
Ransomware Gang Attacks MSI, Demands $4M
Ransomware gang attacks MSI and demands 4m for decryption – that’s the shocking headline that’s been making waves. This massive cyberattack against the tech giant has sent ripples throughout the industry, highlighting the ever-growing threat of ransomware and the devastating consequences it can have. We’ll delve into the specifics of this attack, exploring the potential methods used, the hefty ransom demand, and the broader implications for MSI and the cybersecurity landscape.
The sheer scale of the attack, demanding a staggering $4 million, underscores the sophistication and profitability of these criminal operations. We’ll examine the potential vulnerabilities exploited, the likely impact on MSI’s operations, and the various strategies they might employ for data recovery – including the difficult decision of whether or not to pay the ransom. We’ll also look at the legal ramifications and the crucial steps MSI – and other companies – can take to bolster their cybersecurity defenses.
The Ransomware Attack on MSI
The recent ransomware attack on Micro-Star International (MSI), resulting in a $4 million ransom demand, highlights the increasing sophistication and audacity of cybercriminal groups targeting even large, established technology companies. This incident underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures across all organizations, regardless of size or perceived security posture. The attack’s specifics remain largely undisclosed by MSI, but we can analyze likely attack vectors and potential consequences based on common ransomware attack patterns.
Methods of Infiltration
The ransomware gang likely employed a multi-stage attack to infiltrate MSI’s systems. Initial access could have been achieved through several common methods, including phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links, exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software (such as unpatched servers or endpoints), or leveraging compromised third-party vendor access. Once inside the network, the attackers likely used lateral movement techniques to gain access to sensitive data and critical systems.
This could involve exploiting known vulnerabilities in internal applications or leveraging stolen credentials obtained through previous breaches or social engineering tactics. The use of advanced persistent threats (APTs) to maintain a persistent presence within the network is also a possibility. The attackers likely moved undetected for a period of time, exfiltrating data before deploying the ransomware.
Exploited Vulnerabilities
Several vulnerabilities could have been exploited. Outdated software is a frequent entry point for ransomware attacks, and MSI, like any large organization, likely uses a wide range of software and hardware. Unpatched vulnerabilities in these systems, particularly those related to remote access, network security, or database management, would have presented easy targets. The attackers may have also used zero-day exploits, newly discovered vulnerabilities unknown to the public or MSI’s security team.
Additionally, human error, such as clicking on a malicious link in a phishing email, remains a significant vulnerability. Finally, weak or reused passwords, especially within privileged accounts, could have provided an easy path into the system.
Impact on MSI’s Operations and Reputation
The attack’s impact on MSI’s operations is likely multifaceted. The encryption of critical data could have disrupted manufacturing processes, supply chain management, customer service, and research and development. Downtime resulting from the attack would have incurred significant financial losses. Beyond the direct financial costs of the ransom and operational disruption, the attack will likely damage MSI’s reputation.
Customers may lose trust, impacting future sales. Investors might react negatively, affecting the company’s stock price. Furthermore, regulatory scrutiny and potential legal action are likely consequences. The incident could also lead to a loss of intellectual property and sensitive customer data, potentially leading to further legal and financial liabilities.
