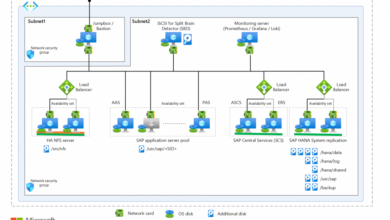
Workload Automation 9-5-0-2 Build Your COE
Workload automation 9 5 0 2 is here create an automation center of excellence to drive your digital transformation – Workload automation 9-5-0-2 is here, and it’s revolutionizing how we work! Creating an Automation Center of Excellence (COE) is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in our always-on world. This post dives into why building a COE is crucial for navigating the demands of a 24/7 operational landscape and driving your digital transformation.
We’ll explore how to identify automation opportunities, implement projects effectively, and measure your success, ultimately boosting efficiency and employee satisfaction.
The modern workplace is anything but 9-to-5. The lines between work and personal life are blurring, creating a need for increased efficiency and flexibility. Workload automation offers a solution, allowing businesses to streamline processes, reduce manual effort, and improve overall productivity. Building a dedicated COE ensures a strategic and cohesive approach to automation, maximizing its impact across the organization.
The Rise of “9-to-5-0-2” and the Need for Automation

The traditional 9-to-5 workday is rapidly becoming a relic of the past. The emergence of the “9-to-5-0-2” model, encompassing a 24/7 always-on globalized economy, necessitates a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and manage their workloads. This constant connectivity blurs the lines between work and personal life, creating both opportunities and significant challenges for productivity and efficiency.The “9-to-5-0-2” environment is characterized by geographically dispersed teams, immediate client expectations, and the constant influx of data requiring rapid processing.
This necessitates a seamless flow of information and tasks across time zones and departments. The challenge for businesses lies in maintaining consistent output, preventing burnout amongst employees, and ensuring operational efficiency in this increasingly complex landscape. Failing to adapt results in missed deadlines, decreased productivity, and ultimately, a loss of competitive advantage.
Challenges of Maintaining Productivity in the “9-to-5-0-2” Environment
Businesses face several key hurdles in managing productivity within the demands of a 24/7 operational model. These include coordinating teams across multiple time zones, ensuring consistent data access and integrity, managing escalating volumes of data, and mitigating the risks of human error in high-pressure situations. Additionally, the pressure to be constantly available can lead to employee burnout and decreased morale, ultimately impacting productivity.
The need for real-time responses and the constant influx of information can overwhelm traditional manual processes.
Benefits of Workload Automation in Addressing These Challenges, Workload automation 9 5 0 2 is here create an automation center of excellence to drive your digital transformation
Workload automation offers a powerful solution to the challenges posed by the “9-to-5-0-2” environment. By automating repetitive tasks, streamlining workflows, and integrating disparate systems, businesses can significantly improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance overall productivity. Automated systems can work around the clock, processing data and completing tasks without the need for constant human intervention. This frees up employees to focus on more strategic and creative tasks, fostering innovation and improving job satisfaction.
Furthermore, automation can significantly reduce operational costs by minimizing manual effort and optimizing resource allocation.
Comparison of Traditional and Automated Workflows
The benefits of automation are clearly demonstrated when comparing traditional and automated workflows. The following table illustrates the significant time savings and efficiency gains that can be achieved:
| Task | Traditional Method | Automated Method | Time Saved (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Entry | Manual data entry by multiple employees | Automated data extraction and input | 75-90% |
| Report Generation | Manual compilation and formatting of reports | Automated report generation with dynamic data updates | 60-80% |
| Invoice Processing | Manual invoice review, data entry, and payment processing | Automated invoice processing and payment approvals | 50-70% |
| Customer Service Inquiries | Manual routing and response to customer inquiries via email/phone | Automated chatbot responses and ticket routing | 40-60% |
Establishing an Automation Center of Excellence (COE)
Building an Automation Center of Excellence (COE) is crucial for successfully navigating the complexities of workload automation and realizing the full potential of digital transformation. A well-structured COE provides the framework, expertise, and governance needed to ensure automation initiatives are strategically aligned, efficiently executed, and deliver measurable business value. It acts as a central hub for best practices, knowledge sharing, and continuous improvement in automation processes.
Establishing a successful COE requires a phased approach, encompassing careful planning, resource allocation, and ongoing evaluation. Key considerations include defining clear roles and responsibilities, selecting appropriate technologies, and developing a robust process for identifying and prioritizing automation opportunities. This ensures the COE effectively supports the organization’s automation journey and contributes to its overall digital transformation goals.
