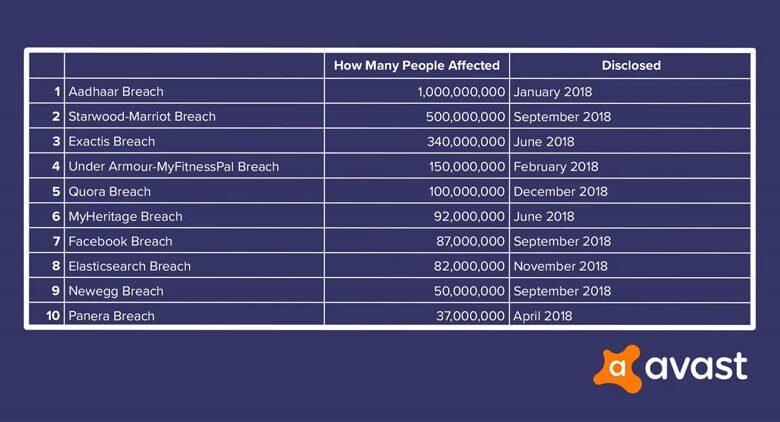
1 Billion Indian Aadhaar Cards Vulnerable to Cyberattack
Data of more than 1 billion indian aadhaar cards is open to cyber attack – Data of more than 1 billion Indian Aadhaar cards is open to cyberattack – a chilling thought, isn’t it? This massive database, containing incredibly sensitive personal information, presents a juicy target for malicious actors. Imagine the potential chaos: identity theft on a scale never before seen, financial ruin for millions, and a devastating blow to public trust in the digital identity system.
This post dives deep into the vulnerabilities, potential impacts, and crucial steps needed to secure this vital national resource.
We’ll explore the technical weaknesses within the Aadhaar system, comparing its current security measures to industry best practices. We’ll also examine the various types of cyberattacks that could exploit these vulnerabilities, from sophisticated SQL injections to more commonplace phishing scams. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting individuals, society, and the Indian economy as a whole. Finally, we’ll discuss preventative measures, mitigation strategies, and the vital role of public awareness in safeguarding this critical data.
The Vulnerability
The recent news regarding the potential compromise of Aadhaar data, affecting over a billion Indian citizens, highlights a critical vulnerability in large-scale biometric identification systems. While the government has claimed the issue has been addressed, understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities remains crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring data security. This analysis delves into the potential weaknesses within the Aadhaar system and compares its security measures against industry best practices.
Aadhaar Data Breach Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the risk of a data breach within the Aadhaar system. These include potential weaknesses in the database infrastructure itself, vulnerabilities in the authentication process, and the potential for insider threats. The sheer scale of the data—over a billion records—magnifies the potential impact of any successful attack. A breach could expose sensitive personal information, including biometric data (fingerprints, iris scans), demographic details, and addresses, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and other serious consequences.
The interconnected nature of Aadhaar with other government services and private sector applications further amplifies the risk.
Technical Aspects of a Potential Data Breach, Data of more than 1 billion indian aadhaar cards is open to cyber attack
Attackers could employ various methods to breach the Aadhaar system. SQL injection attacks, for instance, could exploit vulnerabilities in the database’s code to gain unauthorized access and manipulate data. Phishing campaigns, targeting Aadhaar officials or users, could lead to credential theft. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks could overwhelm the system, making it unavailable and potentially creating opportunities for other attacks.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs), involving sophisticated, long-term intrusions, pose a significant risk, potentially allowing attackers to remain undetected for extended periods. Furthermore, insider threats, from malicious or compromised employees with access to the database, present a significant, often overlooked, vulnerability.
Security Measures vs. Industry Best Practices
While the Aadhaar system employs various security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, a comparison with industry best practices reveals potential areas for improvement. The use of multi-factor authentication, stronger encryption algorithms, and more robust intrusion detection systems could enhance security. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments by independent third-party security experts are also crucial for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses.
Moreover, the implementation of a comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) strategy and robust incident response plan are vital for minimizing the impact of any successful attack. The current system’s reliance on centralized data storage, while offering operational efficiency, presents a significant single point of failure, making it a prime target for attackers. A more decentralized approach, perhaps employing blockchain technology or federated databases, could significantly improve resilience.