Potential Short-Term and Long-Term Consequences for MSI
| Consequence | Short-Term (0-6 months) | Long-Term (6 months – 5 years) | Example/Real-Life Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Losses | Ransom payment, operational downtime, lost sales, incident response costs | Decreased profitability, potential legal settlements, loss of market share | NotPetya ransomware attack on Maersk in 2017 resulted in estimated losses of hundreds of millions of dollars. |
| Reputational Damage | Negative media coverage, customer distrust, loss of investor confidence | Difficulty attracting and retaining customers and talent, reduced brand value | Equifax data breach in 2017 resulted in significant reputational damage and ongoing legal battles. |
| Operational Disruptions | Production delays, supply chain disruptions, service outages | Changes in business processes, increased cybersecurity spending, potential restructuring | Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack in 2021 caused widespread fuel shortages across the US East Coast. |
| Legal and Regulatory Actions | Investigations by regulatory bodies, potential lawsuits from affected customers | Increased regulatory compliance costs, potential fines and penalties | The GDPR has led to significant fines for companies failing to adequately protect customer data. |
The $4 Million Ransom Demand
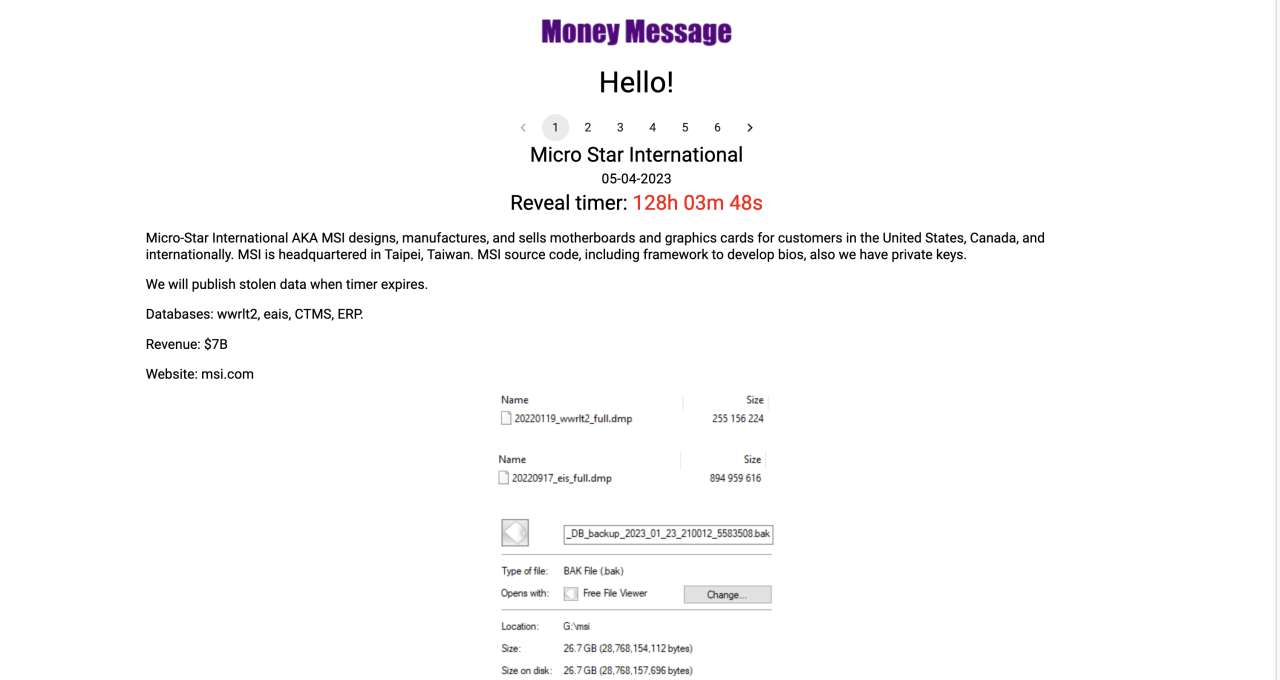
The $4 million ransom demanded by the ransomware gang responsible for the MSI attack is a staggering figure, highlighting the escalating financial stakes in the cybercrime landscape. This sum reflects not only the perceived value of MSI’s data but also the attackers’ confidence in their ability to cause significant disruption and the company’s perceived willingness to pay. Understanding the factors behind this demand is crucial for comprehending the scale of the threat and the challenges faced by victims.
Factors Influencing Ransom Demand Size
Several factors contribute to the size of a ransom demand. In MSI’s case, the attackers likely considered the company’s size, reputation, and the potential damage caused by data leakage. MSI’s global reach and the sensitive nature of its data (including potentially intellectual property, customer information, and financial records) would undoubtedly increase the perceived value of the encrypted data.
The attackers’ assessment of MSI’s financial resources and insurance coverage also plays a role. Finally, the sophistication of the attack and the effectiveness of the encryption used would contribute to the confidence of the attackers in their ability to extract a substantial sum. A successful attack on a similarly sized company might have yielded a lower or higher ransom depending on these factors.
For example, a less sophisticated attack with easily recoverable data might result in a smaller demand, while a highly impactful attack with irreplaceable data might lead to a much larger one.