Key Roles and Responsibilities within an Automation COE
The success of an Automation COE hinges on the clear definition and assignment of roles and responsibilities. A well-defined structure ensures accountability and efficient workflow. The team composition should reflect the diverse skillsets needed for successful automation projects, from technical expertise to business process understanding.
- Automation Architect: Designs the overall automation architecture, selects technologies, and ensures interoperability across systems.
- Automation Developers: Build and maintain automation solutions, utilizing chosen technologies and adhering to established coding standards.
- Business Analysts: Identify automation opportunities, analyze processes, and translate business requirements into technical specifications.
- Process Owners/Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Provide domain expertise, validate automation solutions, and ensure alignment with business needs.
- COE Manager: Oversees the COE’s operations, manages resources, tracks progress, and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
Steps Involved in Establishing an Effective COE
Establishing an effective COE is an iterative process requiring careful planning and execution. A phased approach ensures a structured and manageable implementation, allowing for adjustments based on learnings and evolving needs.
- Define the COE’s mandate and objectives: Clearly articulate the COE’s purpose, scope, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Secure executive sponsorship and resource allocation: Obtain buy-in from senior management and secure necessary funding and personnel.
- Recruit and train the COE team: Assemble a team with the necessary skills and experience, providing training as needed.
- Establish governance processes and standards: Define procedures for project selection, approval, and execution, along with coding standards and quality assurance.
- Implement chosen automation technologies: Deploy the selected technologies and integrate them with existing systems.
- Develop a knowledge base and best practices repository: Create a centralized repository for documentation, tutorials, and lessons learned.
- Continuously monitor and improve: Regularly evaluate the COE’s performance and adapt processes based on feedback and changing business needs.
Selecting and Implementing Automation Technologies
The selection of automation technologies is critical to the COE’s success. The chosen tools must align with the organization’s specific needs, existing infrastructure, and long-term goals. A thorough evaluation process is essential to ensure the right fit.
Factors to consider include scalability, ease of integration, vendor support, cost, and security. A phased implementation approach, starting with pilot projects, can mitigate risks and allow for iterative improvements.
So, you’re thinking about workload automation – the 9-to-5 grind is officially over! Building an automation center of excellence is key to your digital transformation journey. A big part of that involves streamlining app development, and that’s where exploring options like domino app dev the low code and pro code future comes in. This allows you to rapidly build and deploy solutions, freeing up your team to focus on the strategic aspects of your automation center and ultimately driving your overall digital transformation.
| Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Can the technology handle increasing workloads and future growth? |
| Integration | How easily does it integrate with existing systems and applications? |
| Vendor Support | What level of support and maintenance is offered by the vendor? |
| Cost | What are the initial and ongoing costs associated with the technology? |
| Security | Does the technology meet the organization’s security requirements? |
Identifying and Prioritizing Automation Opportunities
A systematic approach to identifying and prioritizing automation opportunities is crucial for maximizing the ROI of automation initiatives. This involves analyzing business processes to identify areas where automation can deliver the greatest impact.
A common method is to use a scoring system that considers factors such as the potential cost savings, the complexity of the process, and the feasibility of automation. This helps to focus efforts on projects with the highest potential for success.
For example, a company might prioritize automating high-volume, repetitive tasks with clear, well-defined processes before tackling more complex or less predictable ones. This phased approach allows the COE to build momentum and demonstrate early successes, fostering further buy-in and investment in automation.
Identifying Automation Opportunities
So, we’ve established the “9-to-5-0-2” reality and the need for an Automation Center of Excellence. Now, let’s get down to brass tacks: finding those juicy automation opportunities within your organization. This isn’t about randomly picking processes; it’s about strategic selection that delivers maximum ROI.Identifying the right processes for automation requires a thorough understanding of your current workflows. We need to pinpoint those tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and consume significant time and resources.
The goal is to free up your human capital for more strategic and creative endeavors.
Five Business Processes Suitable for Automation
The selection of processes should be based on factors such as frequency, volume of transactions, error rate, and the potential for improvement. Here are five examples, keeping in mind that the specifics will vary depending on your industry and business model:
- Invoice Processing: Automating invoice data entry, validation, and routing can drastically reduce processing time and manual errors. Imagine a system that automatically extracts data from invoices (PDF, email, etc.), verifies it against purchase orders, and routes it to the appropriate approvers.