Cyberattack Impact on Aadhaar Data
| Attack Type | Method | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Malicious SQL code injected into input fields | Data modification, deletion, or unauthorized access | Input validation, parameterized queries, regular security audits |
| Phishing | Deceptive emails or websites to obtain credentials | Credential theft, unauthorized access | Security awareness training, multi-factor authentication, strong password policies |
| DDoS Attack | Overwhelming the system with traffic | System unavailability, potential for further attacks | DDoS mitigation solutions, robust infrastructure, capacity planning |
| Man-in-the-Middle Attack | Intercepting communication between user and server | Data interception, credential theft | HTTPS encryption, strong authentication protocols |
Impact Assessment
The potential consequences of a data breach affecting over a billion Indian Aadhaar cards are severe and far-reaching, impacting individuals, society, and the Indian economy significantly. The sheer scale of the data involved magnifies the potential damage, demanding a thorough understanding of the risks. This assessment Artikels the potential repercussions, categorized for clarity.
Individual Impacts
A data breach of this magnitude would expose individuals to a multitude of risks. The Aadhaar card contains highly sensitive personal information, making individuals vulnerable to various forms of identity theft and fraud. Criminals could use this data to open fraudulent bank accounts, apply for loans, access government benefits, or even commit more serious crimes like identity fraud.
- Identity Theft: Criminals could impersonate individuals, accessing their bank accounts, credit lines, and other financial resources. This could lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
- Financial Fraud: Stolen Aadhaar data could facilitate a wide range of financial crimes, including online banking fraud, credit card fraud, and loan scams. The potential for financial losses is substantial.
- Social Engineering Attacks: Phishing scams and other social engineering attacks could become far more effective with access to personal information like name, address, and biometric data. Individuals could be tricked into revealing further sensitive information or transferring money.
Societal Impacts
The consequences extend far beyond individual losses. A massive data breach could severely erode public trust in the Aadhaar system and digital identity initiatives in general. This loss of trust could hinder the adoption of other digital services and initiatives, impacting the nation’s progress towards a digital economy.
- Erosion of Public Trust: A major breach would likely lead to widespread distrust in the government’s ability to protect citizen data, potentially leading to reduced participation in digital government services.
- Political Instability: Widespread public anger and outrage over a data breach could trigger political instability, especially if the government is perceived as having failed to adequately protect citizen data.
- Social Disruption: The potential for widespread identity theft and fraud could lead to social unrest and disruption as individuals struggle to rectify the damage caused by the breach.
Economic Impacts
The economic repercussions of a major Aadhaar data breach would be substantial. The costs associated with addressing the breach, compensating victims, and restoring public trust would be enormous. Furthermore, the damage to India’s reputation as a safe and reliable location for digital transactions could deter foreign investment and hinder economic growth.
- Financial Losses: The direct financial losses due to identity theft, fraud, and the costs of remediation would be significant, potentially reaching billions of rupees.
- Reduced Foreign Investment: A major data breach could damage India’s reputation as a secure location for digital transactions, deterring foreign investment and slowing economic growth.
- Impact on Digital Economy: The breach could severely hamper the development of India’s digital economy, as individuals and businesses become hesitant to use digital services.
Preventive Measures and Mitigation Strategies

The recent revelation regarding the potential vulnerability of the Aadhaar database underscores the critical need for robust preventive measures and mitigation strategies. Securing a database of this magnitude, containing highly sensitive personal information of over a billion Indian citizens, requires a multi-layered approach encompassing technological advancements, procedural improvements, and clearly defined responsibilities across all stakeholders. Failure to implement comprehensive security measures could have catastrophic consequences, leading to widespread identity theft, financial fraud, and erosion of public trust.
The news about more than a billion Indian Aadhaar cards being vulnerable to cyberattacks is seriously alarming. This highlights the urgent need for robust security measures, especially with sensitive data in the cloud. Understanding solutions like bitglass and the rise of cloud security posture management becomes crucial in preventing such breaches. We need stronger defenses now more than ever to protect such massive datasets from falling into the wrong hands.
Best Practices for Securing Large-Scale Databases
Protecting a database the size of Aadhaar requires a combination of established best practices and cutting-edge technologies. Data minimization is paramount; only essential information should be collected and stored. Regular data audits and vulnerability assessments are crucial to identify and address weaknesses proactively. Strong access control mechanisms, employing the principle of least privilege, should restrict access to sensitive data based on roles and responsibilities.
Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is non-negotiable, utilizing strong, regularly updated encryption algorithms. Regular security awareness training for all personnel involved in managing the database is vital to mitigate human error, a major source of security breaches. Finally, a robust incident response plan is essential to effectively manage and contain any potential security incidents.
Cybersecurity Strategy for the Aadhaar System
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for the Aadhaar system must incorporate several key elements. This includes migrating to a zero-trust security model, where every access request is verified regardless of its origin, significantly reducing the impact of compromised credentials. Implementing advanced threat detection systems, including intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), is crucial for identifying and neutralizing malicious activities in real-time.
Regular penetration testing and security audits by independent experts are essential to identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Furthermore, investing in robust data backup and recovery mechanisms is vital to ensure data availability in case of a breach or system failure. Finally, continuous monitoring and logging of all system activities provide valuable insights into potential threats and facilitate timely response.
Roles and Responsibilities of Stakeholders
The responsibility for securing the Aadhaar database is shared among multiple stakeholders. The Government of India provides the overarching policy framework and regulatory oversight. The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) is responsible for the technical implementation and ongoing maintenance of the system, including the development and implementation of security measures. This includes the development and enforcement of stringent security policies and procedures, as well as the provision of adequate resources for security enhancements.
Citizens, on the other hand, have a responsibility to protect their Aadhaar information by choosing strong passwords, avoiding phishing scams, and reporting any suspicious activity. Effective communication and collaboration between these stakeholders are crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the Aadhaar system.
Multi-Factor Authentication and Advanced Encryption Techniques
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication before accessing their Aadhaar data. This could include something they know (password), something they have (OTP), and something they are (biometric authentication). Combining MFA with advanced encryption techniques, such as homomorphic encryption which allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, significantly enhances the security of the Aadhaar system.
This ensures that even if an attacker gains access to the database, the data remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys. Implementing robust key management practices is crucial to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of these encryption keys. For instance, the use of Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for secure key storage and management can mitigate the risks associated with key compromise.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Data Of More Than 1 Billion Indian Aadhaar Cards Is Open To Cyber Attack
The revelation that data pertaining to over a billion Indian Aadhaar cards is potentially vulnerable to cyberattacks raises serious legal and ethical concerns. This vulnerability necessitates a thorough examination of the legal implications for all involved parties and a critical assessment of the ethical framework guiding the Aadhaar system’s operation. The potential for misuse of this sensitive personal data demands immediate and comprehensive action.
Legal Implications of a Data Breach
A data breach of this magnitude could trigger significant legal repercussions under various Indian laws. The Information Technology Act, 2000, along with the recently enacted Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, provides a framework for addressing data breaches and imposing penalties on organizations responsible for data protection. Penalties can range from monetary fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the breach and the negligence demonstrated.
Furthermore, individuals whose data has been compromised could pursue civil lawsuits for damages, including compensation for financial losses, emotional distress, and reputational harm. The liability could extend to the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), the organizations managing the Aadhaar database, and any third-party vendors involved in its operation or security. The legal ramifications are complex and would depend on a detailed investigation into the cause and extent of the breach.
Comparison of Indian Data Protection Laws with International Standards
India’s data protection landscape is evolving. The Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, represents a significant step towards aligning Indian law with international standards. However, it is still relatively new and its effectiveness in practice remains to be seen. Compared to regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, the Indian Act may have certain differences in terms of enforcement mechanisms, data subject rights, and the scope of data protection.
While the Indian Act aims to protect personal data, a thorough comparative analysis is necessary to ascertain its effectiveness in preventing and mitigating data breaches on the scale of the potential Aadhaar vulnerability. For instance, the level of individual control over data usage and the extent of liability for organizations might differ significantly across these jurisdictions.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Aadhaar Data
The ethical considerations surrounding the Aadhaar system are multifaceted and profound. The collection, storage, and use of such extensive biometric and personal data raise significant concerns about individual rights and privacy. The potential for misuse of Aadhaar data for surveillance, discrimination, or other harmful purposes necessitates a robust ethical framework. The principle of informed consent, often central to ethical data handling, needs careful consideration.
Many individuals may not fully understand the implications of providing their biometric data and how it might be used in the future. This raises questions about the transparency and accountability of the Aadhaar system and the need for greater user control over their data. The lack of transparency regarding data sharing practices and the potential for unauthorized access also raise significant ethical concerns.
Key Ethical Principles for the Aadhaar System
The development and operation of the Aadhaar system should be guided by several key ethical principles:
- Privacy by Design: Data minimization and security should be integrated into the system’s design from the outset.