Comparison to Other High-Profile Ransomware Attacks
The $4 million demand places the MSI attack within the upper echelon of ransomware incidents. While precise figures are often kept confidential, several high-profile attacks have resulted in multi-million dollar payouts. The Colonial Pipeline attack, for example, resulted in a $4.4 million ransom payment. Attacks on larger organizations or those involving critical infrastructure often command higher ransom demands due to the potential for widespread disruption and the significant costs associated with downtime.
Comparing this incident to other attacks reveals a concerning trend of increasing ransom demands, reflecting the growing profitability of ransomware for cybercriminal organizations.
Potential Costs Beyond the Ransom
The financial burden on MSI extends far beyond the $4 million ransom. Legal fees associated with regulatory compliance (such as GDPR), investigations, and potential lawsuits could easily add millions more to the overall cost. Recovery efforts, including restoring systems, rebuilding databases, and implementing enhanced security measures, will also incur substantial expenses. The cost of reputational damage, stemming from data breaches and potential loss of customer trust, is difficult to quantify but could significantly impact MSI’s long-term profitability.
These indirect costs often outweigh the ransom itself, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of ransomware attacks.
Hypothetical Negotiation Strategy for MSI
A hypothetical negotiation strategy for MSI should prioritize minimizing financial losses while ensuring the safe recovery of data. This would involve a multi-faceted approach. First, MSI should engage in discreet communication with law enforcement and cybersecurity experts to guide the negotiation process and potentially gather intelligence on the attackers. Second, a thorough assessment of the encrypted data should be conducted to determine the true value of the data and the potential risks associated with non-payment.
Third, MSI should consider the feasibility of data recovery through alternative methods (e.g., backups, forensic analysis) before engaging in negotiations. Finally, if negotiations proceed, they should be conducted with the utmost caution, focusing on securing a phased decryption process to verify the attackers’ capabilities and minimize the risk of further extortion. This might involve paying a smaller sum upfront for the decryption of a sample of the data, ensuring its validity before committing to the full payment.
Throughout the process, meticulous documentation of all communications and transactions is essential.
Data Encryption and Recovery
The $4 million ransom demand levied against MSI highlights the devastating consequences of successful ransomware attacks. Understanding the encryption techniques used and the potential data recovery strategies is crucial not only for MSI but also for any organization aiming to bolster its cybersecurity defenses. This section explores the technical aspects of the attack and potential recovery paths.
The type of encryption used by the ransomware gang in the MSI attack remains unknown publicly. However, several common encryption techniques could have been employed. These range from symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, to asymmetric encryption, utilizing separate public and private keys. Symmetric algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are frequently used due to their speed and robustness, while asymmetric algorithms like RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are often employed for key exchange and digital signatures.
The attackers may have also layered multiple encryption techniques for added security, making decryption significantly more challenging.
Encryption Techniques Employed
Several scenarios are possible. The ransomware could have used AES-256 for its speed and strength, encrypting individual files or entire volumes. This would require the decryption key held by the attackers. Alternatively, a hybrid approach, combining AES for file encryption with RSA for key exchange, is also plausible. This makes the process more secure and complex for potential recovery efforts.
Another possibility is the use of a less common or custom-built algorithm, specifically designed to evade detection and increase the difficulty of decryption. Determining the exact algorithm is crucial for successful data recovery, and often requires forensic analysis.
Data Recovery Methods
MSI’s data recovery options, excluding ransom payment, are limited but not nonexistent. The success of these methods depends heavily on the type of encryption used, the extent of data corruption, and the quality of existing backups.
One approach involves attempting to decrypt the data using publicly available tools or techniques. Some ransomware variants have known vulnerabilities that can be exploited. However, this success rate is highly dependent on the specific ransomware strain and its version. Another possibility is recovering data from backups, provided they were regularly performed and stored securely, ideally offline or in a separate, isolated location.
Finally, data recovery specialists may be able to partially recover data, even if encryption remains intact, by utilizing advanced forensic techniques and potentially recovering fragments of unencrypted data. The success rate of this method is highly variable and costly.
Challenges in Data Recovery
Several significant hurdles can complicate data recovery efforts. Data corruption, caused by the ransomware itself or by attempts to manually recover data, can render files unrecoverable. Incomplete or outdated backups severely limit the ability to restore data to its pre-attack state. Additionally, the attackers might have employed techniques to delete shadow copies or other recovery points, further hindering restoration efforts.
