Insider Threat Detection What You Need to Know
Insider threat detection what you need to know sets the stage for understanding a critical security issue in today’s digital world. We’ll explore the various types of insider threats, from malicious actors to unintentional mistakes, and how to identify, prevent, and respond to them. Knowing the potential consequences of failing to address these threats is crucial for any organization.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of insider threat detection, covering everything from identifying potential threats to implementing robust security policies and responding effectively to incidents. We’ll analyze real-world case studies and examine best practices to equip you with the knowledge to safeguard your organization.
Introduction to Insider Threat Detection: Insider Threat Detection What You Need To Know
Insider threats are a significant security risk in today’s digital landscape, posing a substantial challenge to organizations of all sizes. They stem from individuals within an organization who, intentionally or unintentionally, compromise the security of sensitive data and systems. This encompasses a range of actions, from malicious data breaches to careless mistakes leading to data leaks. Understanding the various types of insider threats and their potential impact is crucial for developing effective detection and mitigation strategies.Insider threats can have devastating consequences, impacting not only an organization’s reputation and financial stability but also potentially endangering individuals and society.
The damage caused can range from financial losses and legal liabilities to severe reputational damage and loss of trust. The scale of potential harm emphasizes the critical need for proactive measures to identify and address these threats.
Different Types of Insider Threats
Insider threats manifest in various forms, each with distinct motivations and consequences. Recognizing these variations is essential for developing targeted countermeasures.
- Malicious Insider Threats: These threats involve deliberate actions by insiders to harm the organization, often motivated by personal gain, revenge, or ideological reasons. Examples include stealing sensitive data, disrupting operations, or sabotaging systems. The motivation behind these actions varies widely, and some cases involve individuals with access to sensitive information, while others may stem from a perceived grievance or dissatisfaction within the organization.
- Negligent Insider Threats: These threats arise from careless or unintentional actions by insiders that compromise security. Examples include failing to follow security protocols, using weak passwords, or leaving sensitive information accessible. These actions, while not necessarily malicious, can have significant consequences if they lead to data breaches or system vulnerabilities. Often, negligent actions are rooted in a lack of awareness or training regarding security best practices.
- Accidental Insider Threats: These threats involve unintentional actions by insiders that result in security breaches. Examples include clicking on malicious links or inadvertently sharing sensitive information with unauthorized individuals. These incidents, often resulting from human error, highlight the importance of establishing clear security guidelines and training programs.
Significance of Insider Threat Detection in Today’s Digital Landscape
The increasing reliance on digital systems and interconnected networks makes organizations more vulnerable to insider threats. Data breaches caused by insiders can have a wide-reaching impact, affecting not only the organization but also its customers and partners. Detecting and mitigating insider threats is therefore paramount in today’s digital landscape.
Potential Consequences of Failing to Identify and Mitigate Insider Threats