- Customer Onboarding: Streamlining the new customer acquisition process through automated email sequences, document delivery, and system updates can significantly improve customer experience and reduce onboarding time. This includes automated KYC (Know Your Customer) checks and account provisioning.
- Data Entry and Reporting: Many businesses spend countless hours manually entering data into spreadsheets and generating reports. Automating this process with robotic process automation (RPA) can significantly reduce errors and free up employees for more valuable tasks. This could involve pulling data from various sources and automatically populating reports.
- Inventory Management: Automating inventory tracking and reordering processes can optimize stock levels, reduce storage costs, and prevent stockouts. Imagine a system that automatically generates purchase orders when inventory levels fall below a certain threshold.
- Human Resources Processes: Automating tasks like recruitment screening, onboarding paperwork, and benefits enrollment can streamline HR operations and improve employee experience. This could include automated candidate screening based on s and criteria.
Potential ROI for Automation Opportunities
Calculating ROI for automation projects is crucial for securing buy-in. It’s not just about the cost of the automation tool; it’s about the total cost of ownership (TCO) versus the return on investment (ROI). This includes:
- Reduced Labor Costs: The most significant ROI driver is often the reduction in labor costs associated with automating repetitive tasks. For example, automating invoice processing might save $X per invoice processed, multiplied by the number of invoices processed annually.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Automation leads to faster processing times, fewer errors, and increased throughput. This translates to increased productivity and potentially higher revenue.
- Reduced Errors and Costs Associated with Errors: Manual processes are prone to errors, which can be costly to correct. Automation minimizes these errors, leading to significant cost savings.
- Improved Compliance and Reduced Risk: Automation can improve compliance with regulations and reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster processing times and improved accuracy lead to better customer experiences.
Automation Tool Comparison
The choice of automation tool depends on the specific process and its complexity. Here’s a simplified comparison:
| Tool Type | Suitable for | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Repetitive, rule-based tasks | Easy to implement, relatively low cost | Limited scalability, can be brittle |
| Business Process Management (BPM) | Complex, multi-step processes | High scalability, improved visibility | Higher implementation cost, requires more technical expertise |
| Intelligent Automation (IA) | Processes requiring decision-making and cognitive abilities | High accuracy, adaptability | High implementation cost, requires specialized skills |
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Automation Projects
A thorough cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is essential before embarking on any automation project. A simple formula is:
Net Present Value (NPV) = Σ [ (Benefitt
Costt) / (1 + r) t ]
Where:* Benefit t = benefits in year t
- Cost t = costs in year t
- r = discount rate
- t = year
The CBA should include all relevant costs (software licenses, implementation, training, maintenance) and benefits (reduced labor costs, increased efficiency, reduced errors). A positive NPV indicates that the project is financially viable. For example, a project with an initial investment of $100,000 and annual savings of $30,000 over five years, with a discount rate of 10%, would need to be calculated using the above formula to determine its viability.
A sensitivity analysis should also be performed to assess the impact of changes in key assumptions.
Implementing and Managing Automation Projects
Successfully implementing automation projects requires a structured approach and diligent management. From initial planning to post-implementation review, each stage demands careful consideration to maximize ROI and minimize disruptions. This section details the crucial steps, best practices, potential risks, and mitigation strategies involved in bringing automation projects to fruition.
The implementation of an automation project isn’t a single event; it’s a carefully orchestrated process. A well-defined methodology, robust project management, and a proactive risk management strategy are vital for success. Ignoring any of these elements can lead to delays, cost overruns, and ultimately, project failure.
Project Implementation Steps
A typical automation project follows a phased approach. Understanding these phases and their interdependencies is crucial for effective execution.
- Requirements Gathering and Analysis: This initial phase involves thoroughly defining the scope of the automation project, identifying specific processes to automate, and documenting the necessary inputs, outputs, and expected outcomes. This often includes stakeholder interviews, process mapping, and detailed documentation.
- Design and Development: Based on the gathered requirements, the automation solution is designed and developed. This includes selecting appropriate tools and technologies, designing workflows, and developing the necessary scripts or code. Thorough testing is crucial at this stage.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing is essential to ensure the automation solution functions as expected and meets the defined requirements. This involves unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT) to identify and resolve any bugs or defects before deployment.
- Deployment and Integration: Once testing is complete, the automation solution is deployed into the production environment. This may involve integrating the solution with existing systems and applications. Careful planning and execution are crucial to minimize disruption during deployment.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: After deployment, continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the automation solution continues to function as expected. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), addressing any issues that arise, and implementing regular maintenance to prevent future problems.