The longer the delay between the attack and the start of recovery attempts, the lower the chances of successful recovery.
Improving Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
The MSI incident underscores the critical need for robust data backup and recovery strategies. To prevent future incidents, MSI should implement the following measures:
- Implement a 3-2-1 backup strategy: Maintain at least three copies of data, on two different media types, with one copy stored offsite.
- Regularly test backups: Verify the integrity and restorability of backups to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Employ immutable backups: Use backup systems that prevent modification or deletion of backups, even with administrator privileges.
- Utilize robust encryption for backups: Encrypt backups both in transit and at rest to protect against unauthorized access.
- Establish a comprehensive incident response plan: Develop a detailed plan outlining steps to take in case of a ransomware attack, including communication protocols and data recovery procedures.
- Invest in advanced security solutions: Implement endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions and other advanced security measures to detect and prevent ransomware attacks.
- Regular employee security awareness training: Educate employees on phishing scams, malware threats, and best practices for cybersecurity hygiene.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
The ransomware attack on MSI, resulting in a $4 million ransom demand, triggers a cascade of legal and regulatory implications for the company. Understanding these implications is crucial for MSI’s response and future preparedness against similar attacks. Failure to navigate these complexities could lead to significant financial penalties and reputational damage.The legal landscape surrounding ransomware attacks is complex and varies depending on jurisdiction.
However, several key areas consistently apply. These include data breach notification laws, consumer protection statutes, and potentially, contractual liabilities. Furthermore, international laws may apply depending on the origin of the attack and the location of affected data.
Applicable Laws and Regulations
Several laws and regulations are relevant to this cyberattack, depending on MSI’s location and the location of its affected customers. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) both impose strict requirements regarding data security and breach notification. In the US, state-specific breach notification laws also apply, each with its own timeline and reporting requirements.
Violation of these laws can result in substantial fines. Furthermore, federal laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) (if protected health information was compromised) and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) (if customer financial data was compromised) may also come into play. The specific applicable laws will depend on the type of data compromised and the jurisdictions involved.
Potential Legal Ramifications for MSI, Ransomware gang attacks msi and demands 4m for decryption
MSI faces several potential legal ramifications. These include private lawsuits from affected individuals or businesses who suffered data breaches or financial losses as a result of the attack. Class-action lawsuits are a significant possibility, especially if a large number of individuals were affected. Regulatory fines from government agencies enforcing data protection laws (like the FTC in the US or the ICO in the UK) are also highly probable, with penalties potentially reaching millions of dollars depending on the severity of the breach and MSI’s compliance efforts.
Furthermore, MSI might face legal challenges from business partners or investors due to the disruption caused by the attack and the potential impact on its reputation and financial stability. The severity of these ramifications will depend on MSI’s response, level of compliance with data protection laws, and the extent of the damage caused by the attack.
Data Breach Notification Requirements
MSI must comply with data breach notification laws, which vary by jurisdiction. These laws typically require companies to notify affected individuals and, in some cases, regulatory authorities within a specific timeframe (often 30-60 days) after discovering a breach. The notification must include information about the breach, the types of data affected, and steps individuals can take to protect themselves.
Failure to comply with these notification requirements can result in significant fines and further legal action. The process involves identifying affected individuals, drafting compliant notification letters, and delivering them through appropriate channels, often involving multiple jurisdictions. The company must also maintain detailed records of its notification efforts to demonstrate compliance. This is a critical step in mitigating legal risks associated with the breach.
Legal Response Process Flowchart
A flowchart illustrating MSI’s legal response process might look like this:[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Ransomware Attack Detected,” branching to “Assess Damage & Data Affected,” then to “Identify Applicable Laws & Regulations,” followed by “Notify Affected Individuals & Authorities,” and finally, “Internal Investigation & Remediation.” Each step would have sub-branches representing different actions and potential outcomes, such as legal counsel consultation, public relations management, and regulatory reporting.]The flowchart would visually represent the sequential steps MSI should take, highlighting the interdependency of different actions and the importance of a coordinated response involving legal counsel, internal IT teams, and public relations specialists.
The process should be documented meticulously to provide evidence of compliance and to aid in future incident response planning.