Failure to proactively identify and mitigate insider threats can lead to severe consequences. These include financial losses, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and potential harm to individuals and society. The potential for substantial losses underscores the need for comprehensive security strategies.
Key Characteristics of Insider Threats
| Type of Insider Threat | Motivation | Methods | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malicious | Personal gain, revenge, ideological reasons | Data theft, sabotage, system disruption | Financial loss, reputational damage, legal liabilities |
| Negligent | Lack of awareness, inadequate training | Weak passwords, non-compliance, careless actions | Data breaches, system vulnerabilities, operational disruption |
| Accidental | Human error, lack of attention | Clicking malicious links, sharing sensitive info | Data breaches, system vulnerabilities, reputational damage |
Identifying Potential Insider Threats
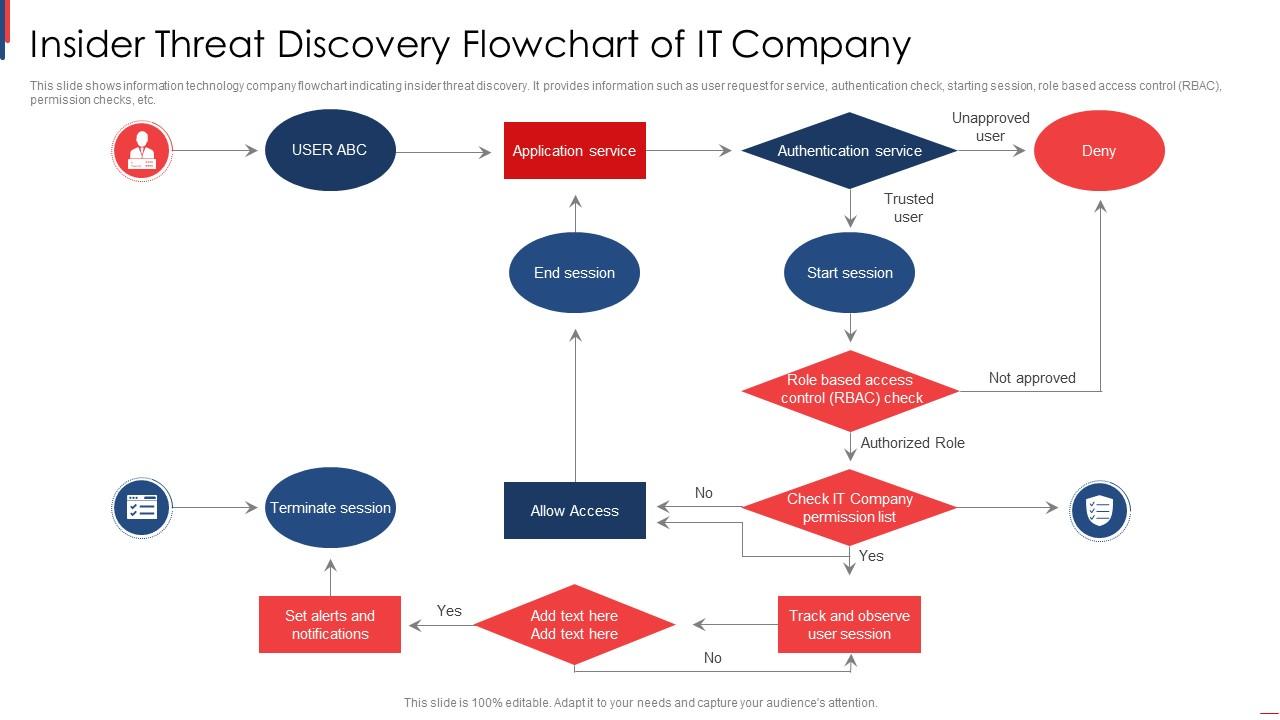
Uncovering potential insider threats requires a proactive approach that goes beyond simple suspicion. It necessitates a deep understanding of normal user behavior patterns, coupled with the ability to detect anomalies that might signal malicious intent. This involves implementing robust monitoring systems and cultivating a culture of security awareness within the organization.Identifying and mitigating insider threats is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of systems.
The cost of a successful insider attack can be devastating, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage and legal repercussions. A well-designed detection system, therefore, is a critical component of a strong overall security posture.
Common Indicators of Potential Insider Threats
Understanding the typical behavior of authorized personnel is essential for identifying deviations that might indicate a threat. These indicators can manifest in various forms, such as unusual access patterns, changes in productivity, or suspicious activity. Examples include accessing data outside of normal working hours, requesting unusual data sets, or exhibiting unusual interest in sensitive information.
Monitoring User Behavior and System Logs
Effective monitoring of user behavior and system logs is a key component of identifying potential insider threats. Real-time monitoring of user activities provides valuable insights into potential anomalies. This involves tracking access patterns, file downloads, and data exfiltration attempts.
Methods for Monitoring User Behavior
Various methods are employed to monitor user behavior, each with its own strengths and limitations. Careful consideration of the resources available and the nature of the threat landscape is essential in choosing the right monitoring methods.
- Network Monitoring: This involves tracking network traffic to identify unusual data transfers or patterns of access to sensitive resources. For instance, a sudden spike in downloads from a specific user’s machine might suggest data exfiltration.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools provide comprehensive visibility into user activity on endpoints. They track keystrokes, file access, and application usage, alerting administrators to suspicious behavior.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and applications. They identify patterns and anomalies, helping administrators pinpoint potential threats.
Factors Increasing Insider Threat Risk
Several factors can increase an individual’s likelihood of becoming an insider threat. These range from personal stressors to organizational vulnerabilities.
- Financial Pressure: Individuals facing financial hardship might be more inclined to engage in malicious activity to resolve their financial difficulties.
- Workplace Disputes: Disagreements with colleagues or management can motivate disgruntled employees to seek retribution.
