identify customers likely to churn and proactively offer them retention incentives, such as discounts or loyalty program upgrades. This proactive approach, powered by the CDP, significantly improves customer retention rates. Furthermore, the integration of CDPs with other marketing technologies, such as CRM systems and marketing automation platforms, will continue to improve, leading to a more seamless and efficient marketing technology stack.
This integration allows for a 360-degree view of the customer, enabling more effective and personalized marketing campaigns.
The Future Role of CDPs in Marketing
CDPs are rapidly becoming the central hub for customer data, empowering marketers to create more personalized and effective campaigns. Their role will only expand as data volumes increase and the demand for hyper-personalization intensifies. We predict that CDPs will play a critical role in enabling real-time personalization, allowing marketers to adapt their messaging and offers based on a customer’s immediate behavior and context.
Imagine a website that instantly adjusts its product recommendations based on a customer’s browsing history and real-time location. This level of personalization is becoming increasingly achievable through advanced CDP capabilities. Moreover, the increasing importance of privacy and data governance will necessitate CDPs that prioritize data security and compliance, ensuring marketers can leverage customer data responsibly and ethically. This will lead to the development of CDPs with enhanced privacy features and robust data governance tools.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Evolving CDP Ecosystem
The rapid evolution of the CDP ecosystem presents both challenges and opportunities. One key challenge is the complexity of integrating CDPs with existing marketing technology stacks. This requires careful planning, technical expertise, and potentially significant investment. However, the rewards of a well-integrated CDP far outweigh the challenges, leading to improved efficiency and more effective marketing campaigns. Another challenge is the need for skilled professionals who can effectively manage and utilize CDP functionalities.
The demand for CDP experts is growing rapidly, creating both opportunities for skilled professionals and a need for increased training and education in this area. The opportunity lies in the ability of CDPs to unlock new levels of customer understanding and engagement. By leveraging the power of AI, predictive analytics, and seamless data integration, marketers can create truly personalized experiences that build stronger customer relationships and drive business growth.
This necessitates a proactive approach to embracing the changes and challenges within the evolving CDP landscape.
Illustrative Example: A CDP in Action
Let’s imagine a fictional company, “Cozy Candles,” a small but rapidly growing online retailer of handcrafted candles. They’re struggling to manage their customer data scattered across various platforms – their e-commerce website, email marketing software, social media ads, and a loyalty program. This fragmented data makes it difficult to understand their customers and personalize their marketing efforts effectively.
Cozy Candles decides to implement a Customer Data Platform (CDP) to consolidate and unify their customer data.Cozy Candles integrates their various data sources into their chosen CDP. This includes website activity (browsing history, abandoned carts), purchase history, email engagement (opens, clicks, unsubscribes), social media interactions (likes, comments, follows), and loyalty program participation. The CDP cleanses and unifies this data, creating a single, comprehensive view of each customer.
Data Integration and Customer Segmentation
The CDP allows Cozy Candles to create detailed customer segments based on their unified data. For example, they identify a segment of “High-Value Customers” who have made multiple purchases, have a high average order value, and frequently engage with their email marketing. Another segment, “Engaged but Not Purchasing,” includes customers who frequently interact on social media and open emails but haven’t made a purchase recently.
A third segment, “Abandoned Cart Customers,” comprises users who added items to their cart but didn’t complete the purchase.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
Using these segments, Cozy Candles tailors its marketing messages. High-Value Customers receive exclusive discounts and early access to new product launches. Engaged but Not Purchasing customers receive personalized email campaigns highlighting products they’ve shown interest in or reminding them of abandoned carts. Abandoned Cart Customers receive automated email reminders about the items left in their cart, potentially including a small discount incentive.
Social media ads are also targeted to specific segments, ensuring the right message reaches the right audience.
Measurement and ROI
The CDP provides Cozy Candles with detailed analytics on the performance of their marketing campaigns. They can track key metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI) for each segment and campaign. For example, they might find that their abandoned cart email campaign has a 20% conversion rate, significantly higher than their overall average.
This data allows them to optimize their campaigns, allocate budget more effectively, and improve their overall marketing ROI. They can also track customer lifetime value (CLTV) across segments to better understand the long-term value of different customer groups. This leads to more informed decisions regarding resource allocation and future marketing strategies. By continuously monitoring and analyzing these metrics, Cozy Candles can refine its targeting and messaging, ultimately leading to increased customer engagement and revenue.
Wrap-Up

So there you have it – 15 critical facts about CDPs that will revolutionize your marketing approach. By understanding the power of unified customer data, personalized campaigns, and robust analytics, you can elevate your marketing strategies to a whole new level. Remember, a CDP isn’t just another marketing tool; it’s the key to unlocking deeper customer understanding and building meaningful, lasting relationships.
Embrace the power of the CDP, and watch your marketing results soar!
User Queries
What’s the difference between a CDP and a CRM?
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system focuses on managing customer interactions and relationships, often handling sales and service data. A CDP focuses specifically on unifying customer data from various sources for marketing purposes, enabling personalized campaigns and advanced analytics.
How much does a CDP typically cost?
CDP pricing varies widely depending on the vendor, features, and data volume. Expect a range from a few hundred dollars per month for smaller solutions to tens of thousands for enterprise-level platforms. Many vendors offer tiered pricing models.
Can a small business benefit from a CDP?
Absolutely! Even small businesses can benefit from a CDP by gaining a clearer understanding of their customers and personalizing their marketing efforts, leading to improved ROI. Many vendors offer solutions tailored to smaller businesses with more affordable pricing options.
Is my data safe in a CDP?
Reputable CDP vendors prioritize data security and privacy, employing robust security measures and adhering to data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. It’s crucial to choose a vendor with a strong security track record and transparent data handling policies.