Best Practices for Managing Automation Projects
Effective project management is crucial for the success of any automation initiative. Following best practices can significantly improve the chances of on-time and within-budget completion.
- Clearly Defined Scope and Objectives: Ensure all stakeholders understand the project’s goals, deliverables, and timelines.
- Agile Methodology: Employing an agile approach allows for flexibility and iterative development, enabling adjustments based on feedback and changing requirements.
- Robust Communication Plan: Establish clear communication channels and regular updates to keep stakeholders informed of progress and any potential issues.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation throughout the project lifecycle, including requirements, design specifications, test results, and deployment procedures.
- Risk Management Plan: Proactively identify and mitigate potential risks, developing contingency plans to address unforeseen challenges.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Automation projects, while offering significant benefits, also present potential risks. Proactive risk management is crucial to minimize their impact.
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Unexpected Integration Issues | Thorough pre-integration testing and planning; dedicated integration team. |
| Lack of User Adoption | Comprehensive training and change management programs; user feedback incorporated into the design. |
| Cost Overruns | Detailed budgeting and cost tracking; regular review of project expenses. |
| Security Vulnerabilities | Security assessments throughout the development lifecycle; implementation of robust security measures. |
| Unforeseen Technical Challenges | Experienced development team; contingency planning for unexpected technical issues. |
Automation Project Lifecycle Flowchart
The following describes a flowchart illustrating the typical lifecycle of an automation project. Imagine a simple flowchart with boxes representing each stage connected by arrows showing the flow. The boxes would be labeled: Requirements Gathering, Design & Development, Testing, Deployment, Monitoring & Maintenance. Arrows would indicate the progression from one stage to the next, with feedback loops from Testing back to Design & Development and from Monitoring & Maintenance back to Requirements Gathering to allow for iterative improvement.
Measuring and Optimizing Automation Efforts: Workload Automation 9 5 0 2 Is Here Create An Automation Center Of Excellence To Drive Your Digital Transformation

Successfully implementing workload automation isn’t just about deploying robots; it’s about ensuring they deliver tangible value. This requires a robust system for measuring and optimizing your automation initiatives, constantly refining processes to maximize efficiency and ROI. Ignoring this crucial step can lead to underperforming automations and missed opportunities for significant gains.
Effective measurement and optimization hinge on establishing clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track progress, regularly monitoring performance, and proactively seeking opportunities for improvement. This iterative process ensures that your automation efforts remain aligned with business objectives and deliver the expected return on investment.
Key Performance Indicators for Automation Success
Selecting the right KPIs is vital for accurately assessing the impact of your automation projects. These metrics should directly reflect the goals of your automation strategy. Focusing on a few key metrics, rather than trying to track everything, will provide a clearer and more actionable picture.
- Automation Rate: The percentage of tasks or processes successfully automated. This metric provides a clear picture of the overall progress of your automation initiatives. For example, if you aim to automate 50 processes and have successfully automated 30, your automation rate is 60%.
- Error Rate: The frequency of errors or exceptions occurring within automated processes. A low error rate signifies robust and reliable automation. Tracking this helps identify areas needing improvement in process design or error handling. For instance, an error rate of less than 1% might be considered acceptable, while a rate exceeding 5% would necessitate investigation.
- Processing Time: The time taken to complete a task or process, both before and after automation. A significant reduction in processing time indicates the efficiency gains achieved through automation. Comparing the pre-automation time of 2 hours to the post-automation time of 15 minutes demonstrates a substantial improvement.
- Cost Savings: The reduction in operational costs achieved through automation. This is a crucial metric for demonstrating the financial benefits of automation initiatives to stakeholders. For example, a reduction in labor costs by 20% due to automation translates to significant savings.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The overall return on investment in automation projects. This metric considers both the costs of implementation and the benefits achieved, providing a comprehensive assessment of the project’s financial viability. An ROI of 200% indicates a substantial return on the investment.
Monitoring and Evaluating Automated Processes
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the ongoing effectiveness of automated processes. This involves actively tracking the KPIs defined earlier and using the data to identify potential issues or areas for improvement.
Regular reviews of process logs, exception reports, and system performance data will highlight areas needing attention. Automated dashboards providing real-time visibility into key metrics can greatly simplify this process. This allows for proactive identification of issues before they significantly impact efficiency or accuracy.
Strategies for Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Automation isn’t a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing process of refinement and optimization. Continuous improvement strategies should be embedded into your automation program from the outset.