- Lack of Security Awareness: A lack of security training can leave employees vulnerable to phishing scams and other social engineering attacks.
Security Awareness Training’s Role
Security awareness training is a critical component in mitigating insider threats. It equips employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and report suspicious activity.
- Regular Training Sessions: Regular security awareness training sessions can help employees understand the risks associated with insider threats and the importance of reporting suspicious activity.
- Simulations and Exercises: Simulated phishing attacks and other security exercises can help reinforce the training and test employees’ understanding.
- Promoting a Culture of Security: Creating a culture of security encourages employees to report potential threats, fostering a collaborative approach to security.
Comparing Monitoring Methods
The table below highlights the strengths and weaknesses of different user activity monitoring methods.
| Monitoring Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Network Monitoring | Identifies unusual data transfers, high-volume traffic. | Can be resource-intensive, may miss encrypted traffic. |
| EDR | Provides detailed endpoint activity, detects malicious software. | May not capture all user actions, requires agent installation. |
| SIEM | Centralized view of security events, detects patterns. | Requires significant configuration, may not provide real-time alerts. |
Implementing Detection Mechanisms
Detecting insider threats requires a multi-layered approach that combines various technologies and methodologies. Simply relying on a single tool is insufficient; a robust system needs a combination of approaches to effectively identify and respond to suspicious activities. This section dives into the practical implementation of detection mechanisms, exploring the technologies available and how to integrate them into a comprehensive security strategy.Effective insider threat detection involves understanding that threats can manifest in diverse ways.
A critical aspect is recognizing subtle deviations from normal user behavior, which can often be a more reliable indicator than explicit malicious intent. Consequently, sophisticated tools that monitor and analyze user activities are essential.
Anomaly Detection Systems
Anomaly detection systems (ADS) are crucial for identifying unusual patterns in user behavior. These systems learn normal user activity and flag any significant deviations, acting as early warning systems for potential threats. They can detect anomalies in access patterns, data usage, and communication protocols. For example, if a user suddenly accesses a restricted database at an unusual hour or downloads a large volume of sensitive data, an ADS can flag these activities for investigation.
Such systems are not just for identifying the “bad” but are equally valuable in uncovering and remediating inefficient processes or errors in the organization’s workflow.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools play a vital role in preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. These tools monitor data access and transmission, detecting potential leaks or unauthorized transfers. By setting policies that restrict access to specific data types or devices, DLP systems can prevent insider threats from exfiltrating sensitive information. Sophisticated DLP systems go beyond simple file filtering, often incorporating behavioral analytics to identify unusual data movement patterns.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems aggregate security logs from various sources within the organization. They correlate events to identify potential threats, including insider threats. By analyzing the flow of events, SIEM systems can pinpoint suspicious activities and alert security personnel. For example, a SIEM system might detect a series of unusual login attempts from a single user account, triggering an alert for investigation.
These systems are essential for a comprehensive security posture, providing a central repository of security events that can be analyzed to understand broader trends and vulnerabilities.
Knowing how to spot insider threats is crucial for any organization. Recent developments like the Department of Justice’s new safe harbor policy for Massachusetts transactions ( Department of Justice Offers Safe Harbor for MA Transactions ) highlight the evolving landscape of data protection. Understanding these policies is just one piece of the puzzle, though; a robust insider threat detection strategy needs to cover many more bases.
Specific Security Tools
Numerous security tools are available for detecting insider threats. Some examples include:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems monitor network traffic for malicious activity, which can include attempts to exfiltrate data or access restricted resources.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): UEBA tools leverage machine learning and statistical analysis to detect deviations from normal user behavior, enabling the identification of potentially malicious insider actions.
- Log Aggregation and Correlation Tools: These tools gather logs from various sources, such as servers, applications, and network devices, and correlate them to identify suspicious patterns.