Preventing Future Attacks

The MSI ransomware attack serves as a stark reminder that even large, established companies are vulnerable to cyber threats. Preventing future incidents requires a multi-layered approach encompassing robust technological safeguards, rigorous employee training, and proactive security management. A comprehensive strategy is crucial, moving beyond reactive measures to establish a truly resilient cybersecurity posture.The following security enhancements are essential for MSI to implement, focusing on prevention, detection, and response.
These measures, while demanding investment and effort, represent a cost-effective approach compared to the financial and reputational damage caused by a successful ransomware attack.
Employee Security Awareness Training
Regular and comprehensive security awareness training is paramount. Employees are often the weakest link in any cybersecurity chain. Training should cover phishing recognition, safe browsing habits, password management best practices, and the potential dangers of malicious attachments or links. Simulated phishing exercises can effectively gauge employee awareness and reinforce training effectiveness. Real-world examples of successful phishing attacks, like those targeting similar organizations, should be used in training to illustrate the risks.
The training should also explicitly address the consequences of security breaches, including potential legal and financial repercussions for the company and individuals.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation
Implementing MFA across all systems and accounts is non-negotiable. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code from a mobile app or email. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if an attacker obtains a password. For example, MFA can prevent an attacker who has compromised an employee’s password from accessing sensitive data.
MSI should prioritize MFA implementation for all employees, especially those with access to critical systems and sensitive data.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Investing in robust IDPS is crucial for early detection and prevention of malicious activity. These systems monitor network traffic and system logs for suspicious patterns and behaviors, alerting security personnel to potential threats in real-time. IDPS can detect and block various types of attacks, including ransomware attempts. The selection of an IDPS should be based on a thorough assessment of MSI’s specific needs and infrastructure.
Regular updates and tuning of the IDPS are crucial to maintain its effectiveness against evolving threats.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing provide a proactive approach to identifying vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. Audits assess the effectiveness of existing security controls, while penetration testing simulates real-world attacks to identify weaknesses. These assessments should be conducted by qualified security professionals and should cover all aspects of MSI’s IT infrastructure, including network security, application security, and data security.
The findings should be used to inform improvements to security policies and procedures.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Implementing a robust data backup and recovery strategy is critical for minimizing the impact of a ransomware attack. Regular backups should be stored offline, ideally in a geographically separate location, to prevent them from being encrypted by ransomware. A well-defined recovery plan should Artikel the steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack, including the restoration of data from backups and the remediation of affected systems.
This plan should be tested regularly to ensure its effectiveness. The 3-2-1 backup rule (3 copies of data, on 2 different media, with 1 copy offsite) is a widely accepted best practice.
Cybersecurity Solution Comparison
Various cybersecurity solutions are available, each with strengths and weaknesses. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities at the endpoint level. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a centralized view of security events. Cloud-based security solutions offer scalability and flexibility, while on-premise solutions provide greater control.
The choice of solution depends on MSI’s specific needs, budget, and technical capabilities. A thorough evaluation of different solutions is necessary to select the most appropriate combination.
Incident Response Planning
A comprehensive incident response plan is essential for effective response to security incidents, including ransomware attacks. The plan should Artikel the roles and responsibilities of different teams, the procedures for containing and eradicating the attack, and the steps for recovering data and systems. Regular training and drills are crucial to ensure that the plan is effective and that personnel are familiar with their roles and responsibilities.
This plan should include communication protocols for notifying stakeholders, including customers and regulatory bodies, in case of a breach.
The Role of Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Agencies
The response to a major ransomware attack like the one targeting MSI, involving a multi-million dollar ransom demand, necessitates a coordinated effort between law enforcement agencies and cybersecurity experts. Their roles are distinct yet intertwined, each contributing crucial expertise to investigate the crime, assist victims, and prevent future incidents. The effectiveness of this response is significantly impacted by the level of international cooperation, given the often transnational nature of ransomware gangs.The investigation and prosecution of ransomware gangs are complex and require specialized skills.
Law enforcement agencies, such as the FBI in the US or Europol in Europe, play a pivotal role in identifying and apprehending the perpetrators. This involves tracing the flow of funds, identifying the infrastructure used by the attackers (servers, command-and-control systems), and gathering digital evidence to build a strong case for prosecution. Success often depends on securing international warrants and collaborating with law enforcement agencies in the countries where the attackers operate.