- Regular Process Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of automated processes to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or areas for improvement. This could involve analyzing process logs, user feedback, and performance data.
- Process Redesign: Based on the findings from process reviews, redesign processes to eliminate inefficiencies and improve performance. This may involve simplifying workflows, optimizing data handling, or incorporating new technologies.
- Automation Expansion: Identify additional opportunities for automation within the organization and expand the scope of your automation program. This iterative approach ensures that the benefits of automation are maximized.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for gathering feedback from users and stakeholders on the performance of automated processes. This could involve surveys, interviews, or feedback forms.
Reporting on Automation Success Metrics
Clear and concise reporting is crucial for communicating the success of automation initiatives to stakeholders. Reports should be tailored to the audience and focus on the key metrics that are most relevant to their interests.
Visualizations such as charts and graphs can effectively communicate complex data and highlight key trends. Regular reporting, perhaps monthly or quarterly, will keep stakeholders informed of progress and allow for timely adjustments to the automation strategy. Executive summaries should emphasize key achievements and areas for future focus.
For example, a report could highlight the percentage increase in efficiency achieved through automation, the cost savings realized, and the overall ROI of the automation program. This allows stakeholders to see the tangible benefits of the investment in automation.
Digital Transformation through Automation
Workload automation isn’t just about streamlining individual tasks; it’s a cornerstone of successful digital transformation. By automating repetitive, manual processes, organizations free up human capital for more strategic and creative endeavors, ultimately accelerating their digital journey and fostering a more agile and responsive business.Automation’s impact on digital transformation is multifaceted, extending beyond simple efficiency gains. It fuels innovation, improves data-driven decision-making, and enhances the overall customer experience.
This section will explore these key aspects in detail.
Improved Employee Satisfaction and Engagement
Automating tedious and error-prone tasks significantly reduces employee frustration and burnout. This frees up valuable time for employees to focus on more challenging and rewarding work that leverages their unique skills and creativity. For example, instead of spending hours on data entry, a finance professional can dedicate that time to analyzing financial trends and contributing to strategic planning.
This shift leads to increased job satisfaction, higher employee morale, and improved retention rates. A more engaged workforce is naturally more productive and innovative, directly contributing to the success of the digital transformation initiative.
Enhanced Business Agility and Market Responsiveness
In today’s rapidly changing market, agility is paramount. Automation empowers businesses to adapt quickly to new trends and customer demands. By automating processes, organizations can reduce lead times, improve product delivery cycles, and respond more effectively to market fluctuations. For instance, an e-commerce company using automated inventory management and order fulfillment can quickly scale its operations to meet peak demand during holiday seasons, avoiding stockouts and ensuring customer satisfaction.
This enhanced responsiveness translates to a competitive advantage and improved profitability.
Visual Representation of Automation and Digital Transformation Interconnectedness
Imagine a central hub representing the organization. Radiating outwards from this hub are numerous spokes, each representing a different business function (e.g., finance, marketing, operations). Each spoke has several smaller branches depicting individual processes. Automation is visualized as a network of interconnected lines flowing through these branches, streamlining and optimizing processes across all functions. The entire system is dynamic and responsive, constantly adapting to changing conditions.
The more lines representing automation, the more efficient and agile the entire digital transformation becomes. This illustrates how automation doesn’t operate in isolation but integrates seamlessly into all aspects of the business, driving holistic digital transformation.
Last Recap
Embracing workload automation isn’t just about technology; it’s about transforming your business culture and driving a future-ready organization. By establishing an Automation Center of Excellence and strategically implementing automation initiatives, you can unlock significant efficiency gains, enhance employee satisfaction, and achieve a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market. The journey might seem daunting, but the rewards of a more agile, responsive, and productive business are well worth the effort.
So, are you ready to build your automation powerhouse?
Common Queries
What is the ROI of building an Automation COE?
The ROI varies depending on the size and complexity of your organization, but it typically includes significant cost savings through reduced manual labor, improved efficiency, faster turnaround times, and minimized errors. A well-structured COE also fosters innovation and improves employee morale by freeing them from repetitive tasks.
How long does it take to establish an Automation COE?
The timeframe depends on your organization’s size and complexity, but a phased approach is generally recommended. You can expect the initial setup and pilot projects to take several months, with ongoing development and expansion continuing thereafter.
What are some common challenges in implementing automation projects?
Common challenges include resistance to change from employees, inadequate training, integration issues with existing systems, and difficulty in identifying the right automation opportunities. Careful planning, change management strategies, and robust training programs are crucial for mitigating these risks.