Setting up a Basic Insider Threat Detection System
Implementing a basic insider threat detection system requires a structured approach. The following table Artikels a step-by-step procedure:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Define Security Policies: Establish clear policies regarding data access, acceptable use, and incident response. These policies should explicitly address insider threat risks. |
| 2 | Install Anomaly Detection Systems: Deploy ADS to monitor user activities and identify unusual patterns. Configure thresholds for detecting deviations from normal behavior. |
| 3 | Implement DLP Tools: Deploy DLP solutions to monitor data access and prevent sensitive data from unauthorized transfer. Establish policies for data classification and access control. |
| 4 | Configure SIEM Systems: Integrate security information sources into a SIEM platform. Configure alerts for suspicious events and activities. |
| 5 | Establish Incident Response Procedures: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan for insider threats, including reporting procedures and escalation protocols. |
| 6 | Regularly Review and Update: Monitor the system’s performance and update policies, tools, and procedures based on emerging threats and organizational changes. |
Establishing Robust Security Policies

Protecting against insider threats requires more than just technology; it demands a comprehensive security culture embedded in well-defined policies. Clear policies act as a guide for all employees, outlining acceptable use of resources and the consequences of violating those guidelines. These policies are the bedrock of any effective insider threat detection strategy.A robust security policy framework not only deters malicious intent but also fosters a security-conscious environment where employees understand their responsibilities and the potential risks associated with their actions.
Understanding insider threat detection is crucial for any organization, especially in today’s digital landscape. A recent vulnerability, like the one detailed in the Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details article, Azure Cosmos DB Vulnerability Details , highlights the importance of proactive security measures. This underscores the need for comprehensive security protocols and regular assessments to mitigate such risks, strengthening your overall insider threat detection strategy.
This proactive approach empowers organizations to identify and mitigate insider threats before they can cause significant damage.
Importance of Clear and Comprehensive Security Policies
Effective security policies are the cornerstone of insider threat prevention. They define acceptable behavior regarding data access, communication, and system use. These policies must be easily understood and consistently enforced to create a strong deterrent against potential threats. The policies should address data handling procedures, password management, and acceptable use of company resources. Furthermore, the policies must clearly articulate the consequences of violating these rules.
Access Controls and Least Privilege Principles
Implementing strict access controls and adhering to the principle of least privilege are crucial for insider threat prevention. Access controls limit the ability of users to access sensitive information and resources based on their job responsibilities. This minimizes the potential damage that a compromised or malicious insider could inflict. The least privilege principle dictates that users should only have access to the resources they absolutely need to perform their duties.
This significantly reduces the attack surface and minimizes the impact of a breach.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are vital for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that security policies remain effective. These assessments should evaluate the current security posture, identify weaknesses, and recommend improvements to existing security controls. Audits should encompass not only technical controls but also employee awareness and compliance with established policies. This proactive approach to security enables organizations to stay ahead of potential threats.
Regular assessments ensure that policies and procedures are updated to reflect current security risks.
Comparison of Different Security Policy Frameworks
Various security policy frameworks offer different approaches to defining and implementing security policies. Some popular frameworks include NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and CIS Controls. Each framework provides a structured approach to security, focusing on different aspects and offering specific guidance. Understanding these frameworks helps organizations choose the most suitable approach to meet their specific needs and comply with relevant regulations.
For example, NIST Cybersecurity Framework emphasizes a risk-based approach, while ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive set of controls. CIS Controls, on the other hand, focuses on the most critical security controls.
Insider Threat Policy Document Template
Insider Threat Policy Policy Statement: [Insert statement outlining the organization's commitment to preventing insider threats.] Scope: [Define the individuals and resources covered by the policy.] Policy Details: - Data Handling Procedures: [Describe procedures for handling sensitive data, including access controls, storage, and disposal.] - Acceptable Use Policy: [Artikel the acceptable use of company resources, including computers, networks, and software.] - Password Management: [Specify password policies, including complexity requirements and frequency of changes.] - Access Controls: [Describe the principle of least privilege and procedures for granting and revoking access.] - Reporting Procedures: [Establish a clear process for reporting suspected insider threats.] - Consequences of Violations: [Clearly Artikel the disciplinary actions for violating the policy.] Enforcement: [Describe how the policy will be enforced and monitored.] Review and Updates: [Specify the frequency of policy reviews and updates.] Contact Information: [Provide contact information for questions or concerns regarding the policy.]
Responding to Insider Threat Incidents
Responding to suspected insider threats requires a swift and methodical approach.
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for mitigating damage, preventing further breaches, and maintaining business continuity. This crucial step often determines the long-term impact of an incident. Effective response involves a structured investigation, escalation procedures, and meticulous documentation.
A proactive approach to insider threat incidents is essential. By establishing clear protocols and procedures, organizations can minimize the negative consequences of such events. This includes the timely identification, containment, and resolution of suspected insider threats. Implementing these procedures safeguards sensitive information, maintains operational efficiency, and protects the organization’s reputation.