Law Enforcement’s Investigative and Prosecutorial Actions
Law enforcement’s actions typically begin with victim reporting, followed by digital forensics to analyze the attack’s methods and identify potential leads. Investigators then work to trace the cryptocurrency payments, often involving cooperation with cryptocurrency exchanges and blockchain analysis firms. This investigative phase is crucial in building a case for prosecution, which may involve complex legal procedures and international cooperation to extradite suspects.
Successful prosecutions not only bring perpetrators to justice but also serve as a deterrent to others. For example, the successful prosecution of individuals involved in the NotPetya ransomware attack demonstrated the global commitment to pursuing these criminals.
Cybersecurity Agency Assistance to Victims
Cybersecurity agencies, such as CISA in the US or NCSC in the UK, offer critical support to victims of ransomware attacks. This assistance ranges from technical guidance on data recovery and incident response to threat intelligence sharing and vulnerability assessments. They may help victims understand the attack’s impact, implement security improvements to prevent future attacks, and work with law enforcement to gather evidence.
Furthermore, they often provide resources and best practices to help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture and resilience against future ransomware attacks. The assistance provided is tailored to the specific needs of the victim, ranging from small businesses to large multinational corporations.
The news about the ransomware gang attacking MSI and demanding a $4 million ransom got me thinking about data security. It highlights the importance of robust systems, and I started wondering how developments like those discussed in this article on domino app dev the low code and pro code future might help businesses better protect themselves. Ultimately, though, the MSI attack underscores the ever-present threat of ransomware and the need for constant vigilance.
International Cooperation in Combating Ransomware
Ransomware attacks often transcend national borders, requiring international cooperation to effectively combat them. This cooperation involves sharing intelligence, coordinating investigations, and harmonizing legal frameworks. International organizations like Interpol play a key role in facilitating this collaboration. Effective international cooperation is crucial in tracking down perpetrators, seizing assets, and disrupting ransomware operations globally. The sharing of threat intelligence, particularly details on new ransomware variants and tactics, is vital in preventing future attacks and improving global cybersecurity preparedness.
Without this cooperation, ransomware gangs can easily operate across borders with impunity.
Timeline of Law Enforcement and Cybersecurity Agency Response
The response to a ransomware attack typically follows a structured timeline:
- Initial Response (0-24 hours): Victim reports the incident; initial containment measures are implemented; law enforcement and cybersecurity agencies are notified.
- Investigation and Evidence Gathering (1-7 days): Forensic analysis of affected systems; identification of attack vectors and actors; tracing of ransom payments.
- Data Recovery and System Restoration (1-30 days): Attempts to decrypt data; restoration of systems; implementation of security enhancements.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance (Ongoing): Notification of relevant authorities; compliance with data breach notification laws; potential legal action against attackers.
- Long-Term Mitigation and Prevention (Ongoing): Vulnerability assessments; security awareness training; implementation of advanced security measures to prevent future attacks.
Conclusion: Ransomware Gang Attacks Msi And Demands 4m For Decryption
The MSI ransomware attack serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threat of sophisticated cybercrime. The $4 million ransom demand highlights the financial stakes involved, while the potential for long-term reputational damage and operational disruption underscores the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. Ultimately, proactive strategies, including employee training, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, are vital for preventing future attacks.
The incident also underscores the importance of international cooperation in combating these global cyber threats.
Commonly Asked Questions
What type of ransomware was likely used in the MSI attack?
Determining the exact ransomware variant requires detailed forensic analysis. However, given the scale of the attack and the ransom demand, it was likely a sophisticated, highly-evolved strain.
What are MSI’s options beyond paying the ransom?
MSI could attempt data recovery from backups (if available and uncompromised), engage specialized cybersecurity firms for decryption efforts, or potentially pursue legal action against the attackers.
Could this attack have been prevented?
While no system is entirely impenetrable, implementing robust security measures, including multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and employee training, significantly reduces the likelihood of a successful ransomware attack.
What legal repercussions could MSI face?
MSI may face legal ramifications depending on the specifics of the attack, including potential lawsuits from affected customers and regulatory fines for failing to meet data protection standards.