- Transparency and Accountability: Clear and accessible information about data collection, storage, and usage practices should be provided to users.
- Informed Consent: Individuals should provide explicit and informed consent for the collection and use of their data.
- Data Security: Robust security measures should be implemented to protect Aadhaar data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
- Purpose Limitation: Data should only be collected and used for specified, legitimate purposes.
- Data Minimization: Only necessary data should be collected.
- Accountability and redressal: Mechanisms for accountability and redressal should be in place for individuals whose rights have been violated.
Public Awareness and Education
The recent vulnerability affecting Aadhaar data underscores the critical need for a comprehensive public awareness campaign. Educating the Indian population about cybersecurity best practices is paramount to mitigating the risks associated with Aadhaar and preventing widespread fraud. This requires a multi-pronged approach, leveraging various communication channels and focusing on clear, concise messaging.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Aadhaar Protection
Protecting your Aadhaar information requires a proactive approach to online safety. This includes understanding and implementing strong password practices, recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts, and promptly reporting suspicious activities. Ignoring these practices significantly increases your vulnerability to identity theft and financial fraud.
Public Awareness Campaign: Protecting Your Aadhaar
This campaign targets the diverse Indian population, focusing specifically on vulnerable groups like the elderly and those with limited digital literacy. Messaging will be simple, easily understandable, and available in multiple regional languages. Communication channels will include television and radio advertisements, social media campaigns, community outreach programs, and partnerships with local leaders and influencers. The campaign’s core message will be: “Your Aadhaar is your identity; protect it.” Visuals will depict everyday scenarios demonstrating the potential risks and the simple steps individuals can take to stay safe.
For instance, one advertisement might show a senior citizen receiving a suspicious phone call requesting Aadhaar details, contrasted with another showing the same person securely accessing their Aadhaar information through the official app.
Secure Password Creation and Phishing Awareness
Creating a strong password involves using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or pet names. A password manager can help generate and securely store complex passwords. Phishing attempts often involve deceptive emails or text messages mimicking legitimate organizations. These messages typically urge immediate action, often threatening account suspension or financial penalties.
Always verify the sender’s authenticity before clicking any links or providing personal information. Look for inconsistencies in email addresses, unusual language, or requests for sensitive information.
Reporting Suspicious Activity
Reporting suspicious activity is crucial in preventing further harm and helping authorities track down perpetrators. Individuals should report any unauthorized access to their Aadhaar account, suspicious emails or messages, or any instances of identity theft to the UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India) helpline, cybercrime cells, and local law enforcement. Prompt reporting significantly increases the chances of successful investigation and recovery.
The campaign will provide clear instructions on how and where to report such incidents, including contact details and online reporting portals.
The news about the vulnerability of over a billion Indian Aadhaar cards to cyberattacks is seriously alarming. We need robust, secure systems to protect such sensitive data, and that’s where advancements like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future become crucial. Improving the security of our digital infrastructure is paramount, especially given the scale of the Aadhaar data breach threat.
Closure
The vulnerability of over a billion Aadhaar cards to cyberattack is a serious issue demanding immediate attention. While the UIDAI has implemented security measures, the sheer scale of the data and the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats necessitate a multi-pronged approach. This includes technological upgrades, improved procedures, increased public awareness, and a robust legal framework to protect citizen data.
Ultimately, securing Aadhaar is not just a technological challenge; it’s a matter of national security and the protection of fundamental rights. The stakes are incredibly high, and proactive measures are essential to prevent a catastrophic breach.
Question Bank
What is the UIDAI’s role in Aadhaar security?
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) is responsible for the Aadhaar system’s overall security and maintenance. This includes implementing and updating security measures, responding to security incidents, and educating the public about protecting their Aadhaar information.
What should I do if I suspect my Aadhaar data has been compromised?
Immediately report any suspicious activity to the UIDAI and local law enforcement. Change your passwords for all online accounts and monitor your financial transactions closely.
How can I protect my Aadhaar number from phishing scams?
Never share your Aadhaar number or OTP with anyone over the phone, email, or through suspicious websites. Be wary of unsolicited calls or emails requesting your Aadhaar information.
Are there any penalties for unauthorized access or misuse of Aadhaar data?
Yes, both civil and criminal penalties exist under Indian law for unauthorized access, misuse, or disclosure of Aadhaar data. Penalties can include fines and imprisonment.