Incident Response Framework
A robust framework for responding to suspected insider threat incidents involves several key stages. These stages should be clearly Artikeld in the organization’s incident response plan. The framework should include a dedicated team with specific roles and responsibilities. This ensures that the response is well-coordinated and efficient.
Investigation Procedures
Thorough investigation is paramount in determining the validity of suspected insider threats. A structured approach is necessary to collect evidence, interview witnesses, and analyze potential motives. This process involves examining logs, reviewing user activity, and potentially engaging external forensic experts.
Escalation Procedures
Establishing clear escalation procedures for suspected insider threat incidents is vital. These procedures dictate when and how incidents should be escalated to higher levels of management or law enforcement. Escalation should be based on the severity of the threat and the potential impact on the organization. Examples of escalation triggers include unauthorized access to sensitive data, attempts to exfiltrate confidential information, or evidence of malicious intent.
Maintaining Incident Logs and Reporting
Maintaining detailed incident logs is critical for tracking the progress of investigations and identifying trends. Comprehensive logs should record the date and time of the incident, the affected systems, the nature of the suspected threat, and the actions taken to address it. These logs are crucial for future audits, compliance requirements, and improving the organization’s overall security posture.
Understanding insider threat detection requires a multifaceted approach. It’s not just about traditional security measures; it’s also about proactively identifying potential risks, like vulnerabilities in code. This is where deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed Deploying AI Code Safety Goggles Needed comes in. Ultimately, a robust insider threat detection strategy needs a combination of technological solutions and a sharp eye for potential problems.
Regular reporting on insider threat incidents to relevant stakeholders is essential for transparency and accountability.
Flowchart for Responding to an Insider Threat Incident
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Detection | Identify potential insider threat indicators (e.g., unusual login attempts, suspicious data access patterns, unusual work hours). |
| 2. Initial Assessment | Confirm the validity of the suspected threat. Determine the scope and severity of the potential impact. |
| 3. Containment | Isolate affected systems and data to prevent further compromise. |
| 4. Investigation | Gather evidence, interview relevant personnel, and analyze potential motives. |
| 5. Escalation | Determine the appropriate escalation level based on the severity and potential impact. |
| 6. Remediation | Implement corrective actions to address the threat and mitigate potential damage. |
| 7. Documentation | Maintain detailed records of the incident, including investigation findings, actions taken, and outcomes. |
| 8. Review and Improvement | Review the incident response process and identify areas for improvement to prevent future incidents. |
Case Studies of Insider Threats
Insider threats, often underestimated, pose a significant risk to organizations. Understanding real-world examples, their contributing factors, and the lessons learned is crucial for proactive defense. This section delves into specific cases, analyzing the vulnerabilities and consequences, offering valuable insights for mitigating future incidents.
Examples of Insider Threat Incidents
Insider threats manifest in various forms, from data breaches to sabotage. Examining specific cases provides a concrete understanding of the potential damage.
- The Case of the Disgruntled Employee: A disgruntled employee, unhappy with their compensation and perceived lack of recognition, accessed sensitive financial data and leaked it to a competitor. This act resulted in significant financial losses for the organization and reputational damage. The employee’s motivation was driven by a desire for revenge and a sense of injustice. The company’s failure to recognize early warning signs and address employee concerns contributed significantly to the incident.
- The Accidental Data Leak: A junior employee, unfamiliar with data security protocols, accidentally sent a confidential report to an external email address during a company-wide email chain. This incident highlights the importance of employee training and clear communication regarding data handling procedures. The consequences were a breach of confidentiality, but did not result in immediate financial loss. However, it exposed the vulnerability of relying solely on technical safeguards without proper employee education.
- The Malicious Insider: A highly-skilled employee with access to critical infrastructure used their knowledge to disrupt operations, causing significant downtime and financial losses. Motivated by personal gain or a desire for disruption, this malicious insider exploited existing vulnerabilities in security measures. The company lacked robust monitoring and detection systems to identify this insider’s malicious activities.
Analysis of Contributing Factors, Insider threat detection what you need to know
Examining the factors that led to these incidents provides valuable insights for prevention.
- Poor Security Practices: Inadequate security policies, weak access controls, and insufficient employee training often play a significant role in insider threats. These failures create opportunities for unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Lack of Supervision: Insufficient monitoring and oversight of employees with high-level access can allow malicious activity to go undetected. This lack of oversight can be a key contributor to insider threats, particularly those involving intentional sabotage or data breaches.
- Employee Dissatisfaction: Frustration, dissatisfaction, and a lack of recognition can drive disgruntled employees to engage in harmful actions, such as leaking confidential information. This highlights the importance of fostering a positive and supportive work environment.
Lessons Learned
The consequences of insider threats can be severe. Learning from past cases is crucial for preventing future incidents.
- Proactive Security Measures: Implementing strong security policies, robust access controls, and comprehensive employee training are essential for mitigating insider threats. These measures include multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and regular security awareness training.
- Monitoring and Detection: Establishing robust monitoring systems to identify suspicious activities and anomalies in user behavior can significantly reduce the risk of insider threats. This can include anomaly detection software, user behavior analytics, and intrusion detection systems.
- Employee Engagement: Creating a culture of trust and transparency within the organization can foster a sense of responsibility among employees. This includes open communication channels, regular feedback mechanisms, and opportunities for professional development.
Consequences of Insider Threats
The impact of insider threats can be profound, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage.
- Financial Losses: Data breaches and disruptions can result in substantial financial losses due to lost revenue, legal fees, and damage control efforts. The losses can be even greater if the breached data involves intellectual property or trade secrets.
- Reputational Damage: Public exposure of sensitive information or operational disruptions can severely damage an organization’s reputation. This can lead to a loss of customer trust and a decline in market share.
- Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Failure to comply with data protection regulations can lead to significant legal and regulatory penalties. These penalties can be substantial and have a long-lasting impact on the organization’s financial stability.
Best Practices for Insider Threat Detection
Protecting your organization from insider threats requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond reactive measures. A proactive strategy, focusing on prevention and early detection, is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with malicious or negligent insiders. This approach should be built upon a foundation of strong security policies, ongoing training, and a culture of vigilance.
Effective insider threat detection is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It demands a nuanced understanding of your organization’s unique vulnerabilities, potential threats, and the specific behaviors that might indicate suspicious activity. This includes recognizing the various motivations behind insider threats, ranging from financial gain to personal vendettas.
Proactive Measures to Mitigate Insider Threats
Proactive measures are fundamental to a robust insider threat strategy. These measures go beyond simply identifying potential threats; they aim to prevent them from materializing in the first place. This involves creating a secure organizational culture, implementing stringent access controls, and fostering a reporting mechanism that encourages employees to come forward with concerns.
Implementing Robust Security Policies
Security policies are the cornerstone of any effective insider threat prevention program. These policies should clearly define acceptable use of company resources, Artikel data handling procedures, and establish consequences for violations. This includes defining access levels, outlining data classification protocols, and explicitly addressing the handling of sensitive information.
Recommendations for Reducing Insider Threat Risk
A comprehensive approach to reducing insider threat risk encompasses multiple layers of security and preventative measures.
- Establish clear and unambiguous security policies: These policies should cover acceptable use of company resources, data handling procedures, and consequences for violations. Regular updates and training on these policies are vital to ensure their effectiveness.
- Implement strong access controls: Limit access to sensitive data and systems based on the principle of least privilege. Employ multi-factor authentication and regularly review and adjust access rights as needed.
- Promote a culture of security awareness: Educate employees about insider threats, their potential impact, and the reporting procedures available. Encourage a sense of shared responsibility for security.
- Conduct regular security audits: Identify vulnerabilities in your security infrastructure and processes. Regular reviews and audits help to identify weaknesses and strengthen defenses.
- Monitor user activity: Implement systems that track and monitor user activity, particularly access to sensitive data and systems. This enables timely detection of unusual or suspicious behavior.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools: These tools help to identify and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, either intentionally or accidentally.
- Encourage open communication channels: Create a secure environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activity or concerns without fear of retaliation. Establish a clear and confidential reporting mechanism.
Matrix of Recommended Practices for Insider Threat Prevention
This matrix Artikels recommended practices for insider threat prevention across different organizational aspects.
| Aspect | Recommended Practices |
|---|---|
| Security Policies | Develop clear policies on acceptable use, data handling, and incident reporting. Implement a strong code of conduct. |
| Access Controls | Employ the principle of least privilege. Utilize multi-factor authentication. Regularly review and adjust access rights. |
| Employee Training | Provide comprehensive training on insider threats, data security, and reporting procedures. Conduct regular awareness campaigns. |
| Monitoring & Detection | Implement systems for monitoring user activity and system logs. Utilize anomaly detection tools. |
| Incident Response | Establish a well-defined incident response plan for insider threats. Include procedures for containment, eradication, and recovery. |
| Culture of Security | Foster a culture of security awareness and shared responsibility. Encourage reporting of suspicious activity. |
Future Trends in Insider Threat Detection
The landscape of insider threats is constantly evolving, mirroring the dynamic nature of modern workplaces and technologies. As organizations become increasingly reliant on cloud services, remote workforces, and sophisticated data analytics, the methods for detecting and mitigating insider threats must adapt. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for proactively safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining a secure digital environment.
The evolving nature of work, from remote work to the cloud, and the growing complexity of data, present new challenges and opportunities for insider threat detection. These trends demand a shift from reactive to proactive strategies, moving beyond traditional methods to leverage emerging technologies and adapt to new threats.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Several emerging technologies are significantly impacting the landscape of insider threat detection. Machine learning algorithms are being increasingly employed to analyze vast datasets of user behavior, network activity, and application usage, allowing for the identification of subtle anomalies that might indicate malicious intent. These algorithms can identify patterns and deviations that human analysts might miss, leading to earlier detection and prevention of potential threats.
Similarly, the use of behavioral biometrics is gaining traction, analyzing subtle changes in typing patterns, mouse movements, and other behavioral indicators to detect potential anomalies and deviations from normal user behavior.
Potential Future Challenges
Despite the advancements in technology, future challenges remain. Data privacy concerns are paramount, as sophisticated algorithms may require access to sensitive user data. Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, is crucial to building trust and avoiding legal ramifications. Another significant challenge lies in the ever-increasing volume and velocity of data generated by modern organizations.
Effectively processing and analyzing this massive influx of data to identify relevant anomalies requires significant computational resources and sophisticated analytical capabilities.
Potential Future Opportunities
The evolving landscape presents significant opportunities. Integration of AI and machine learning into existing security infrastructures can lead to more sophisticated and accurate threat detection capabilities. This will allow for the identification of previously undetected patterns of behavior and the implementation of more tailored security responses. The use of blockchain technology can further enhance the security of sensitive data, making it more difficult for malicious actors to tamper with or exfiltrate information.
Proactive security measures, like employee training programs and security awareness campaigns, will become even more critical in the future.
Projected Growth of Insider Threat Incidents
| Year | Projected Insider Threat Incidents (Millions) |
|---|---|
| 2024 | 1.2 |
| 2025 | 1.5 |
| 2026 | 1.8 |
| 2027 | 2.1 |
| 2028 | 2.5 |
Note: This table represents a hypothetical projection based on industry trends and data. Actual numbers may vary. Factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and technological advancements could influence the growth rate.
Last Word
In conclusion, insider threat detection is not a one-size-fits-all solution. A multi-faceted approach combining strong policies, vigilant monitoring, and proactive training is essential. By understanding the different types of threats, implementing appropriate detection mechanisms, and establishing a robust response framework, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to insider threats. This knowledge empowers organizations to proactively mitigate risks and safeguard their valuable assets.
FAQ Corner
What are some common indicators of potential insider threats?
Unusual access patterns, such as logging in from unusual locations or at unusual times, and suspicious activity like data exfiltration attempts or unauthorized file sharing are common indicators. Also, changes in employee behavior, such as increased isolation or secretive actions, can signal potential problems.
What technologies can be used to detect insider threats?
Anomaly detection systems, data loss prevention (DLP) tools, user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) solutions, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems are all useful for detecting suspicious behavior. Choosing the right tools depends on the specific needs and resources of the organization.
How important is security awareness training in reducing insider threat risk?
Security awareness training plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of insider threats. By educating employees about potential threats, best practices, and the importance of adhering to security policies, organizations can significantly decrease the likelihood of accidental or malicious insider actions.
What are some common types of insider threats?
Insider threats can be malicious (deliberate), negligent (unintentional mistakes), or accidental (unforeseen circumstances). Understanding the motivations behind each type helps in developing targeted prevention strategies.





